Abstract
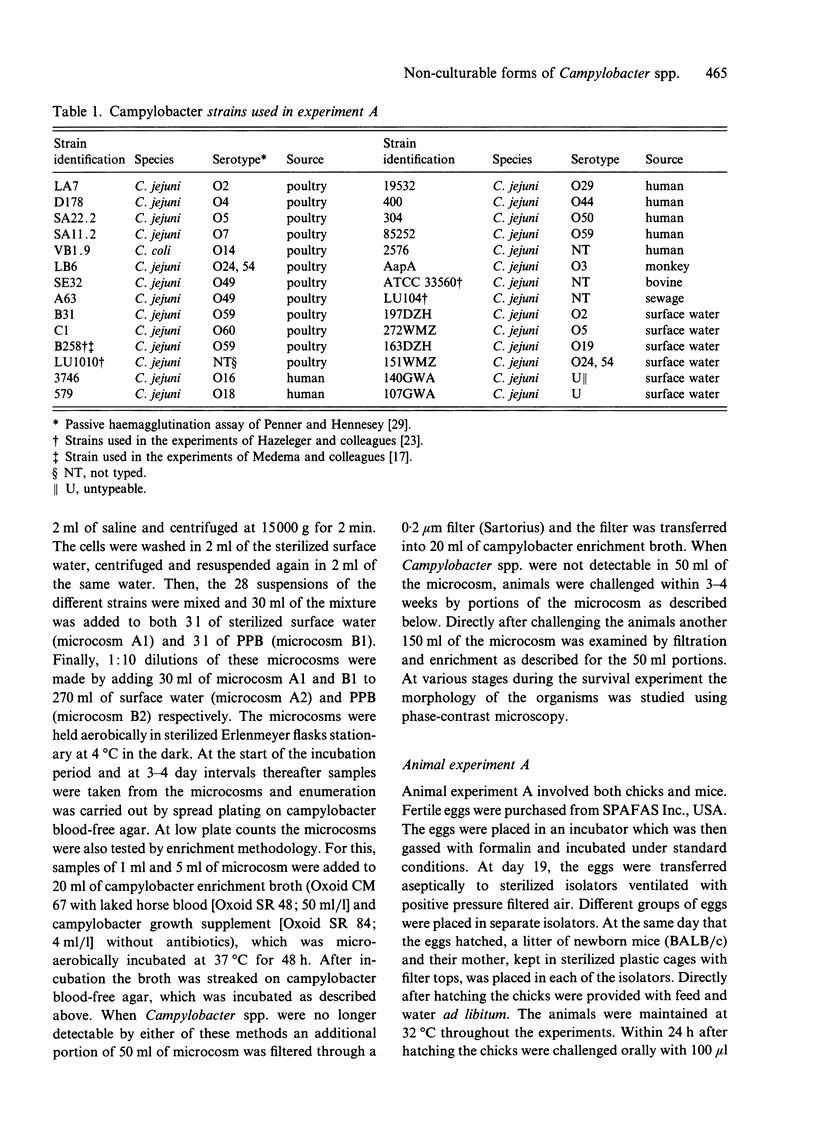
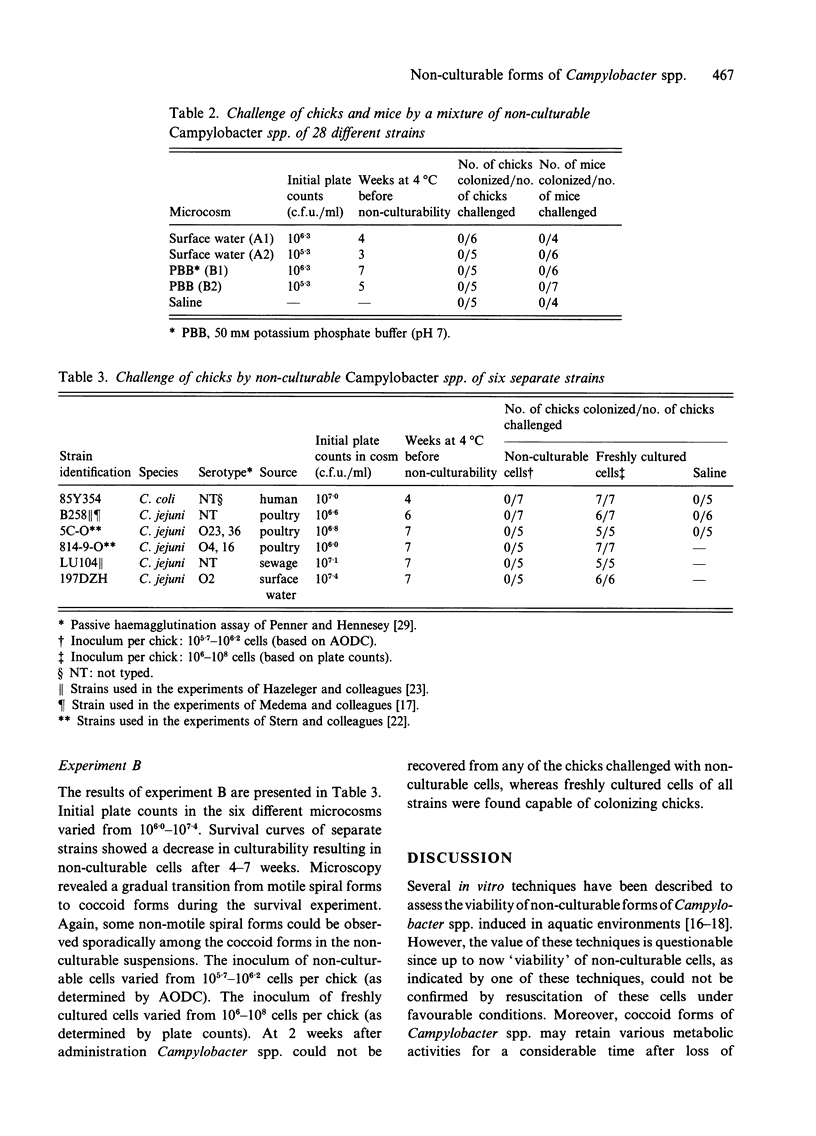
The significance of non-culturable forms of Campylobacter spp., especially with regard to the epidemiology of this organism in poultry flocks, was explored. Two different experiments were conducted to produce non-culturable Campylobacter spp. and test their ability to colonize the animal gut. In the first experiment a mixture of 28 different strains of Campylobacter spp. from various sources was inoculated in both sterilized surface water and potassium phosphate buffer and stored at 4 degrees C. After Campylobacter spp. were no longer detectable by culture in the microcosms, the mixtures of non-culturable cells were used to challenge both chicks and mice. Recovery of non-culturable Campylobacter spp. from the animals was not successful at 4 weeks after administration. In the second experiment the survival of six individual strains of Campylobacter spp. in sterilized surface water at 4 degrees C was studied and the resulting non-culturable cells were used to challenge chicks. None of the campylobacter strains could be recovered from the chicks at 2 weeks after administration. We conclude that occurrence of non-culturable forms of Campylobacter spp. capable of colonizing chicks is not a common phenomenon and that non-culturable forms of Campylobacter spp. are likely to be insignificant for importantly to the epidemiology of the organism in Dutch broiler flocks.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beumer R. R., de Vries J., Rombouts F. M. Campylobacter jejuni non-culturable coccoid cells. Int J Food Microbiol. 1992 Jan-Feb;15(1-2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(92)90144-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Feldman R. A. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:157–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. L. Morphological changes of Campylobacter jejuni growing in liquid culture. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1993 Oct;17(4):152–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1993.tb00382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazeleger W. C., Janse J. D., Koenraad P. M., Beumer R. R., Rombouts F. M., Abee T. Temperature-dependent membrane fatty acid and cell physiology changes in coccoid forms of Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995 Jul;61(7):2713–2719. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.7.2713-2719.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. J., Henley A., Lanning D. G. The colonization of broiler chickens with Campylobacter jejuni: some epidemiological investigations. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Jun;110(3):601–607. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800051025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. J. Techniques for the optimum recovery of cold injured Campylobacter jejuni from milk or water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;61(2):125–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Reitsma W. F., van de Giessen A. W., Bolder N. M., Mulder R. W. Epidemiology of Campylobacter spp. at two Dutch broiler farms. Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Jun;114(3):413–421. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800052122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Sutcliffe E. M., Curry A. Recovery of viable but non-culturable Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2477–2482. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Skjerve E., Bean N. H., Ostroff S. M., Lassen J. Risk factors for sporadic Campylobacter infections: results of a case-control study in southeastern Norway. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3117–3121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3117-3121.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Skjerve E., Vik L., Hauge K., Lysaker A., Aalmen I., Ostroff S. M., Potter M. Epidemiological investigation of risk factors for campylobacter colonization in Norwegian broiler flocks. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Oct;111(2):245–255. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800056958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema G. J., Schets F. M., van de Giessen A. W., Havelaar A. H. Lack of colonization of 1 day old chicks by viable, non-culturable Campylobacter jejuni. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;72(6):512–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb01868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NG L. K., Sherburne R., Taylor D. E., Stiles M. E. Morphological forms and viability of Campylobacter species studied by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):338–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.338-343.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterom J., den Uyl C. H., Bänffer J. R., Huisman J. Epidemiological investigations on Campylobacter jejuni in households with a primary infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Oct;93(2):325–332. doi: 10.1017/s002217240006486x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson A. D., Greenwood M., Healing T. D., Rollins D., Shahamat M., Donaldson J., Colwell R. R. Colonization of broiler chickens by waterborne Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Apr;59(4):987–996. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.4.987-996.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. M., Colwell R. R. Viable but nonculturable stage of Campylobacter jejuni and its role in survival in the natural aquatic environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):531–538. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.531-538.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S. K., Saha S., Sanyal S. C. Recovery of injured Campylobacter jejuni cells after animal passage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3388–3389. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3388-3389.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Giessen A., Mazurier S. I., Jacobs-Reitsma W., Jansen W., Berkers P., Ritmeester W., Wernars K. Study on the epidemiology and control of Campylobacter jejuni in poultry broiler flocks. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1913–1917. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1913-1917.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


