Abstract
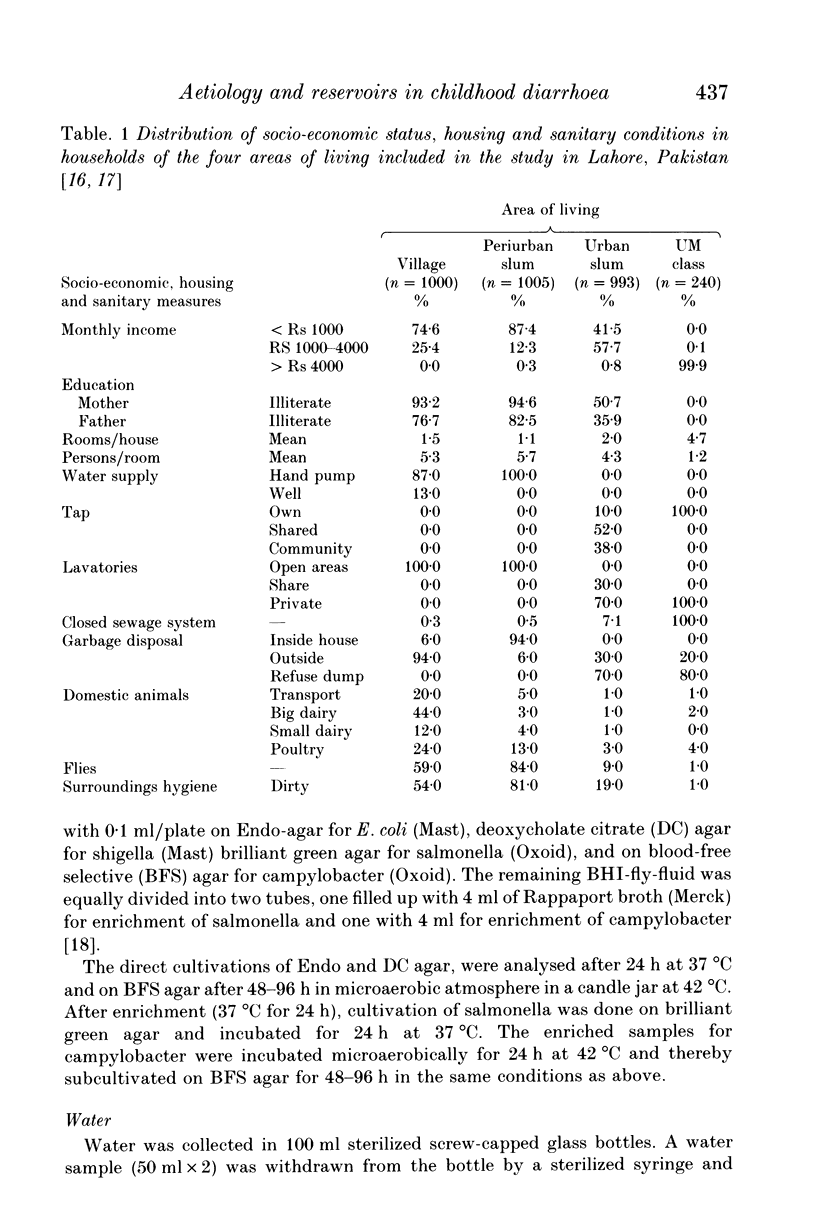
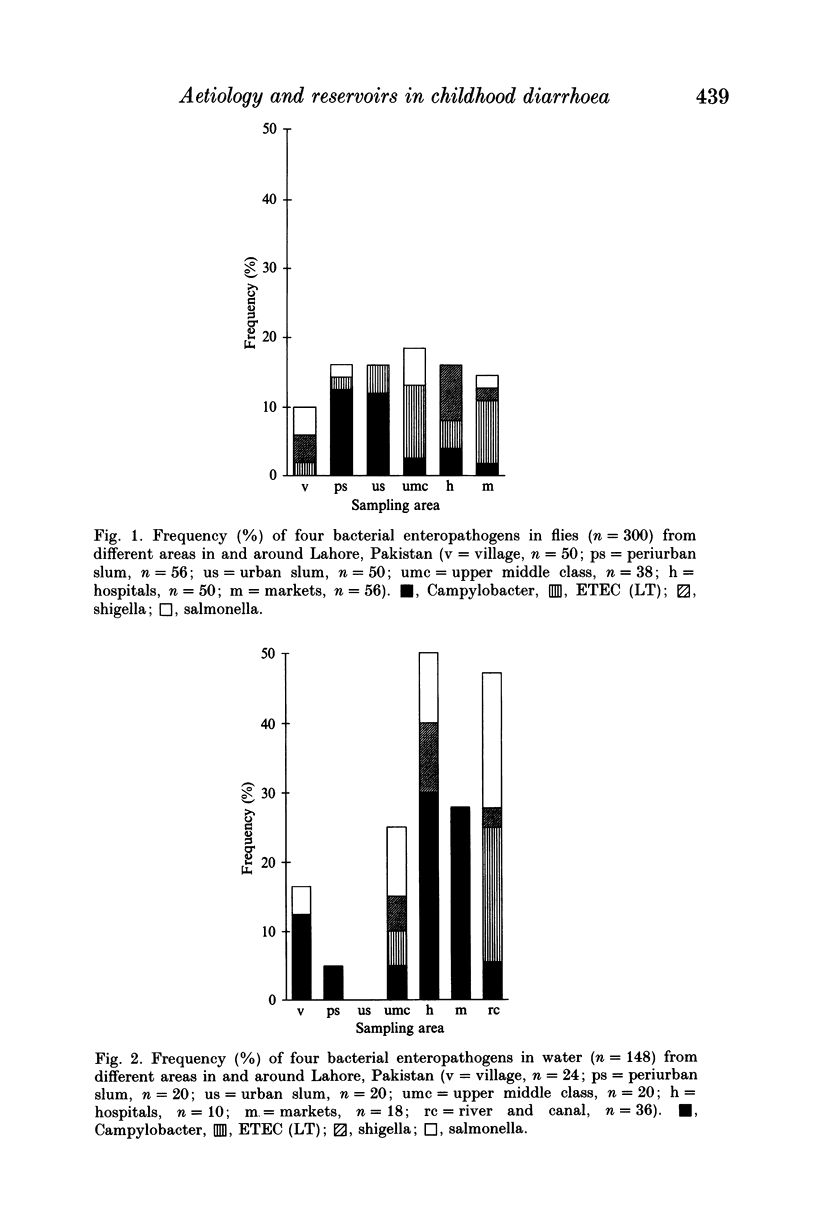
The study was conducted to isolate and characterize campylobacter, enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-labile toxin (ETEC-LT), shigella and salmonella in flies and water. The material for the study, flies (n = 300) and water samples (n = 148), was collected from different localities in and around Lahore, Pakistan. Cultivation of the samples was performed on conventional standard media. Membrane filtration technique was used for water prior to culture. Determination of ETEC-LT was done by GM1 ELISA. Results of our study showed that flies and water were reservoirs for all the four pathogens, campylobacter, ETEC-LT, shigella and salmonella. Flies from the village were carrying fewer enteropathogens, while water from the village was found to be more contaminated as compared to the city. Campylobacter and ETEC-LT were the most frequently isolated pathogens in both flies and water. Thus the incidence of diarrhoeal disease in children of developing countries may be decreased by providing plenty of safe drinking water, improving excreta disposal, toilet facilities and giving education in personal hygiene.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awadzi K., Dadzie K. Y., Schulz-Key H., Gilles H. M., Fulford A. J., Aziz M. A. The chemotherapy of onchocerciasis. XI. A double-blind comparative study of ivermectin, diethylcarbamazine and placebo in human onchocerciasis in northern Ghana. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1986 Aug;80(4):433–442. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1986.11812044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Brown K. H., Becker S., Alim A. R., Merson M. H. Contamination of weaning foods and transmission of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea in children in rural Bangladesh. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. M., Pacha R. E., Clark G. W., Williams E. A. Seasonal occurrence of Campylobacter spp. in surface waters and their correlation with standard indicator bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):523–526. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.523-526.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Green M., Block C., Slepon R., Ambar R., Wasserman S. S., Levine M. M. Reduction of transmission of shigellosis by control of houseflies (Musca domestica) Lancet. 1991 Apr 27;337(8748):993–997. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92657-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cravioto A., Reyes R. E., Ortega R., Fernández G., Hernández R., López D. Prospective study of diarrhoeal disease in a cohort of rural Mexican children: incidence and isolated pathogens during the first two years of life. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Aug;101(1):123–134. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Levine M. M., Hornick R. B., Formal S. B. Inoculum size in shigellosis and implications for expected mode of transmission. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jun;159(6):1126–1128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.6.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Harrison B. A., Tirapat C., McFarland A. Flies as a source of enteric pathogens in a rural village in Thailand. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):32–36. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.32-36.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekanem E. E., Akitoye C. O., Adedeji O. T. Food hygiene behaviour and childhood diarrhoea in Lagos, Nigeria: a case-control study. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1991 Sep;9(3):219–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esrey S. A., Feachem R. G., Hughes J. M. Interventions for the control of diarrhoeal diseases among young children: improving water supplies and excreta disposal facilities. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(4):757–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feachem R. G. Interventions for the control of diarrhoeal diseases among young children: promotion of personal and domestic hygiene. Bull World Health Organ. 1984;62(3):467–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagekull B., Nazir R., Jalil F., Karlberg J. Early child health in Lahore, Pakistan: III. Maternal and family situation. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1993 Aug;82 (Suppl 390):27–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb12904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalil F., Lindblad B. S., Hanson L. A., Khan S. R., Ashraf R. N., Carlsson B., Zaman S., Karlberg J. Early child health in Lahore, Pakistan: I. Study design. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1993 Aug;82 (Suppl 390):3–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb12902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khin Nwe O. o., Sebastian A. A., Aye T. Carriage of enteric bacterial pathogens by house flies in Yangon, Myanmar. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1989 Sep-Dec;7(3-4):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman J. S. Diarrhea and school toilet hygiene in Cali, Colombia. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 May;107(5):412–420. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Rennels M. B., Cisneros L., Hughes T. P., Nalin D. R., Young C. R. Lack of person-to-person transmission of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli despite close contact. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Mar;111(3):347–355. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom G. B., Johny M., Khalil K., Mazhar K., Ruiz-Palacios G. M., Kaijser B. Enterotoxigenicity and frequency of Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli and C. laridis in human and animal stool isolates from different countries. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):163–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb03990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud A., Jalil F., Karlberg J., Lindblad B. S. Early child health in Lahore, Pakistan: VII. Diarrhoea. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1993 Aug;82 (Suppl 390):79–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb12908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhail I. A., Hyams K. C., Podgore J. K., Haberberger R. L., Boghdadi A. M., Mansour N. S., Woody J. N. Microbiologic and clinical study of acute diarrhea in children in Aswan, Egypt. Scand J Infect Dis. 1989;21(1):59–65. doi: 10.3109/00365548909035681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., McBride H., Saunders F., Dehele Y., Pearson A. D. The virulence of clinical and environmental isolates of Campylobacter jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Feb;94(1):45–54. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSEN N. J., HINES V. D. The relation of summertime gastrointestinal illness to the sanitary quality of the water supplies in six Rocky Mountain communities. Am J Hyg. 1960 May;71:314–320. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A. Infective dose of Campylobacter jejuni in milk. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 16;282(6276):1584–1584. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6276.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosef O., Kapperud G. House flies (Musca domestica) as possible vectors of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):381–383. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.381-383.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Koplan J. P., Wachsmuth I. K., Wells J. G., Gangarosa E. J., Guerrant R. L., Sack D. A. Epidemic diarrhea at Crater Lake from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. A large waterborne outbreak. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):714–718. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks J. J., Lieb S., Baldy L. M., Berta S., Patton C. M., White M. C., Bigler W. J., Witte J. J. Epidemic campylobacteriosis associated with a community water supply. Am J Public Health. 1986 Apr;76(4):424–428. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.4.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakdisiwasdi O., Achananuparp S., Limsuwan A., Nanna P., Barnyen L. Salmonella and Shigella carrier rates and environmental sanitation in a rural district, Central Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1982 Sep;13(3):380–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shane S. M., Montrose M. S., Harrington K. S. Transmission of Campylobacter jejuni by the housefly (Musca domestica). Avian Dis. 1985 Apr-Jun;29(2):384–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedhem A., Kaijser B. Isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from domestic animals and pets: probable origin of human infection. J Infect. 1981 Mar;3(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)92261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umoh J. U., Adesiyun A. A., Adekeye J. O., Nadarajah M. Epidemiological features of an outbreak of gastroenteritis/cholera in Katsina, Northern Nigeria. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Aug;91(1):101–111. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman S., Jalil F., Karlberg J. Early child health in Lahore, Pakistan: IV. Child care practices. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1993 Aug;82 (Suppl 390):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb12905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


