Abstract
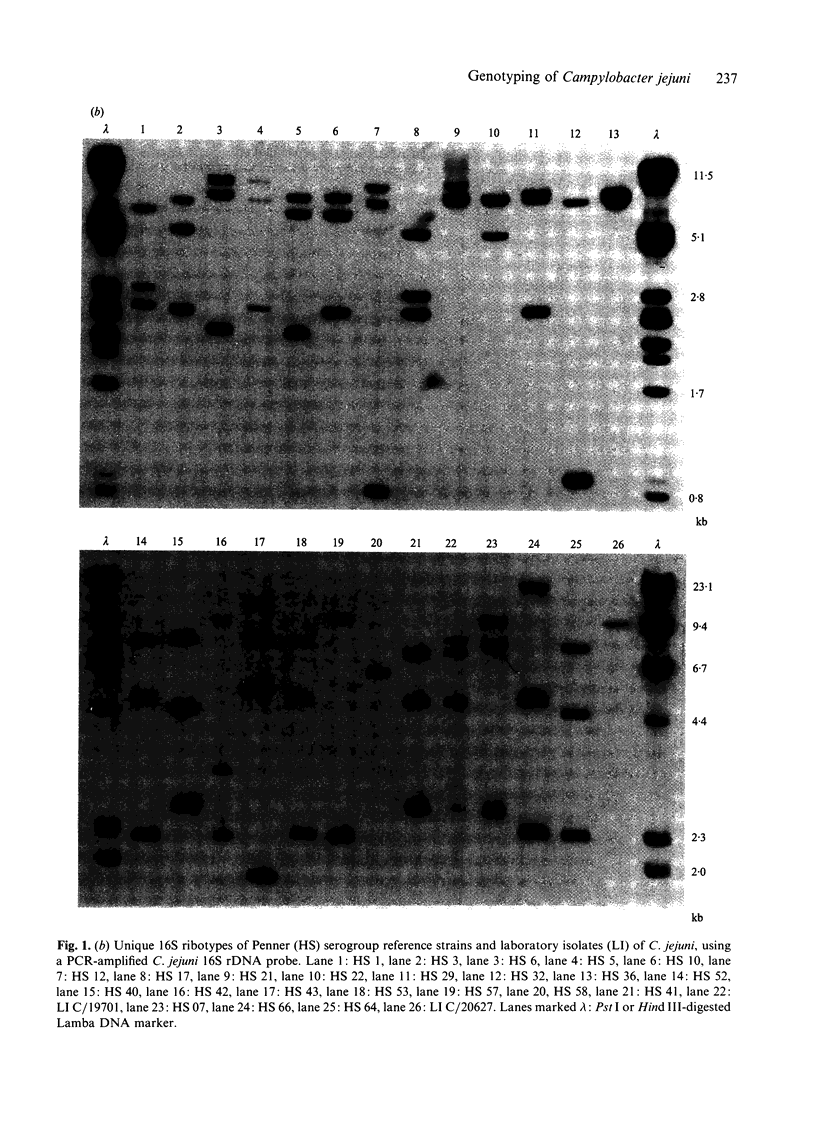
Campylobacter jejuni serogroup reference strains and collections of sporadic and outbreak-associated isolates were examined for restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), using C. jejuni random chromosomal and 16S rRNA gene probes. A collection of 48 Penner (HS) and 14 Lior (HL) serogroup reference strains, plus 10 clinical isolates, generated 35 RFLP and 26 ribotype patterns. In combination the two loci generated 48 distinct genotypes. Both probes were able to differentiate between certain random isolates of the same HS/HL serogroups but greater discrimination was obtained with RFLP than with ribotyping. Genotyping distinguished accurately between related and unrelated strains when applied to several outbreaks. Genotypic analysis of C. jejuni by restriction fragment length polymorphisms is a valuable technique for epidemiological typing. Chromosomal variation detected by the two unlinked probe loci provides some information about the genetic relationship between isolates.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Holt A. V., Hutchinson D. N. Campylobacter biotyping scheme of epidemiological value. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):677–681. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnens A. P., Wagner J., Lior H., Nicolet J., Frey J. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms among the flagellar genes of the Lior heat-labile serogroup reference strains and field strains of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli. Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Jun;114(3):423–431. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800052134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowden J. Campylobacter: epidemiological paradoxes. BMJ. 1992 Jul 18;305(6846):132–133. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6846.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayos A., Owen R. J., Hernandez J., Jones C., Lastovica A. Molecular subtyping by genome and plasmid analysis of Campylobacter jejuni serogroups O1 and O2 (Penner) from sporadic and outbreak cases of human diarrhoea. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Dec;111(3):415–427. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800057149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes K. J., Fang Z., Pennington T. H. Allelic variation in the Helicobacter pylori flagellin genes flaA and flaB: its consequences for strain typing schemes and population structure. Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Apr;114(2):257–266. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800057927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E. H., Deslandes S., Veilleux S., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D. Typing Chlamydia trachomatis by detection of restriction fragment length polymorphism in the gene encoding the major outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1103–1107. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. R., Fitzgerald C., Owen R. J. Comparison of PFGE, ribotyping and phage-typing in the epidemiological analysis of Campylobacter jejuni serotype HS2 infections. Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Oct;115(2):215–225. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800058349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Abbott J. D., Painter M. J., Sutcliffe E. M. A comparison of biotypes and serotypes of Campylobacter sp. isolated from patients with enteritis and from animal and environmental sources. J Infect. 1984 Jul;9(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)94498-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehlbauch J. A., Cameron D. N., Wachsmuth I. K. Evaluation of ribotyping techniques as applied to Arcobacter, Campylobacter and Helicobacter. Mol Cell Probes. 1994 Apr;8(2):109–115. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1994.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni H., Knight A. I., Cartwright K. A., McFadden J. J. Phylogenetic and epidemiological analysis of Neisseria meningitidis using DNA probes. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Oct;109(2):227–239. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800050184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr K. E., Lightfoot N. F., Sisson P. R., Harkis B. A., Tweddle J. L., Boyd P., Carroll A., Jackson C. J., Wareing D. R., Freeman R. Direct milk excretion of Campylobacter jejuni in a dairy cow causing cases of human enteritis. Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Feb;114(1):15–24. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800051876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Fitzgerald C., Sutherland K., Borman P. Flagellin gene polymorphism analysis of Campylobacter jejuni infecting man and other hosts and comparison with biotyping and somatic antigen serotyping. Epidemiol Infect. 1994 Oct;113(2):221–234. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800051657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Sutherland K., Fitzgerald C., Gibson J., Borman P., Stanley J. Molecular subtyping scheme for serotypes HS1 and HS4 of Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Apr;33(4):872–877. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.4.872-877.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston M. A., Penner J. L. Characterization of cross-reacting serotypes of Campylobacter jejuni. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Feb;35(2):265–273. doi: 10.1139/m89-040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salama S. M., Bolton F. J., Hutchinson D. N. Application of a new phagetyping scheme to campylobacters isolated during outbreaks. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Jun;104(3):405–411. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Linton D., Sutherland K., Jones C., Owen R. J. High-resolution genotyping of Campylobacter coli identifies clones of epidemiologic and evolutionary significance. J Infect Dis. 1995 Oct;172(4):1130–1134. doi: 10.1093/infdis/172.4.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Arbeit R. D., Goering R. V., Mickelsen P. A., Murray B. E., Persing D. H., Swaminathan B. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Sep;33(9):2233–2239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.9.2233-2239.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth I. K., Kiehlbauch J. A., Bopp C. A., Cameron D. N., Strockbine N. A., Wells J. G., Blake P. A. The use of plasmid profiles and nucleic acid probes in epidemiologic investigations of foodborne, diarrheal diseases. Int J Food Microbiol. 1991 Jan;12(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(91)90049-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




