Abstract
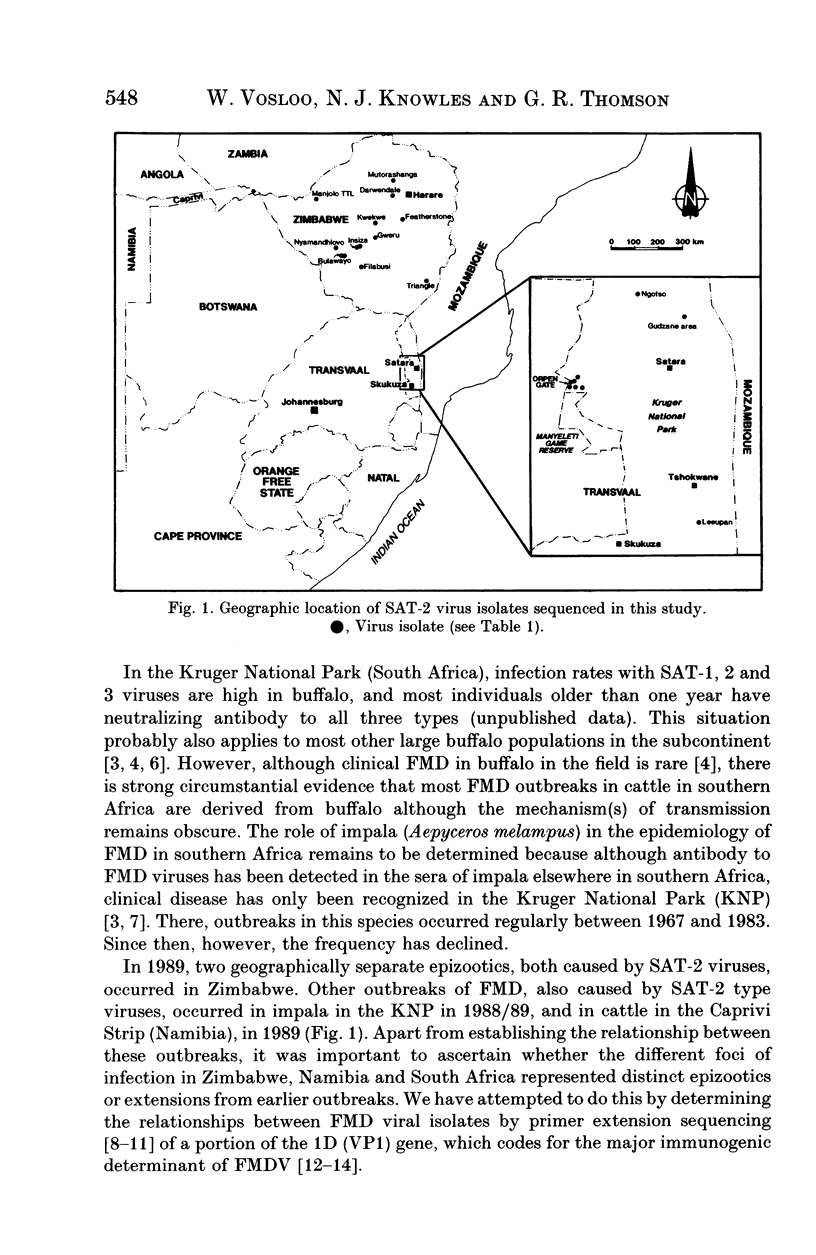
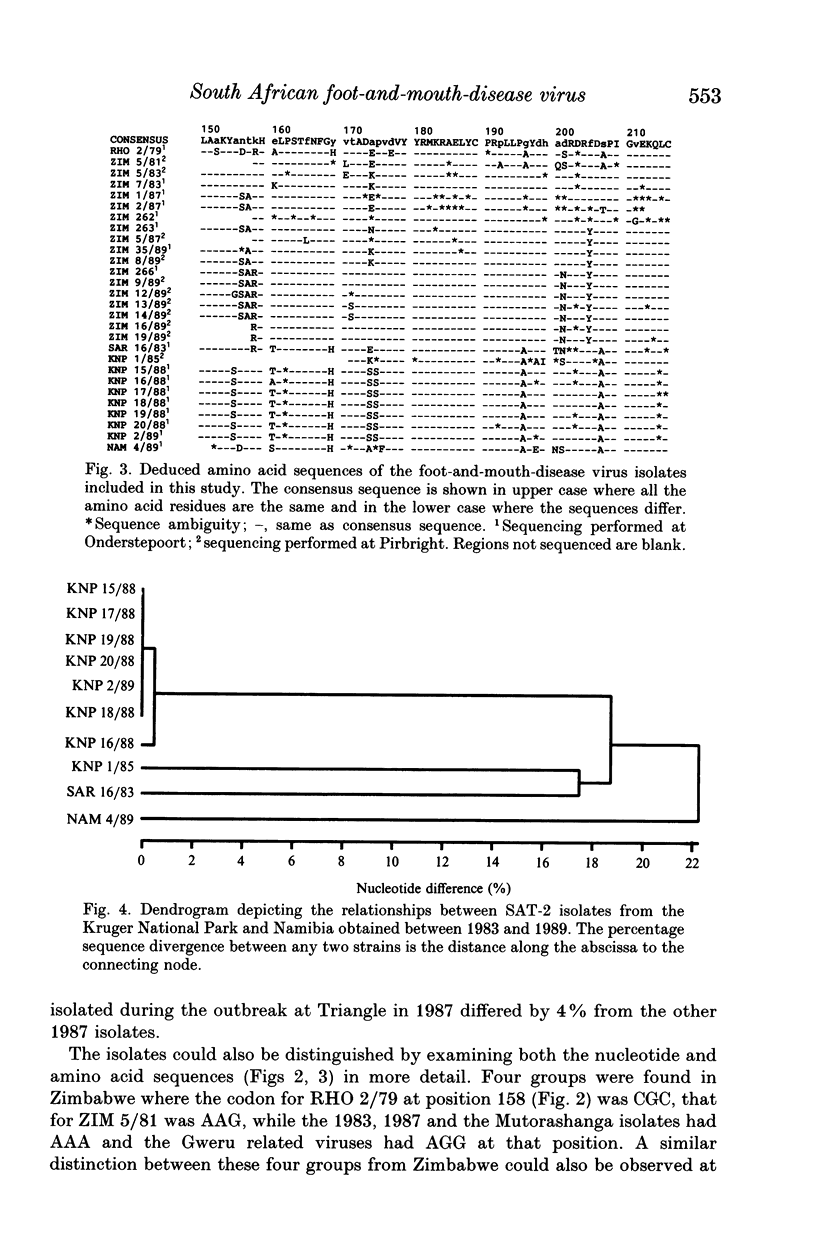
Sequencing of part of the 1D gene of foot-and-mouth disease virus was used to determine the relationships between SAT-2 viruses isolated from outbreaks which occurred in cattle in Zimbabwe and Namibia and in impala in South Africa between 1979 and 1989. The results demonstrated that the outbreaks in different countries were unrelated. Surprisingly close relationships were shown between all SAT-2 viruses isolated from cattle in Zimbabwe since 1983 but the two major epizootics which occurred in 1989 were caused by viruses which were clearly different. Conversely, two apparently unrelated outbreaks in impala in South Africa were caused by viruses which could not be distinguished.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachrach H. L., Morgan D. O., Moore D. M. Foot-and-mouth disease virus immunogenic capsid protein VPT: N-terminal sequences and immunogenic peptides obtained by CNBr and tryptic cleavages. Intervirology. 1979;12(2):65–72. doi: 10.1159/000149070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Strohmaier K. Subtyping of European foot-and-mouth disease virus strains by nucleotide sequence determination. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1621–1629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1621-1629.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo C., Dopazo J., Moya A., Gonzalez M., Martínez M. A., Saiz J. C., Sobrino F. Comparison of vaccine strains and the virus causing the 1986 foot-and-mouth disease outbreak in Spain: epizootiological analysis. Virus Res. 1990 Jan;15(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90012-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condy J. B., Herniman K. A., Hedger R. S. Foot-and-mouth disease in wildlife in Rhodesia and other African territories. A serological survey. J Comp Pathol. 1969 Jan;79(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(69)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Dávila M., Ortín J. Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of the RNA from a natural population of foot-and-mouth-disease virus. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):333–346. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterhuysen J. J., Thomson G. R., Flammand J. R., Bengis R. G. Buffalo in the northern Natal game parks show no serological evidence of infection with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1985 Jun;52(2):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainaru M. D., Thomson G. R., Bengis R. G., Esterhuysen J. J., Bruce W., Pini A. Foot-and-mouth disease and the African buffalo (Syncerus caffer). II. Virus excretion and transmission during acute infection. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1986 Jun;53(2):75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebauer F., de la Torre J. C., Gomes I., Mateu M. G., Barahona H., Tiraboschi B., Bergmann I., de Mello P. A., Domingo E. Rapid selection of genetic and antigenic variants of foot-and-mouth disease virus during persistence in cattle. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2041–2049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2041-2049.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Barteling S. J., Meloen R. H. Small peptides induce antibodies with a sequence and structural requirement for binding antigen comparable to antibodies raised against the native protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):178–182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedger R. S. Foot-and-mouth disease and the African buffalo (Syncerus caffer). J Comp Pathol. 1972 Jan;82(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(72)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Underwood B. O., McCahon D., Newman J. W., Brown F. Biochemical identification of viruses causing the 1981 outbreaks of foot and mouth disease in the UK. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):479–480. doi: 10.1038/293479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M. A., Carrillo C., Plana J., Mascarella R., Bergada J., Palma E. L., Domingo E., Sobrino F. Genetic and immunogenic variations among closely related isolates of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Gene. 1988;62(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90581-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccone M. E., Kaplan G., Giavedoni L., Domingo E., Palma E. L. VP1 of serotype C foot-and-mouth disease viruses: long-term conservation of sequences. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1469–1473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1469-1473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rico-Hesse R., Pallansch M. A., Nottay B. K., Kew O. M. Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus type 1 genotypes. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel A. R., Knowles N. J., Kitching R. P. Serological and biochemical analysis of some recent type A foot-and-mouth disease virus isolates from the Middle East. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Dec;101(3):577–590. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino F., Dávila M., Ortín J., Domingo E. Multiple genetic variants arise in the course of replication of foot-and-mouth disease virus in cell culture. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):310–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino F., Palma E. L., Beck E., Dávila M., de la Torre J. C., Negro P., Villanueva N., Ortín J., Domingo E. Fixation of mutations in the viral genome during an outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease: heterogeneity and rate variations. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmaier K., Franze R., Adam K. H. Location and characterization of the antigenic portion of the FMDV immunizing protein. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):295–306. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weddell G. N., Yansura D. G., Dowbenko D. J., Hoatlin M. E., Grubman M. J., Moore D. M., Kleid D. G. Sequence variation in the gene for the immunogenic capsid protein VP1 of foot-and-mouth disease virus type A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2618–2622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q. C., McCahon D., Crowther J. R., Belsham G. J., McCullough K. C. Neutralization of foot-and-mouth disease virus can be mediated through any of at least three separate antigenic sites. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1637–1647. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D., Kaesberg P. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA determined by reverse transcriptase and chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


