Abstract
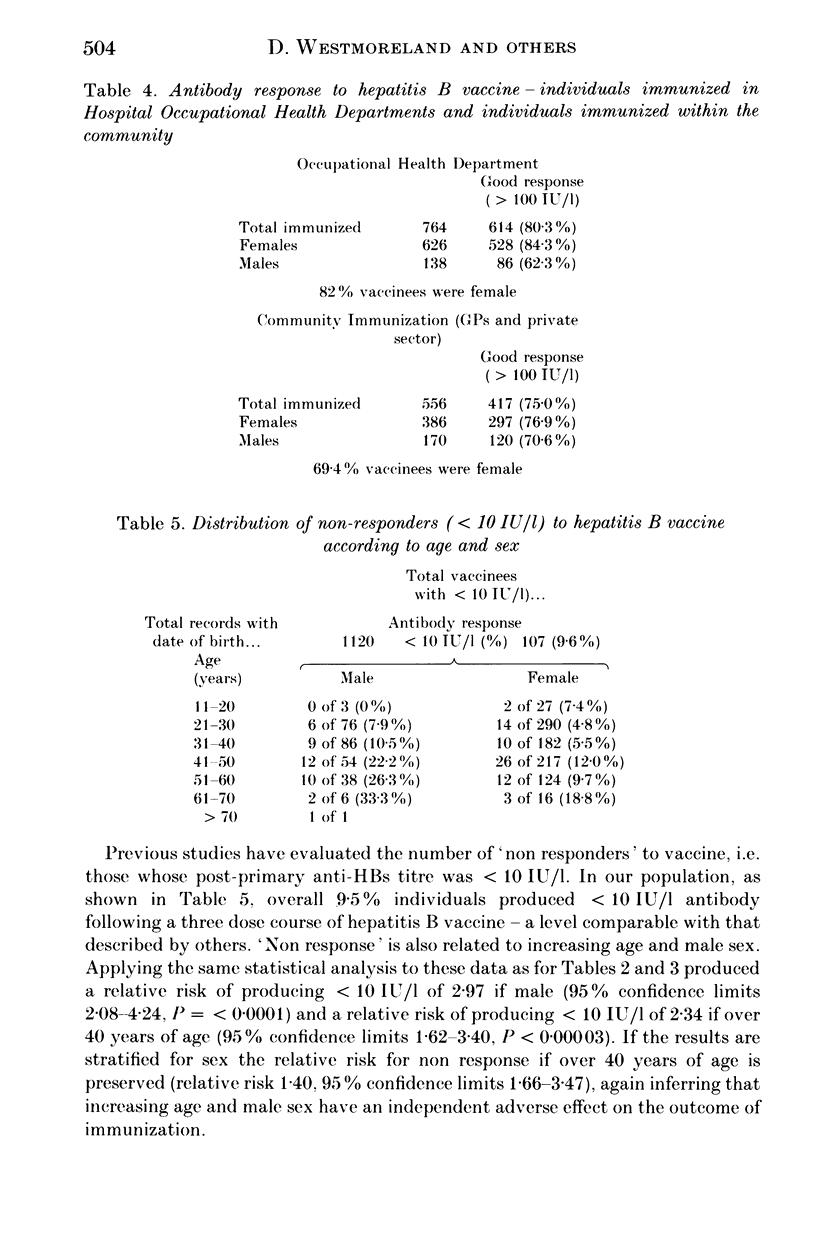
One thousand three hundred and twenty adults at risk of occupational exposure to hepatitis B were immunized using genetically engineered surface antigen and their antibody response (anti-HBs IU/l) assessed. Sex was known for all subjects and age for 1120 (range from 17-71 years). Seven hundred and sixty-four subjects were immunized in the local Department of Occupational Health, the remainder mainly by general practitioners. Analysis of 'good responders' (anti-HBs greater than 100 IU/l) according to age and sex showed that increasing age and male sex had independent adverse effects on the likelihood of developing a satisfactory level of antibody to HBsAg. Furthermore even those most likely to respond well (young women), had a 1/5 to 1/6 failure rate to achieve greater than 100 IU/l anti-HBs. Of 63 persons who received a fourth dose of vaccine, 26 developed anti-HBs titres greater than 100 IU/l when tested after 6 months. Subjects who had a low level of anti-HBs following primary immunization were more likely to develop greater than 100 IU/l anti-HBs following a booster dose than were non-responders (less than 10 IU/l).
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrosch F., Frisch-Niggemeyer W., Kremsner P., Kunz C., André F., Safary A., Wiedermann G. Persistence of vaccine-induced antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen and the need for booster vaccination in adult subjects. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 2):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruguera M., Cremades M., Mayor A., Sánchez Tapias J. M., Rodés J. Immunogenicity of a recombinant hepatitis B vaccine in haemodialysis patients. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 2):155–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. D., Hambling M. H., Pinnington P. A., Lees E. Efficacy of hepatitis B vaccine. J Soc Occup Med. 1988 Spring-Summer;38(1-2):46–47. doi: 10.1093/occmed/38.1-2.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan E. A., Tolley P., Smith H. M., Peters M. P., Coleman J., Elliott P., Williams R., Eddleston A. L. Hepatitis B vaccine: immunogenicity and follow-up including two year booster doses in high-risk health care personnel in a London teaching hospital. J Med Virol. 1987 Jan;21(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890210107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan E. A., Williams R., Eddleston A. L. Hepatitis B vaccine: responder status and timing of additional booster doses. Lancet. 1987 Sep 5;2(8558):561–561. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92937-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan E. A., Williams R. Hepatitis B vaccination. Br J Clin Pract. 1987 Jan;41(1):569–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Symington I. S., Cameron M. G. Experience with hepatitis B vaccination in nurses in a hospital for the mentally handicapped. Lancet. 1987 Sep 26;2(8561):728–731. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudeau A., Denis F., Mounier M., Dubois F., Klein J., Godefroy A., Ballet M., Mountij A. Comparative multicentre study of the immunogenicity of different hepatitis B vaccines in healthy volunteers. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 2):125–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenland S., Robins J. M. Estimation of a common effect parameter from sparse follow-up data. Biometrics. 1985 Mar;41(1):55–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler S. C. Are booster doses of hepatitis B vaccine necessary? Ann Intern Med. 1988 Mar;108(3):457–458. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-3-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler S. C., Francis D. P., Maynard J. E., Thompson S. E., Judson F. N., Echenberg D. F., Ostrow D. G., O'Malley P. M., Penley K. A., Altman N. L. Long-term immunogenicity and efficacy of hepatitis B vaccine in homosexual men. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 24;315(4):209–214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607243150401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. M., Chen D. S., Chuang C. H., Lu J. C., Jwo D. M., Lee C. C., Lu H. C., Cheng S. H., Wang Y. F., Wang C. Y. Efficacy of a mass hepatitis B vaccination program in Taiwan. Studies on 3464 infants of hepatitis B surface antigen-carrier mothers. JAMA. 1988 Oct 21;260(15):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just M., Berger R., Just V. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of a recombinant hepatitis B vaccine compared with a plasma-derived vaccine in young adults. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 2):121–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplanche A., Courouce A. M., Benhamou E., Jungers P. Timing of hepatitis B revaccination in healthy adults. Lancet. 1987 May 23;1(8543):1206–1207. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunn J. A. Intradermal hepatitis B vaccine. Lancet. 1989 Mar 18;1(8638):625–625. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91663-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pead P. J. Immune responses to hepatitis B vaccination in hospital staff. Biomed Pharmacother. 1986;40(7):251–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pead P. J., Saeed A. A. Hepatitis B vaccination: effect of re-vaccination and injection site in suboptimal responders. Eur J Epidemiol. 1986 Sep;2(3):240–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00211538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinsen H., Goilav C., Safary A., André F. E., Piot P. Immunogenicity and tolerance of a yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccine in homosexual men. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 2):147–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiermann N., Gesemann K. M., Kreuzfelder E., Paar D. Effects of a recombinant yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccine in healthy adults. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 2):115–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickler A. C., Pavone E. D. Hepatitis B immunization: effect of 4th and 5th injections following suboptimal seroconversion in health care workers. Can J Public Health. 1987 Sep-Oct;78(5):315–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong M. J., Howard A. M., Schatz G. C., Kane M. A., Roskamp D. A., Co R. L., Boone C. A hepatitis B vaccination program in a community teaching hospital. Infect Control. 1987 Mar;8(3):102–107. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700067266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukena T. E., Rosenkrantz H., Bessette R. E., Esber H. J. Immune response of hospital workers to hepatitis B vaccine. J Infect. 1987 Jan;14(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(87)90782-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeley S. M., Boxall E. H., Tarlow M. J. Prognosis of children who are carriers of hepatitis B. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jan 24;294(6566):211–213. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6566.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedermann G., Ambrosch F., Kremsner P., Kunz C., Hauser P., Simoen E., André F., Safary A. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of different lots of a yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccine. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 2):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yvonnet B., Coursaget P., Chotard J., Sarr M., NDoye R., Chiron J. P., Diop-Mar I. Hepatitis B vaccine in infants from an endemic area: long-term anti-HBs persistence and revaccination. J Med Virol. 1987 Aug;22(4):315–321. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


