Abstract
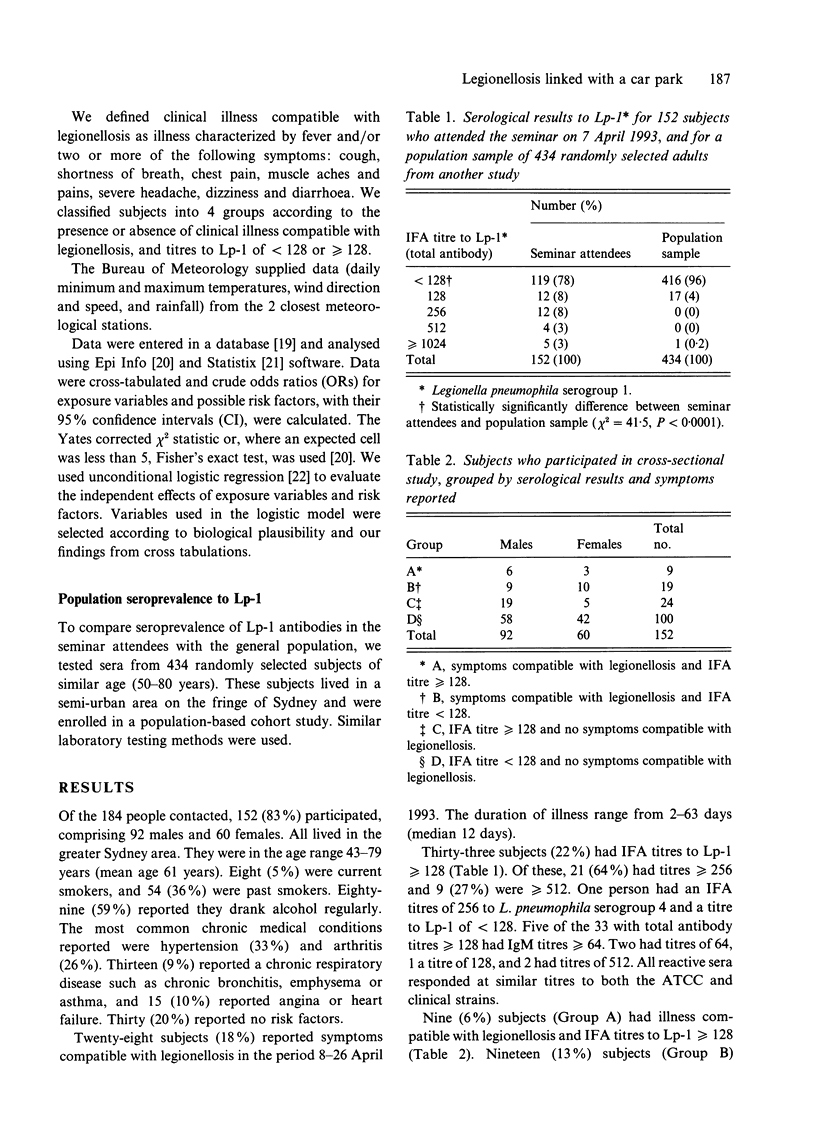
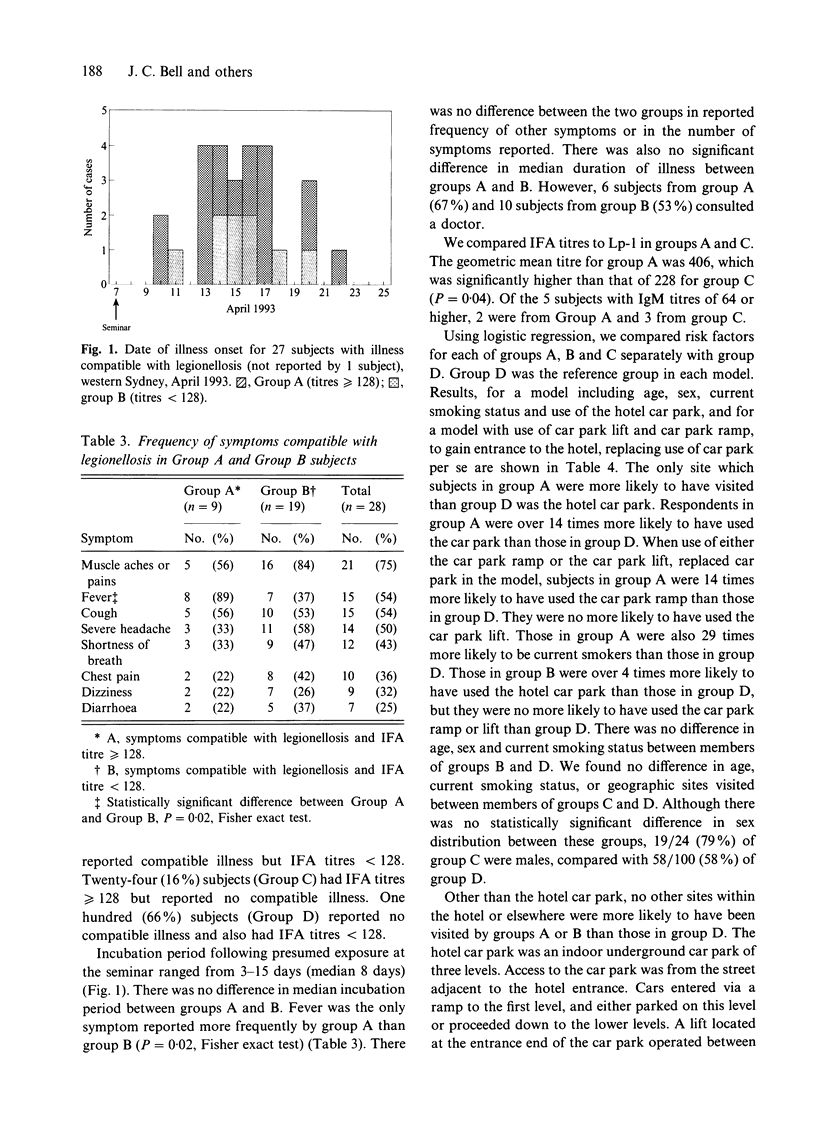
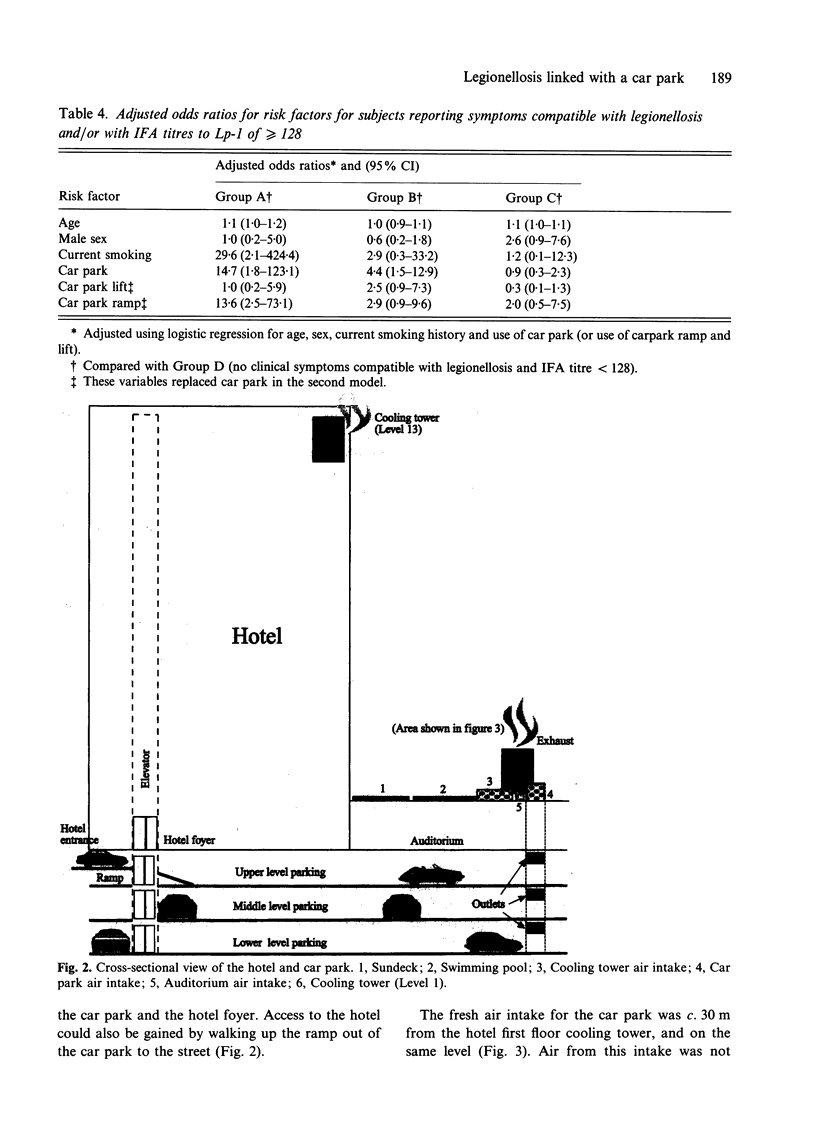
An outbreak of legionellosis associated with a hotel in Sydney, Australia, and the subsequent epidemiological and environmental investigations are described. Four cases of Legionnaires' disease were notified to the Public Health Unit. A cross-sectional study of 184 people who attended a seminar at the hotel was carried out. Serological and questionnaire data were obtained for 152 (83%) of these. Twenty-eight (18%) respondents reported symptoms compatible with legionellosis. Thirty-three subjects (22%) had indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) titres to Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 (Lp-1) of 128 or higher. The only site which those with symptoms of legionellosis and IFA titre > or = 128 were more likely to have visited than controls was the hotel car park (adjusted odds ratio [OR] 14.7, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.8-123.1). Those with symptoms compatible with legionellosis, but whose IFA titres were < 128 were also more likely to have visited the hotel car park (adjusted OR 4.4, 95% CI: 1.5-12.9). Seroprevalence of Lp-1 antibodies was higher in those who attended the seminar than in a population sample of similar age. Findings suggested that the 4 cases represented a small fraction of all those infected, and highlighted difficulties in defining illness caused by Lp-1 and in interpreting serology.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addiss D. G., Davis J. P., LaVenture M., Wand P. J., Hutchinson M. A., McKinney R. M. Community-acquired Legionnaires' disease associated with a cooling tower: evidence for longer-distance transport of Legionella pneumophila. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 Sep;130(3):557–568. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhopal R. S., Diggle P., Rowlingson B. Pinpointing clusters of apparently sporadic cases of Legionnaires' disease. BMJ. 1992 Apr 18;304(6833):1022–1027. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6833.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Outbreak of pneumonia associated with a cruise ship, 1994. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1994 Jul 22;43(28):521–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher P. J., Noonan L. M., Chiew R. Epidemic of Legionnaires' disease in Wollongong. Med J Aust. 1987 Aug 3;147(3):127–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colville A., Crowley J., Dearden D., Slack R. C., Lee J. V. Outbreak of Legionnaires' disease at University Hospital, Nottingham. Epidemiology, microbiology and control. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Feb;110(1):105–116. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800050731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Laboratory diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):317–327. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Orenstein W., Parkin W. E., Beecham H. J., Sharrar R. G., Harris J., Mallison G. F., Martin S. M., McDade J. E. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girod J. C., Reichman R. C., Winn W. C., Jr, Klaucke D. N., Vogt R. L., Dolin R. Pneumonic and nonpneumonic forms of legionellosis. The result of a common-source exposure to Legionella pneumophila. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):545–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlady W. G., Mullen R. C., Mintz C. S., Shelton B. G., Hopkins R. S., Daikos G. L. Outbreak of Legionnaire's disease linked to a decorative fountain by molecular epidemiology. Am J Epidemiol. 1993 Oct 15;138(8):555–562. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoge C. W., Breiman R. F. Advances in the epidemiology and control of Legionella infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:329–340. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. A., Cartwright K. A., Smith M. C., Middleton J., Bartlett C. L., Lee J. V., Dennis P. J., Harper D. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease in Gloucester. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Aug;107(1):133–141. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann A. F., McDade J. E., Patton C. M., Bennett J. V., Skaliy P., Feeley J. C., Anderson D. C., Potter M. E., Newhouse V. F., Gregg M. B. Pontiac fever: isolation of the etiologic agent (Legionella pneumophilia) and demonstration of its mode of transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Sep;114(3):337–347. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaucke D. N., Vogt R. L., LaRue D., Witherell L. E., Orciari L. A., Spitalny K. C., Pelletier R., Cherry W. B., Novick L. F. Legionnaires' disease: the epidemiology of two outbreaks in Burlington, Vermont, 1980. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Mar;119(3):382–391. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser J., Adams M., Doyle R., Hewitt P., Sangster N. Genetic characterization of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 associated with respiratory disease in Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):706–708. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.706-708.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney F. J., Hoge C. W., Farley T. A., Barbaree J. M., Breiman R. F., Benson R. F., McFarland L. M. Communitywide outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a grocery store mist machine. J Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;165(4):736–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.4.xxxx. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E., O'Mahony M., Watson J. M., Lynch D., Joseph C., Quigley C., Aston R., Constable G. N., Farrand R. J., Maxwell S. Two outbreaks of Legionnaires' disease in Bolton Health District. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Apr;104(2):159–170. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005932x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Chereshsky A., Haskell A. J., Brieseman M. A. Legionellosis in New Zealand: first recorded outbreak. N Z Med J. 1991 Jul 10;104(915):275–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony M. C., Stanwell-Smith R. E., Tillett H. E., Harper D., Hutchison J. G., Farrell I. D., Hutchinson D. N., Lee J. V., Dennis P. J., Duggal H. V. The Stafford outbreak of Legionnaires' disease. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Jun;104(3):361–380. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peiris V., Prasad M. K., Bradley D., Zawistowicz W., Sivayoham S., Naqvi S. N., Hutchinson D. N. Legionnaires' disease in elderly people: the first sign of an outbreak in the community? Age Ageing. 1992 Nov;21(6):451–455. doi: 10.1093/ageing/21.6.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redd S. C., Lin F. Y., Fields B. S., Biscoe J., Plikaytis B. B., Powers P., Patel J., Lim B. P., Joseph J. M., Devadason C. A rural outbreak of Legionnaires' disease linked to visiting a retail store. Am J Public Health. 1990 Apr;80(4):431–434. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.4.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. L., Mundy L. M., Tucker P. C. Hot tub legionellosis. Legionnaires' disease and Pontiac fever after a point-source exposure to Legionella pneumophila. Arch Intern Med. 1993 Nov 22;153(22):2597–2599. doi: 10.1001/archinte.153.22.2597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timbury M. C., Donaldson J. R., McCartney A. C., Fallon R. J., Sleigh J. D., Lyon D., Orange G. V., Baird D. R., Winter J., Wilson T. S. Outbreak of Legionnaires' disease in Glasgow Royal Infirmary: microbiological aspects. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Dec;97(3):393–403. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


