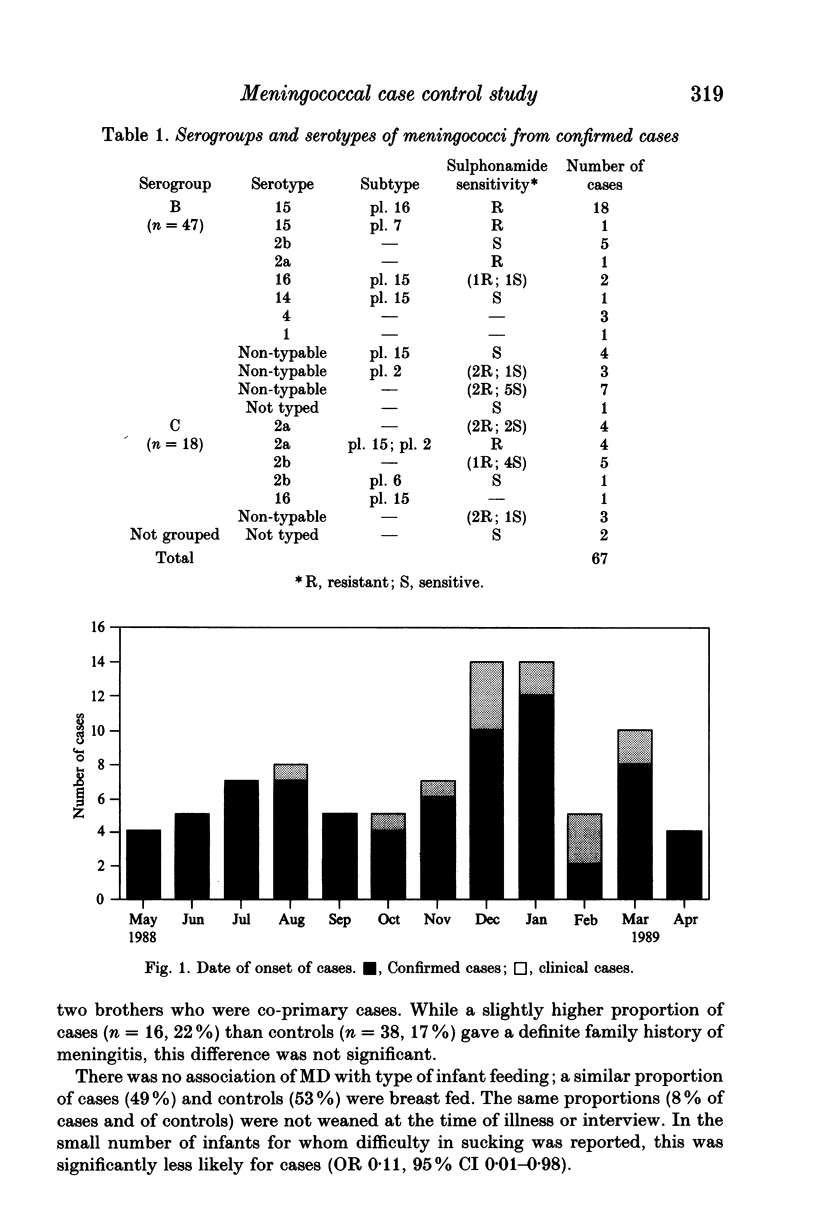
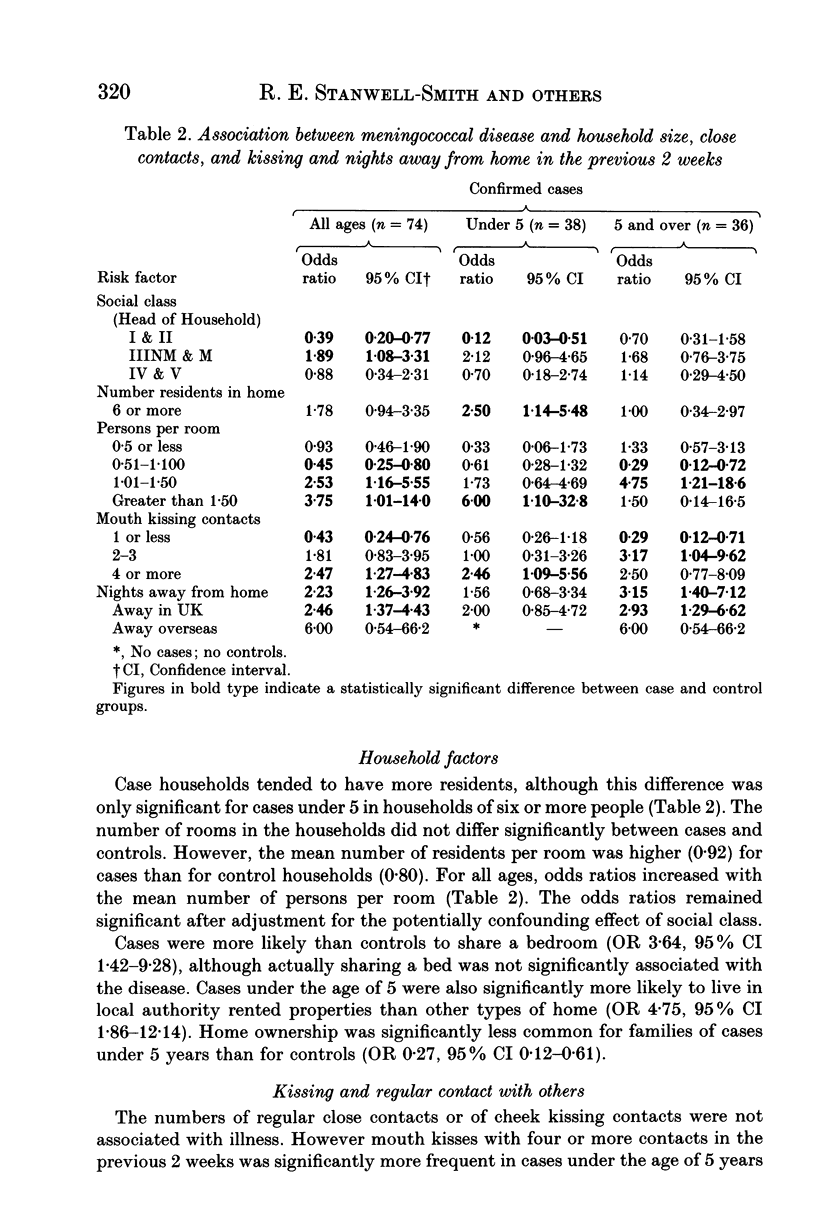
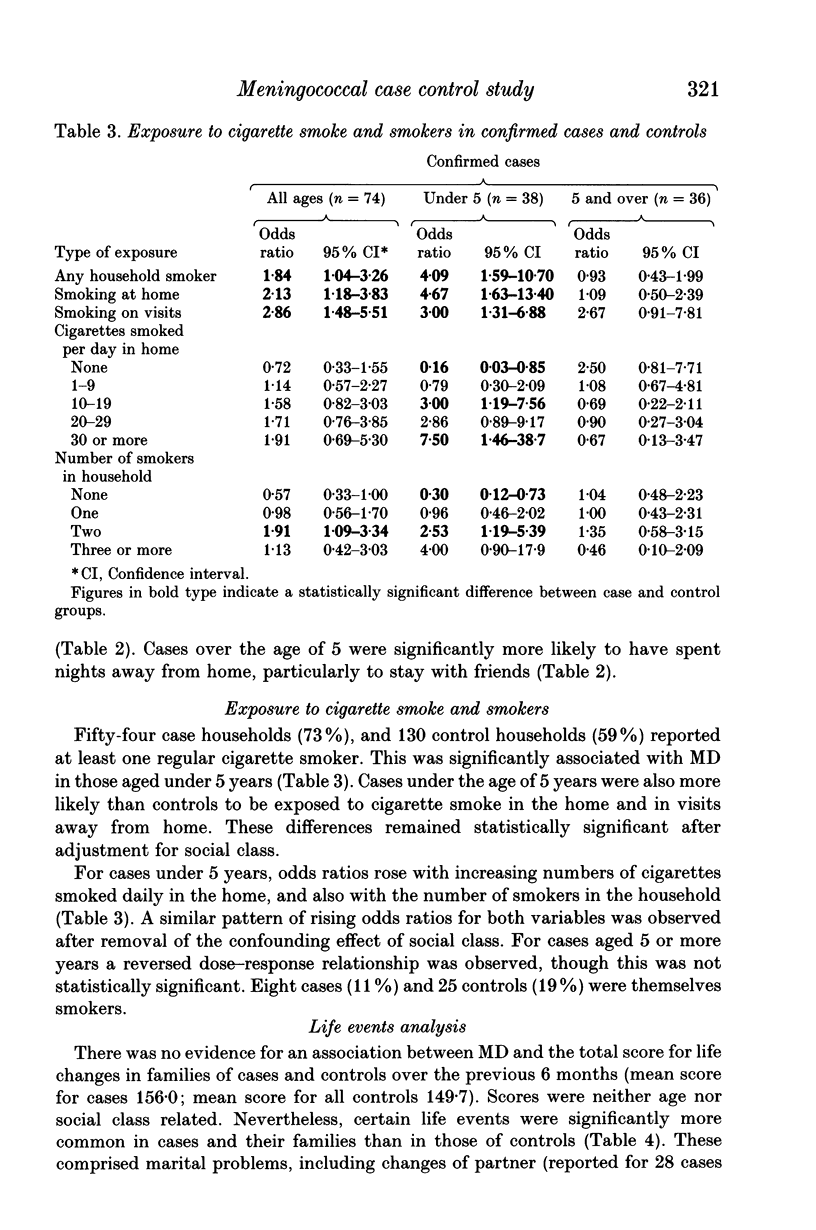
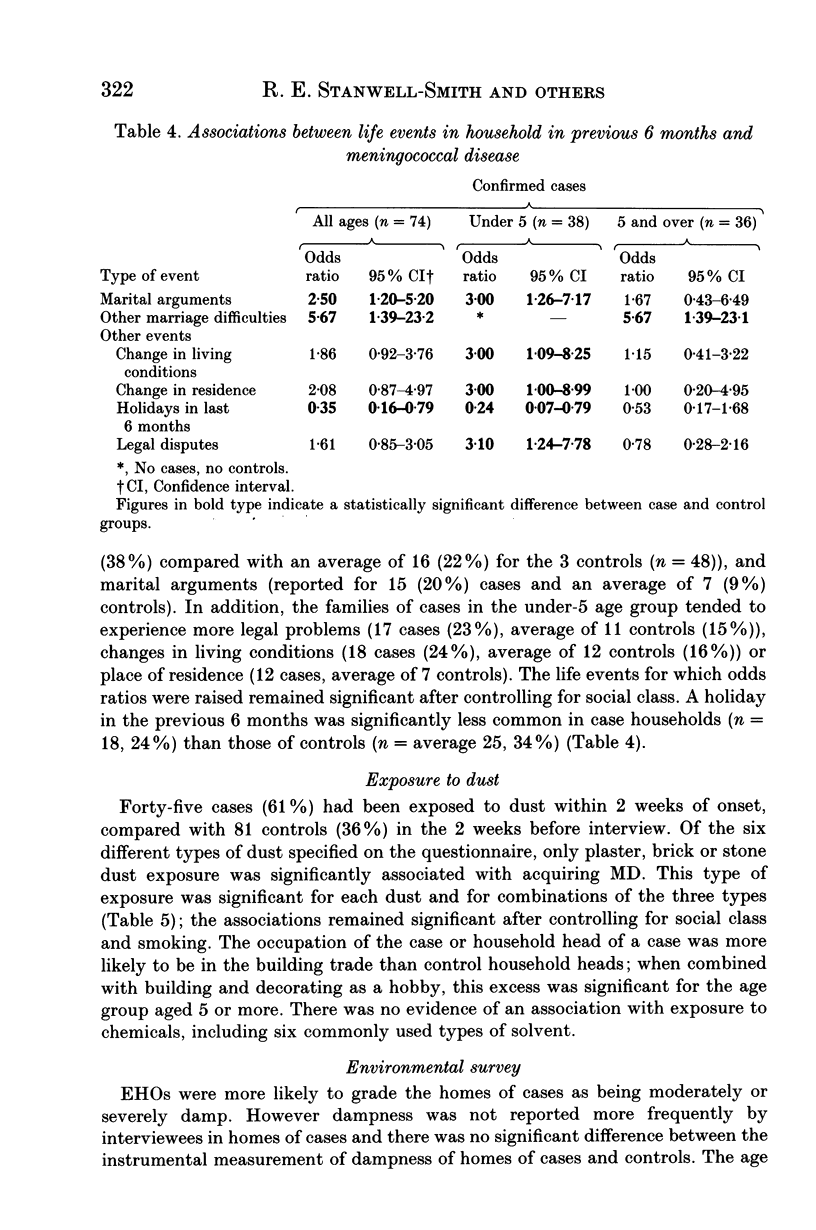
Abstract
This case control study investigated environmental factors in 74 confirmed cases of meningococcal disease (MD). In children aged under 5, passive smoking in the home (30 or more cigarettes daily) was associated with an odds ratio (OR) of 7.5 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.46-38.66). ORs increased both with the numbers of cigarettes smoked and with the number of smokers in the household, suggesting a dose-response relationship. MD in this age group was also significantly associated with household overcrowding (more than 1.5 persons per room) (OR 6.0, 95% CI 1.10-32.8), with kisses on the mouth with 4 or more contacts in the previous 2 weeks (OR 2.46, 95% CI 1.09-5.56), with exposure to dust from plaster, brick or stone in the previous 2 weeks (OR 2.24, 95% CI 1.07-4.65); and with changes in residence (OR 3.0, 95% CI 1.0-8.99), marital arguments (OR 3.0, 95% CI 1.26-7.17) and legal disputes in the previous 6 months (OR 3.10, 95% CI 1.24-7.78). These associations were independent of social class. Public health measures to lower the prevalence of cigarette smoking by parents of young children may reduce the incidence of MD. The influence of building dust and stressful life events merits further investigation.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott J. D., Jones D. M., Painter M. J., Young S. E. The epidemiology of meningococcal infections in England and Wales, 1912-1983. J Infect. 1985 Nov;11(3):241–257. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)93294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg A. T., Shapiro E. D., Capobianco L. A. Group day care and the risk of serious infectious illnesses. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 Jan 15;133(2):154–163. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjune G., Høiby E. A., Grønnesby J. K., Arnesen O., Fredriksen J. H., Halstensen A., Holten E., Lindbak A. K., Nøkleby H., Rosenqvist E. Effect of outer membrane vesicle vaccine against group B meningococcal disease in Norway. Lancet. 1991 Nov 2;338(8775):1093–1096. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91961-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell C. C., Jónsdóttir K., Hanson M., Todd W. T., Chaudhuri A. K., Mathew B., Brettle R. P., Weir D. M. Non-secretion of ABO antigens predisposing to infection by Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Lancet. 1986 Aug 2;2(8501):284–285. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell C. C., Weir D. M., James V. S., Todd W. T., Banatvala N., Chaudhuri A. K., Gray H. G., Thomson E. J., Fallon R. J. Secretor status, smoking and carriage of Neisseria meningitidis. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Apr;104(2):203–209. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800059367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce W. T., Jensen E. W., Cassel J. C., Collier A. M., Smith A. H., Ramey C. T. Influence of life events and family routines on childhood respiratory tract illness. Pediatrics. 1977 Oct;60(4 Pt 2):609–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadhead W. E., Kaplan B. H., James S. A., Wagner E. H., Schoenbach V. J., Grimson R., Heyden S., Tibblin G., Gehlbach S. H. The epidemiologic evidence for a relationship between social support and health. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 May;117(5):521–537. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright K. A., Jones D. M., Smith A. J., Stuart J. M., Kaczmarski E. B., Palmer S. R. Influenza A and meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1991 Aug 31;338(8766):554–557. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright K. A., Stuart J. M., Noah N. D. An outbreak of meningococcal disease in Gloucestershire. Lancet. 1986 Sep 6;2(8506):558–561. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright K. A., Stuart J. M., Robinson P. M. Meningococcal carriage in close contacts of cases. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Feb;106(1):133–141. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800056491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Tyrrell D. A., Smith A. P. Psychological stress and susceptibility to the common cold. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 29;325(9):606–612. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108293250903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Williamson G. M. Stress and infectious disease in humans. Psychol Bull. 1991 Jan;109(1):5–24. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.109.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wals P., Hertoghe L., Borlée-Grimée I., De Maeyer-Cleempoel S., Reginster-Haneuse G., Dachy A., Bouckaert A., Lechat M. F. Meningococcal disease in Belgium. Secondary attack rate among household, day-care nursery and pre-elementary school contacts. J Infect. 1981 Mar;3(1 Suppl):53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)80009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. T., 3rd, Kohler P. F., Curd J. G., Judson F. N., Reller L. B. Prevalence of congenital or acquired complement deficiency in patients with sporadic meningocococcal disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 21;308(16):913–916. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304213081601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon R. J., Brown W. M., Lore W. Meningococcal infections in Scotland 1972-82. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Oct;93(2):167–180. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400064688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster M. T., Jr, Sanders E., Ginter M. Epidemiology of sulfonamide-resistant meningococcal infections in a civilian population. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 May;93(5):346–353. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham N. M., Douglas R. M., Ryan P. Stress and acute respiratory infection. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Sep;124(3):389–401. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Greenwood A. M., Bradley A. K., Williams K., Hassan-King M., Shenton F. C., Wall R. A., Hayes R. J. Factors influencing susceptibility to meningococcal disease during an epidemic in The Gambia, West Africa. J Infect. 1987 Mar;14(2):167–184. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(87)92052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneberg B., Tønjum T., Rodahl K., Gedde-Dahl T. W. Factors preceding the onset of meningococcal disease, with special emphasis on passive smoking, symptoms of ill health. NIPH Ann. 1983 Dec;6(2):169–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes T. H., Rahe R. H. The Social Readjustment Rating Scale. J Psychosom Res. 1967 Aug;11(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(67)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman S. J. Housing dampness and health amongst British Bengalis in east London. Soc Sci Med. 1990;30(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(90)90336-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemmott J. B., 3rd, Locke S. E. Psychosocial factors, immunologic mediation, and human susceptibility to infectious diseases: how much do we know? Psychol Bull. 1984 Jan;95(1):78–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser A. B., Hennekens C. H., Saslaw M. S., Hayes P. S., Bennett J. V. Seroepidemiology and chemoprophylaxis disease due to sulfonamide-resistant Neisseria meningitidis in a civillian population. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):217–224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpi T., Anttila M., Kallio M. J., Peltola H. Severity of childhood bacterial meningitis and duration of illness before diagnosis. Lancet. 1991 Aug 17;338(8764):406–409. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91032-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. O., Feigin R. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Report of the Task Force on Diagnosis and Management of Meningitis. Pediatrics. 1986 Nov;78(5 Pt 2):959–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasinski K., Nelson J. D., Butler S., Luby J. P., Kusmiesz H. Possible association of mycoplasma and viral respiratory infections with bacterial meningitis. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Mar;125(3):499–508. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry S. Health and housing: Noise, space, and light. BMJ. 1989 Dec 9;299(6713):1439–1442. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6713.1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda M., Holmes T. H. Magnitude estimations of social readjustments. J Psychosom Res. 1967 Aug;11(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(67)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. S., Hierholzer J., DeWitt W., Gouan K., Djoré D., Lippeveld T., Plikaytis B., Broome C. V. Respiratory viruses and mycoplasma as cofactors for epidemic group A meningococcal meningitis. JAMA. 1990 Sep 12;264(10):1271–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olcén P., Kjellander J., Danielsson D., Lindquist B. L. Epidemiology of Neisseria meningitidis; prevalence and symptoms from the upper respiratory tract in family members to patients with meningococcal disease. Scand J Infect Dis. 1981;13(2):105–109. doi: 10.3109/inf.1981.13.issue-2.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen S. F., Djurhuus B., Rasmussen K., Joensen H. D., Larsen S. O., Zoffman H., Lind I. Pharyngeal carriage of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria lactamica in households with infants within areas with high and low incidences of meningococcal disease. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Jun;106(3):445–457. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., MacGregor R. R., Beaty H. N. Bactericidal antibody after colonization with Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jan;127(1):56–62. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Cartwright K. A., Dawson J. A., Rickard J., Noah N. D. Risk factors for meningococcal disease: a case control study in south west England. Community Med. 1988 May;10(2):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Cartwright K. A., Robinson P. M., Noah N. D. Does eradication of meningococcal carriage in household contacts prevent secondary cases of meningococcal disease? BMJ. 1989 Mar 4;298(6673):569–570. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6673.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Cartwright K. A., Robinson P. M., Noah N. D. Effect of smoking on meningococcal carriage. Lancet. 1989 Sep 23;2(8665):723–725. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90781-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. C., Bendana N. S., Waterman S. H., Rathbun M., Arakere G., Frasch C. E., Wenger J. D., Magsombol V., Clark J. H. Risk factors for carriage of meningococcus in the Los Angeles County men's jail system. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 Feb 1;133(3):286–295. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., LaForce F. M., Head J. J., Feeley J. C., Bennett J. V. A simultaneous outbreak of meningococcal and influenza infections. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jul 6;287(1):5–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197207062870102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


