Abstract
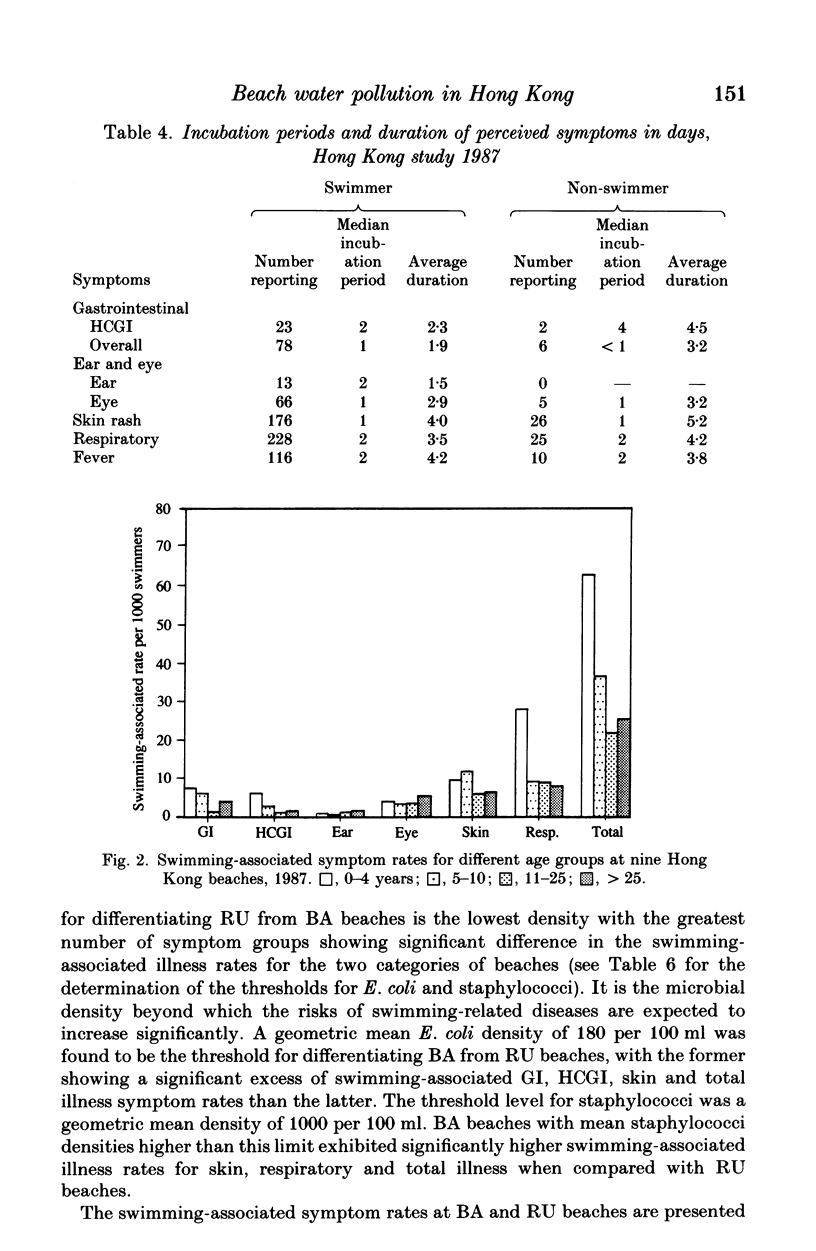
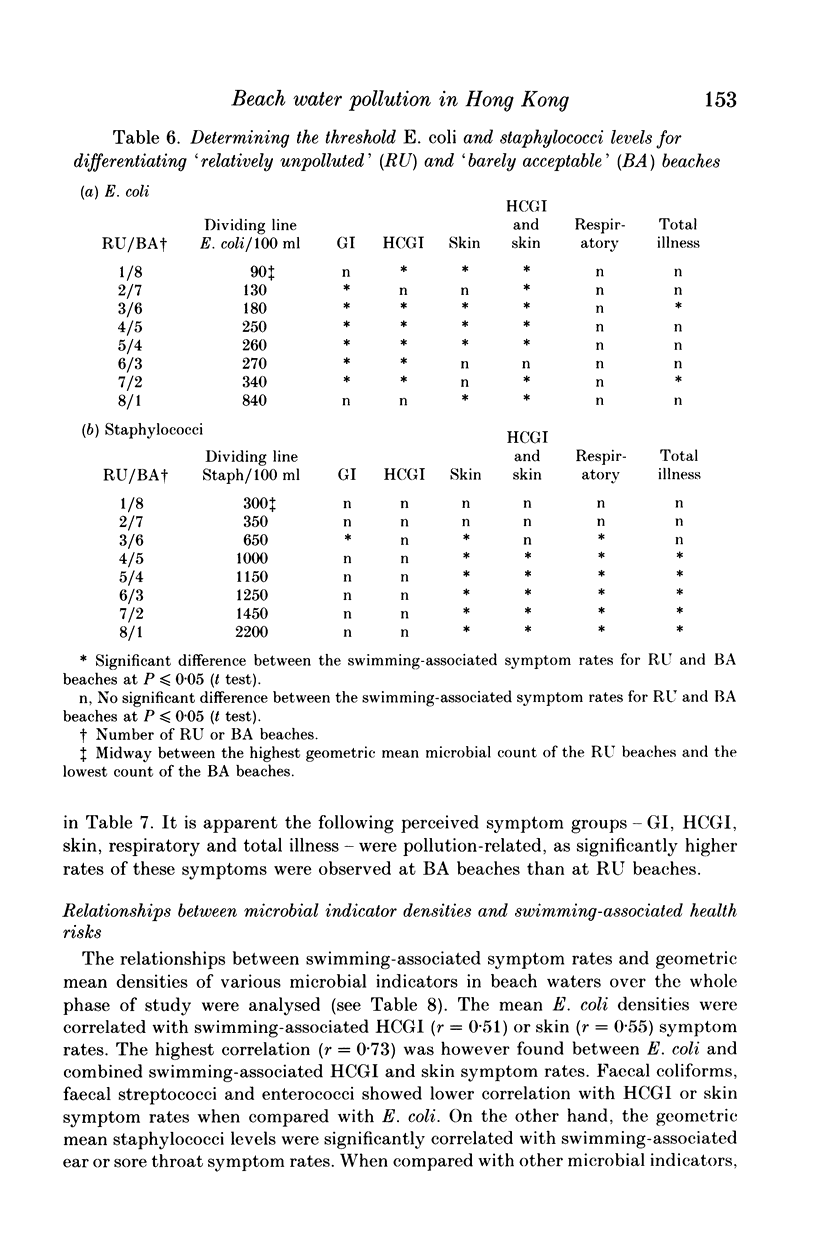
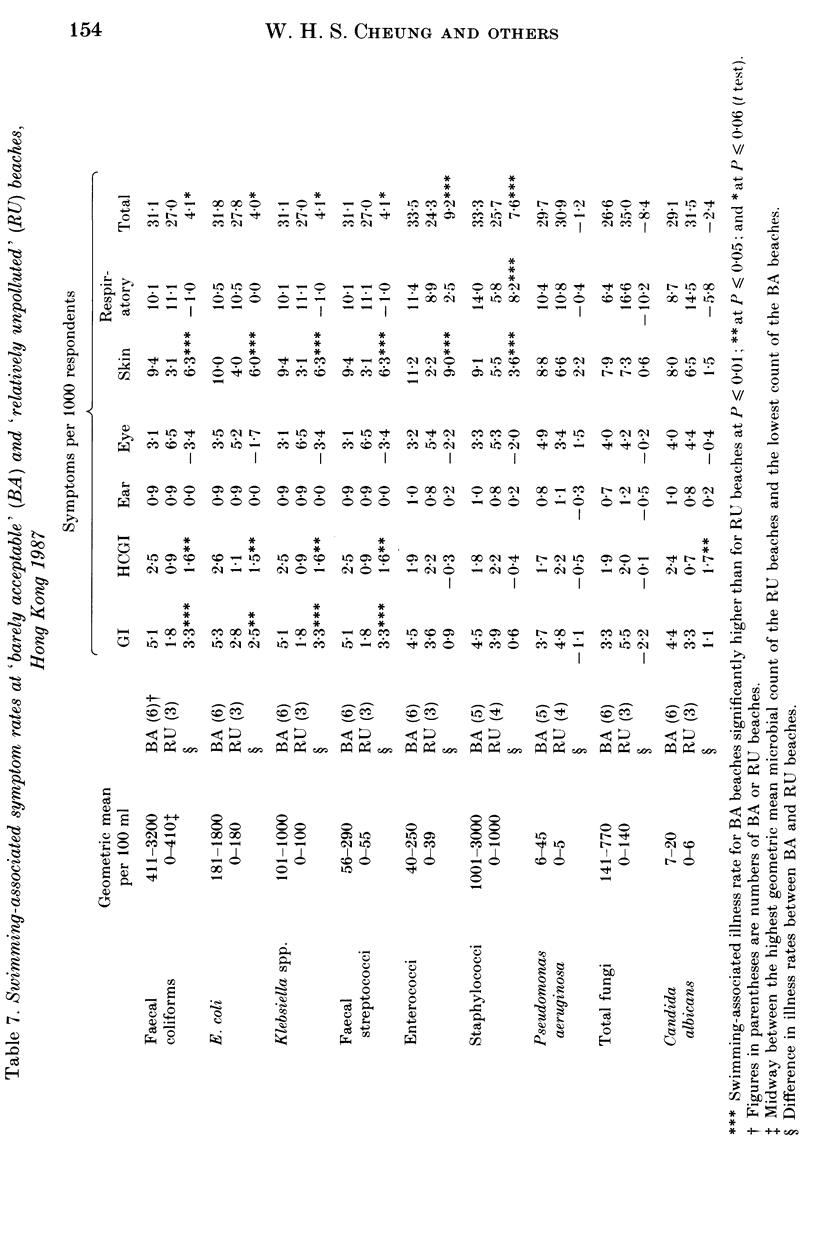
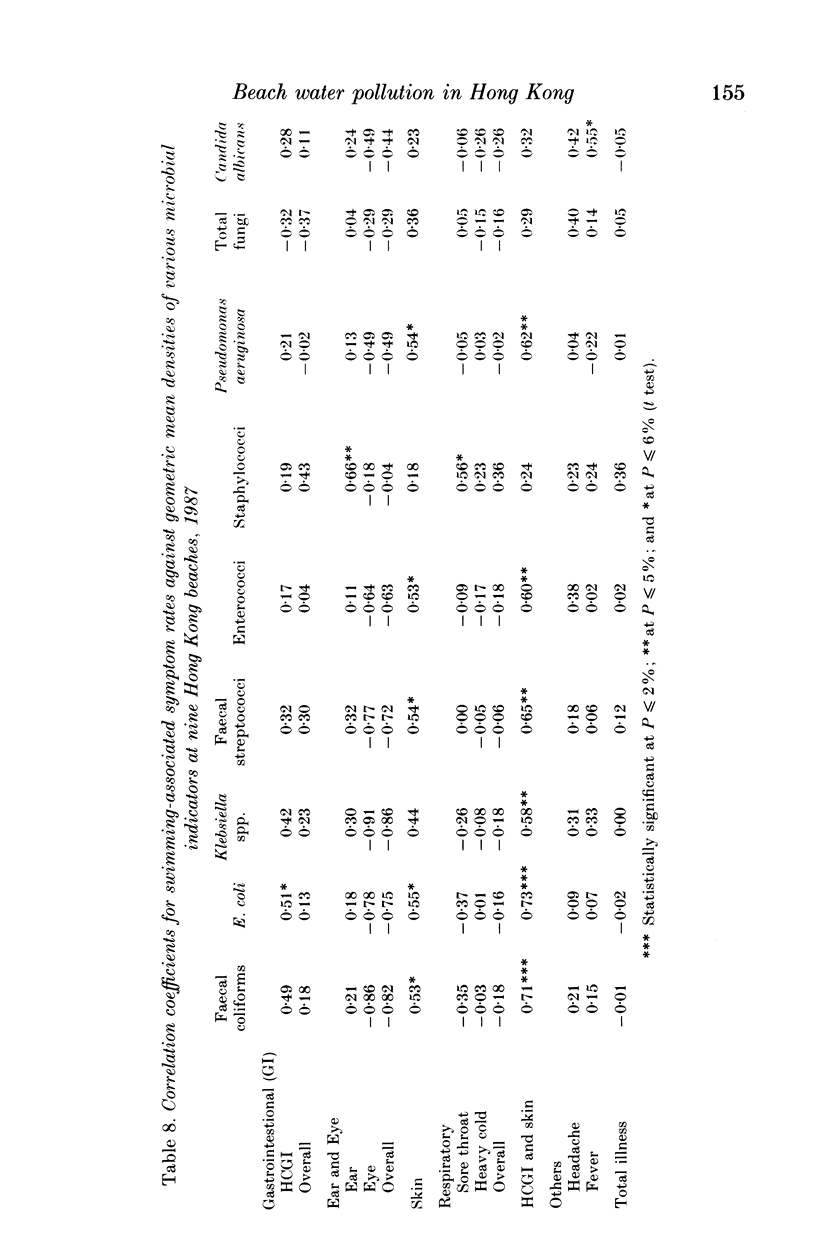
Prospective epidemiological studies of beach water pollution were conducted in Hong Kong in the summers of 1986 and 1987. For the main study in 1987, a total of 18741 usable responses were obtained from beachgoers on nine beaches at weekends. The study indicated the overall perceived symptom rates for gastrointestinal, ear, eye, skin, respiratory, fever and total illness were significantly higher for swimmers than non-swimmers; and the swimming-associated symptom rates for gastrointestinal, skin, respiratory and total illness were higher at 'barely acceptable' beaches than at 'relatively unpolluted' ones. Escherichia coli was found to be the best indicator of the health effects associated with swimming in the beaches of Hong Kong. It showed the highest correlation with combined swimming-associated gastroenteritis and skin symptom rates when compared with other microbial indicators. A linear relationship between E. coli and the combined symptom rates was established. Staphylococci were correlated with ear, respiratory and total illness, but could not be used for predicting swimming-associated health risks. They should be used to complement E. coli. The setting of health-related bathing-water quality standards based on such a study is discussed.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alico R. K., Dragonjac M. F. Evaluation of culture media for recovery of Staphylococcus aureus from swimming pools. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):699–702. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.699-702.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R. C., Murphy F. D., Greenberg H. B., Davis C. E., Bregman D. J., Gary G. W., Hughes J. M., Schonberger L. B. Norwalk gastrointestinal illness: an outbreak associated with swimming in a recreational lake and secondary person-to-person transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Feb;115(2):163–172. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. M., Campbell E. A., Rickards A. D., Wheeler D. Sewage pollution of bathing water. Lancet. 1987 Nov 21;2(8569):1208–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91342-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. A., Lehmann J. D., Setiady I. F., Hatch M. H. An outbreak of hepatitis-A associated with recreational lake water. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Feb;99(2):145–154. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck J. D., Bubucis P. M. Membrane filter procedure for enumeration of Candida albicans in natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):237–242. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.237-242.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli V. J., Dufour A. P., McCabe L. J., Levin M. A. Swimming-associated gastroenteritis and water quality. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Apr;115(4):606–616. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio D., Minor T. E., Allen C. I., Tsiatis A. A., Nelson D. B. A study of the proportions of swimmers among well controls and children with enterovirus-like illness shedding or not shedding an enterovirus. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 May;113(5):533–541. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis F. A., Blanchouin E., de Lignieres A., Flamen P. Letter: Coxsackie A16 infection from lake water. JAMA. 1974 Jun 10;228(11):1370–1371. doi: 10.1001/jama.1974.03230360018009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufour A. P. Bacterial indicators of recreational water quality. Can J Public Health. 1984 Jan-Feb;75(1):49–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley H. B., Morin D. P., Geraghty M. E., Tomkow J., Phillips C. A. Coxsackievirus B epidemic at a Boy's Summer Camp. Isolation of virus from swimming water. JAMA. 1973 Oct 1;226(1):33–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNER B. A., CLARK H. F., KABLER P. W. Fecal Streptococci. I. Cultivation and enumeration of Streptococci in surface waters. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Jan;9:15–20. doi: 10.1128/am.9.1.15-20.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapes N. A. Comparison of Vogel-Johnson and Baird-Parker media for membrane filtration recovery of staphylococci in swimming pool water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Dec;46(6):1318–1322. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.6.1318-1322.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman J. S., Eckert E. A., Greenberg H. B., Strohm B. C., Isaacson R. E., Monto A. S. Norwalk virus enteric illness acquired by swimming exposure. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Feb;115(2):173–177. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makintubee S., Mallonee J., Istre G. R. Shigellosis outbreak associated with swimming. Am J Public Health. 1987 Feb;77(2):166–168. doi: 10.2105/ajph.77.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Hazlet K. K., Schaefer J., Wells J. G., Pruneda R. C. Shigellosis from swimming. JAMA. 1976 Oct 18;236(16):1849–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLANETZ L. W., BARTLEY C. H. Numbers of enterococci in water, sewage, and feces determined by the membrane filter technique with an improved medium. J Bacteriol. 1957 Nov;74(5):591–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.5.591-595.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENSON A. H. Studies of bathing water quality and health. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1953 May;43(5 Pt 1):529–538. doi: 10.2105/ajph.43.5_pt_1.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfried P. L., Tobin R. S., Brown N. E., Ness P. F. A prospective study of swimming-related illness. I. Swimming-associated health risk. Am J Public Health. 1985 Sep;75(9):1068–1070. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.9.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfried P. L., Tobin R. S., Brown N. E., Ness P. F. A prospective study of swimming-related illness. II. Morbidity and the microbiological quality of water. Am J Public Health. 1985 Sep;75(9):1071–1075. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.9.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vicente A., Borrego J. J., Arrabal F., Romero P. Comparative study of selective media for enumeration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from water by membrane filtration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):832–840. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.832-840.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


