Abstract
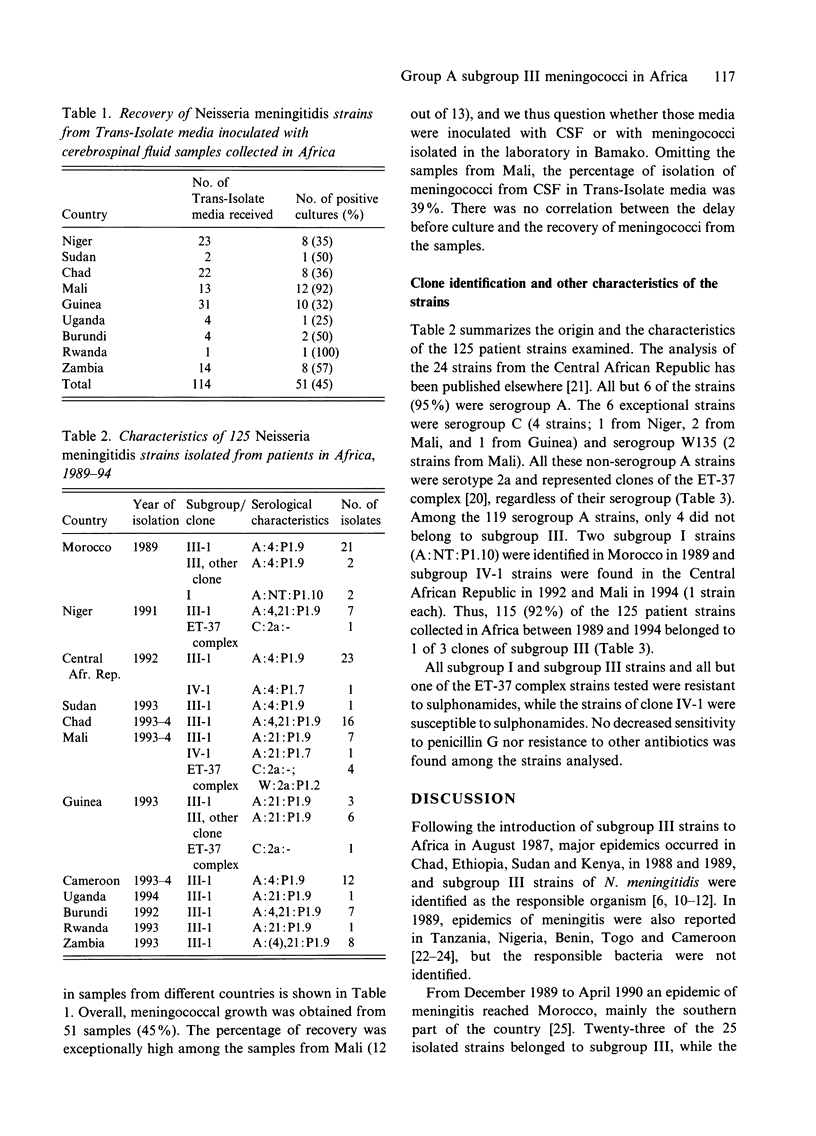
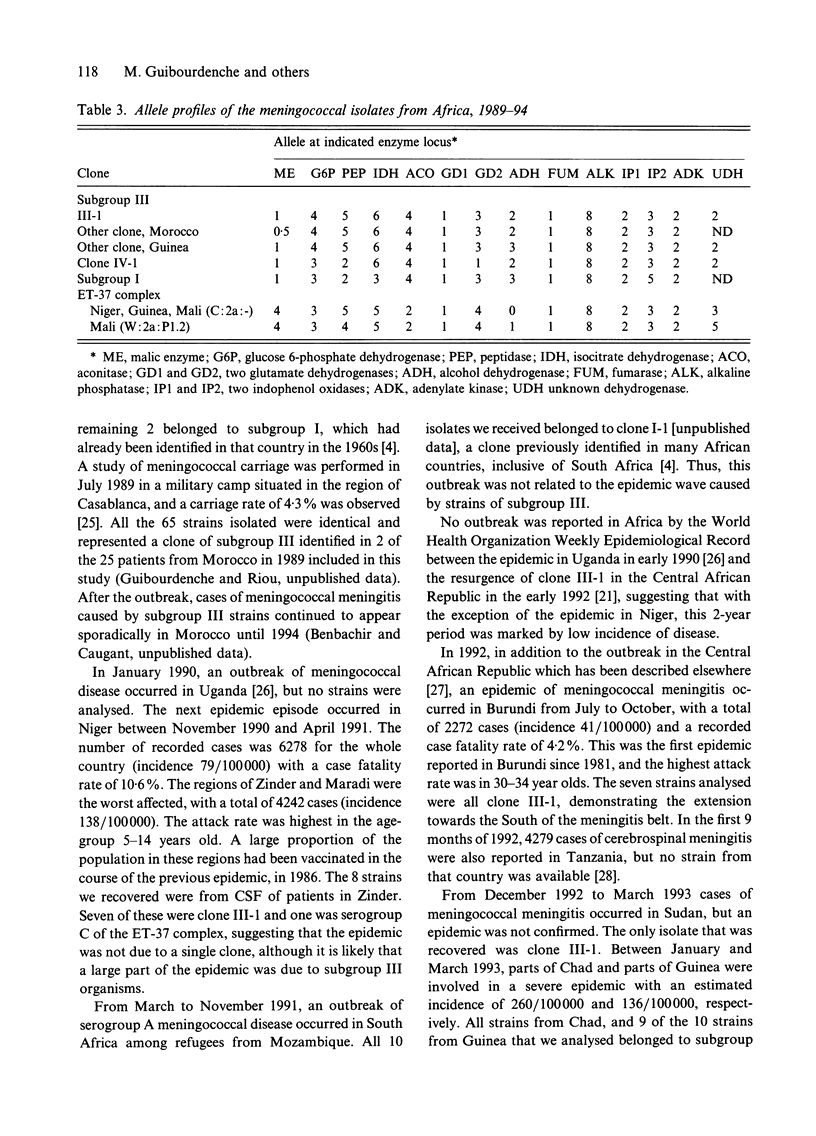
A total of 125 strains of Neisseria meningitidis recovered in the course of outbreaks from patients with systemic disease in 11 African countries between 1989 and 1994 were analysed by serogrouping, serotyping and multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Of the 125 patient strains 115 (92%) belonged to the clone-complex of serogroup A meningococci, designated subgroup III. Among the remaining strains, 4 were also serogroup A, but belonged to the clonal groups I and IV-1 (2 strains each), whilst 6 strains (4 serogroup C and 2 serogroup W135) represented clones of the ET-37 complex. Our results indicated that the second pandemic caused by clones of subgroup III is still spreading in Africa. Towards the West it has reached Niger, Mali, Guinea and The Gambia, and towards the South, the Central African Republic, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania and Zambia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Kusecek B., Morelli G., Eickmann K., Wang J. F., Crowe B., Wall R. A., Hassan-King M., Moore P. S., Zollinger W. A comparison of the variable antigens expressed by clone IV-1 and subgroup III of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):53–68. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ajello G. W., Feeley J. C., Hayes P. S., Reingold A. L., Bolan G., Broome C. V., Phillips C. J. Trans-isolate medium: a new medium for primary culturing and transport of Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):55–58. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.55-58.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Bol P., Høiby E. A., Zanen H. C., Frøholm L. O. Clones of serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis causing systemic disease in The Netherlands, 1958-1986. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):867–874. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Høiby E. A., Magnus P., Scheel O., Hoel T., Bjune G., Wedege E., Eng J., Frøholm L. O. Asymptomatic carriage of Neisseria meningitidis in a randomly sampled population. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Feb;32(2):323–330. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.2.323-330.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheesbrough J. S., Morse A. P., Green S. D. Meningococcal meningitis and carriage in western Zaire: a hypoendemic zone related to climate? Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Feb;114(1):75–92. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800051931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimanot R. T., Caugant D. A., Fekadu D., Bjune G., Belete B., Frøholm L. O., Høiby E. A., Rosenqvist E., Selander R. K., Bjorvatn B. Characteristics of serogroup A Neisseria meningitidis responsible for an epidemic in Ethiopia, 1988-89. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22(2):171–174. doi: 10.3109/00365549009037898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Sutcliffe E. M. Group A meningococcal disease in England associated with the Haj. J Infect. 1990 Jul;21(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(90)90577-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. S., Harrison L. H., Telzak E. E., Ajello G. W., Broome C. V. Group A meningococcal carriage in travelers returning from Saudi Arabia. JAMA. 1988 Nov 11;260(18):2686–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. S. Meningococcal meningitis in sub-Saharan Africa: a model for the epidemic process. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;14(2):515–525. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.2.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. S., Reeves M. W., Schwartz B., Gellin B. G., Broome C. V. Intercontinental spread of an epidemic group A Neisseria meningitidis strain. Lancet. 1989 Jul 29;2(8657):260–263. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nejmi S., Belhaj A., Guibourdenche M., Riou J. Y. Etude de quatre-vingt dix souches de Neisseria meningitidis de sérogroupe a isolées du liquide céphalorachidien (25) et du rhinopharynx (65) au Maroc (décembre 1989-avril 1990). Pathol Biol (Paris) 1992 Dec;40(10):993–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olyhoek T., Crowe B. A., Achtman M. Clonal population structure of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A isolated from epidemics and pandemics between 1915 and 1983. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9(4):665–692. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H. Meningococcal disease: still with us. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):71–91. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinner R. W., Onyango F., Perkins B. A., Mirza N. B., Ngacha D. M., Reeves M., DeWitt W., Njeru E., Agata N. N., Broome C. V. Epidemic meningococcal disease in Nairobi, Kenya, 1989. The Kenya/Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Meningitis Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;166(2):359–364. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. Y., Caugant D. A., Selander R. K., Poolman J. T., Guibourdenche M., Collatz E. Characterization of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A strains from an outbreak in France by serotype, serosubtype, multilocus enzyme genotype and outer membrane protein pattern. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 May;10(5):405–409. doi: 10.1007/BF01968019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salih M. A., Danielsson D., Bäckman A., Caugant D. A., Achtman M., Olcén P. Characterization of epidemic and nonepidemic Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A strains from Sudan and Sweden. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1711–1719. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1711-1719.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerkove M., Bradstreet P., Faucon R., Benech S. Milieu de transport pour méningocoques. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Aug;113(2):260–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. F., Caugant D. A., Li X., Hu X., Poolman J. T., Crowe B. A., Achtman M. Clonal and antigenic analysis of serogroup A Neisseria meningitidis with particular reference to epidemiological features of epidemic meningitis in the People's Republic of China. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5267–5282. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5267-5282.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. F., Caugant D. A., Morelli G., Koumaré B., Achtman M. Antigenic and epidemiologic properties of the ET-37 complex of Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1320–1329. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedege E., Høiby E. A., Rosenqvist E., Frøholm L. O. Serotyping and subtyping of Neisseria meningitidis isolates by co-agglutination, dot-blotting and ELISA. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Mar;31(3):195–201. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-3-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


