Abstract
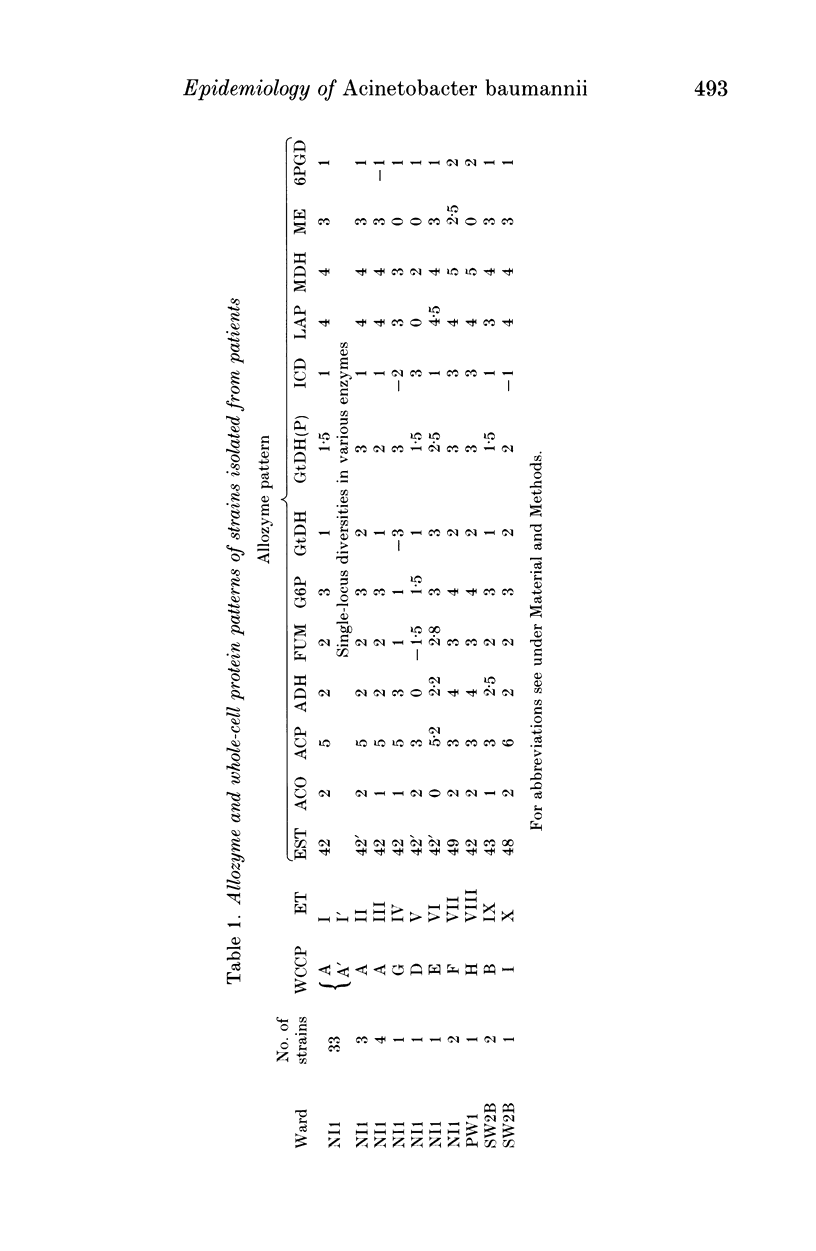
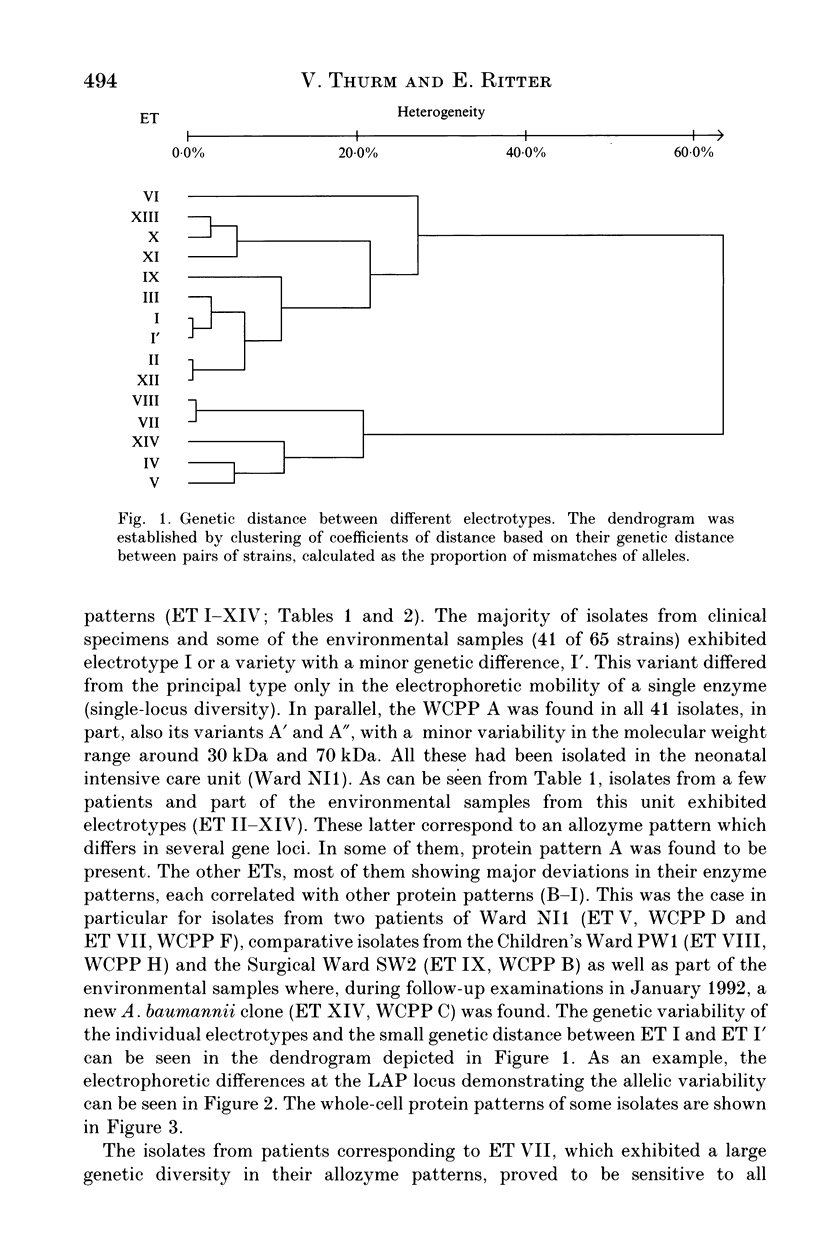
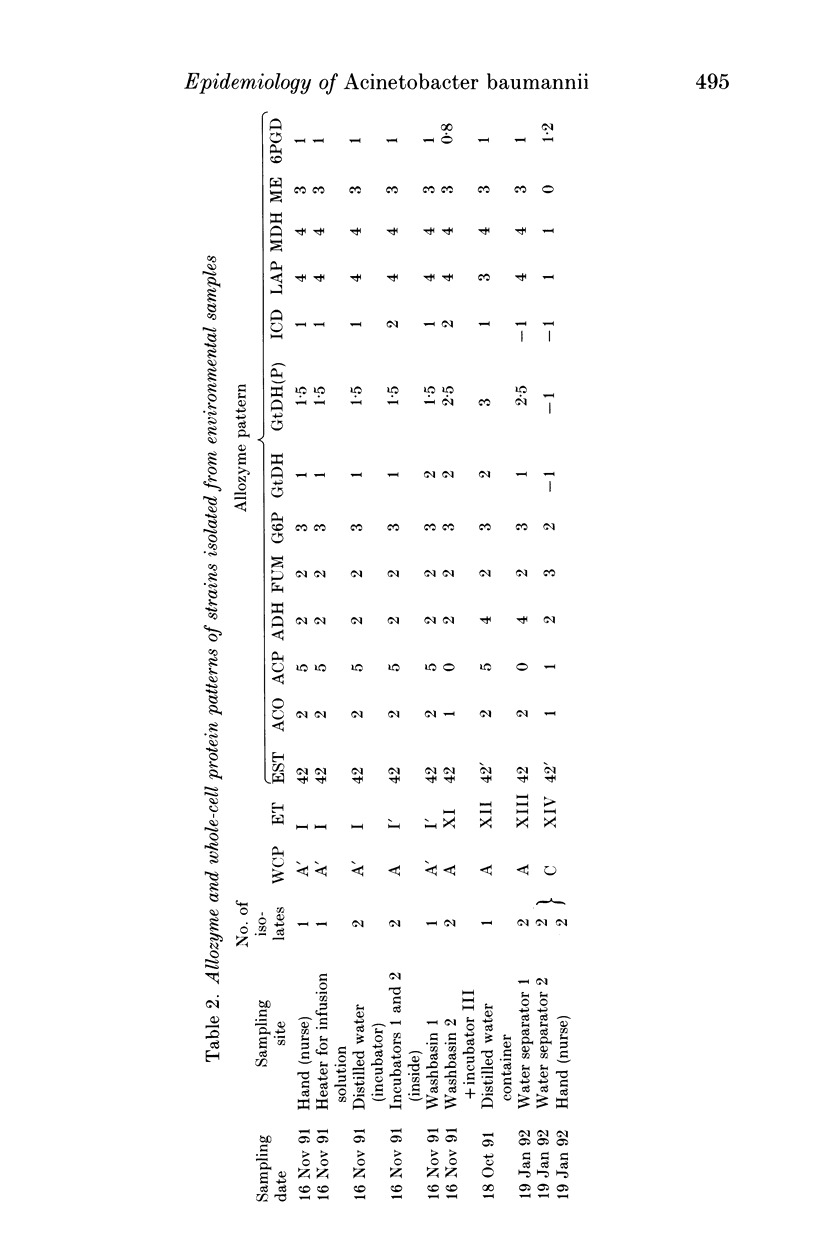
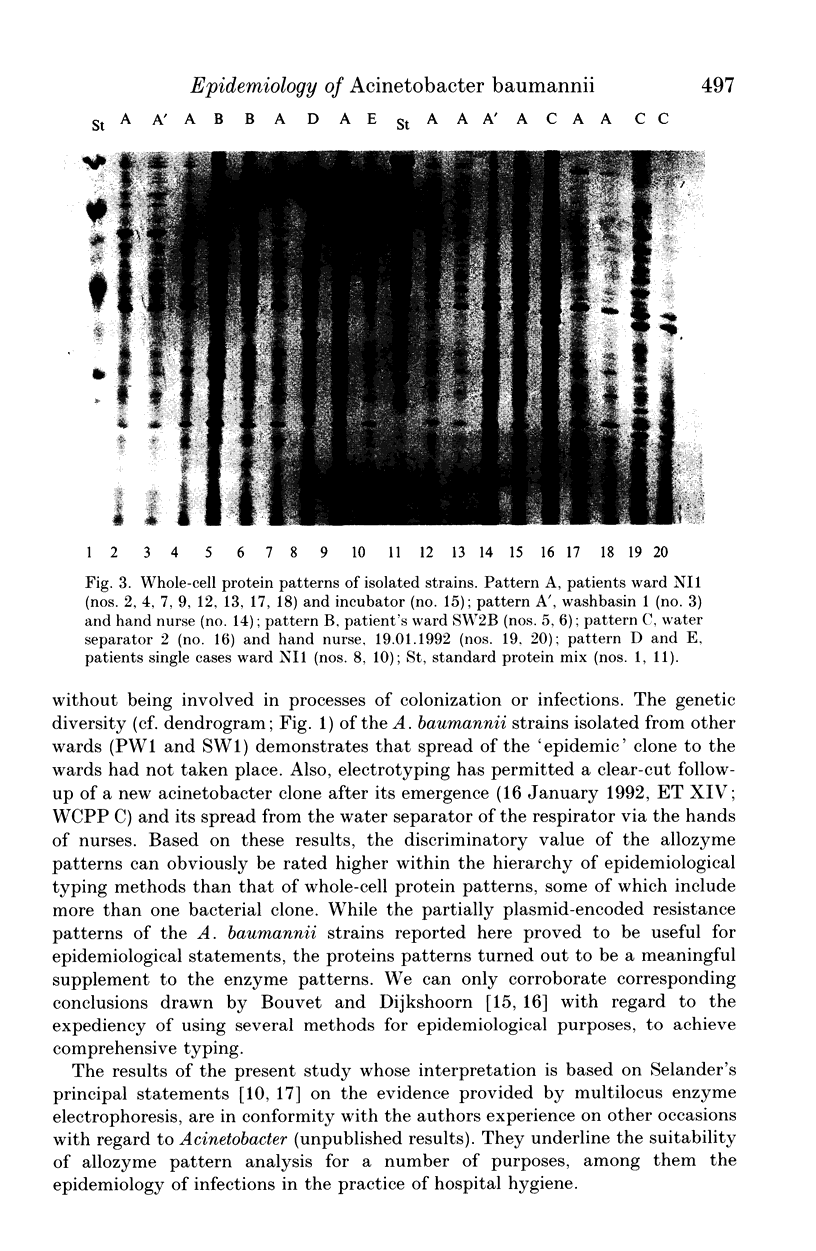
Sixty-five strains of Acinetobacter baumannii which had been isolated from patients and the indoor environment of a neonatal intensive care unit and, for comparative purposes, isolates from three other wards, were examined by means of electrotyping and analysis of whole-cell protein and antibiotic resistance patterns. Fourteen different electrotypes were determined. The predominant type, a multiply resistant acinetobacter clone, persisted in the neonatal ward over several months. The results underline the usefulness of electrophoretic subtyping, in particular by means of allozyme pattern and as a supplement to whole-cell protein pattern analysis, in epidemiological investigations into the routes of transmission of nosocomial A. baumannii infections.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck-Sagué C. M., Jarvis W. R., Brook J. H., Culver D. H., Potts A., Gay E., Shotts B. W., Hill B., Anderson R. L., Weinstein M. P. Epidemic bacteremia due to Acinetobacter baumannii in five intensive care units. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Oct;132(4):723–733. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergogne-Bérézin E., Joly-Guillou M. L. Hospital infection with Acinetobacter spp.: an increasing problem. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Jun;18 (Suppl A):250–255. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90030-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Grimont P. A. Identification and biotyping of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Sep-Oct;138(5):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Jeanjean S., Vieu J. F., Dijkshoorn L. Species, biotype, and bacteriophage type determinations compared with cell envelope protein profiles for typing Acinetobacter strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.170-176.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M. Numerical analysis of sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic protein patterns for the classification, identification and typing of medically important bacteria. Electrophoresis. 1990 May;11(5):382–391. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkshoorn L., Michel M. F., Degener J. E. Cell envelope protein profiles of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus strains isolated in hospitals. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Jun;23(4):313–319. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-4-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkshoorn L., Van Ooyen A., Hop W. C., Theuns M., Michel M. F. Comparison of clinical Acinetobacter strains using a carbon source growth assay. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Jun;104(3):443–453. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter E., Thurm V., Becker-Boost E., Thomas P., Finger H., Wirsing von König C. H. Epidemisches Vorkommen multiresistenter Acinetobacter baumannii-Stämme auf einer neonatologischen Intensivstation. Zentralbl Hyg Umweltmed. 1993 Feb;193(5):461–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Williams P. H., Pattison P. E., Caugant D. A. Genetic relationships and clonal structure of strains of Escherichia coli causing neonatal septicemia and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):213–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.213-222.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Acinetobacter baumannii serotyping for delineation of outbreaks of nosocomial cross-infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2713–2716. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2713-2716.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Spohr M. Antimicrobial drug susceptibility of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter species (A. baumannii, A. haemolyticus, genospecies 3, and genospecies 6). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1617–1619. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]