Abstract
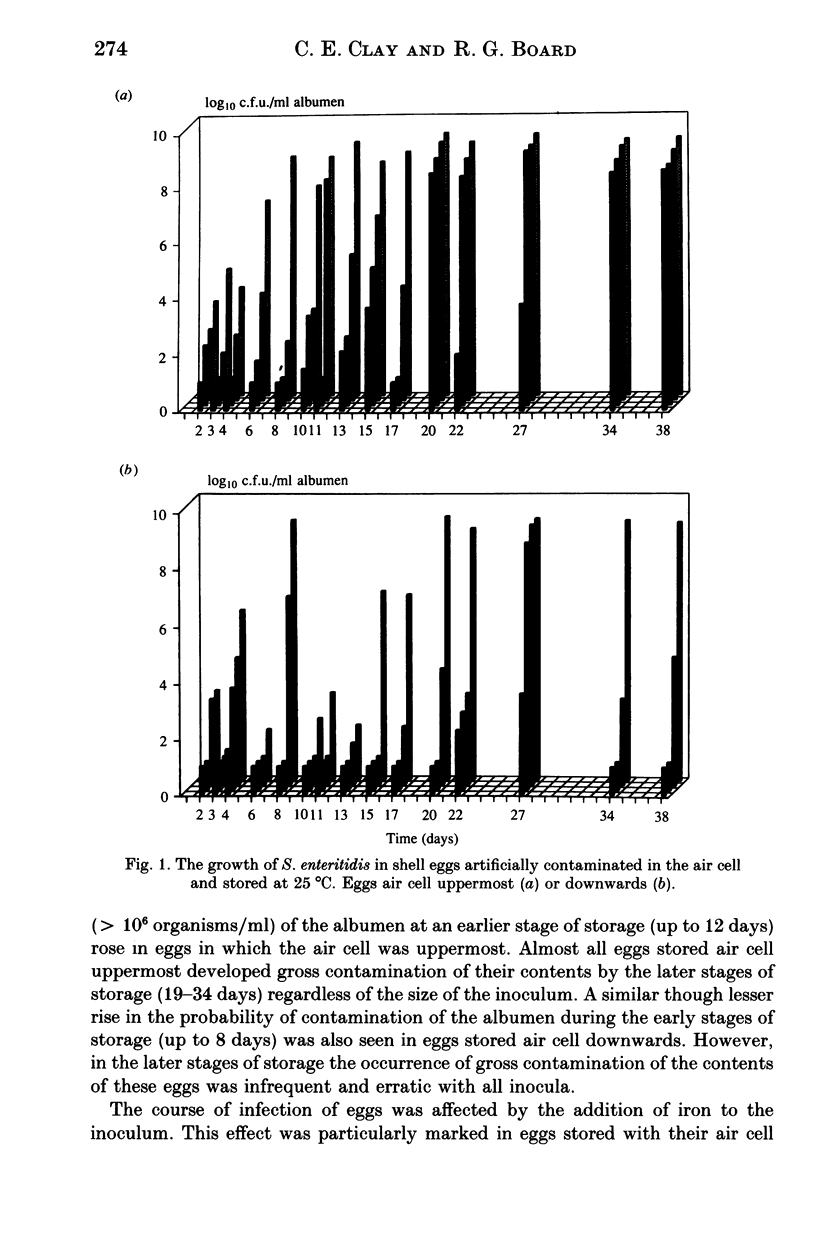
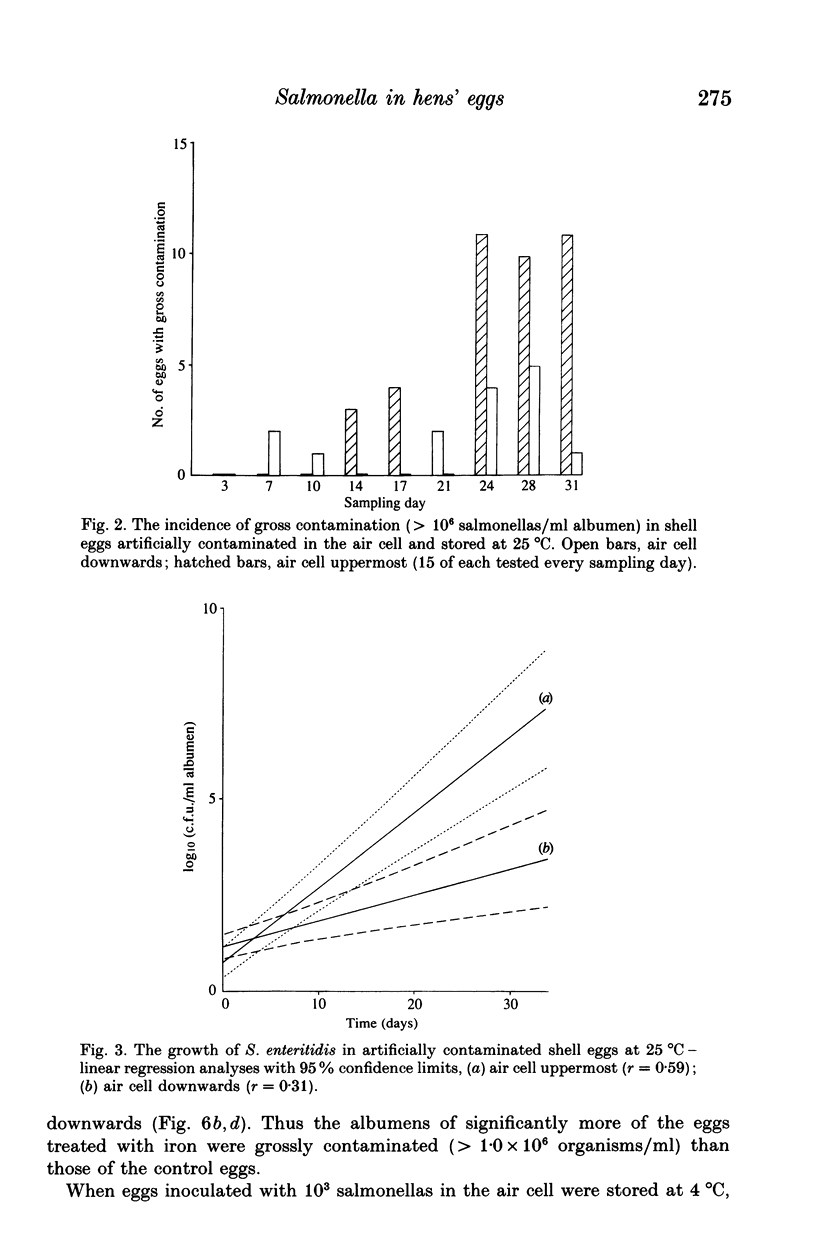
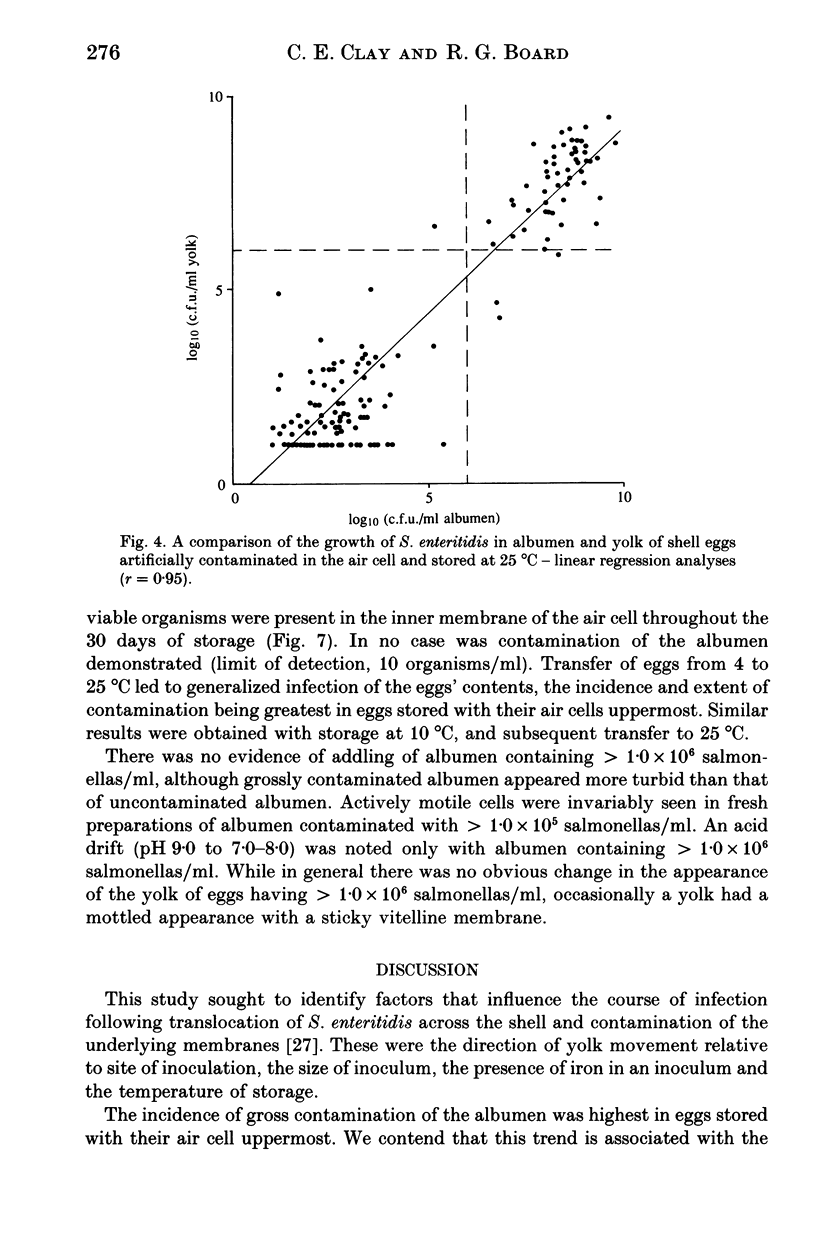
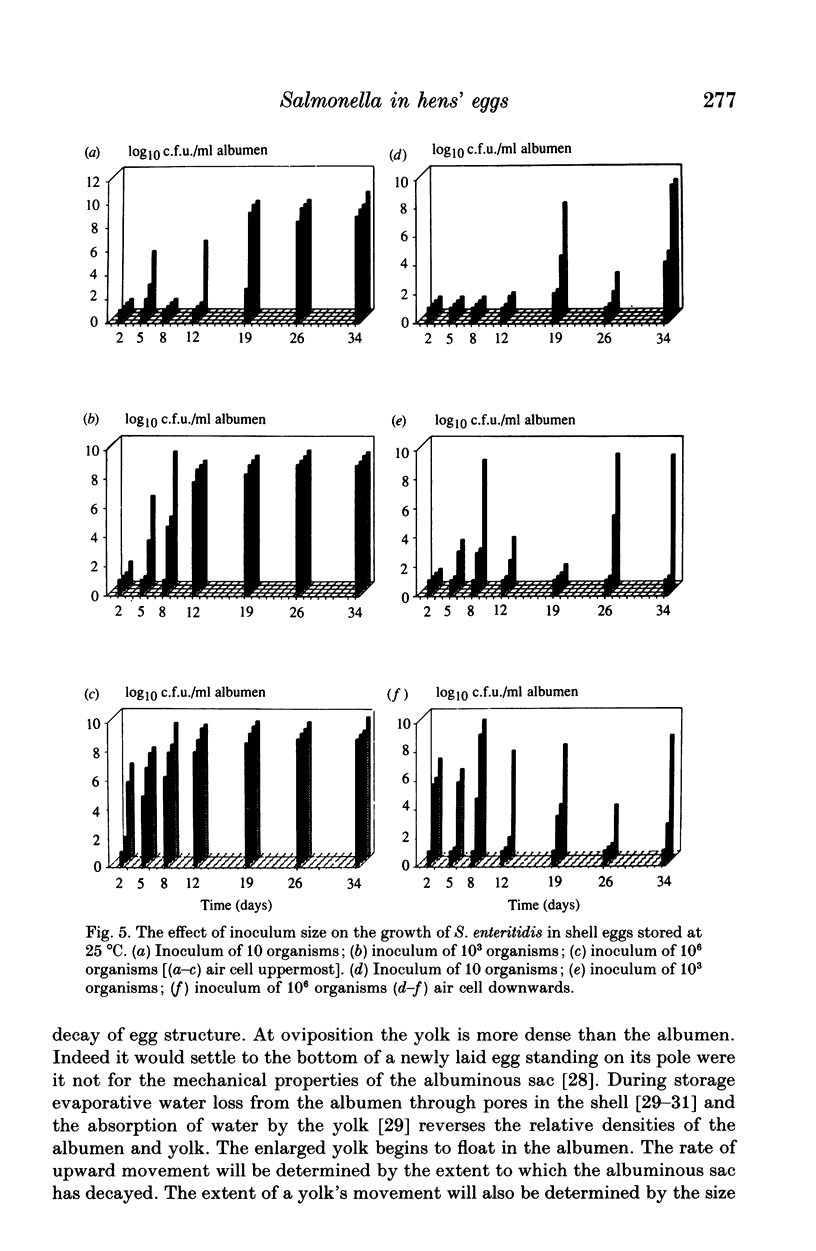
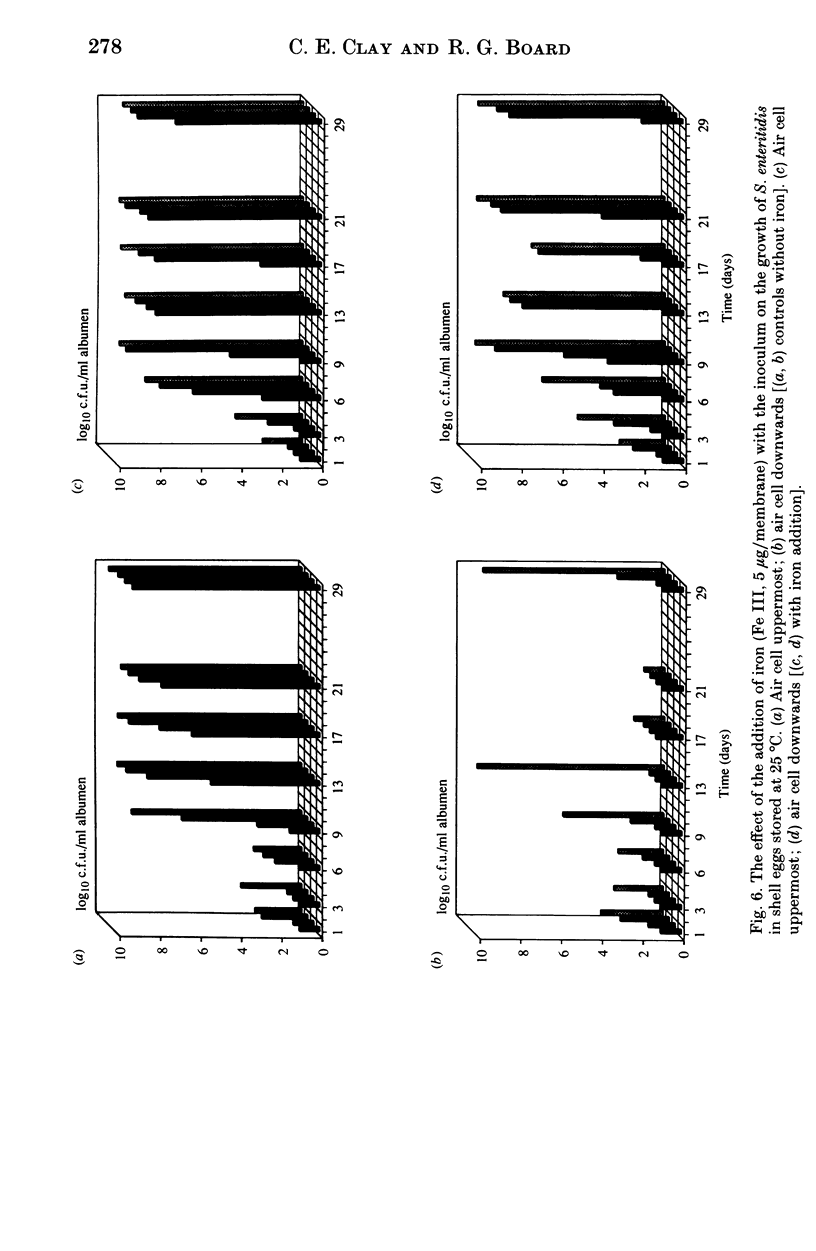
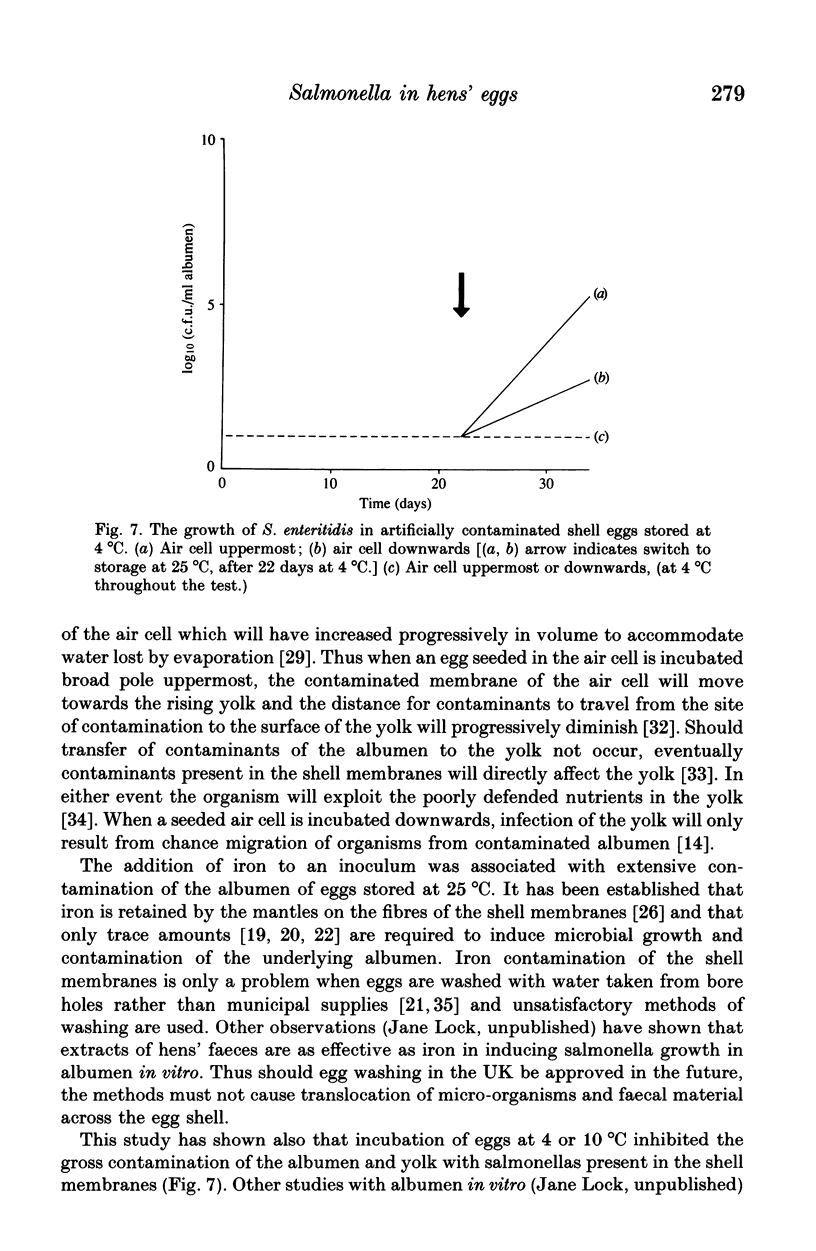
The effect of some factors on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 in artificially contaminated shell eggs was investigated. Salmonella enteritidis was found to be resistant to the antimicrobial properties of the albumen. Growth occurred on storage at 25 degrees C but not at 4 or 10 degrees C. The rate and extent of infection was influenced by the size of inoculum, the site of contamination relative to yolk movement, and the presence of iron in the inoculum.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOARD R. G., AYRES J. C. INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON BACTERIAL INFECTION OF THE HEN'S EGG. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:358–364. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.358-364.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKS J., HALE H. P. The mechanical properties of the thick white of the hen's egg. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Mar;32(1):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90574-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Board P. A., Board R. G. A diagnostic dey for identifying organisms recovered from rotten eggs. Br Poult Sci. 1968 Jan;9(1):111–120. doi: 10.1080/00071666808415699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Board P. A., Henden L. P., Board R. G. The influence of iron on the course of bacterial infection of the hen's egg. Br Poult Sci. 1968 Apr;9(2):211–215. doi: 10.1080/00071666808415710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Board R. G. Review article: the course of microbial infection of the hen's egg. J Appl Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;29(2):319–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1966.tb03482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Board R. G. The properties and classification of the predominant bacteria in rotten eggs. J Appl Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;28(3):437–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1965.tb02175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave A. C., Gallagher J. Transmission of Salmonella enteritidis in poultry. Vet Rec. 1989 May 27;124(21):571–571. doi: 10.1136/vr.124.21.571-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle E. F., Palmer S. R., Ribeiro C. D., Jones H. I., Howard A. J., Ward L., Rowe B. Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 infection: association with hen's eggs. Lancet. 1988 Dec 3;2(8623):1295–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92902-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton M. Salmonella infection in chicks following the consumption of artificially contaminated feed. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Apr;100(2):247–256. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper S. A., Mawer S. Salmonella enteritidis in a commercial layer flock. Vet Rec. 1988 Sep 24;123(13):351–351. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.13.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. J., Baskerville A., Mawer S., Rowe B., Hopper S. Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 from the contents of intact eggs: a study involving naturally infected hens. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Dec;103(3):415–423. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister S. A. Salmonella enteritidis infection in broilers and broiler breeders. Vet Rec. 1988 Sep 24;123(13):350–350. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.13.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. D. Salmonella enteritidis infection in broiler chickens. Vet Rec. 1988 Feb 27;122(9):214–214. doi: 10.1136/vr.122.9.214-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perales I., Audicana A. Salmonella enteritidis and eggs. Lancet. 1988 Nov 12;2(8620):1133–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90542-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade A. L., Caroline L. RAW HEN EGG WHITE AND THE ROLE OF IRON IN GROWTH INHIBITION OF SHIGELLA DYSENTERIAE, STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, ESCHERICHIA COLI AND SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Science. 1944 Jul 7;100(2584):14–15. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2584.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Louis M. E., Morse D. L., Potter M. E., DeMelfi T. M., Guzewich J. J., Tauxe R. V., Blake P. A. The emergence of grade A eggs as a major source of Salmonella enteritidis infections. New implications for the control of salmonellosis. JAMA. 1988 Apr 8;259(14):2103–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


