Abstract
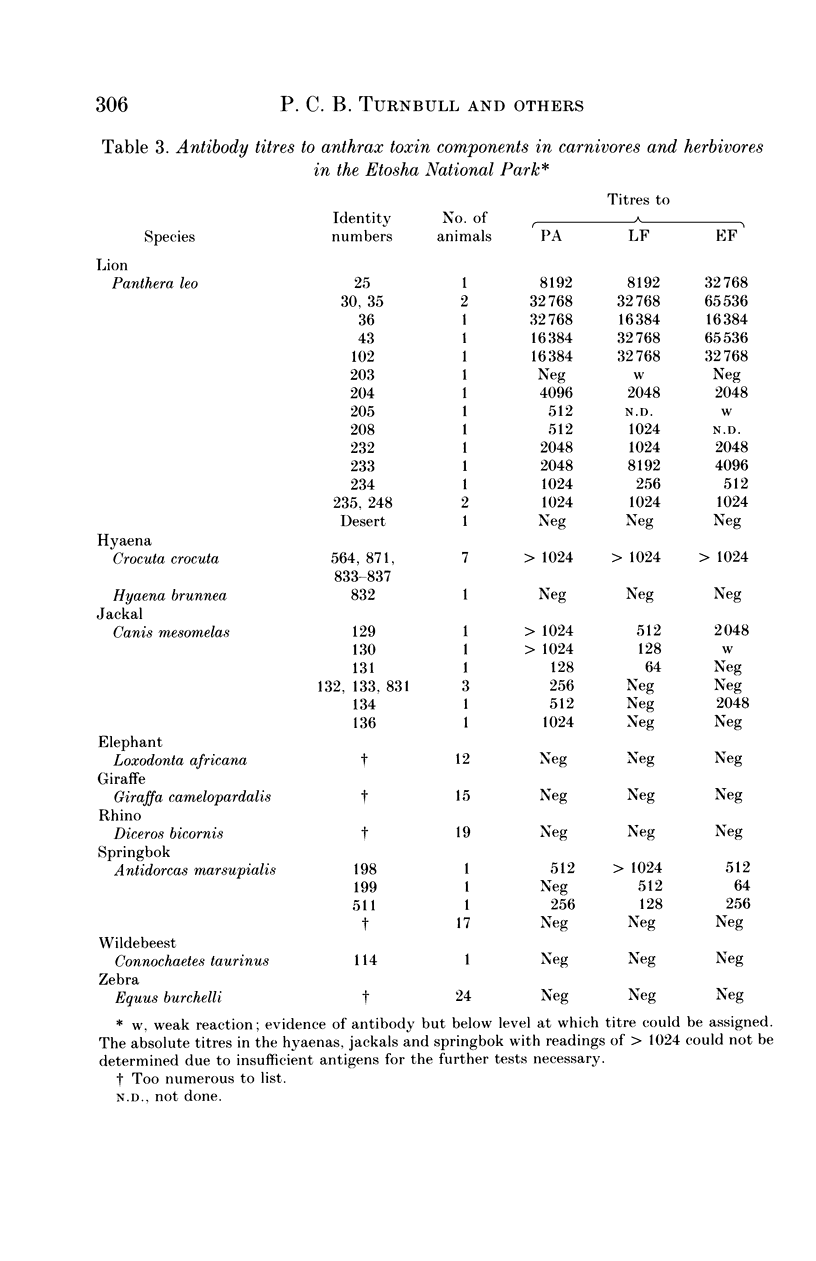
Results are presented from a number of epidemiological studies using enzyme immunoassays (EIA) based on the purified anthrax toxin antigens, protective antigen, lethal factor and oedema factor. Studies on sera from a group of 62 human anthrax patients in Turkey and from cattle in Britain following two unrelated outbreaks of anthrax show that EIA using protective antigen can be a useful diagnostic aid and will detect subclinical infections in appropriate circumstances. A serological survey on wildlife in the Etosha National Park, Namibia, where anthrax is endemic, showed that naturally acquired anthrax-specific antibodies are rare in herbivores but common in carnivores; in carnivores, titres appear to reflect the prevalence of anthrax in their ranges. Problems, as yet unresolved, were encountered in studies on sera from pigs following an outbreak of anthrax on a farm in Wales. Clinical details, including treatment, of the human and one of the bovine outbreaks are summarized and discussed in relation to the serological findings.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchanan T. M., Feeley J. C., Hayes P. S., Brachman P. S. Anthrax indirect microhemagglutination test. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1631–1636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlow H. M., Pride N. B. Serological diagnosis of anthrax. Lancet. 1969 Aug 23;2(7617):430–430. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edginton A. B. An outbreak of anthrax in pigs: a practitioner's account. Vet Rec. 1990 Sep 29;127(13):321–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish D. C., Lincoln R. E. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of anthrax toxin. Fed Proc. 1967 Sep;26(5):1534–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish D. C., Mahlandt B. G., Dobbs J. P., Lincoln R. E. Purification and properties of in vitro-produced anthrax toxin components. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):907–918. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.907-918.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. H., Ezzell J. W., Abshire T. G., Kidd S., Kaufmann A. F. Evaluation of serologic tests for diagnosis of anthrax after an outbreak of cutaneous anthrax in Paraguay. J Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;160(4):706–710. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.4.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B. E., Ezzell J. W., Jr, Jemski J., Hedlund K. W., Ristroph J. D., Leppla S. H. Immunization studies with attenuated strains of Bacillus anthracis. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):454–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.454-458.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B. E., Welkos S. L., Knudson G. B., Little S. F. Immunization against anthrax with aromatic compound-dependent (Aro-) mutants of Bacillus anthracis and with recombinant strains of Bacillus subtilis that produce anthrax protective antigen. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):303–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.303-308.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B. E., Welkos S. L. Recent advances in the development of an improved, human anthrax vaccine. Eur J Epidemiol. 1988 Mar;4(1):12–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00152686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Winegar A. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent and indirect hemagglutination assays for determining anthrax antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):357–361. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.357-361.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. P., Martin K. L. Investigation of spore surface antigens in the genus Bacillus by the use of polyclonal antibodies in immunofluorescence tests. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;64(1):47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb02428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn C. P., Shone C. C., Turnbull P. C., Melling J. Purification of anthrax-toxin components by high-performance anion-exchange, gel-filtration and hydrophobic-interaction chromatography. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):753–758. doi: 10.1042/bj2520753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY J. G., Jr, KADULL P. J. AGAR-GEL PRECIPITIN TECHNIQUE IN ANTHRAX ANTIBODY DETERMINATIONS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:349–354. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.349-354.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirisanthana T., Nelson K. E., Ezzell J. W., Abshire T. G. Serological studies of patients with cutaneous and oral-oropharyngeal anthrax from northern Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Dec;39(6):575–581. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORNE C. B., BELTON F. C. An agar-diffusion method for titrating Bacillus anthracis immunizing antigen and its application to a study of antigen production. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Oct;17(2):505–516. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-2-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Bell R. H., Saigawa K., Munyenyembe F. E., Mulenga C. K., Makala L. H. Anthrax in wildlife in the Luangwa Valley, Zambia. Vet Rec. 1991 Apr 27;128(17):399–403. doi: 10.1136/vr.128.17.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Broster M. G., Carman J. A., Manchee R. J., Melling J. Development of antibodies to protective antigen and lethal factor components of anthrax toxin in humans and guinea pigs and their relevance to protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):356–363. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.356-363.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Leppla S. H., Broster M. G., Quinn C. P., Melling J. Antibodies to anthrax toxin in humans and guinea pigs and their relevance to protective immunity. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1988;177(5):293–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00189414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie M. H., Ward M. K. Characterization of anthrax toxin. Fed Proc. 1967 Sep;26(5):1527–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


