Abstract
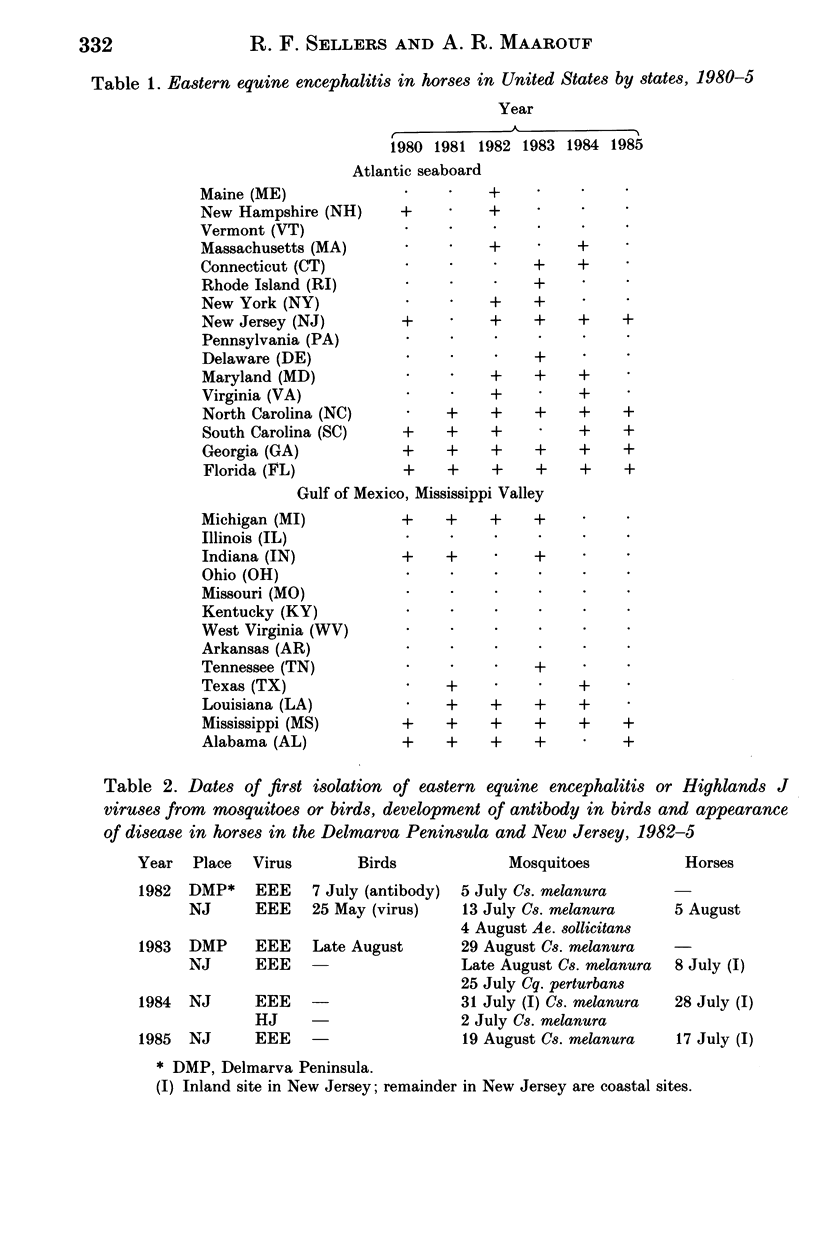
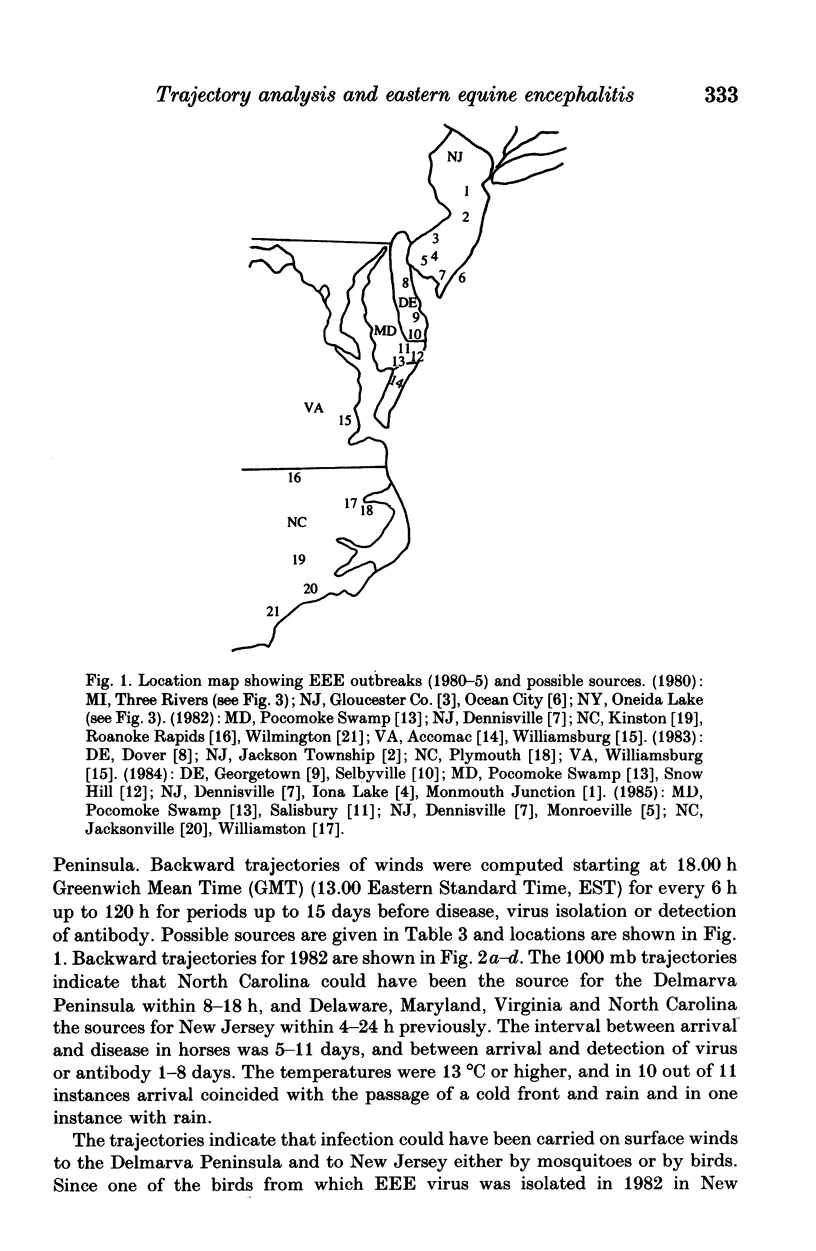
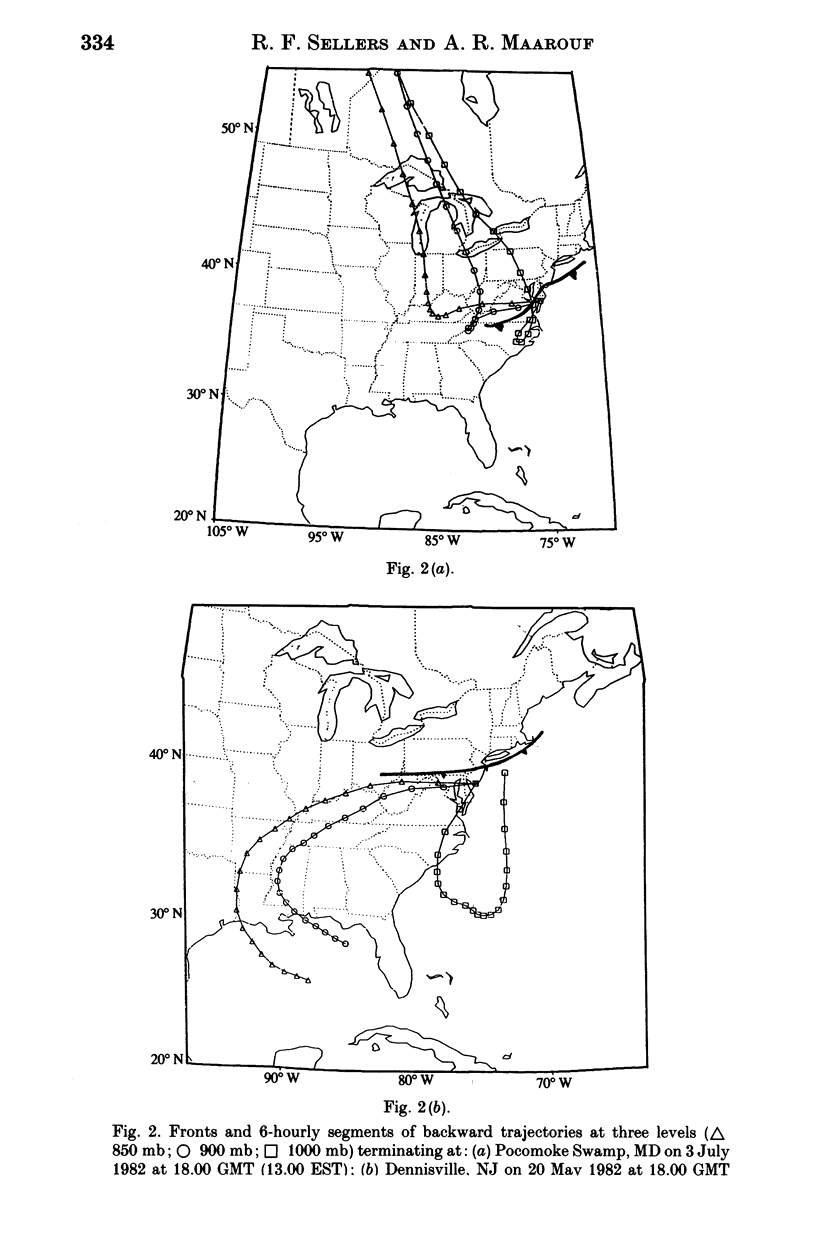
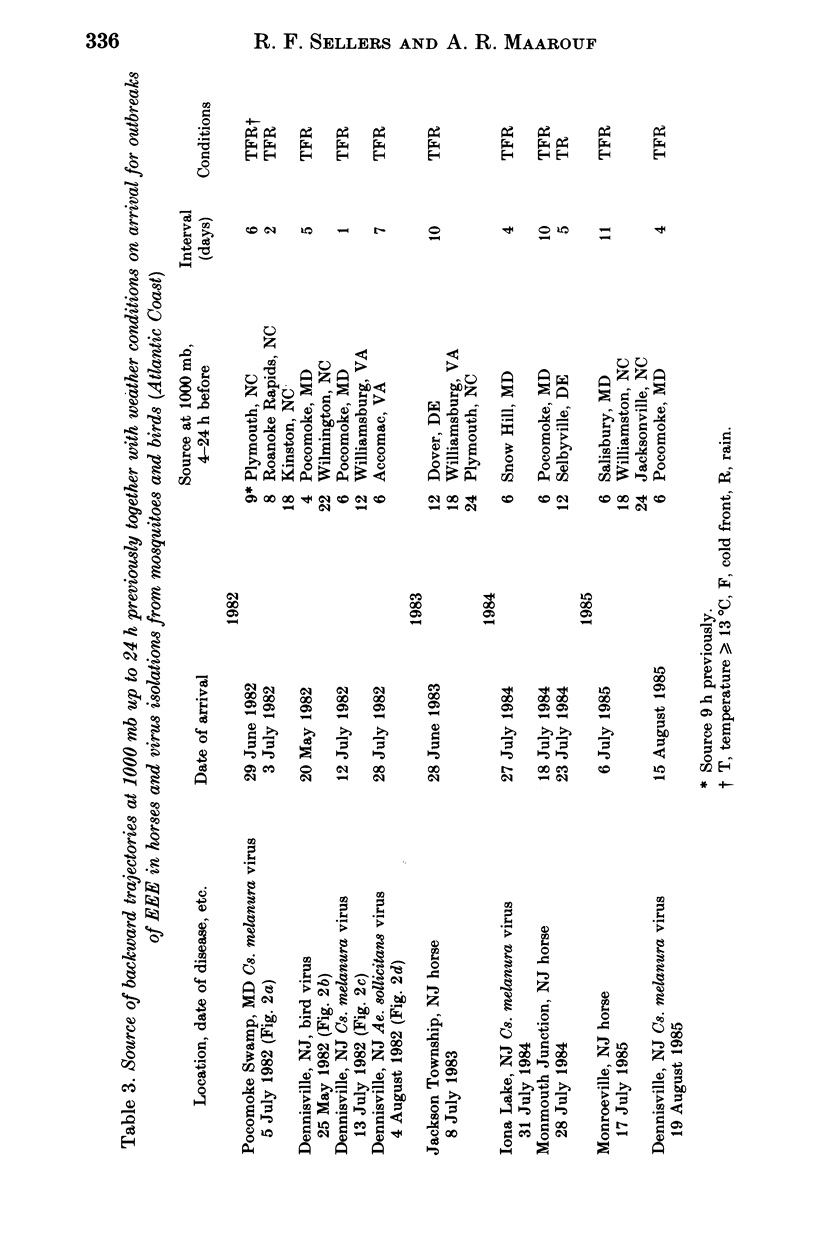
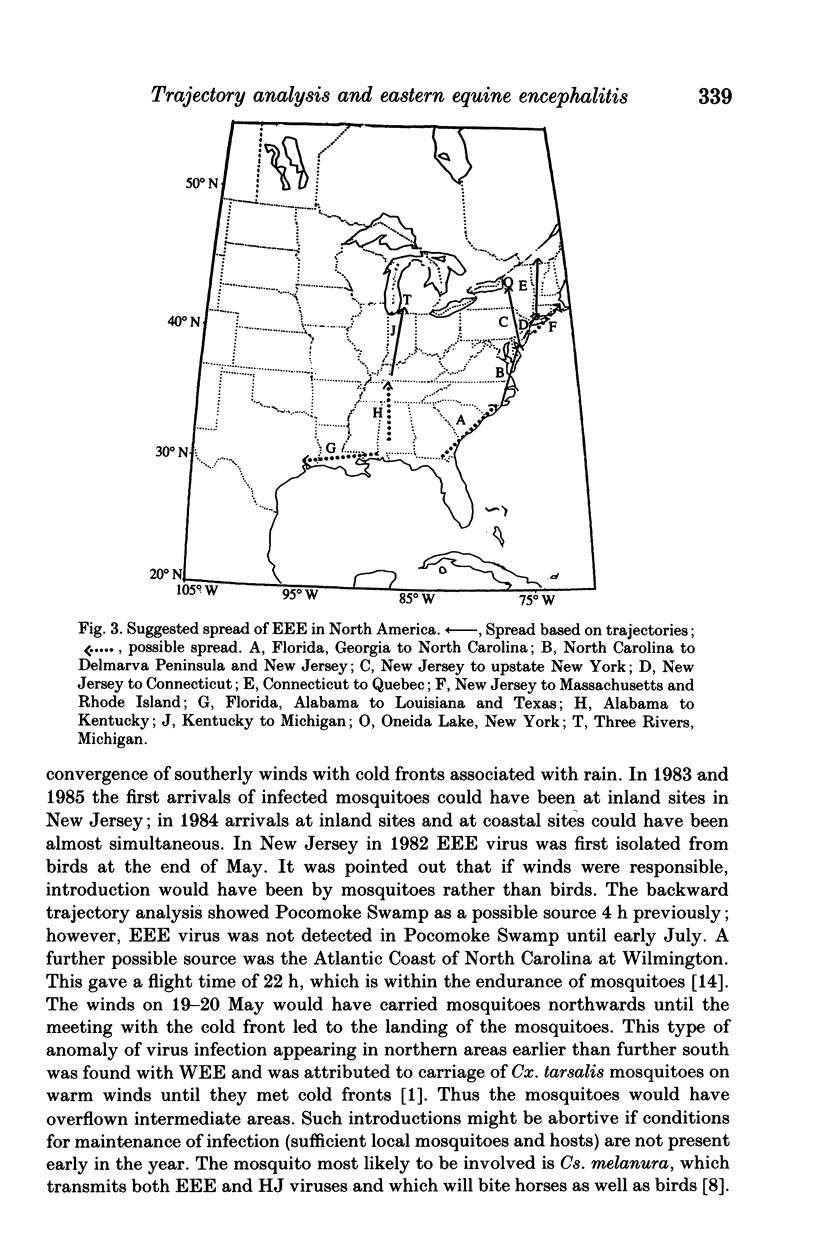
Backward trajectories of winds were determined to identify possible sources of eastern equine encephalitis virus associated with isolation of virus from mosquitoes or birds or outbreaks in horses between 1980 and 1985 in Maryland, New Jersey, New York and Michigan, USA. The results of the trajectory analyses suggested that eastern equine encephalitis virus could have been carried by infected mosquitoes on surface winds at temperatures 13 degrees C or higher from North Carolina north-eastwards along the Atlantic Coast to Maryland and New Jersey and thence to upstate New York and from western Kentucky to Michigan. Landing of mosquitoes was associated with the presence of a cold front and rain leading to variations in the location and timing of outbreaks from year to year. The mosquito responsible was most likely to have been Culiseta melanura, but Coquillettidia perturbans and Aedes sollicitans could also have been involved. There may be a continual cycle of eastern equine encephalitis virus in mosquitoes and birds in south-eastern USA, from where the virus could be distributed by infected mosquitoes on the wind along the Gulf and Atlantic Coasts and up the Mississippi Valley.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BYRNE R. J., FRENCH G. R., YANCEY F. S., GOCHENOUR W. S., RUSSELL P. K., RAMSBURG H. H., BRAND O. A., SCHEIDER F. G., BUESCHER E. L. CLINICAL AND IMMUNOLOGIC INTERRELATIONSHIP AMONG VENEZUELAN, EASTERN, AND WESTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALOMYELITIS VIRUSES IN BURROS. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Jan;25:24–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler W. J., Lassing E. B., Buff E. E., Prather E. C., Beck E. C., Hoff G. L. Endemic eastern equine encephalomyelitis in Florida: a twenty-year analysis, 1955-1974. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Nov;25(6):884–890. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boromisa R. D., Copeland R. S., Grimstad P. R. Oral transmission of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus by a northern Indiana strain of Coquillettidia perturbans. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1987 Mar;3(1):102–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASALS J. ANTIGENIC VARIANTS OF EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:547–565. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLAIN R. W., SIKES R. K., NELSON D. B. Infection of Mansonia perturbans and Psorophora ferox mosquitoes with Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):215–216. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLAIN R. W., SUDIA W. D. Mechanism of transmission of viruses by mosquitoes. Annu Rev Entomol. 1961;6:371–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.06.010161.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calisher C. H., Maness K. S., Lord R. D., Coleman P. H. Identification of two South American strains of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus from migrant birds captured on the Mississippi delta. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Aug;94(2):172–178. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Arboviral encephalitides--United States, 1983. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1983 Nov 4;32(43):557–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Arboviral infections of the central nervous system--United States, 1984. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1985 May 24;34(20):283-6, 291-4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Arboviral infections of the central nervous system--United States, 1985. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1986 May 30;35(21):341-4, 349-50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain R. W., Sudia W. D., Coleman P. H., Johnston J. G., Jr, Work T. H. Arbovirus isolations from mosquitoes collected in Waycross, Georgia, 1963, during an outbreak of equine encephalitis. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Jan;89(1):82–88. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. G., Crans W. J., Crabbs C. L. Absence of eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus in immature Coquillettidia perturbans associated with equine cases of EEE. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1985 Dec;1(4):540–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crans W. J. Failure of chickens to act as sentinels during an epizootic of eastern equine encephalitis in southern New Jersey, USA. J Med Entomol. 1986 Dec 4;23(6):626–629. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/23.6.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crans W. J., McNelly J., Schulze T. L., Main A. Isolation of eastern equine encephalitis virus from Aedes sollicitans during an epizootic in southern New Jersey. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1986 Mar;2(1):68–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. D., Webber L. A., Kale H. W., 2nd Host-feeding patterns of Florida mosquitoes. II. Culiseta. J Med Entomol. 1972 Sep 30;9(5):429–434. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/9.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimstad P. R. Mosquitoes and the incidence of encephalitis. Adv Virus Res. 1983;28:357–438. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60727-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES R. O., DANIELS J. B., ANDERSON K. S., PARSONS M. A., MAXFIELD H. K., LAMOTTE L. C. Detection of eastern encephalitis virus and antibody in wild and domestic birds in Massachusetts. Am J Hyg. 1962 Mar;75:183–189. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes C. G., Wallis R. C. Ecology of Western equine encephalomyelitis in the eastern United States. Adv Virus Res. 1977;21:37–83. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60761-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. J., Emord D. E., Morris C. D. Epizootiology of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus in upstate New York, USA. V. Habitat preference of host-seeking mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol. 1983 Jan 27;20(1):62–69. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/20.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. J., Morris C. D., Emord D. E., Grayson M. A. Epizootiology of eastern equine encephalitis virus in upstate New York, USA. VII. Virus surveillance 1978-85, description of 1983 outbreak, and series conclusions. J Med Entomol. 1988 Nov;25(6):501–514. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/25.6.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord R. D., Calisher C. H. Further evidence of southward transport of arboviruses by migratory birds. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Jul;92(1):73–78. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. G., Frier G., Parham G. L., Francy D. B., Monath T. P., Campos E. G., Therrien A., Kerschner J., Calisher C. H. Investigations of the vertebrate hosts of eastern equine encephalitis during an epizootic in Michigan, 1980. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Nov;34(6):1190–1202. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. D., Srihongse S. An evaluation of the hypothesis of transovarial transmission of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus by Culiseta melanura. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1246–1250. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muul I., Johnson B. K., Harrison B. A. Ecological studies of Culiseta melanura (Diptera: Culicidae) in relation to eastern and western equine encephalomyelitis viruses on the eastern shore of Maryland. J Med Entomol. 1975 Jan 10;11(6):739–748. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/11.6.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. C. Overwintering of arboviruses. Prog Med Virol. 1974;17(0):193–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen L. Overwintering mechanisms of mosquito-borne arboviruses in temperate climates. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Nov;37(3 Suppl):69S–76S. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.69s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEFFER M., ARNOLD E. H. Studies on the North American arthropod-borne encephalitides. I. Introduction; contributions of newer field-laboratory approaches. Am J Hyg. 1954 Nov;60(3):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saugstad E. S., Dalrymple J. M., Eldridge B. F. Ecology of arboviruses in a Maryland freshwater swamp. I. Population dynamics and habitat distribution of potential mosquito vectors. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Aug;96(2):114–122. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. W., Hildreth S. W., Beaty B. J. The distribution and development of eastern equine encephalitis virus in its enzootic mosquito vector, Culiseta melanura. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Mar;33(2):300–310. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers R. F. Eastern equine encephalitis in Quebec and Connecticut, 1972: introduction by infected mosquitoes on the wind? Can J Vet Res. 1989 Jan;53(1):76–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers R. F., Maarouf A. R. Impact of climate on western equine encephalitis in Manitoba, Minnesota and North Dakota, 1980-1983. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Dec;101(3):511–535. doi: 10.1017/s095026880002940x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempelis C. H. Host-feeding patterns of mosquitoes, with a review of advances in analysis of blood meals by serology. J Med Entomol. 1975 Jan 10;11(6):635–653. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/11.6.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts D. M., Clark G. G., Crabbs C. L., Rossi C. A., Olin T. R., Bailey C. L. Ecological evidence against vertical transmission of eastern equine encephalitis virus by mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) on the Delmarva Peninsula, USA. J Med Entomol. 1987 Jan;24(1):91–98. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/24.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


