Abstract
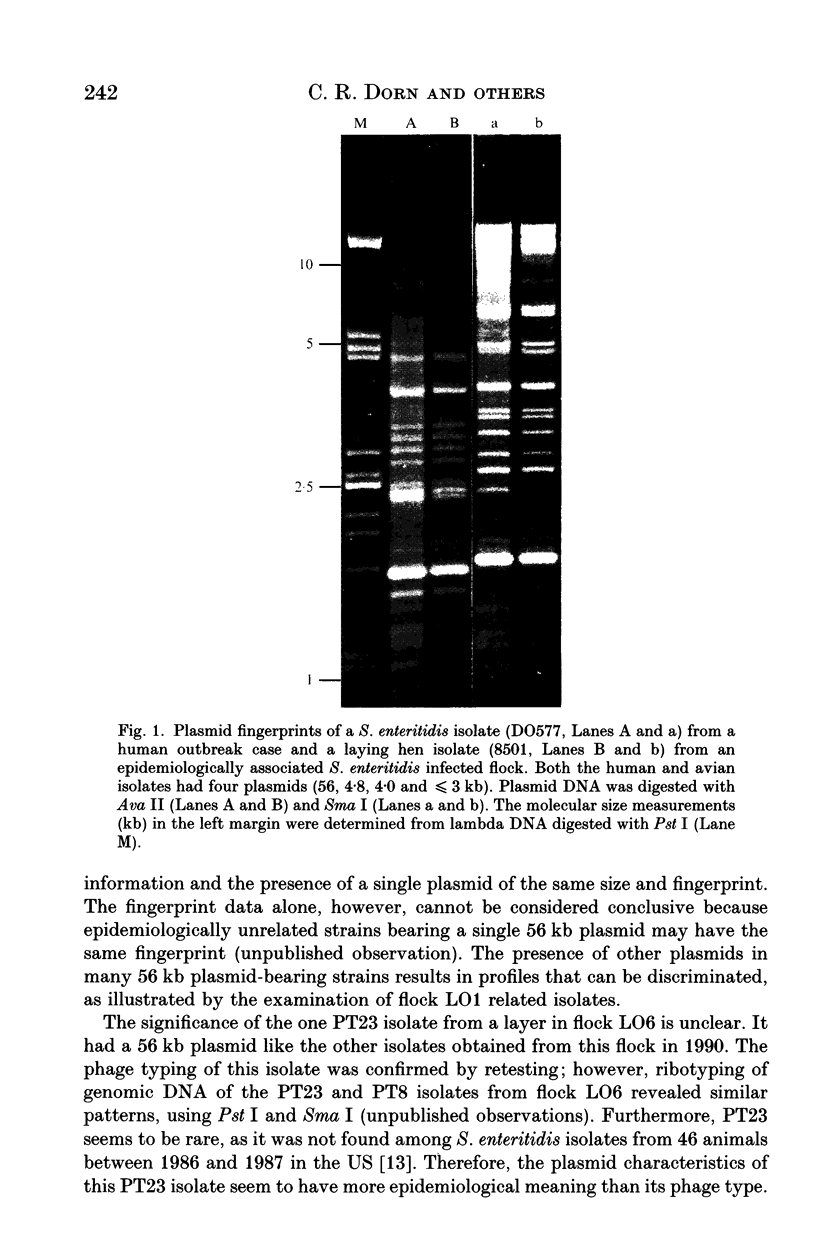
Plasmid analysis of Salmonella enteritidis isolates from human gastroenteritis cases and from two commercial egg-producing poultry flocks was performed to determine if the poultry flocks were the source of the human infections. The plasmid profile and restriction fragment pattern (fingerprint) of five S. enteritidis isolates from human cases matched those of nine isolates from internal organs of egg-laying hens in one flock which was the source of eggs consumed by the cases. Another commercial flock was epidemiologically associated as the source of eggs consumed by affected persons in four separate gastroenteritis outbreaks from which S. enteritidis isolates were available. Five S. enteritidis isolates from human cases in these four outbreaks had the same profile and fingerprint, and they all matched those of the 24 isolates from hens in this flock. These results provide further documentation of egg-borne transmission of S. enteritidis to humans.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Outbreak of Salmonella enteritidis infection associated with consumption of raw shell eggs, 1991. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1992 May 29;41(21):369–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn C. R., Silapanuntakul R., Angrick E. J., Shipman L. D. Plasmid analysis and epidemiology of Salmonella enteritidis infection in three commercial layer flocks. Avian Dis. 1992 Oct-Dec;36(4):844–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gast R. K., Beard C. W. Production of Salmonella enteritidis-contaminated eggs by experimentally infected hens. Avian Dis. 1990 Apr-Jun;34(2):438–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Stubbs A. D., Farmer J. J., 3rd Phage typing of Salmonella enteritidis in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2817–2823. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2817-2823.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton M., Pearson G. R., Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Woodward M., Wray C. Experimental Salmonella enteritidis infection in chicks. Vet Rec. 1989 Mar 4;124(9):223–223. doi: 10.1136/vr.124.9.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera M. J., Rivera N., Castillo J., Rubio M. C., Gómez-Lus R. Molecular and epidemiological study of Salmonella clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):927–932. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.927-932.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigue D. C., Cameron D. N., Puhr N. D., Brenner F. W., St Louis M. E., Wachsmuth I. K., Tauxe R. V. Comparison of plasmid profiles, phage types, and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella enteritidis isolates in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):854–857. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.854-857.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigue D. C., Tauxe R. V., Rowe B. International increase in Salmonella enteritidis: a new pandemic? Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Aug;105(1):21–27. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivaprasad H. L., Timoney J. F., Morales S., Lucio B., Baker R. C. Pathogenesis of Salmonella enteritidis infection in laying chickens. I. Studies on egg transmission, clinical signs, fecal shedding, and serologic responses. Avian Dis. 1990 Jul-Sep;34(3):548–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Louis M. E., Morse D. L., Potter M. E., DeMelfi T. M., Guzewich J. J., Tauxe R. V., Blake P. A. The emergence of grade A eggs as a major source of Salmonella enteritidis infections. New implications for the control of salmonellosis. JAMA. 1988 Apr 8;259(14):2103–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Ward L. R. Subdivision of Salmonella enteritidis phage types by plasmid profile typing. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Jun;102(3):459–465. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003017x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Shivaprasad H. L., Baker R. C., Rowe B. Egg transmission after infection of hens with Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4. Vet Rec. 1989 Dec 9;125(24):600–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth K. Molecular epidemiology of bacterial infections: examples of methodology and of investigations of outbreaks. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):682–692. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]