Abstract
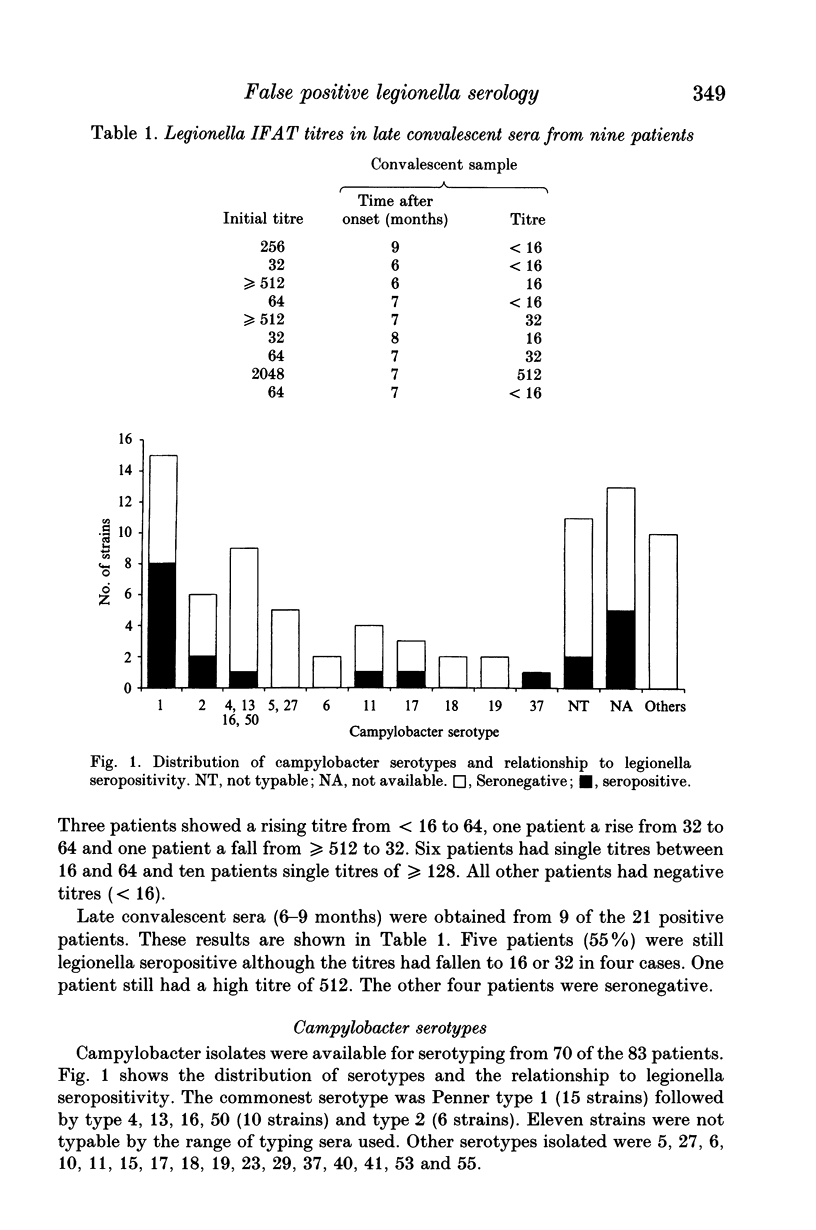
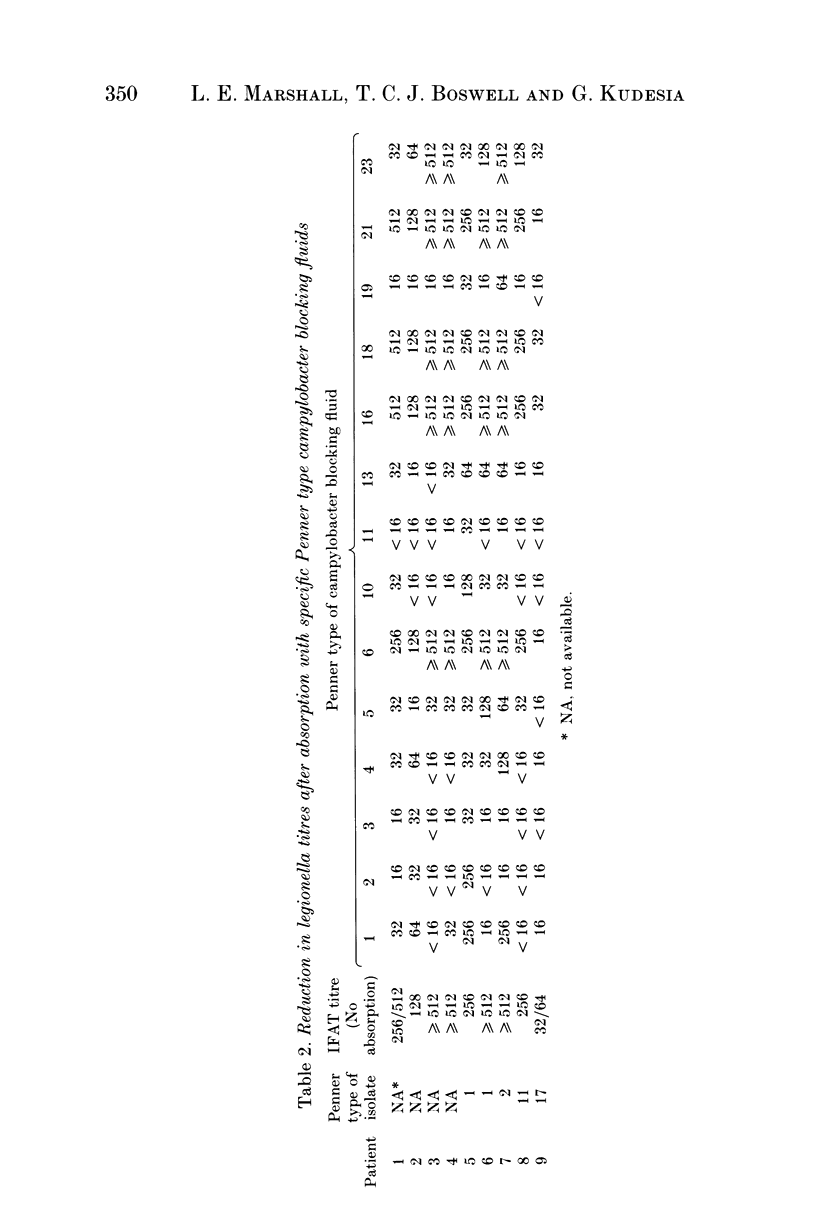
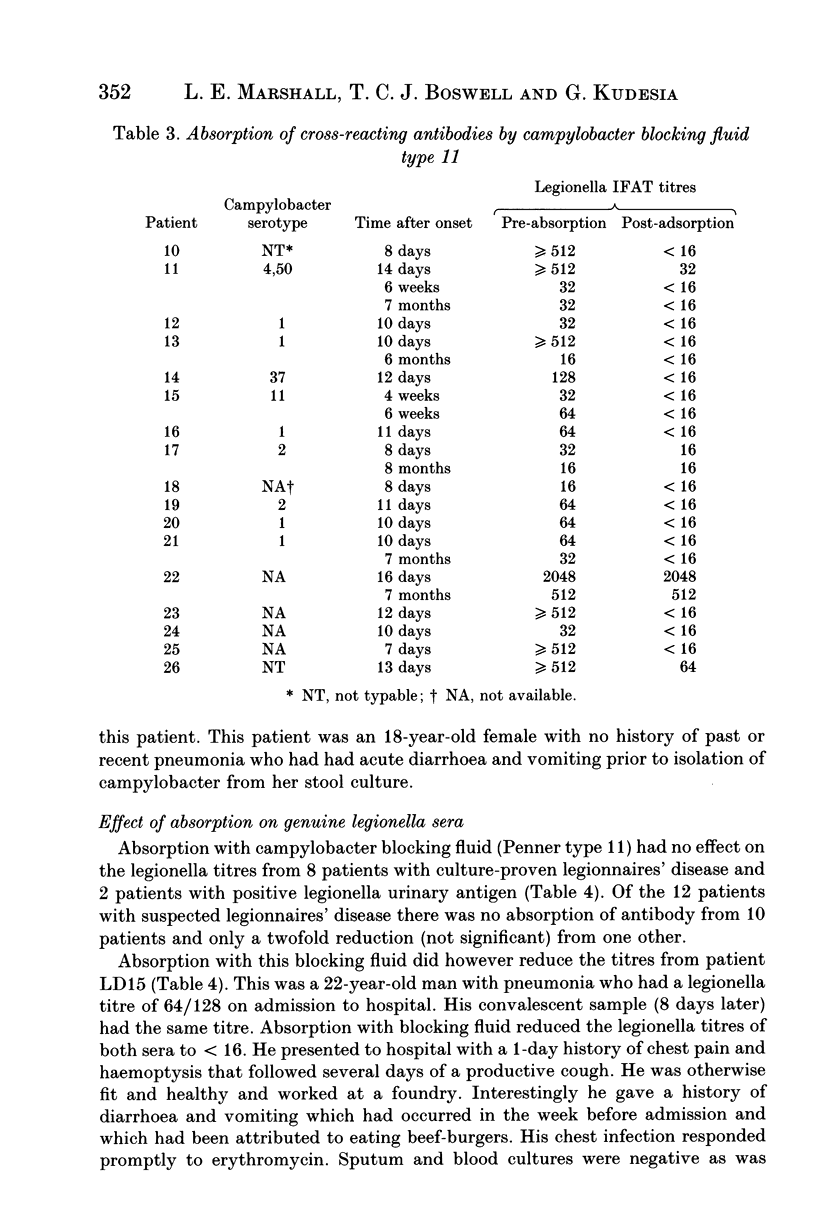
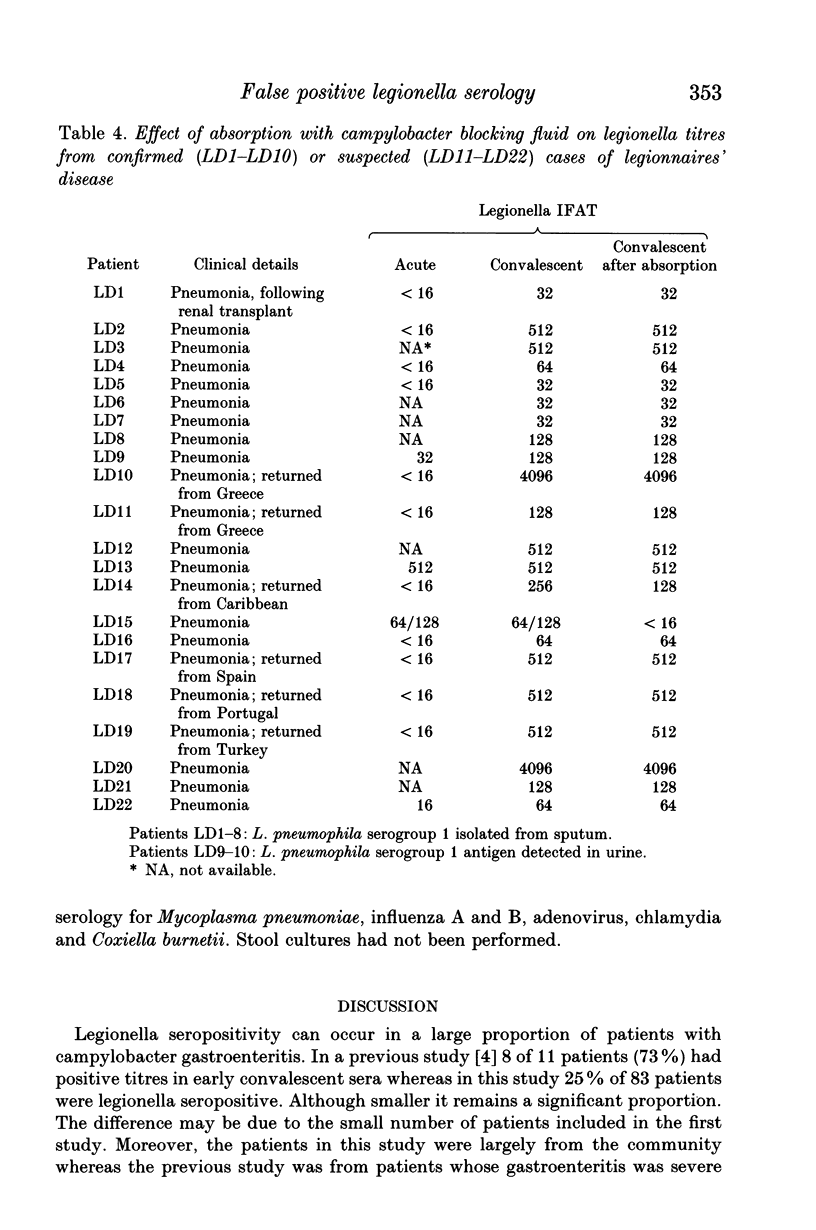
Sera from 83 patients with campylobacter gastroenteritis were examined for the presence of legionella antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence. Twenty-one patients (25%) had positive titres (> or = 16) including 11 patients with titres of > or = 128. Legionella seropositivity persisted in 5 of 9 patients (55%) studied for 6-9 months. Campylobacter isolates were serotyped by the Penner scheme. Isolates associated with legionella seropositivity included Penner types 1, 2 and 4, the common endemic serotypes in England. Campylobacter blocking fluids were prepared from a range of Penner reference strains. The blocking fluid prepared from Penner type 11 was the most efficient at inhibiting the false-positive legionella titres. Using this absorption step legionella titres were inhibited from 24 of 26 patients (92%) with campylobacter but not from 8 patients with culture-proven legionnaires' disease. We recommend that this method is incorporated into routine diagnostic legionella serology in order to eliminate false-positive reactions due to campylobacter.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boswell T. C., Kudesia G. Serological cross-reaction between Legionella pneumophila and campylobacter in the indirect fluorescent antibody test. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Oct;109(2):291–295. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005024x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell T. C., Kudesia G. Seropositivity for Legionella in Campylobacter infection. Lancet. 1992 Jan 18;339(8786):191–191. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheesbrough J. S., Makin T., Taxman B. C., Beeching N. J., Mutton K. J. False-positive legionella serology in campylobacter infection. Lancet. 1992 Feb 15;339(8790):429–429. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90113-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon R. J., Abraham W. H. Crossreactions between Legionella and Campylobacter spp. Lancet. 1992 Aug 29;340(8818):551–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T. G., Taylor A. G. Diagnosis of Legionella pneumophila infections by means of formolised yolk sac antigens. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Feb;35(2):211–214. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall E. J., Tanner E. I. Campylobacter enteritis in general practice. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):155–163. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson A. D., Healing T. D. The surveillance and control of campylobacter infection. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1992 Nov 6;2(12):R133–R139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch G., Hayes P. S., Hill D. L., Baine W. B. Prevalence of antibody to Legionella pneumophila in middle-aged and elderly Americans. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):784–788. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. G., Harrison T. G., Dighero M. W., Bradstreet C. M. False positive reactions in the indirect fluorescent antibody test for Legionnaires' disease eliminated by use of formolised yolk-sac antigen. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):686–689. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Cruce D. D., Broome C. V. Validation of Legionella pneumophila indirect immunofluorescence assay with epidemic sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.139-146.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Farshy C. E., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D., Yealy L. P. Measure of immunoglobulin G-, M-, and A-specific titers against Legionella pneumophila and inhibition of titers against nonspecific, gram-negative bacterial antigens in the indirect immunofluorescence test for legionellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):685–689. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.685-689.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


