Abstract
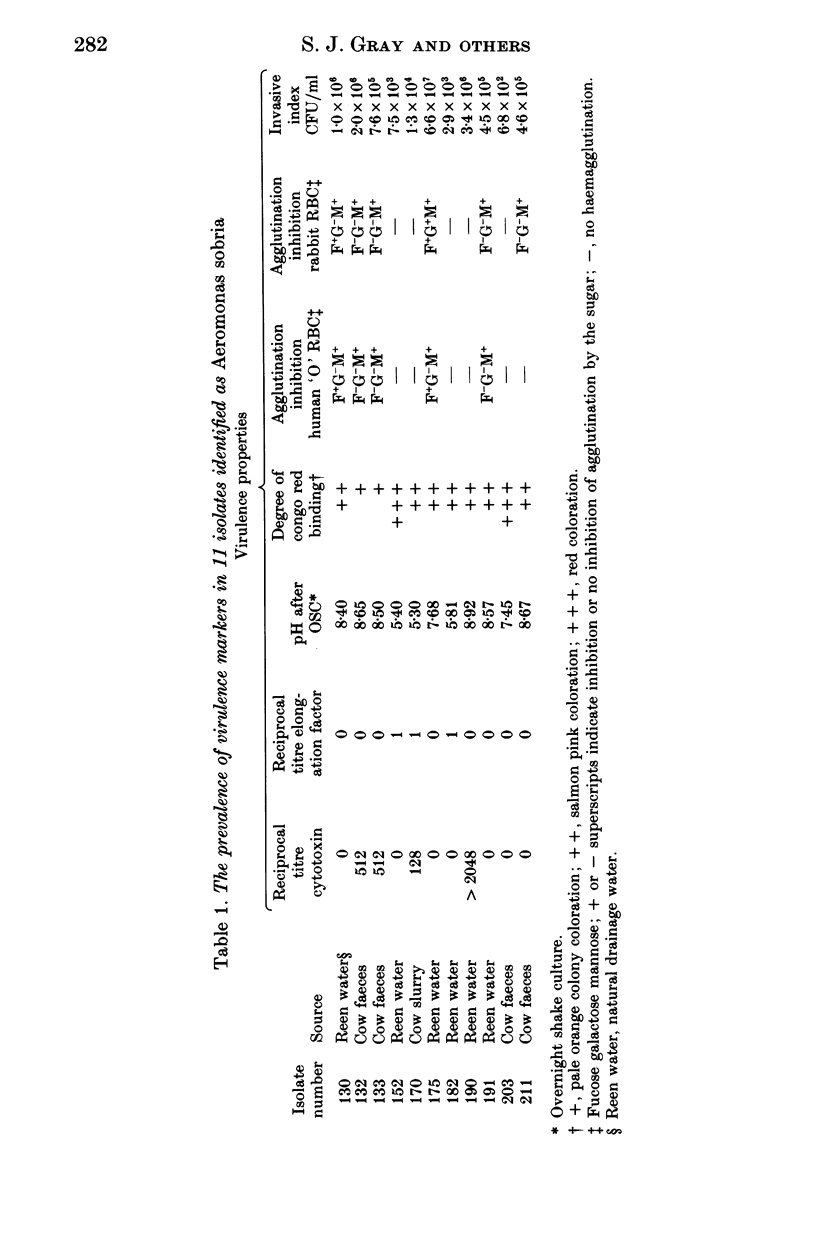
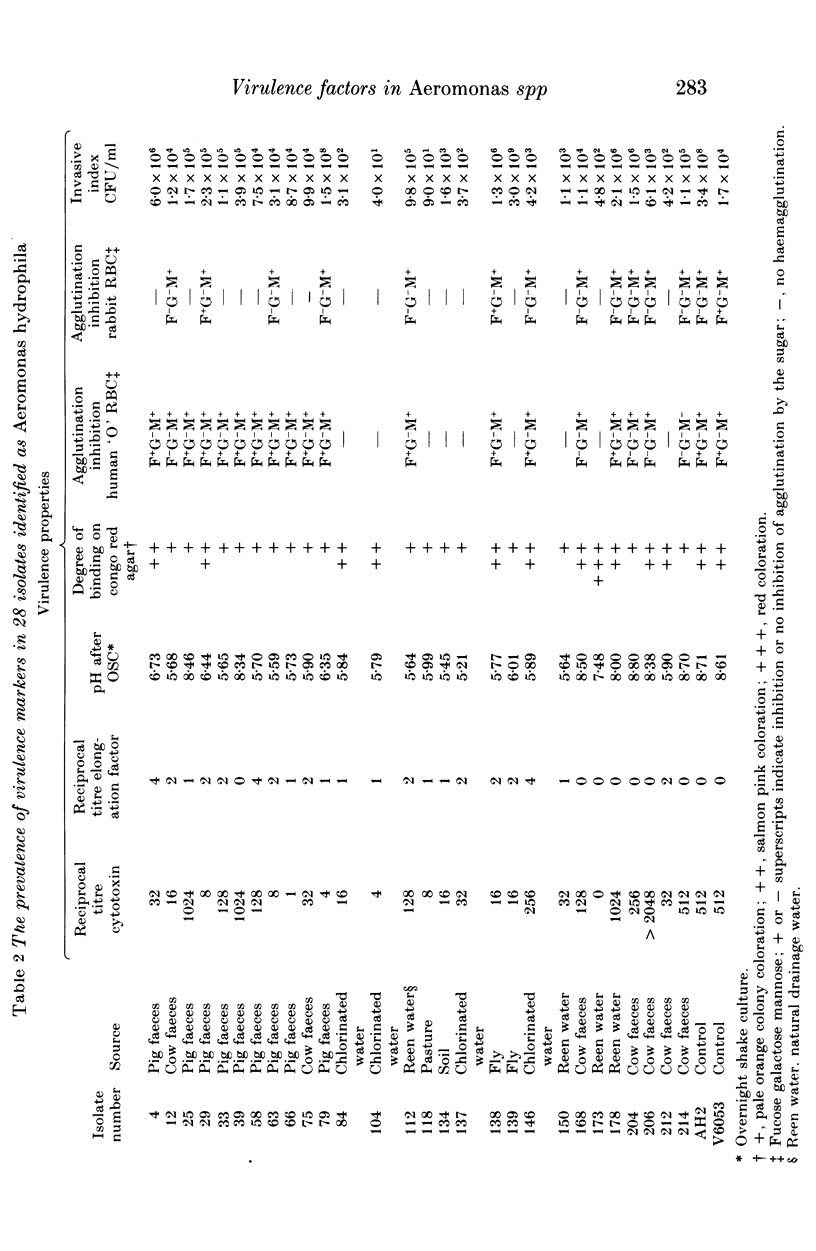
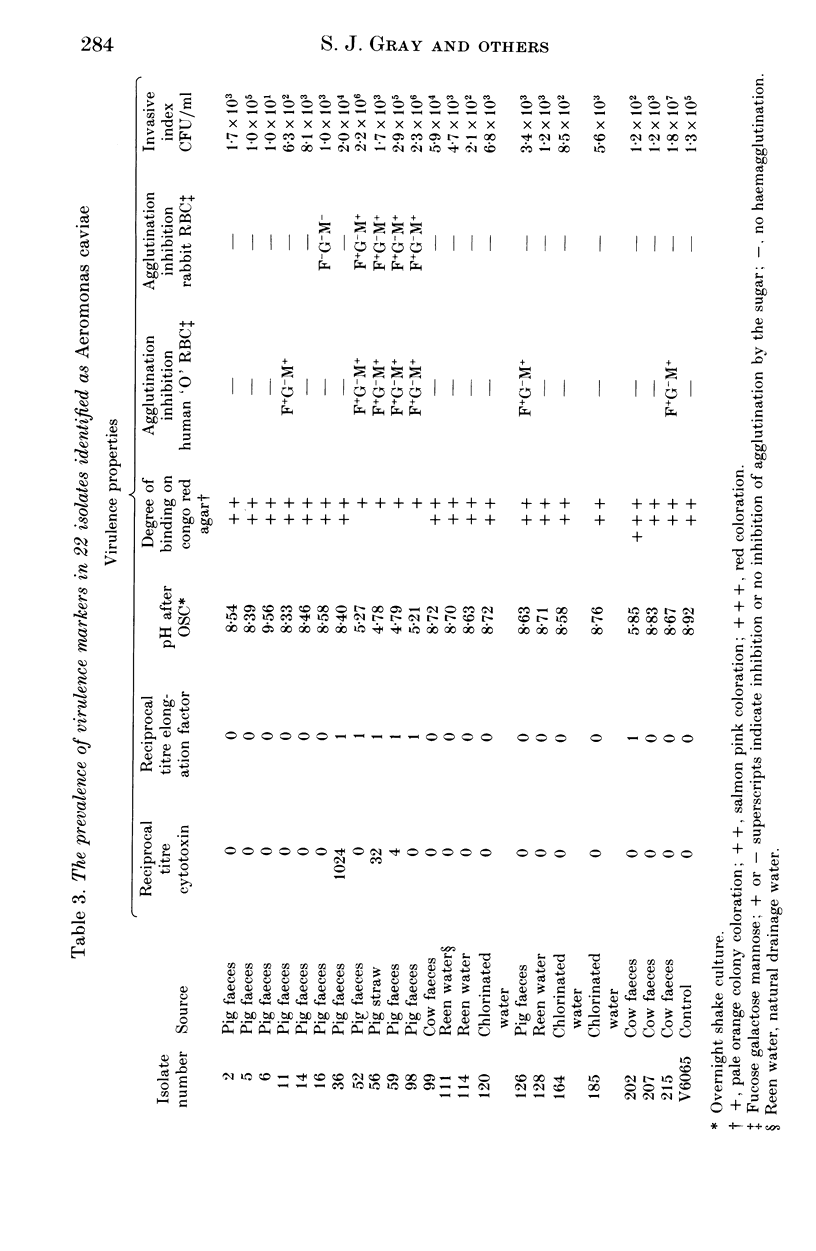
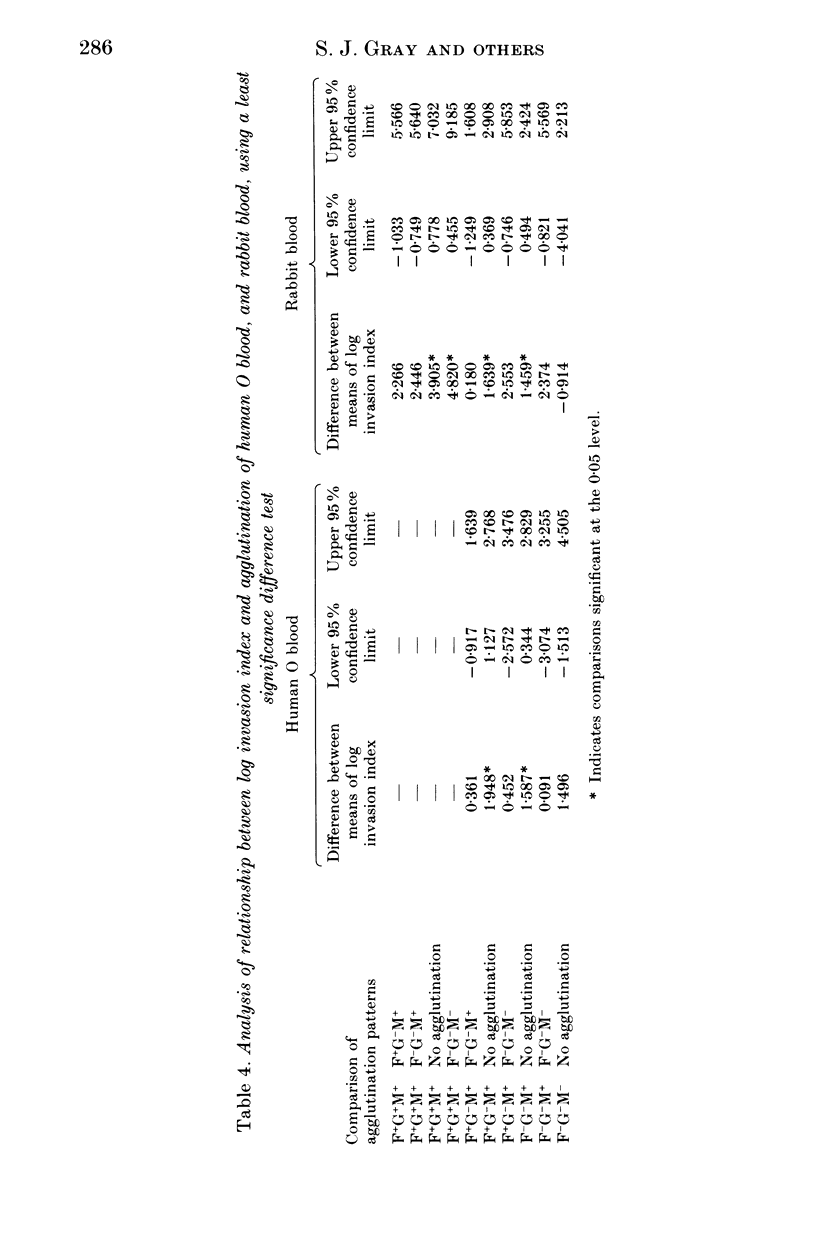
Sixty-one isolates of Aeromonas spp. from the faeces of pigs, cows and a variety of associated environmental sources were examined for the characteristics that are reputed to have roles in pathogenicity. Most isolates of Aeromonas hydrophila were cytotoxic (96.4%) and were capable of producing cell elongation factor (75%) and haemagglutinins (67.9%). In contrast few of the Aeromonas caviae isolates produced these three markers (13.6%, 27.3% and 36.4% respectively). In general, Aeromonas sobria occupied an intermediate position (36.4%, 27.3% and 54.5%), but they did produce the highest mean invasion index for HEp-2 cells. Statistical analysis revealed significant associations between the carriage of these factors and it was clear that many isolates of aeromonads from water and animals possessed the full battery of putative virulence factors.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D., Atkinson H. M., Woods W. H. Aeromonas hydrophila typing scheme based on patterns of agglutination with erythrocytes and yeast cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):422–427. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.422-427.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asao T., Kinoshita Y., Kozaki S., Uemura T., Sakaguchi G. Purification and some properties of Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):122–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.122-127.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson H. M., Trust T. J. Hemagglutination properties and adherence ability of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.938-946.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barer M. R., Millership S. E., Tabaqchali S. Relationship of toxin production to species in the genus Aeromonas. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Dec;22(4):303–309. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-4-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundell C. S., Watson I. M., Burke V., Gracey M. Protection of rats against cholera toxin and cholera-like enterotoxins by immunization with enteric-coated cholera toxin. Ann Trop Paediatr. 1986 Sep;6(3):199–204. doi: 10.1080/02724936.1986.11748439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunning V. K., Crawford R. G., Stelma G. N., Jr, Kaylor L. O., Johnson C. H. Melanogenesis in murine B16 cells exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila cytotoxic enterotoxin. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Oct;32(10):814–819. doi: 10.1139/m86-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Cooper M., Robinson J., Gracey M., Lesmana M., Echeverria P., Janda J. M. Hemagglutination patterns of Aeromonas spp. in relation to biotype and source. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.39-43.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Cooper M., Robinson J. Haemagglutination patterns of Aeromonas spp. related to species and source of strains. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1986 Dec;64(Pt 6):563–570. doi: 10.1038/icb.1986.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Atkinson H. M., Gracey M. Biochemical characteristics of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.48-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Gracey M., Peterson D., Partridge K. Isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila from a metropolitan water supply: seasonal correlation with clinical isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):361–366. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.361-366.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Agger W. A. Enumeration and characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas caviae isolated from grocery store produce. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):249–253. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.249-253.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Huhle B., Hof H., Bergbauer H., Goebel W. Marker exchange mutagenesis of the aerolysin determinant in Aeromonas hydrophila demonstrates the role of aerolysin in A. hydrophila-associated systemic infections. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2274–2280. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2274-2280.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Montenegro M. A., Sanyal S. C., Helmuth R., Bulling E., Timmis K. N. Cloning of enterotoxin gene from Aeromonas hydrophila provides conclusive evidence of production of a cytotonic enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.435-441.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra A. K., Houston C. W., Genaux C. T., Dixon J. D., Kurosky A. Evidence for production of an enterotoxin and cholera toxin cross-reactive factor by Aeromonas hydrophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):661–664. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.661-664.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch N., Gurwith M. J., Langston C., Sack R. B., Brunton J. L. Cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila: relationship of toxigenic isolates to diarrheal disease. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):829–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.829-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daily O. P., Joseph S. W., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I., Merrell B. R., Rollins D. M., Seidler R. J., Colwell R. R., Lissner C. R. Association of Aeromonas sobria with human infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):769–777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.769-777.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Haddow A. D. Cytotoxic activity of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):989–993. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.989-993.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubey R. S., Sanyal S. C. Characterisation and neutralisation of Aeromonas hydrophila enterotoxin in the rabbit ileal-loop model. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Aug;12(3):347–354. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubey R. S., Sanyal S. C. Enterotoxicity of Aeromonas hydrophila: skin responses and in vivo neutralisation. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Dec;242(4):487–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlhaber K., Scheibner G. Untersuchungen über Eigenschaften von Aeromonas-hydrophila-Enterotoxinen aus lebensmittelhygienischer Sicht. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1987 Jan;41(1):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figura N., Marri L. Isolation of Aeromonas species from animals. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):354–355. doi: 10.1007/BF02013674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figura N., Marri L., Verdiani S., Ceccherini C., Barberi A. Prevalence, species differentiation, and toxigenicity of Aeromonas strains in cases of childhood gastroenteritis and in controls. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):595–599. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.595-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. J., Knepp I. G. Seafood shucking as an etiology for Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Oct;147(10):1816–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giugliano L. G., Mann G. F., Drasar B. S. Response of mammalian cell lines to the toxins of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):531–539. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. J. Aeromonas hydrophila in livestock: incidence, biochemical characteristics and antibiotic susceptibility. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Jun;92(3):365–375. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400064585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. J., Stickler D. J. Some observations on the faecal carriage of mesophilic Aeromonas species in cows and pigs. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Dec;103(3):523–537. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Ainsworth T., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Congo red agar, a differential medium for Aeromonas salmonicida, detects the presence of the cell surface protein array involved in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1233–1237. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1233-1237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabłońska-Strynkowska W., Potapa M. Aeromonas hydrophila var. anaerogenes jako przypuszczalny czynnik etiologiczny zatrucia pokarmowego. Przegl Epidemiol. 1983;37(3-4):455–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Brenden R. Importance of Aeromonas sobria in Aeromonas bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):589–591. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa S. F. Enterotoxigenicity, hemagglutination and cell-surface hydrophobicity in Aeromonas hydrophila, A. sobria and A. salmonicida. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Feb;8(1):17–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Burke V., Chang B. J. Invasion of HEp-2 cells by fecal isolates of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):680–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.680-683.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Popoff M., Wadstrom T. Aeromonas hydrophila in acute diarrheal disease: detection of enterotoxin and biotyping of strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):96–100. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.96-100.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Wadström T. Aeromonas toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):339–354. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marandon J. L., Oeding P. Investigations on animal Staphylococcus aureus strains. 1. Biochemical characteristics and phage typing. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;67(1):149–156. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.67.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellergaard S. Purification and characterization of a new proteolytic enzyme produced by Aeromonas salmonicida. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;54(2):289–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb02619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel J. R., Traganza E. D., Mukherjee B. B., Griffin T. B., Prescott J. M. Proteolytic activity and general characteristics of a marine bacterium, Aeromonas proteolytica sp. N. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1227–1233. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1227-1233.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Havelaar A., Jansen W., Kozaki S., Guinée P. Production of "Asao toxin" by Aeromonas strains isolated from feces and drinking water. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1140–1142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1140-1142.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly T., Day D. F. Effects of cultural conditions on protease production by Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1132–1135. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1132-1135.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okitsu T., Asai Y., Yasuda T., Takizawa K. [Studies of Aeromonas spp. isolated from patients with sporadic diarrhea]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1985 Oct;59(10):977–983. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.59.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitarangsi C., Echeverria P., Whitmire R., Tirapat C., Formal S., Dammin G. J., Tingtalapong M. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides: prevalence among individuals with and without diarrhea in Thailand. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.666-673.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahim Z., Sanyal S. C., Aziz K. M., Huq M. I., Chowdhury A. A. Isolation of enterotoxigenic, hemolytic, and antibiotic-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila strains from infected fish in Bangladesh. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):865–867. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.865-867.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Agarwal R. K., Annapurna E. Haemagglutination properties & fimbriation in enterotoxigenic Aeromonas hydrophila strains. Indian J Med Res. 1983 Sep;78:324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Singh S. J., Sen P. C. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):195–198. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharmann W. Vorkommen von Elastase bei Pseudomonas und Aeromonas. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 May;220(1):435–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statner B., George W. L. Congo red uptake by motile Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):876–878. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.876-878.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson I. M., Robinson J. O., Burke V., Gracey M. Invasiveness of Aeromonas spp. in relation to biotype, virulence factors, and clinical features. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):48–51. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.48-51.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


