Abstract
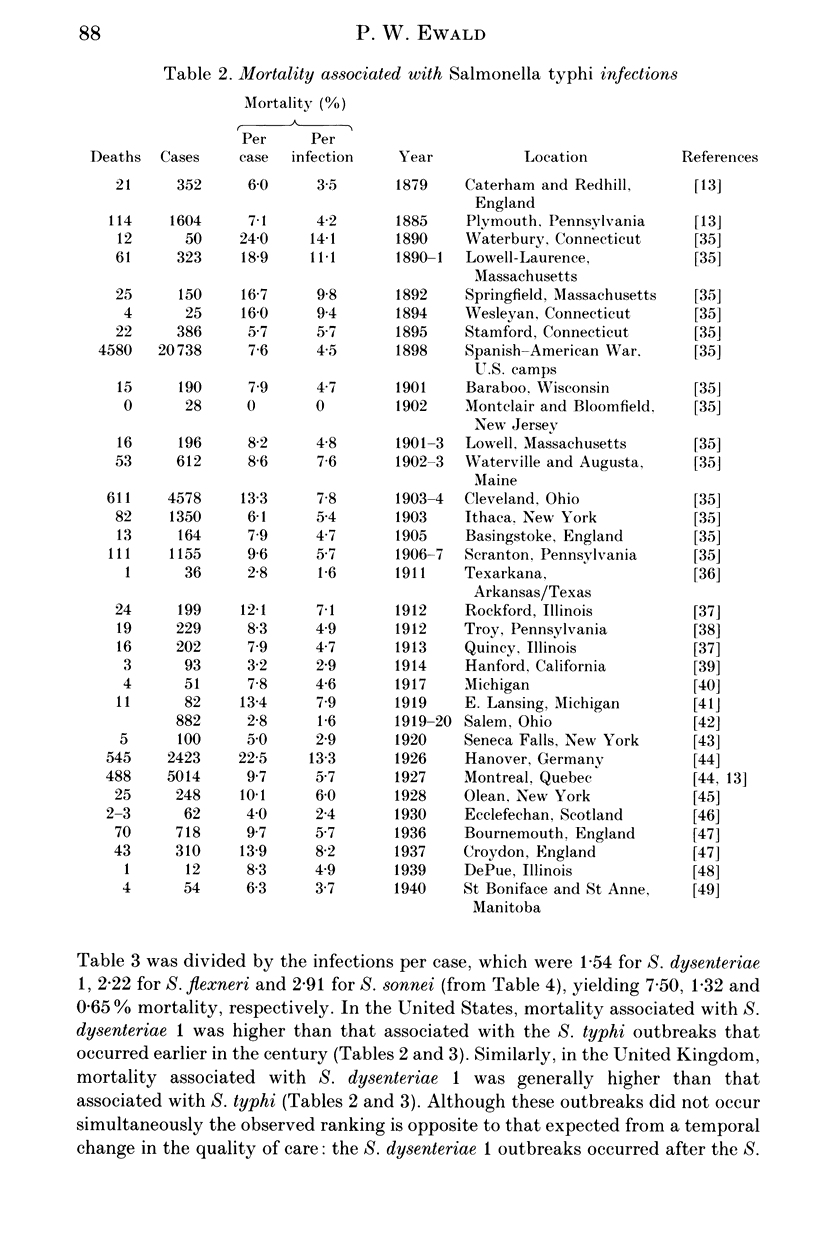
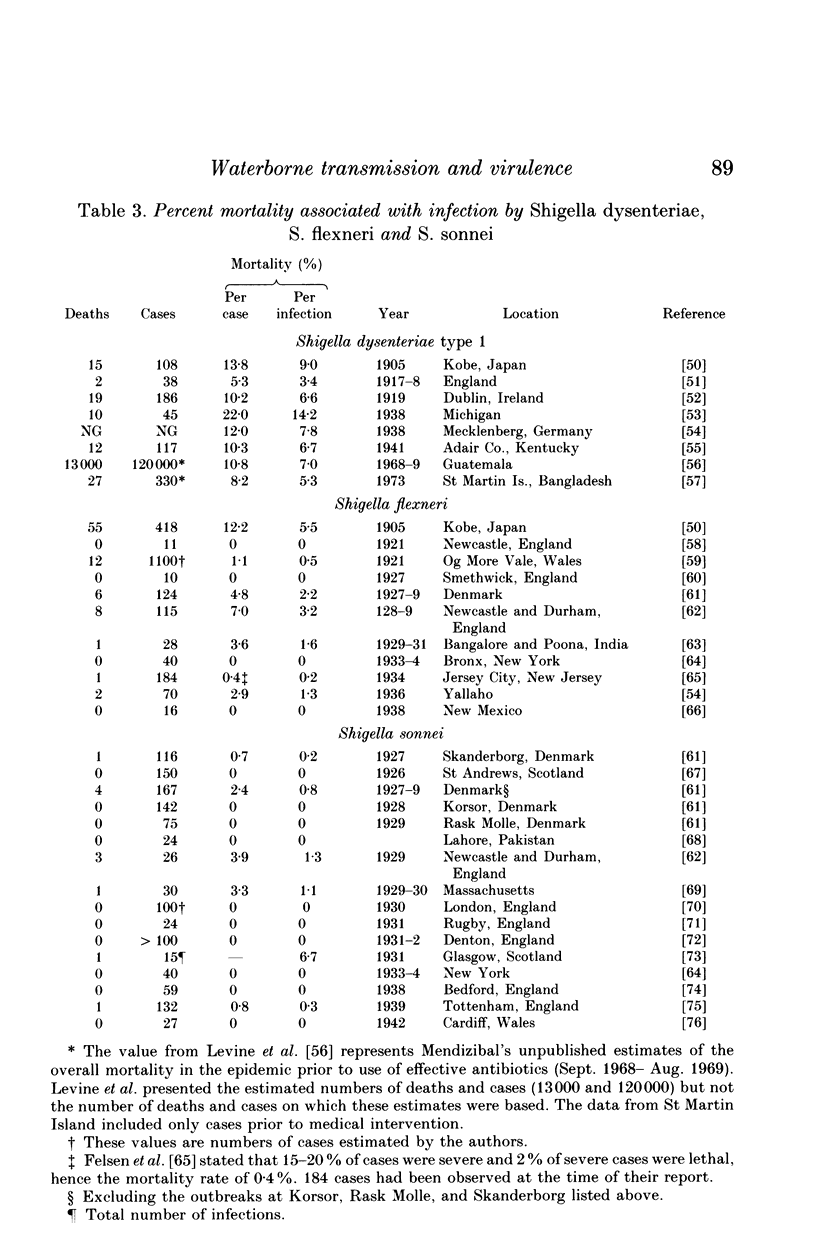
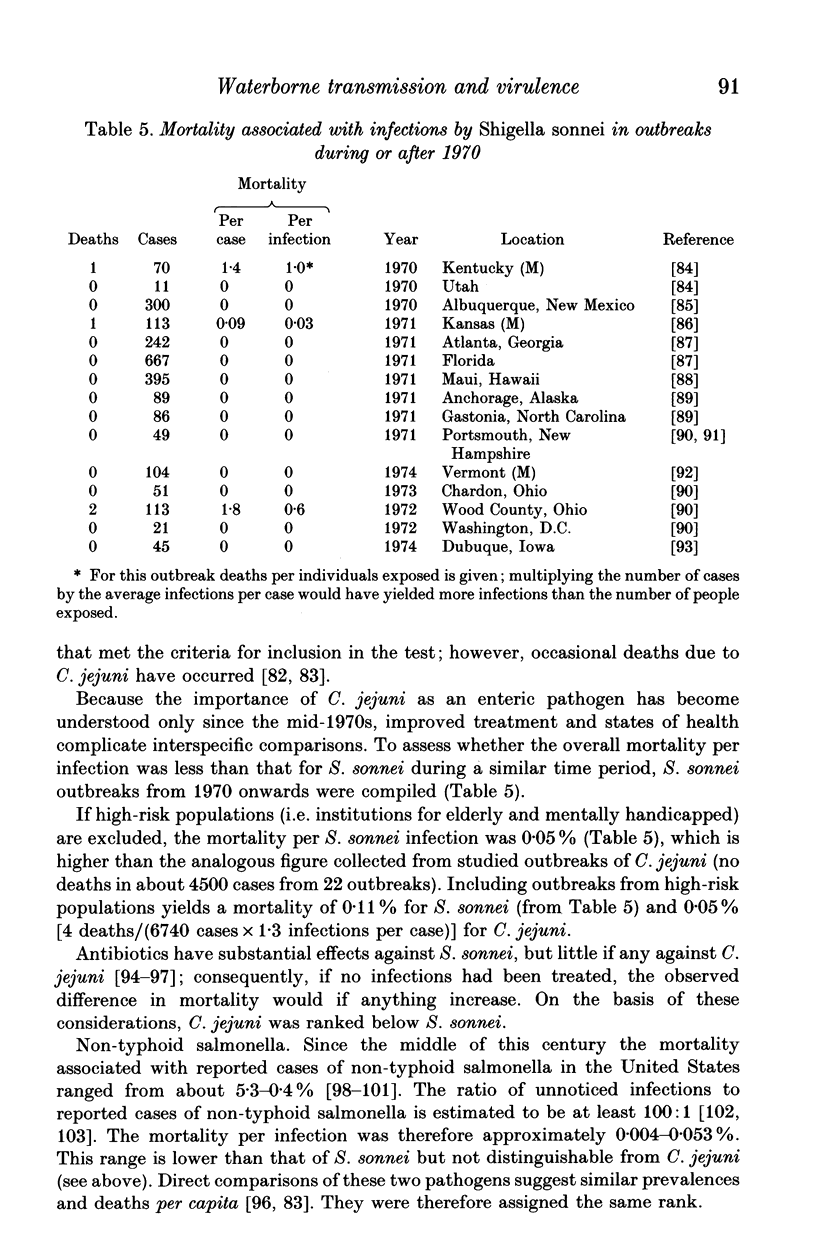
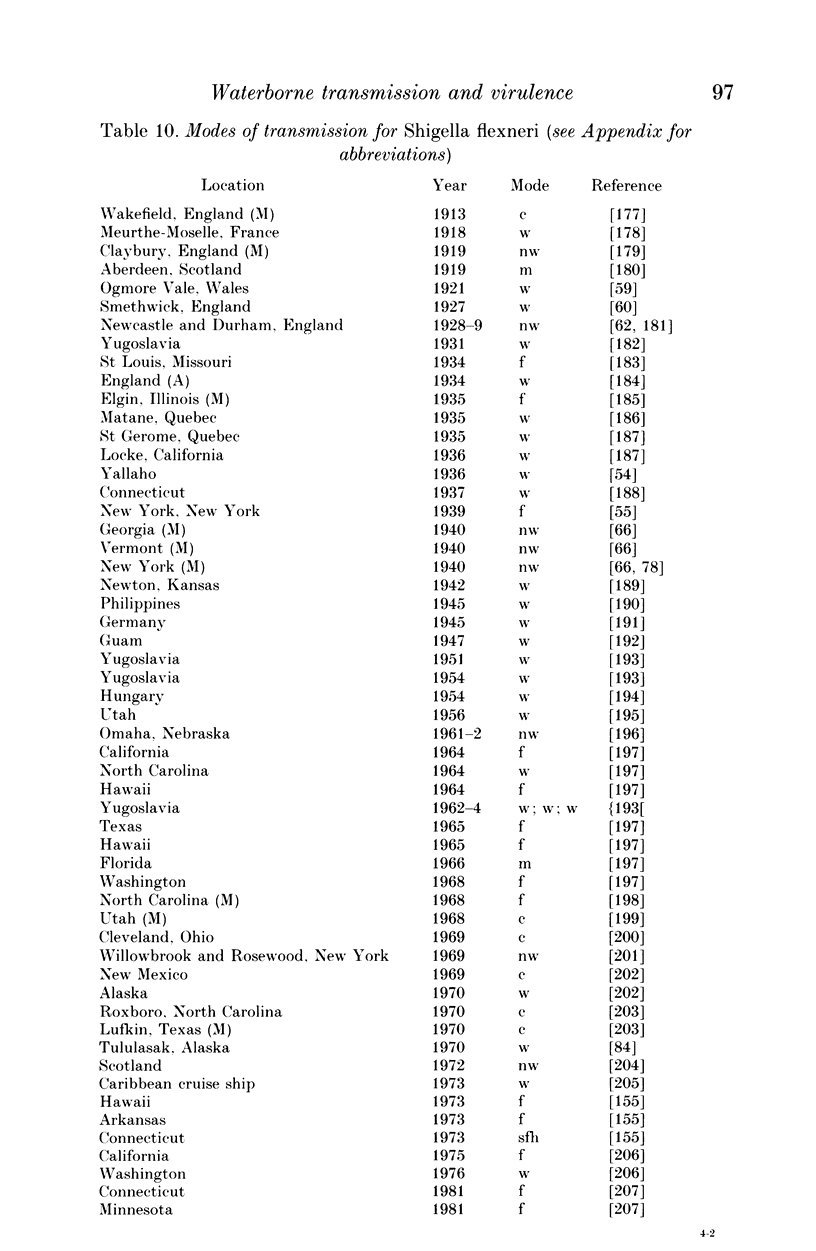
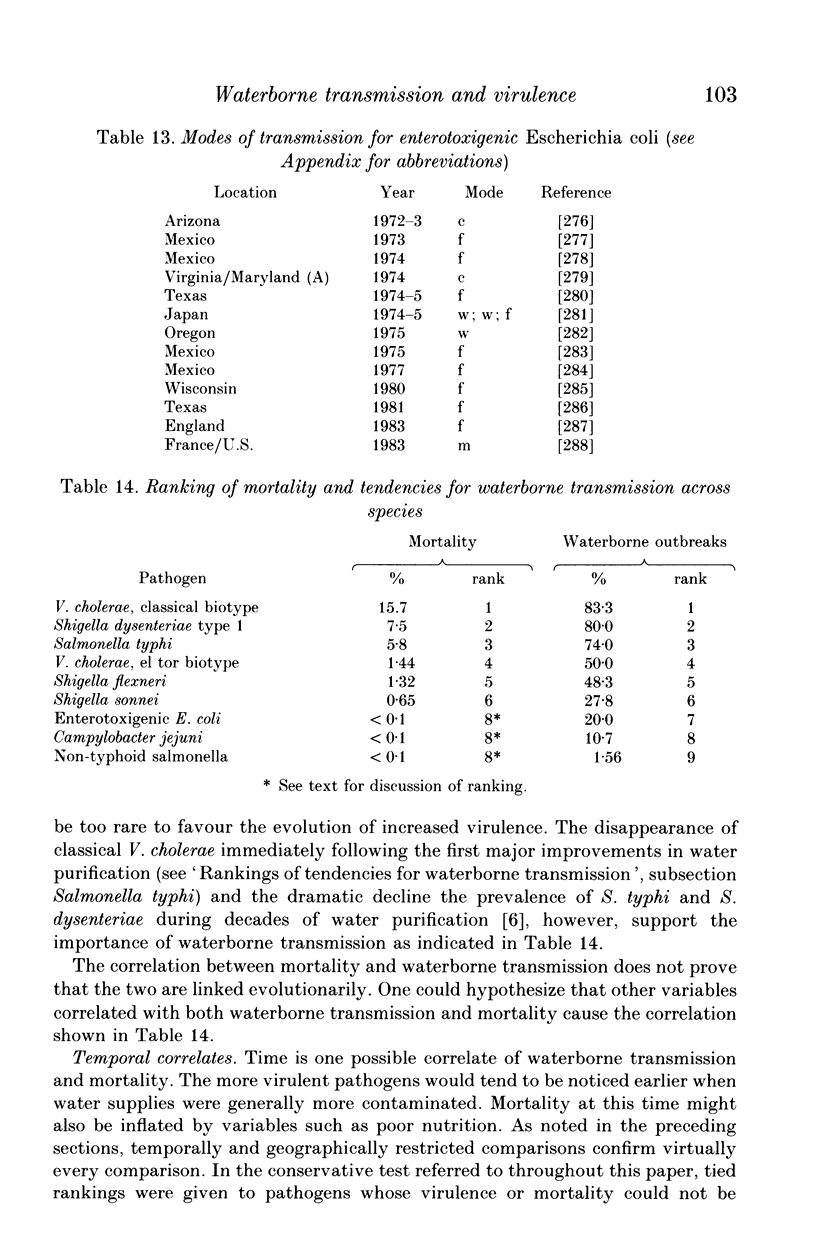
Diarrhoeal diseases are primary contributors to millions of deaths annually. Yet, little is known about the evolutionary reasons for the differences in virulence among gastrointestinal pathogens. Applying the comparative, cost/benefit approach of evolutionary biology this paper proposes that waterborne transmission should favour evolution towards high virulence. This hypothesis is supported by a cross-specific test, which shows that waterborne transmission is strongly correlated with the virulence of bacterial gastrointestinal pathogens of humans. Alternative explanations of this correlation are not supported by available data. These findings bear on public health policy because they draw attention to a previously unrecognized long-range benefit gained from purification of water supplies; diarrhoeal pathogens may evolve to lower levels of virulence.
Full text
PDF





























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. M., May R. M. Coevolution of hosts and parasites. Parasitology. 1982 Oct;85(Pt 2):411–426. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000055360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bart K. J., Huq Z., Khan M., Mosley W. H. Seroepidemiologic studies during a simultaneous epidemic of infection with El Tor Ogawa and classical Inaba Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(Suppl):17+–17+. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.supplement.s17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S., Bhattacharya P., Mukerjee S. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio El Tor. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;34(3):371–378. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Rosenberg M. L., Costa J. B., Ferreira P. S., Guimaraes C. L., Gangarosa E. J. Cholera in Portugal, 1974.I. Modes of transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Apr;105(4):337–343. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Campylobacter enteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1444–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Feldman R. A. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:157–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block N. B., Ferguson W. An Outbreak of Shiga Dysentery in Michigan, 1938. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1940 Jan;30(1):43–52. doi: 10.2105/ajph.30.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G. K. Sonne Dysentery due to Milk. Br Med J. 1938 May 21;1(4037):1092–1094. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4037.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M., Hughes J. M., Alim A. R., Khan M., Aziz K. M., Wells J. G., Curlin G. T. Patterns of Shigella infection in families in rural Bangladesh. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 Sep;31(5):1015–1020. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer K. M., Petersen N. J., Farzaneh I., Pattison C. P., Hart M. C., Maynard J. E. An outbreak og gastroenteritis due to E. coli 0142 in a neonatal nursery. J Pediatr. 1975 Jun;86(6):919–927. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe J. Water supply and health in developing countries: selective primary health care revisited. Am J Public Health. 1984 Sep;74(9):1009–1013. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.9.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer R., Mertens M. J., Siem T. H., Katchaki J. An explosive outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis in soldiers. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(3):517–519. doi: 10.1007/BF00443293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill K. M., Davies J. A., Johnson R. Report on an epidemic due to Shigella dysenteriae, type 1, in the Somali interior. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Jan;15(1):52–56. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis associated with raw milk--Kansas. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1981 May 15;30(18):218–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Typhoid fever--San Antonio, Texas, 1981. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1981 Nov 6;30(43):540, 545-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury M. N. Campylobacter jejuni enteritis; a review. Trop Geogr Med. 1984 Sep;36(3):215–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Baudry B., Sansonetti P. J. Plasmid-mediated contact haemolytic activity in Shigella species: correlation with penetration into HeLa cells. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):267–278. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J. B. M. Symptomless carriers in home contacts in Sonne dysentery. Br Med J. 1952 Jul 26;2(4777):191–192. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4777.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRACHMAN R. H., PAYNE F. J., JENKINS A. A., MACKEL D. C., PETERSEN N. J., BORING J. R., 3rd, GAREAU F. E., FRASER R. S., MYERS G. G. An outbreak of water-borne Shigella gastroenteritis. Am J Hyg. 1960 Nov;72:321–334. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale D. C., Mata L. J. Studies of diarrheal disease in Central America. XI. Intestinal bacterial flora in malnourished children with shigellosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 May;17(3):397–403. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. S. The Olean City Epidemic of Typhoid Fever in 1928. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1931 Apr;21(4):390–402. doi: 10.2105/ajph.21.4.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dordević D., Sokolovski B., Miladinović T. Hidricne epidemije dizenterije u garnizonu N u toku 1962-1964. godine. Vojnosanit Pregl. 1965 Jan;22(6):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dordević D., Sokolovski B., Miladinović T. Hidricne epidemije dizenterije u garnizonu N u toku 1962-1964. godine. Vojnosanit Pregl. 1965 Jan;22(6):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Gangarosa E. J., Reller L. B., Woodward W. E., Armstrong R. W., Hammond J., Glaser K., Morris G. K. Shigellosis in custodial institutions. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Sep;92(3):172–179. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutt A. K., Alwi S., Velauthan T. A shellfish-borne cholera outbreak in Malaysia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65(6):815–818. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(71)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Harrison B. A., Tirapat C., McFarland A. Flies as a source of enteric pathogens in a rural village in Thailand. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):32–36. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.32-36.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Taylor D. N., Changchawalit S., Smyth C. J., Twohig J., Rowe B. Plasmids coding for colonization factor antigens I and II, heat-labile enterotoxin, and heat-stable enterotoxin A2 in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):626–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.626-630.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson C. D., Pickering L. K., Sullivan P., DuPont H. L. The role of location of food consumption in the prevention of travelers' diarrhea in Mexico. Gastroenterology. 1980 Nov;79(5 Pt 1):812–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esrey S. A., Habicht J. P. Epidemiologic evidence for health benefits from improved water and sanitation in developing countries. Epidemiol Rev. 1986;8:117–128. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewald P. W. Evolutionary biology and the treatment of signs and symptoms of infectious disease. J Theor Biol. 1980 Sep 7;86(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(80)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD O., JATANASEN S., BUSPAVANICH S., THAVARAMARA B., NANTHAVANIJ S., MORGAN F. M., PANNIOM W. E1 Tor vibrios of the Ogawa subtype occurring in an epidemic of diarrhoea with vomiting in Ubol, Thailand. J Trop Med Hyg. 1961 Aug;64:207–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOYD T. M. The incidence of Shigella organisms in a group of Egyptian village children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1954 Mar;3(2):294–302. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1954.3.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUERST H. T. THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF SALMONELLA INFECTIONS IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1964 Dec;40:948–960. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feachem R. G. Environmental aspects of cholera epidemiology. I. A review of selected reports of endemic and epidemic situations during 1961-1980. Trop Dis Bull. 1981 Aug;78(8):675–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feachem R. G. Environmental aspects of cholera epidemiology. III. Transmission and control. Trop Dis Bull. 1982 Jan;79(1):1–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feachem R., Miller C., Drasar B. Environmental aspects of cholera epidemiology. II. Occurrence and survival of Vibrio cholerae in the environment. Trop Dis Bull. 1981 Oct;78(10):865–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch M. J., Blake P. A. Foodborne outbreaks of campylobacteriosis: the United States experience, 1980-1982. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Aug;122(2):262–268. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes G. I. An outbreak of cholera El Tor in Hong Kong: the Temple Street well. Public Health. 1966 May;80(4):188–193. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(66)80037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes G. I., Lockhart J. D., Robertson M. J., Allan W. G. Cholera case investigation and the detection and treatment of cholera carriers in Hong Kong. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(3):381–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON J. E., ASCOLI W., PIERCE V., GUZMAN M. A., MATA L. J. STUDIES OF DIARRHEAL DISEASE IN CENTRAL AMERICA. VI. AN EPIDEMIC OF DIARRHEA IN A GUATEMALAN HIGHLAND VILLAGE, WITH A COMPONENT DUE TO SHIGELLA DYSENTERIAE, TYPE 1. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangarosa E. J., Perera D. R., Mata L. J., Mendizábal-Morris C., Guzmán G., Reller L. B. Epidemic Shiga bacillus dysentery in Central America. II. Epidemiologic studies in 1969. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):181–190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Kean B. H., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Bessudo D. Travelers' diarrhea and toxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):933–936. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. A., Macleod M. C. Explosive Epidemic of Sonne Dysentery. Br Med J. 1943 Aug 28;2(4312):259–261. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4312.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. M., Scott S. S., Mowat D. A., Shearer E. J., Thomson J. M. Water-borne outbreak of viral gastroenteritis and Sonne dysentery. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Sep;66(3):383–392. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400041255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Dickens M. D., Wenzel R. P., Kapikian A. Z. Toxigenic bacterial diarrhea: nursery outbreak involving multiple bacterial strains. J Pediatr. 1976 Dec;89(6):885–891. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80591-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn R. A., Kimball A. M., Mathew P. P., Dutta S. R., Rifaat A. H. Cholera in Bahrain: epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(1):61–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES E. S. Treatment of carcinoma of the rectum. Med J Aust. 1960 Jul 16;47(2):81–84. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1960.tb87010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Protein synthesis in HeLa or Henle 407 cells infected with Shigella dysenteriae 1, Shigella flexneri 2a, or Salmonella typhimurium W118. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.137-144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Oaks E. V., Formal S. B. Identification and antigenic characterization of virulence-associated, plasmid-coded proteins of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):620–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.620-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. D. The genetical evolution of social behaviour. II. J Theor Biol. 1964 Jul;7(1):17–52. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(64)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamood A. N., Sublett R. D., Parker C. D. Plasmid-mediated changes in virulence of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):476–483. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.476-483.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry F. J., Huttly S. R., Patwary Y., Aziz K. M. Environmental sanitation, food and water contamination and diarrhoea in rural Bangladesh. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Apr;104(2):253–259. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800059422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Harris J. R., Kay D. E., Hargrett N. T., Parker R. D., Kansou N., Rao N. U., Blake P. A. Foodborne transmission of cholera in Micronesian households. Lancet. 1984 Feb 11;1(8372):325–328. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. S., Olmsted R., Istre G. R. Endemic Campylobacter jejuni infection in Colorado: identified risk factors. Am J Public Health. 1984 Mar;74(3):249–250. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. S., Scott A. S. Handling raw chicken as a source for sporadic Campylobacter jejuni infections. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):770–770. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson P. J., Vogt R. L., Brondum J., Patton C. M. Isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from milk during an outbreak of campylobacteriosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):789–789. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Boyce J. M., Levine R. J., Khan M., Aziz K. M., Huq M. I., Curlin G. T. Epidemiology of eltor cholera in rural Bangladesh: importance of surface water in transmission. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(3):395–404. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J., Hinchliffe P. M., Dawkins H. C., Horsley S. D., Jessop E. G., Robertshaw P. A., Counter D. E. Evidence of udder excretion of Campylobacter jejuni as the cause of milk-borne campylobacter outbreak. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Apr;94(2):205–215. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaäcson M., Clarke K. R., Ellacombe G. H., Smit W. A., Smit P., Koornhof H. J., Smith L. S., Kriel L. J. The recent cholera outbreak in the South African gold mining industry. A preliminary report. S Afr Med J. 1974 Dec 14;48(61):2557–2560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Istre G. R., Blaser M. J., Shillam P., Hopkins R. S. Campylobacter enteritis associated with undercooked barbecued chicken. Am J Public Health. 1984 Nov;74(11):1265–1267. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.11.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. H., Willis A. T., Robinson D. A., Skirrow M. B., Josephs D. S. Campylobacter enteritis associated with the consumption of free school milk. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Oct;87(2):155–162. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph P. R., Tamayo J. F., Mosley W. H., Alvero M. G., Dizon J. J., Henderson D. A. Studies of cholera El Tor in the Philippines. 2. A retrospective investigation of an explosive outbreak in Bacolod City and Talisay, November 1961. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;33(5):637–643. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER M. D., ROBBINS M. L. An outbreak of Shigella gastroenteritis. Public Health Rep. 1956 Sep;71(9):856–862. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. A., Srivastava R., Sinha V. B., Srivastava B. S. Regulation of toxin biosynthesis by plasmids in Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Oct;131(10):2653–2657. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-10-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. R., Huq F. Disease agents carried by flies in Dacca city. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 1978 Dec;4(2):86–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. U. Interruption of shigellosis by hand washing. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(2):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. U., Roy N. C., Islam R., Huq I., Stoll B. Fourteen years of shigellosis in Dhaka: an epidemiological analysis. Int J Epidemiol. 1985 Dec;14(4):607–613. doi: 10.1093/ije/14.4.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. U., Shahidullah M., Ahmed W. U., Barua D. K., Begum T., Purification D., Rahman N. Changes in the trend of shigellosis in Dhaka: family study on secondary infection, clinical manifestation and sensitivity pattern: 1980. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M., Curlin G. T., Huq I. Epidemiology of Shigella dysenteriae, type 1 infections, in Dacca urban area. Trop Geogr Med. 1979 Jun;31(2):213–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M., Shahidullah M. Contrasting epidemiology of shigellae dysenteriae and shigellae flexneri, Dacca. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):528–533. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaman C. H., Beelman F. C. An Epidemic of 3,000 Cases of Bacillary Dysentery Involving a War Industry and Members of the Armed Forces. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1944 Sep;34(9):948–954. doi: 10.2105/ajph.34.9.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B. S., Vergeront J. M., Blaser M. J., Edmonds P., Brenner D. J., Janssen D., Davis J. P. Campylobacter infection associated with raw milk. An outbreak of gastroenteritis due to Campylobacter jejuni and thermotolerant Campylobacter fetus subsp fetus. JAMA. 1986 Jan 17;255(3):361–364. doi: 10.1001/jama.255.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolvin J. L., Roberts D. Studies on the growth of Vibrio cholerae biotype eltor and biotype classical in foods. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):243–252. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korlath J. A., Osterholm M. T., Judy L. A., Forfang J. C., Robinson R. A. A point-source outbreak of campylobacteriosis associated with consumption of raw milk. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):592–596. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt A. N., Barrett T., Morris G. K., Tosh F. E. Epidemiologic and laboratory investigation of an outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis associated with raw milk. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Nov;122(5):884–889. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudoh Y., Zen-Yoji H., Matsushita S., Sakai S., Maruyama T. Outbreaks of acute enteritis due to heat-stable enterotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(3):175–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa N. H., Takai R. A cholera epidemic in North Sumatra, Indonesia. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1985 Dec;34(4):451–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSAY D. R., STEWART W. H., WATT J. Effect of fly control on diarrheal disease in an area of moderate morbidity. Public Health Rep. 1953 Apr;68(4):361–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasch E. E., Abed Y., Marcus O., Shbeir M., El Alem A., Ali Hassan N. Cholera in Gaza in 1981: epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(4):554–557. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Gangarosa E. J. Epidemic Shiga dysentery in Central America. Lancet. 1970 Sep 19;2(7673):607–608. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Epidemiol Rev. 1984;6:31–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. J., Khan M. R., D'Souza S., Nalin D. R. Cholera transmission near a cholera hospital. Lancet. 1976 Jul 10;2(7976):84–86. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92298-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. J., Khan M. R., D'Souza S., Nalin D. R. Failure of sanitary wells to protect against cholera and other diarrhoeas in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1976 Jul 10;2(7976):86–89. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. N., Loewenstein M. S., Guthrie L. C., Sugi M. Shigella sonnei outbreak on the island of Maui. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Jul;96(1):50–58. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long-Krug S. A., Weikel C. S., Tiemens K. T., Hewlett E. L., Levine M. M., Guerrant R. L. Does enteropathogenic Escherichia coli produce heat-labile enterotoxin, heat-stable enterotoxins a or b, or cholera toxin A subunits? Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):612–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.612-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSLEY W. H., ADAMS B., LYMAN E. D. Epidemiologic and sociologic features of a large urban outbreak of shigellosis. JAMA. 1962 Dec 29;182:1307–1311. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050520005002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald K. L., Eidson M., Strohmeyer C., Levy M. E., Wells J. G., Puhr N. D., Wachsmuth K., Hargrett N. T., Cohen M. L. A multistate outbreak of gastrointestinal illness caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in imported semisoft cheese. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):716–720. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata L. J., Gangarosa E. J., Cáceres A., Perera D. R., Mejicanos M. L. Epidemic Shiga bacillus dysentery in Central America. I. Etiologic investigations in Guatemala, 1969. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):170–180. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathan V. I., Bhat P., Kapadia C. R., Ponniah J., Baker S. J. Epidemic dysentery caused by the Shiga bacillus in a southern Indian village. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1984 Mar;2(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May R. M., Anderson R. M. Epidemiology and genetics in the coevolution of parasites and hosts. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Oct 22;219(1216):281–313. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre R. C., Tira T., Flood T., Blake P. A. Modes of transmission of cholera in a newly infected population on an atoll: implications for control measures. Lancet. 1979 Feb 10;1(8111):311–314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90719-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton R. D., Leyland R., Mueller L. Outbreak of Campylobacter enteritis due to consumption of raw milk. Can Med Assoc J. 1982 Mar 15;126(6):657–658. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendis N. M., De La Motte P. U., De Silva A. V., Maheswaran K., Sivayoham S. The spread of cholera El Tor in Sri Lanka in 1974. Ceylon Med J. 1977 Mar;22(1):24–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendizábal-Morris C. A., Mata L. J., Gangarosa E. J., Guzmán G. Epidemic Shiga-bacillus dysentery in Central America. Derivation of the epidemic and its progression in Guatemala, 1968-69. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Nov;20(6):927–933. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzing L. O. Waterborne outbreaks of campylobacter enteritis in central Sweden. Lancet. 1981 Aug 15;2(8242):352–354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90658-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Morris G. K., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Creech W. B., Kapikian A. Z., Gangarosa E. J. Travelers' diarrhea in Mexico. A prospective study of physicians and family members attending a congress. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 10;294(24):1299–1305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606102942401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Tenney J. H., Meyers J. D., Wood B. T., Wells J. G., Rymzo W., Cline B., DeWitt W. E., Skaliy P., Mallison F. Shigellosis at sea: an outbreak aboard a passenger cruise ship. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Feb;101(2):165–175. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mhalu F. S., Mmari P. W., Ijumba J. Rapid emergence of El Tor Vibrio cholerae resistant to antimicrobial agents during first six months of fourth cholera epidemic in Tanzania. Lancet. 1979 Feb 17;1(8112):345–347. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92889-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mhalu F. S., Mmari P. W., Ijumba J. Rapid emergence of El Tor Vibrio cholerae resistant to antimicrobial agents during first six months of fourth cholera epidemic in Tanzania. Lancet. 1979 Feb 17;1(8112):345–347. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92889-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley W. H., Ahmad S., Benenson A. S., Ahmed A. The relationship of vibriocidal antibody titre to susceptibility to cholera in family contacts of cholera patients. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(5):777–785. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley W. H., Alvero M. G., Joseph P. R., Tamayo J. F., Gomez C. Z., Montague T., Dizon J. J., Henderson D. A. Studies of cholera El Tor in the Philippines. 4. Transmission of infection among neighbourhood and community contacts of cholera patients. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;33(5):651–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkrans G., Svedhem A. Epidemiological aspects of Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Aug;89(1):163–170. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterom J., den Uyl C. H., Bänffer J. R., Huisman J. Epidemiological investigations on Campylobacter jejuni in households with a primary infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Oct;93(2):325–332. doi: 10.1017/s002217240006486x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseasohn R., Ahmad S., Islam M. A., Rahman A. S. Clinical and bacteriological findings among families of cholera patients. Lancet. 1966 Feb 12;1(7433):340–342. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91322-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S. R., Gully P. R., White J. M., Pearson A. D., Suckling W. G., Jones D. M., Rawes J. C., Penner J. L. Water-borne outbreak of campylobacter gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1983 Feb 5;1(8319):287–290. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter I. A., Reid T. M. A milk-borne outbreak of Campylobacter infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Jun;84(3):415–419. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. E., Blaser M. J., Sikes R. K., Kaufmann A. F., Wells J. G. Human Campylobacter infection associated with certified raw milk. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Apr;117(4):475–483. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for FEBRUARY 16, 1912. Public Health Rep. 1912 Feb 16;27(7):219–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for JULY 24, 1942. Public Health Rep. 1942 Jul 24;57(30):1079–1114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for MARCH 9, 1945. Public Health Rep. 1945 Mar 9;60(10):261–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS A. I., GILLESPIE E. H. An outbreak of water-borne gastro-enteritis and sonne dysentery. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1952 Feb;11:36–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman M. M., Khan M. M., Aziz K. M., Islam M. S., Kibriya A. K. An outbreak of dysentery caused by Shigella dysenteriae type 1 on a coral island in the Bay of Bengal. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):15–19. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Gangarosa E. J., Brachman P. S. From the national communicable disease center. Shigellosis in the United States. 1964-1968. J Infect Dis. 1969 Sep;120(3):393–396. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.3.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Gangarosa E. J., Brachman P. S. Shigellosis in the United States: five-year review of nationwide surveillance, 1964-1968. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Feb;91(2):161–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Rivas E. N., Masferrer R., Bloch M., Gangarosa E. J. Epidemic shiga-bacillus dysentery in Central America. Evolution of the outbreak in El Salvador, 1969-70. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Nov;20(6):934–940. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich E. D. A TYPHOID FEVER EPIDEMIC TRACED TO CHEESE. Am J Public Health (N Y) 1923 Mar;13(3):210–215. doi: 10.2105/ajph.13.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan T., Gross R. J., Rowe B., Scotland S. M., Johnston S. M. An outbreak of food-borne enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea in England. J Infect. 1985 Sep;11(2):167–171. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)92147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A., Edgar W. J., Gibson G. L., Matchett A. A., Robertson L. Campylobacter enteritis associated with consumption of unpasteurised milk. Br Med J. 1979 May 5;1(6172):1171–1173. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6172.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A., Jones D. M. Milk-borne campylobacter infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Apr 25;282(6273):1374–1376. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6273.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde J. E., Northrup R. S. Taking science where the diarrhoea is. Ciba Found Symp. 1976;(42):339–366. doi: 10.1002/9780470720240.ch18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Hazlet K. K., Schaefer J., Wells J. G., Pruneda R. C. Shigellosis from swimming. JAMA. 1976 Oct 18;236(16):1849–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Koplan J. P., Wachsmuth I. K., Wells J. G., Gangarosa E. J., Guerrant R. L., Sack D. A. Epidemic diarrhea at Crater Lake from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. A large waterborne outbreak. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):714–718. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland M. G., Cole T. J., Whitehead R. G. A quantitative study into the role of infection in determining nutritional status in Gambian village children. Br J Nutr. 1977 May;37(3):441–450. doi: 10.1079/bjn19770047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S. K., Chowdhury A. K., Rahaman M. M. Excess mortality among children discharged from hospital after treatment for diarrhoea in rural Bangladesh. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Oct 15;287(6399):1097–1099. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6399.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAPHRA I., WINTER J. W. Clinical manifestations of salmonellosis in man; an evaluation of 7779 human infections identified at the New York Salmonella Center. N Engl J Med. 1957 Jun 13;256(24):1128–1134. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195706132562402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha A. L., Pain G. C., Chowdhury K., Mukherjee S., Basu B. K. Cholera epidemics (1964-1965) in Brahmaputra Valley of Assam. J Indian Med Assoc. 1970 Nov 1;55(9):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Sakai T., Murayama S. Y., Makino S., Yoshikawa M. Molecular alteration of the 140-megadalton plasmid associated with loss of virulence and Congo red binding activity in Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):470–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.470-475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathe P. V., Karandikar V. N., Gupte M. D., Niphadkar K. B., Joshi B. N., Polakhare J. K., Jahagirdar P. L., Deodhar N. S. Investigation report of an epidemic of typhoid fever. Int J Epidemiol. 1983 Jun;12(2):215–219. doi: 10.1093/ije/12.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears F. W. A Water-Borne Typhoid Fever Outbreak : With Unusual Epidemiological Features. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1931 Sep;21(9):1019–1023. doi: 10.2105/ajph.21.9.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltmann G., Pál T., Tschäpe H. Surface hydrophobicity of plasmid-carrying virulent Shigella flexneri and their avirulent variants. J Basic Microbiol. 1986;26(5):283–287. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3620260508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahid N. S., Samadi A. R., Khan M. U., Huq M. I. Classical vs El Tor cholera: a prospective family study of a concurrent outbreak. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1984 Jun;2(2):73–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair G. S., Mphahlele M., Duvenhage H., Nichol R., Whitehorn A., Küstner H. G. Determination of the mode of transmission of cholera in Lebowa. An epidemiological investigation. S Afr Med J. 1982 Nov 13;62(21):753–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha R., Deb B. C., De S. P., Abou-Gareeb A. H., Shrivastava D. L. Cholera carrier studies in Calcutta in 1966-67. Bull World Health Organ. 1967;37(1):89–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerman F. J., Formal S. B., Falkow S. Plasmid-associated enterotoxin production in a strain of Escherichia coli isolated from humans. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):622–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.622-624.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Fidoe R. G., Jones D. M. An outbreak of presumptive food-borne campylobacter enteritis. J Infect. 1981 Sep;3(3):234–236. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)90819-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. S., Blaser M. J. Fatalities associated with Campylobacter jejuni infections. JAMA. 1985 May 17;253(19):2873–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Woodward W. E. The influence of protected water supplies on the spread of classical-Inaba and El Tor-Ogawa cholera in rural East Bengal. Lancet. 1972 Nov 11;2(7785):985–987. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soper G. A. The Curious Career of Typhoid Mary. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1939 Oct;15(10):698–712. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Khan M. U., Saeed Y. A., Sattar M. A. Microbiological surveillance of intra-neighbourhood E1 Tor cholera transmission in rural Bangladesh. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(5):731–740. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Glass R. I., Huq M. I., Khan M. U., Banu H., Holt J. Epidemiologic and clinical features of patients infected with Shigella who attended a diarrheal disease hospital in Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):177–183. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. G. An outbreak of cholera in Australia due to food served in flight on an international aircraft. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Jun;72(3):441–451. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON S. The numbers of pathogenic bacilli in faeces in intestinal diseases. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Jun;53(2):217–224. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400000681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamayo J. F., Mosley W. H., Alvero M. G., Joseph P. R., Gomez C. Z., Montague T., Dizon J. J., Henderson D. A. Studies of cholera El Tor in the Philippines. 3. Transmission of infection among household contacts of cholera patients. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;33(5):645–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., McDermott K. T., Little J. R., Wells J. G., Blaser M. J. Campylobacter enteritis from untreated water in the Rocky Mountains. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):38–40. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. R., Weinstein W. M., Bryner J. H. Campylobacter fetus infection in human subjects: association with raw milk. Am J Med. 1979 May;66(5):779–783. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)91116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Schell W. L., Wells J. G., Choi K., Kinnunen D. E., Heiser P. T., Helstad A. G. A foodborne outbreak of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 6;306(18):1093–1095. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205063061807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrier A., Altwegg M., Bader P., von Graevenitz A. Hospital epidemic of neonatal Campylobacter jejuni infection. Lancet. 1985 Nov 23;2(8465):1182–1182. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92698-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. E., Noah N. D., Tillett H. E., Dadswell J. V., Walker P. H. Recurrent gastroenteritis in a preparatory school caused by Shigella sonnei and another agent. Lancet. 1974 May 18;1(7864):978–981. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. E., Tillett H. E. Dysentery in general practice: a study of cases and their contacts in Enfield and an epidemiological comparison with salmonellosis. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Jun;71(2):373–389. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L., Sullivan P., Pickering L. K., Holguin A. H., Olarte J., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr Location of food consumption and travelers' diarrhea. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Jul;106(1):61–66. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Still C. S., Isaäcson M., Ahmad Q. S. In vitro and in vivo cholera toxin production by classical and El Tor isolates of Vibrio cholerae. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):884–890. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.884-890.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt R. L., Sours H. E., Barrett T., Feldman R. A., Dickinson R. J., Witherell L. Campylobacter enteritis associated with contaminated water. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Mar;96(3):292–296. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-3-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATT J., LINDSAY D. R. Diarrheal disease control studies; effect of fly control in a high morbidity area. Public Health Rep. 1948 Oct 8;63(41):1319–1333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A., Warren K. S. Selective primary health care: an interim strategy for disease control in developing countries. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 1;301(18):967–974. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911013011804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Nakamura A. Identification of Shigella sonnei form I plasmid genes necessary for cell invasion and their conservation among Shigella species and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):352–358. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.352-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber R. H., Mwakalukwa J. The epidemiology of cholera in south-west Tanzania. East Afr Med J. 1983 Dec;60(12):848–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman J. B., Gangorosa E. J., Schmerler A., Marier R. L., Lewis J. N. Shigellosis in day-care centres. Lancet. 1975 Jan 11;1(7898):88–90. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman J. B., Marton K. I., Lewis J. N., Friedmann C. T., Gangarosa E. J. Impact in the United States of the Shiga dysentery pandemic of Central America and Mexico: a review of surveillance data through 1972. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):218–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff H. L., van Zijl W. J. Houseflies, the availability of water, and diarrhoeal diseases. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(6):952–959. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood L. V., Wolfe W. H., Ruiz-Palacios G., Foshee W. S., Corman L. I., McCleskey F., Wright J. A., DuPont H. L. An outbreak of gastroenteritis due to a heat-labile enterotoxin-producing strain of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):931–934. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.931-934.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward W. E., Mosley W. H. The spectrum of cholera in rural Bangladesh. II. Comparison of El Tor Ogawa and classical Inaba infection. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Nov;96(5):342–351. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yala F., Dodin A., Diana Y. Role de la contamination interhumaine pendant l'épidémie de choléra en République Populaire du Congo (1978-1979). Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1982 Aug-Oct;75(4):345–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


