Abstract
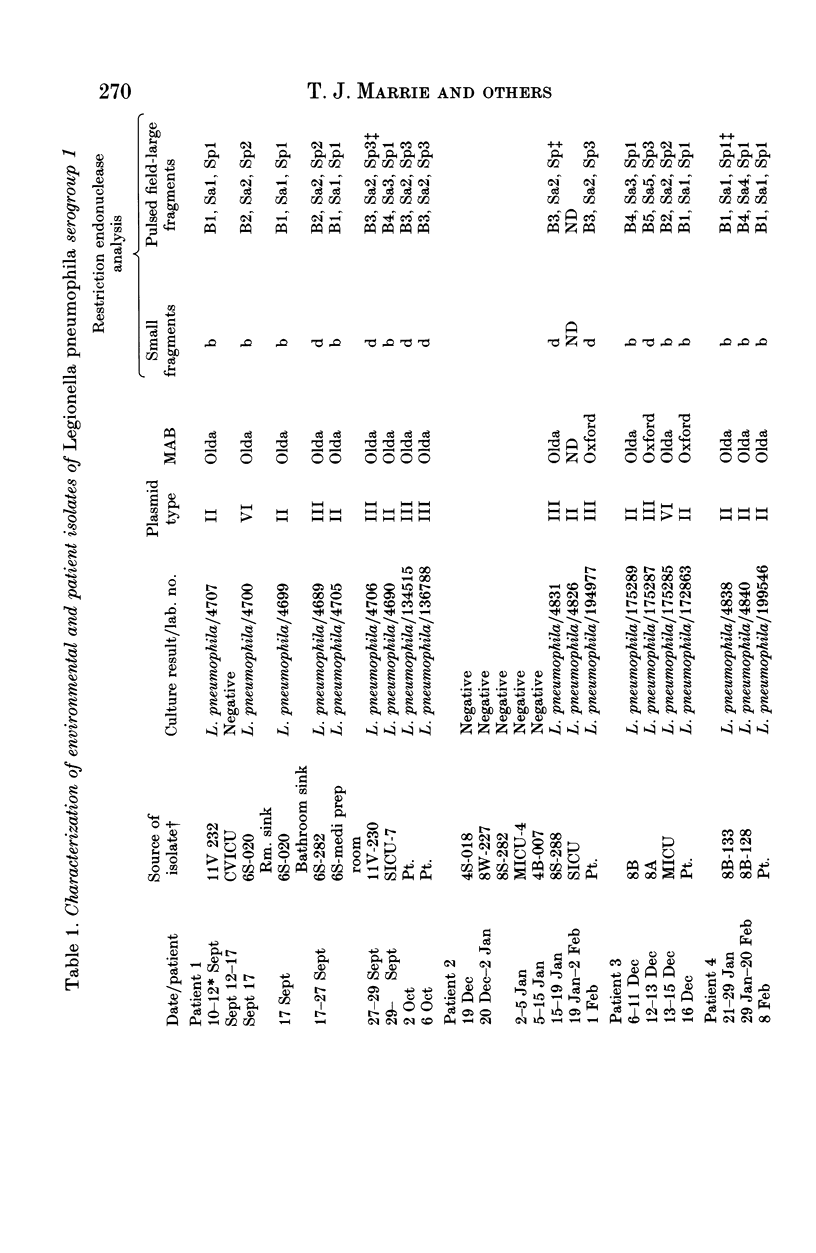
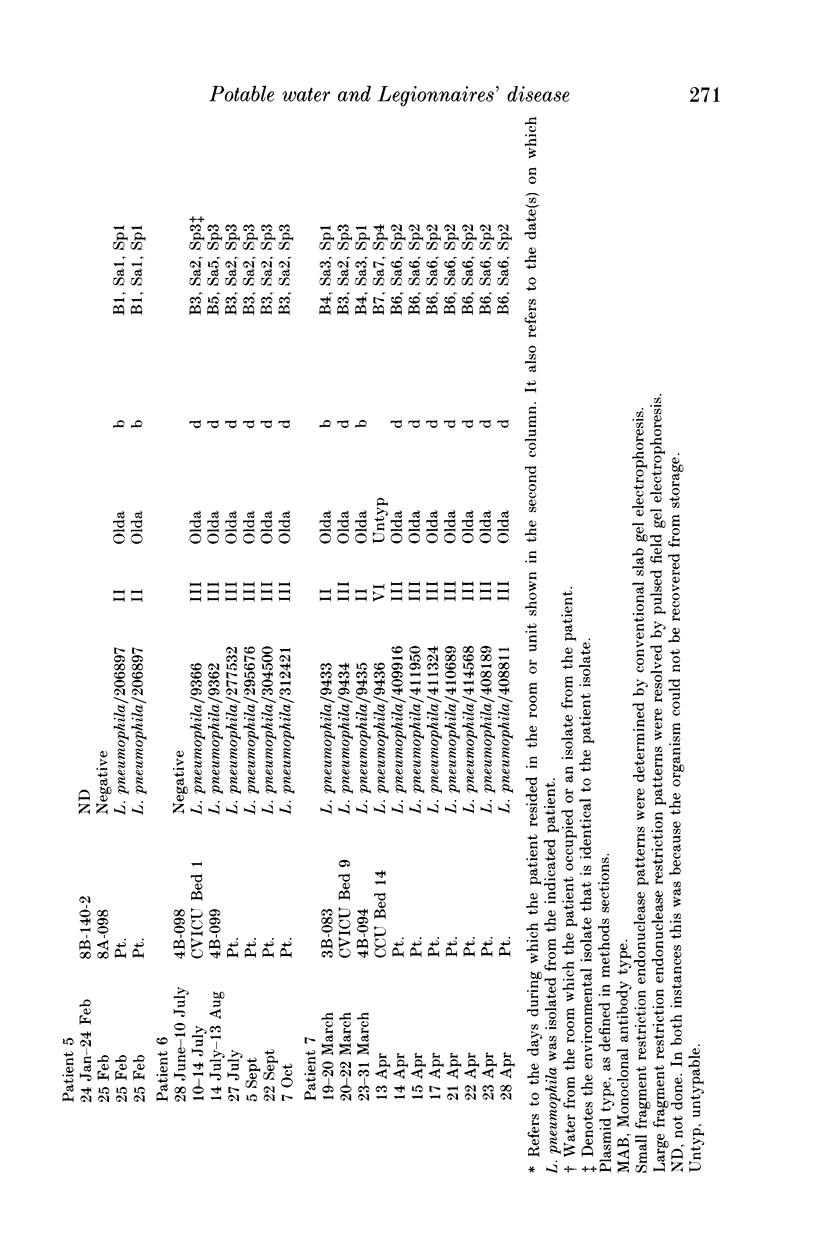
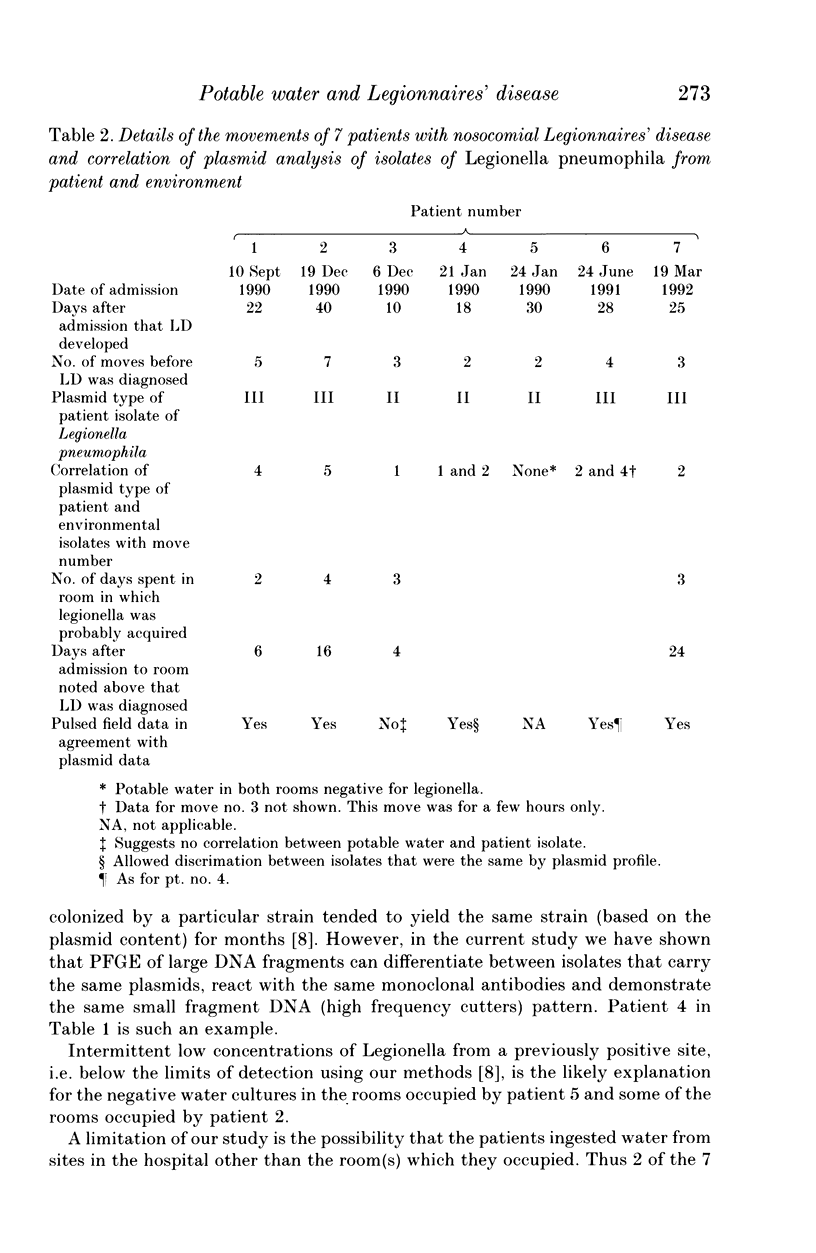
We studied 7 patients with nosocomial Legionnaires' disease to determine the relationship between isolates of Legionella pneumophila recovered from potable water and those recovered from patients. Potable water was cultured from all rooms in which patients had stayed prior to the diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. The 38 isolates of L. pneumophila (31 environmental, 7 patient) were resolved into 9 distinct patterns by pulse-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), 3 by plasmid content and 2 each with monoclonal antibodies and conventional agarose gel electrophoresis of small fragments of DNA. Using PFGE it was determined that 4 of the 7 patients were infected with L. pneumophila identical to an isolate recovered from the potable water supply in one of the rooms each had occupied prior to the diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. Patients had resided in a mean of 3.57 rooms before a diagnosis of nosocomial Legionnaires' disease. We conclude that in the setting of contaminated potable water and nosocomial Legionnaires' disease water from all the rooms which the patient has occupied prior to this diagnosis should be cultured. PFGE of large DNA fragments discriminated best among the isolates of L. pneumophila.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bezanson G., Burbridge S., Haldane D., Yoell C., Marrie T. Diverse populations of Legionella pneumophila present in the water of geographically clustered institutions served by the same water reservoir. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):570–576. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.570-576.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt S. P., Parkinson M. D., Pace E., Hoffman P., Dolan D., Lauderdale P., Zajac R. A., Melcher G. P. Nosocomial Legionnaires' disease: aspiration as a primary mode of disease acquisition. Am J Med. 1993 Jul;95(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90227-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge J. A., Edelstein P. H. Oropharyngeal colonization with Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1108–1112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1108-1112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doebbeling B. N., Wenzel R. P. The epidemiology of Legionella pneumophila infections. Semin Respir Infect. 1987 Dec;2(4):206–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang G. D., Fine M., Orloff J., Arisumi D., Yu V. L., Kapoor W., Grayston J. T., Wang S. P., Kohler R., Muder R. R. New and emerging etiologies for community-acquired pneumonia with implications for therapy. A prospective multicenter study of 359 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990 Sep;69(5):307–316. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199009000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Lus P., Fields B. S., Benson R. F., Martin W. T., O'Connor S. P., Black C. M. Comparison of arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction, ribotyping, and monoclonal antibody analysis for subtyping Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1940–1942. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1940-1942.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T. G., Saunders N. A., Haththotuwa A., Hallas G., Birtles R. J., Taylor A. G. Phenotypic variation amongst genotypically homogeneous Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 isolates: implications for the investigation of outbreaks of Legionnaires' disease. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Apr;104(2):171–180. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800059331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C. M., Massanari R. M., Wenzel R. P., Pfaller M. A., Moyer N. P., Hall N. Legionnaires' disease associated with a hospital water system. A five-year progress report on continuous hyperchlorination. JAMA. 1988 Apr 22;259(16):2423–2427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., Chen Y. Y., Ramsay D. Serogrouping and subtyping of Legionella pneumophila with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1040–1046. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1040-1046.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., Snyder K. M., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: report of sixty-five nosocomially acquired cases of review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1980 May;59(3):188–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry P. W., Blankenship R. J., Gridley W., Troup N. J., Tompkins L. S. A cluster of legionella sternal-wound infections due to postoperative topical exposure to contaminated tap water. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 10;324(2):109–113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101103240207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Bezanson G., Haldane D. J., Burbridge S. Colonisation of the respiratory tract with Legionella pneumophila for 63 days before the onset of pneumonia. J Infect. 1992 Jan;24(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(92)91094-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Haldane D., Bezanson G., Peppard R. Each water outlet is a unique ecological niche for Legionella pneumophila. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Apr;108(2):261–270. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800049736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Haldane D., MacDonald S., Clarke K., Fanning C., Le Fort-Jost S., Bezanson G., Joly J. Control of endemic nosocomial legionnaires' disease by using sterile potable water for high risk patients. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Dec;107(3):591–605. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800049293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M., Bender L., Marre R., Hacker J. Pulsed field electrophoresis of genomic restriction fragments for the detection of nosocomial Legionella pneumophila in hospital water supplies. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):813–815. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.813-815.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel A. F., Chabbert Y. A. Taxonomy and epidemiology of gram-negative bacterial plasmids studied by DNA-DNA filter hybridization in formamide. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):269–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonmaker D., Heimberger T., Birkhead G. Comparison of ribotyping and restriction enzyme analysis using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for distinguishing Legionella pneumophila isolates obtained during a nosocomial outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1491-1498.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. E., Yu V. L., Muraca P., Joly J., Troup N., Tompkins L. S. Potable water as a cause of sporadic cases of community-acquired legionnaires' disease. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 16;326(3):151–155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201163260302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J., Yu V. L., Vickers R. M., Zuravleff J., Best M., Brown A., Yee R. B., Wadowsky R. Ubiquitousness of Legionella pneumophila in the water supply of a hospital with endemic Legionnaires' disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 25;306(8):466–468. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202253060807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N. J., Woods T., Bibb W., McKinney R. M. Molecular epidemiology of Legionella species by restriction endonuclease and alloenzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1875–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1875-1880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers R. M., Stout J. E., Yu V. L., Rihs J. D. Manual of culture methodology for Legionella. Semin Respir Infect. 1987 Dec;2(4):274–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]