Abstract
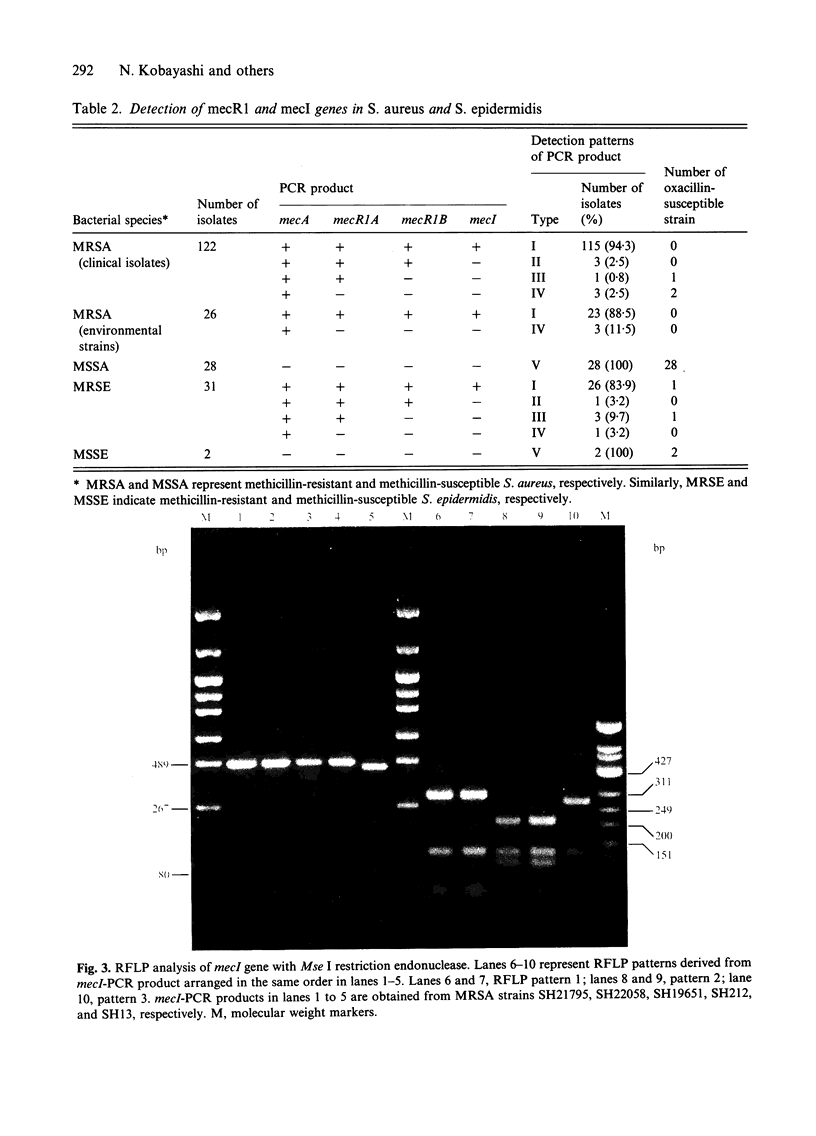
Low-affinity penicillin-binding protein PBP-2a encoded by mecA is closely related to methicillin resistance in staphylococci, and expression of PBP-2a is controlled by regulator elements encoded by mecR1 and mecI which are located adjacent to mecA on the chromosome. Deletion or mutation which occurred in mec regulator gene is considered to be associated with constitutive production of PBP-2a. The distribution of the mec regulator genes in 176 strains of Staphylococcus aureus and 33 strains of S. epidermidis isolated from a single hospital was studied by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Most clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) (94.3%) and S. epidermidis (MRSE) (83.9%) possessed both mecI and mecR1 genes (type I), whereas no mec regulator genes were detected in mecA-negative isolates. In contrast, 7 MRSA and 5 MRSE isolates were found to have incomplete regulator genes, and they were classified into three groups; strains which lacked only mecI gene (type II), strains which lacked mecI and 3'-end of mecR1 gene (type III), and strains which lacked both regulator genes (type IV). Analysis of mecI gene from all the strains having mecI by restriction fragment length polymorphism after Mse I digestion indicated that three MRSA strains possessed one of the known point mutations identified previously. These findings indicated the predominance of a single type of MRSA possessing both mecI and mecR1 in the study period and also suggested a high genomic diversity in mec regulator region of staphylococci.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L. Molecular epidemiology of multiresistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):133–138. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Niemeyer D. M., Thanassi J. A., Pucci M. J. Dissemination among staphylococci of DNA sequences associated with methicillin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Mar;38(3):447–454. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B., Barberis-Maino L., Strässle A., Kayser F. H. FemA, a host-mediated factor essential for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: molecular cloning and characterization. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00261186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger-Bächi B., Strässle A., Gustafson J. E., Kayser F. H. Mapping and characterization of multiple chromosomal factors involved in methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jul;36(7):1367–1373. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.7.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carles-Nurit M. J., Christophle B., Broche S., Gouby A., Bouziges N., Ramuz M. DNA polymorphisms in methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2092–2096. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2092-2096.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coia J. E., Noor-Hussain I., Platt D. J. Plasmid profiles and restriction enzyme fragmentation patterns of plasmids of methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from hospital and the community. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Dec;27(4):271–276. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-4-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez M. A., de Lencastre H., Linares J., Tomasz A. Spread and maintenance of a dominant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clone during an outbreak of MRSA disease in a Spanish hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Sep;32(9):2081–2087. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.9.2081-2087.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Low-affinity penicillin-binding protein associated with beta-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.513-516.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu K., Asada K., Suzuki E., Okonogi K., Yokota T. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of the regulator region of mecA gene in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 24;298(2-3):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80039-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu K., Kihara H., Yokota T. Analysis of borderline-resistant strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using polymerase chain reaction. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(5):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb02043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hürlimann-Dalel R. L., Ryffel C., Kayser F. H., Berger-Bächi B. Survey of the methicillin resistance-associated genes mecA, mecR1-mecI, and femA-femB in clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2617–2621. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis B., Matthews P. R., Stewart P. R. The expression in Staphylococcus aureus of cloned DNA encoding methicillin resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1465–1469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Wu H., Kojima K., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Uehara N., Omizu Y., Kishi Y., Yagihashi A., Kurokawa I. Detection of mecA, femA, and femB genes in clinical strains of staphylococci using polymerase chain reaction. Epidemiol Infect. 1994 Oct;113(2):259–266. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800051682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B., Kornblum J., Arbeit R. D., Eisner W., Maslow J. N., McGeer A., Low D. E., Novick R. P. Evidence for a clonal origin of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):227–230. doi: 10.1126/science.8093647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Grinsted J. Genetic analysis of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus; evidence for their evolution from a single clone. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Nov;6(4):511–526. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-4-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maple P. A., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W. World-wide antibiotic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1989 Mar 11;1(8637):537–540. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Kapur V. Clonal analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from intercontinental sources: association of the mec gene with divergent phylogenetic lineages implies dissemination by horizontal transfer and recombination. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2058–2063. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2058-2063.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard P., Meyran M., Carpentier E., Thabaut A., Drugeon H. B. Comparison of phenotypic methods and DNA hybridization for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Mar;32(3):613–617. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.3.613-617.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel C., Kayser F. H., Berger-Bächi B. Correlation between regulation of mecA transcription and expression of methicillin resistance in staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel C., Tesch W., Birch-Machin I., Reynolds P. E., Barberis-Maino L., Kayser F. H., Berger-Bächi B. Sequence comparison of mecA genes isolated from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Gene. 1990 Sep 28;94(1):137–138. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song M. D., Wachi M., Doi M., Ishino F., Matsuhashi M. Evolution of an inducible penicillin-target protein in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by gene fusion. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki E., Hiramatsu K., Yokota T. Survey of methicillin-resistant clinical strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci for mecA gene distribution. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):429–434. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki E., Kuwahara-Arai K., Richardson J. F., Hiramatsu K. Distribution of mec regulator genes in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus clinical strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1219–1226. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesch W., Ryffel C., Strässle A., Kayser F. H., Berger-Bächi B. Evidence of a novel staphylococcal mec-encoded element (mecR) controlling expression of penicillin-binding protein 2'. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1703–1706. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesch W., Strässle A., Berger-Bächi B., O'Hara D., Reynolds P., Kayser F. H. Cloning and expression of methicillin resistance from Staphylococcus epidermidis in Staphylococcus carnosus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1494–1499. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Nonoguchi R., Matsuhashi M., Konno M. Expression and inducibility in Staphylococcus aureus of the mecA gene, which encodes a methicillin-resistant S. aureus-specific penicillin-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2882–2885. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2882-2885.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge B. L., Chang Y. S., Gage D., Tomasz A. Peptidoglycan composition of a highly methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain. The role of penicillin binding protein 2A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11248–11254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




