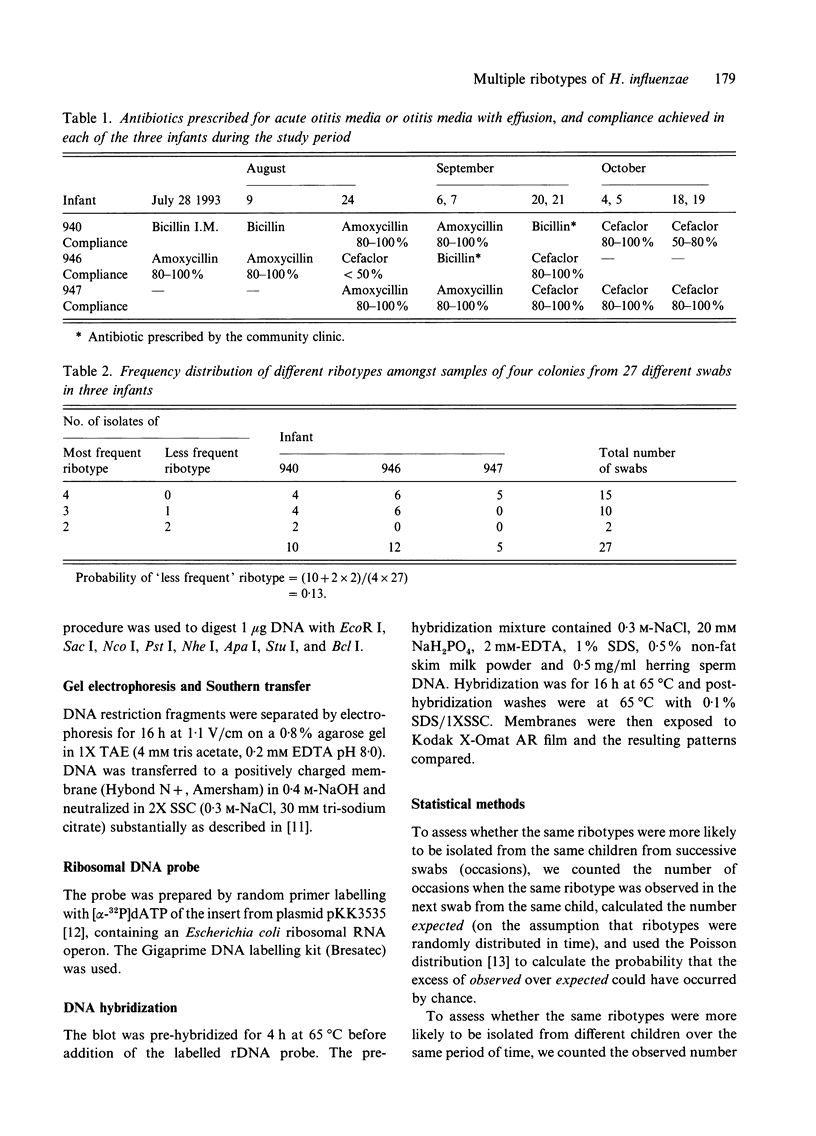
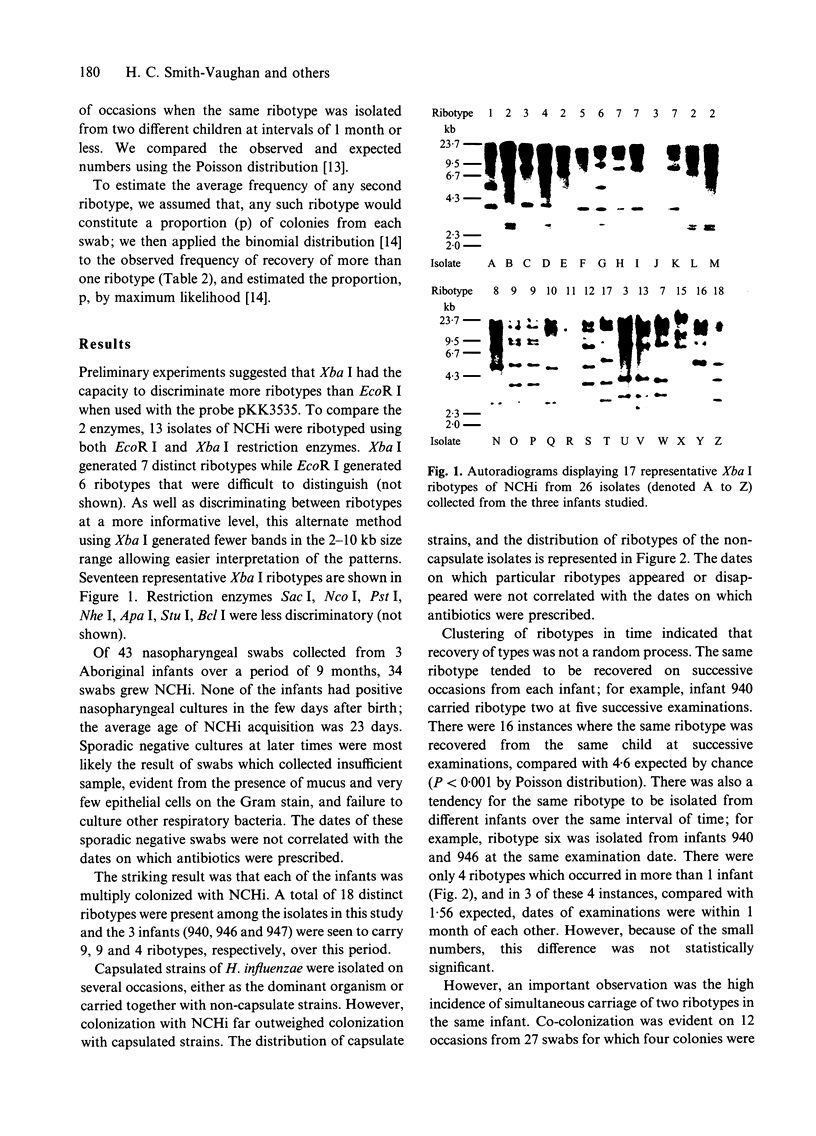
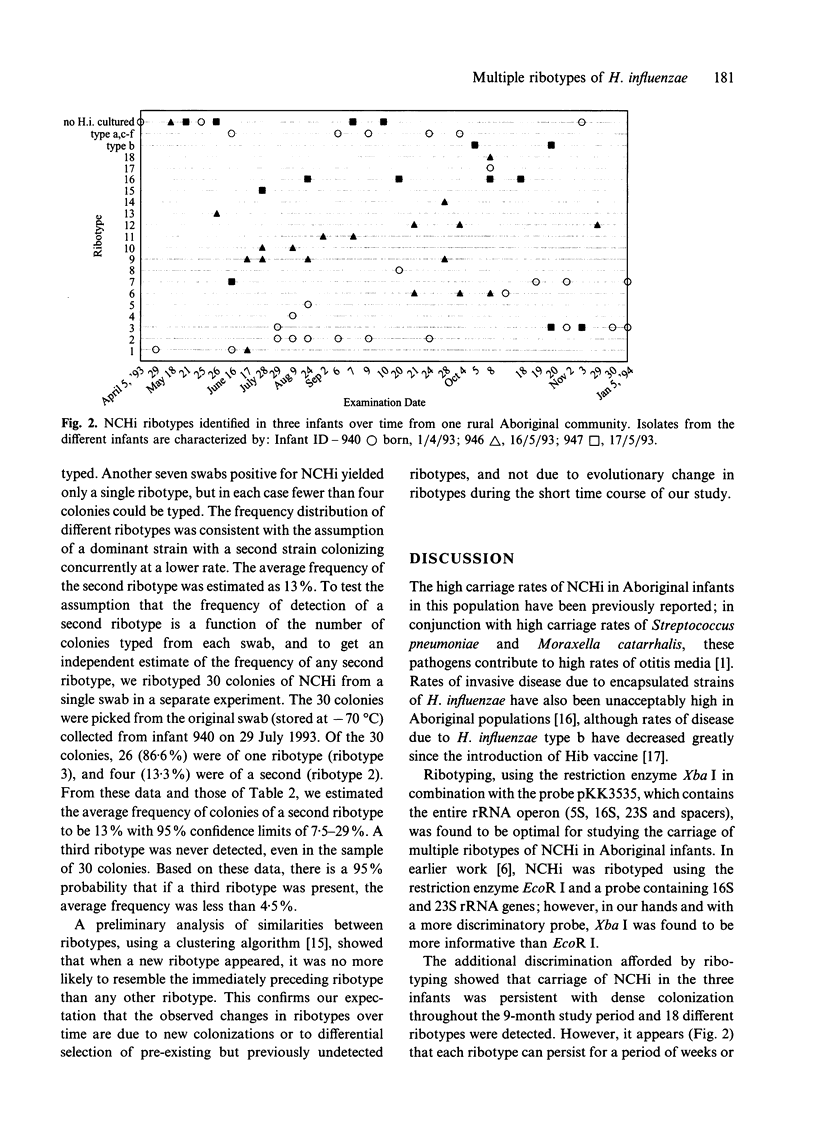
Abstract
Ribotyping with the restriction enzyme XbaI was used to study the dynamics of Carriage of non-encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae (NCHi) in Aboriginal infants at risk of otitis media. Carriage rates of NCHi in the infants in the community were very high; the median age for detection was 50 days and colonization was virtually 100% by 120 days of age and persisted at a high level throughout the first year of life [1]. Eighteen different ribotypes of NCHi were identified from 34 positive swabs taken from 3 infants over a period of 9 months. The same ribotypes were recovered for up to 3 months from consecutive swabs of individual infants, and 12 of 27 swabs (44.4%) yielded two ribotypes from four colonies typed. Statistical analysis suggested that most swabs would have been positive for two ribotypes if enough colonies had been typed although the second most frequent ribotype was detected on average in only 13% of strains. Early colonization and carriage of multiple ribotypes of NCHi may help to explain the chronicity of carriage and thus the persistence of otitis media in Aboriginal infants.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bale J. R. Creation of a research program to determine the etiology and epidemiology of acute respiratory tract infection among children in developing countries. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Nov-Dec;12 (Suppl 8):S861–S866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_8.s861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce K. D., Jordens J. Z. Characterization of noncapsulate Haemophilus influenzae by whole-cell polypeptide profiles, restriction endonuclease analysis, and rRNA gene restriction patterns. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):291–296. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.291-296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapin K. C., Doern G. V. Selective media for recovery of Haemophilus influenzae from specimens contaminated with upper respiratory tract microbial flora. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1163–1165. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1163-1165.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Bernstein J., Brodsky L., Stanievich J., Krystofik D., Shuff C., Hong J. J., Ogra P. L. Otitis media in children. I. The systemic immune response to nontypable Hemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):999–1004. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna J. N. The epidemiology of invasive Haemophilus influenzae infections in children under five years of age in the Northern Territory: a three-year study. Med J Aust. 1990 Mar 5;152(5):234-6, 238, 240. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1990.tb120916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordens J. Z., Leaves N. I., Anderson E. C., Slack M. P. Polymerase chain reaction-based strain characterization of noncapsulate Haemophilus influenzae. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Nov;31(11):2981–2987. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.11.2981-2987.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach A. J., Boswell J. B., Asche V., Nienhuys T. G., Mathews J. D. Bacterial colonization of the nasopharynx predicts very early onset and persistence of otitis media in Australian aboriginal infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1994 Nov;13(11):983–989. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199411000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bernstein J. M., Dryja D. M., Campagnari A. A., Apicella M. A. Outer membrane protein and lipooligosaccharide analysis of paired nasopharyngeal and middle ear isolates in otitis media due to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenetic and epidemiological observations. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):723–731. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Vaughan H. C., Sriprakash K. S., Mathews J. D., Kemp D. J. Long PCR-ribotyping of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 May;33(5):1192–1195. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.5.1192-1195.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trottier S., Stenberg K., Svanborg-Edén C. Turnover of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae in the nasopharynges of healthy children. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2175–2179. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2175-2179.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk D. C. The pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


