Abstract
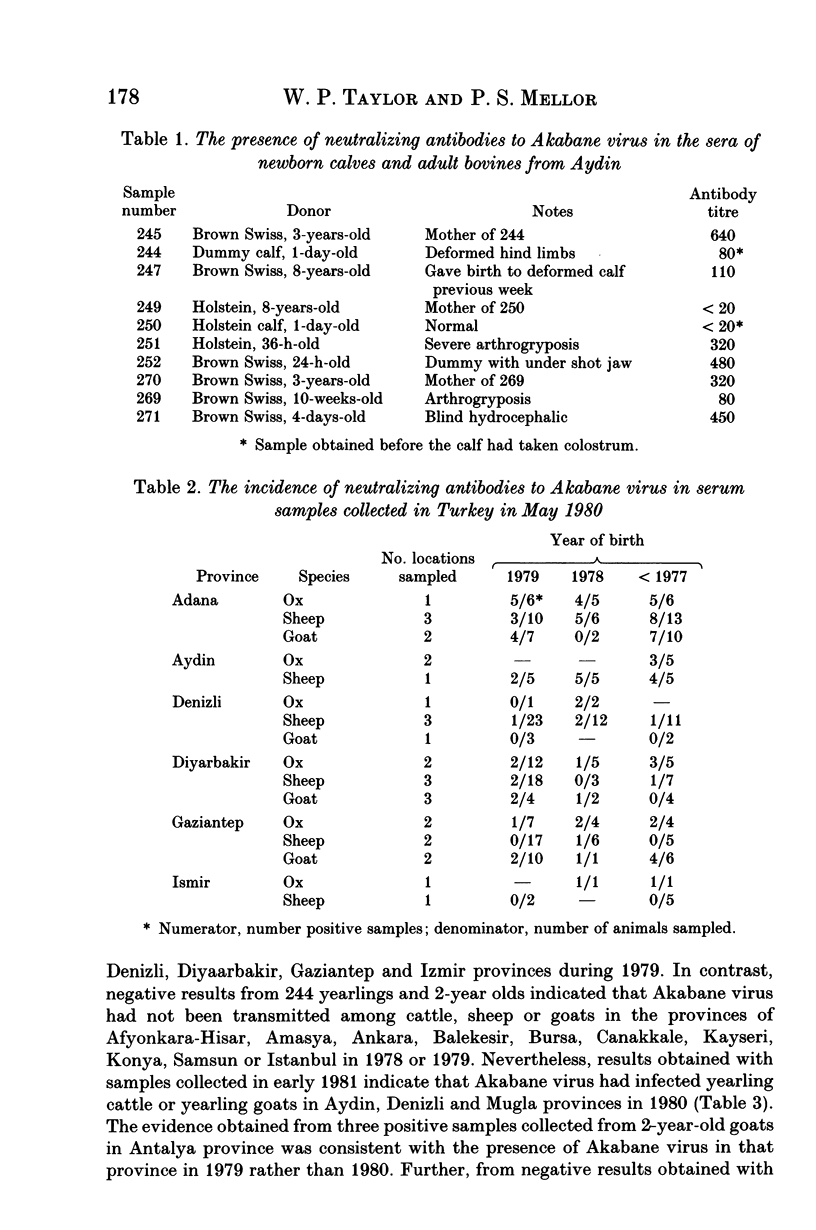
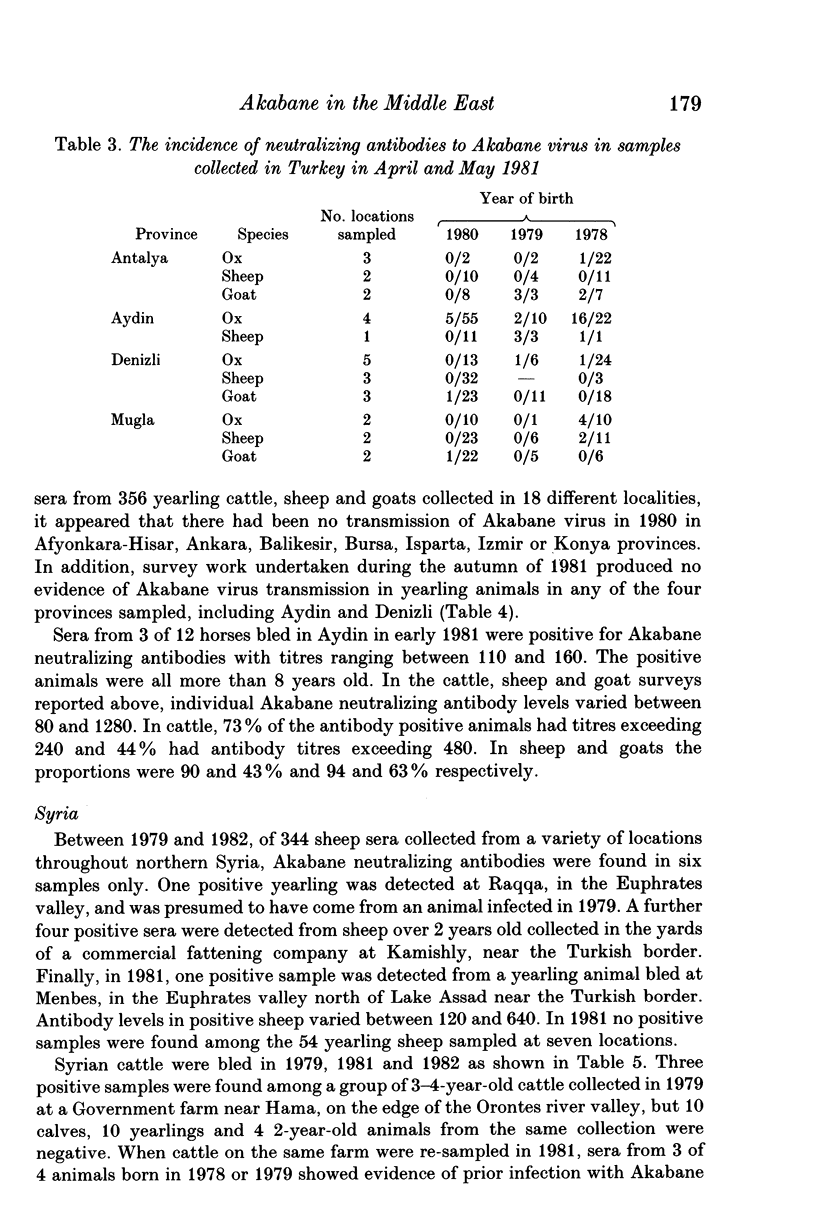
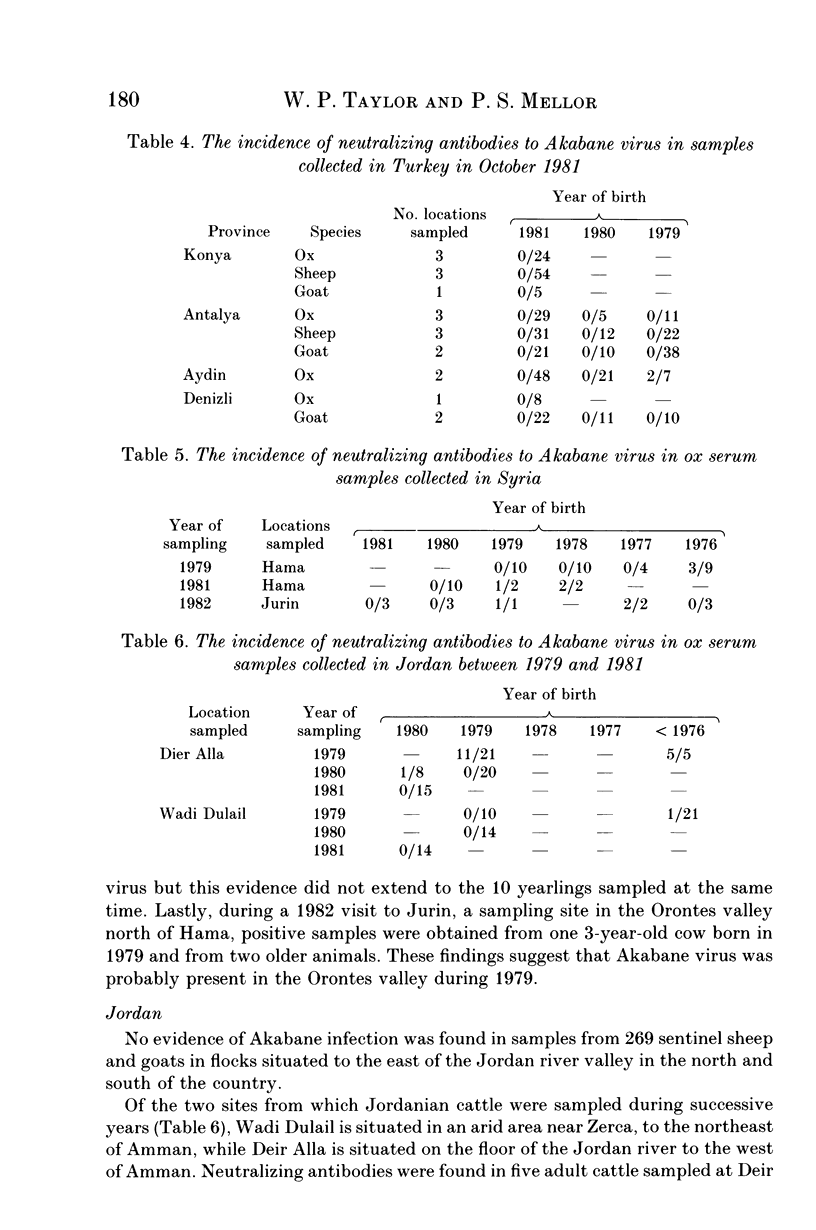
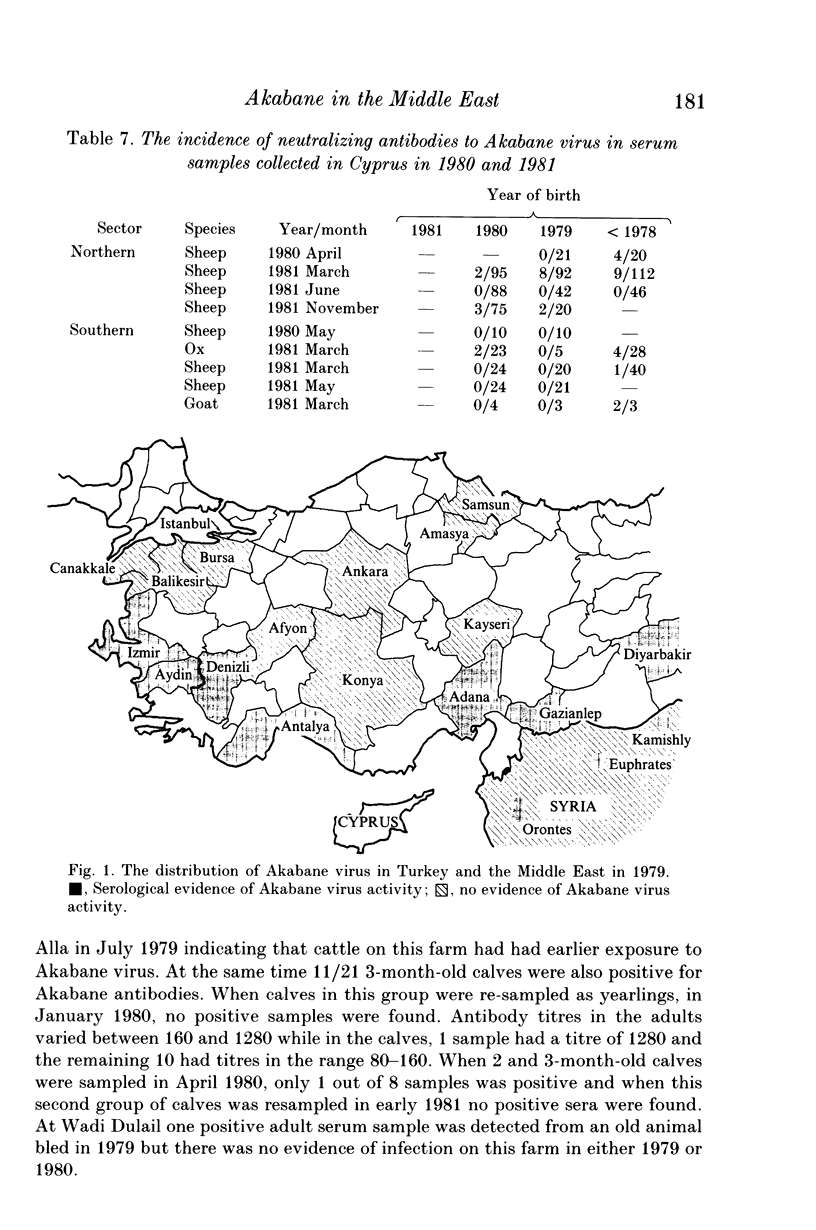
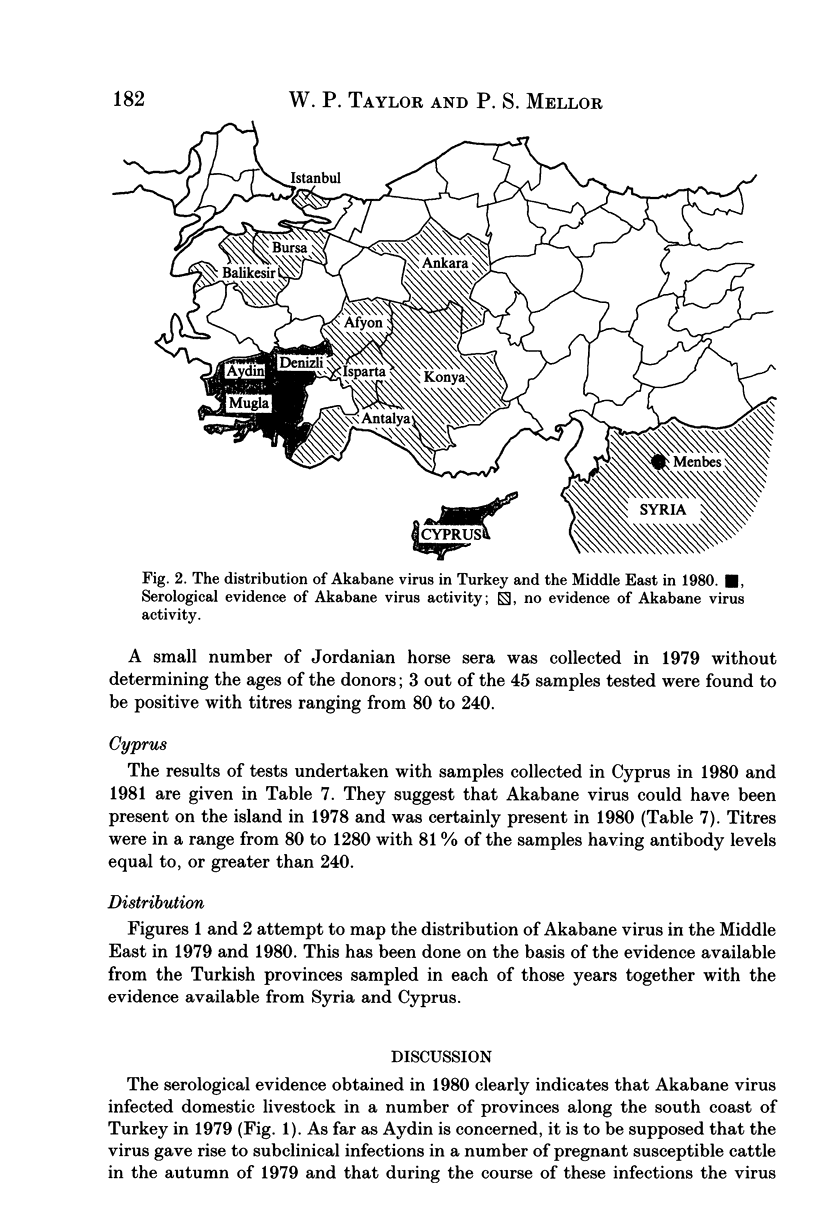
Serological evidence was used to confirm an outbreak of Akabane disease in cattle in the Turkish Province of Aydin in 1980. Thereafter, serum collections from the Middle East were screened for the presence of neutralizing antibodies to Akabane virus. The results indicate that the virus was present in a number of provinces on the south Turkish coast in 1979 and 1980 but that it probably did not persist into 1981; the virus had also been present on Cyprus in 1980 and on at least one previous occasion. There was also evidence of limited virus transmission in the Orontes river valley in Syria in 1979 and less precise evidence to show that occasional infection occurred in the lower Jordan river valley. The failure of Akabane virus to persist in southern Turkey for more than two years indicates that this area is open to epidemic rather than endemic infection. The presence of neutralizing antibodies in the eastern Turkish Provinces of Gaziantep and Diyarbakir suggests that this might be the route whereby Akabane virus occasionally invades the Middle East region.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Busaidy S. M., Mellor P. S., Taylor W. P. Prevalence of neutralising antibodies to Akabane virus in the Arabian peninsula. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Jun;17(2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Busaidy S., Hamblin C., Taylor W. P. Neutralising antibodies to Akabane virus in free-living wild animals in Africa. Trop Anim Health Prod. 1987 Nov;19(4):197–202. doi: 10.1007/BF02242116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della-Porta A. J., Murray M. D., Cybinski D. H. Congenital bovine epizootic arthrogryposis and hydranencephaly in Australia. Distribution of antibodies to Akabane virus in Australian Cattle after the 1974 epizootic. Aust Vet J. 1976 Nov;52(11):496–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1976.tb06983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty R. L., Carley J. G., Standfast H. A., Dyce A. L., Snowdon W. A. Virus strains isolated from arthropods during an epizootic of bovine ephemeral fever in Queensland. Aust Vet J. 1972 Mar;48(3):81–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1972.tb02220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurogi H., Inaba Y., Goto Y., Miura Y., Takahashi H. Serologic evidence for etiologic role of Akabane virus in epizootic abortion-arthrogryposis-hydranencephaly in cattle in Japan, 1972-1974. Arch Virol. 1975;47(1):71–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01315594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matumoto M., Inaba Y. Akabane disease and Akabane virus. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1980 Jun;53(1-2):1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metselaar D., Robin Y. Akabane virus isolated in Kenya. Vet Rec. 1976 Jul 31;99(5):86–86. doi: 10.1136/vr.99.5.86-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OYA A., OKUNO T., OGATA T., KOBAYASHII, MATSUYAMA T. Akabane, a new arbor virus isolated in Japan. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1961 Jun;14:101–108. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.14.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers R. F., Gibbs E. P., Herniman K. A., Pedgley D. E., Tucker M. R. Possible origin of the bluetongue epidemic in Cyprus, August 1977. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Dec;83(3):547–555. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers R. F., Herniman K. A. Neutralising antibodies to Akabane virus in ruminants in Cyprus. Trop Anim Health Prod. 1981 Feb;13(1):57–60. doi: 10.1007/BF02237891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers R. F., Mellor P. S. Temperature and the persistence of viruses in Culicoides spp. during adverse conditions. Rev Sci Tech. 1993 Sep;12(3):733–755. doi: 10.20506/rst.12.3.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers R. F., Pedgley D. E. Possible windborne spread to western Turkey of bluetongue virus in 1977 and of Akabane virus in 1979. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Aug;95(1):149–158. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


