Abstract
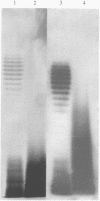
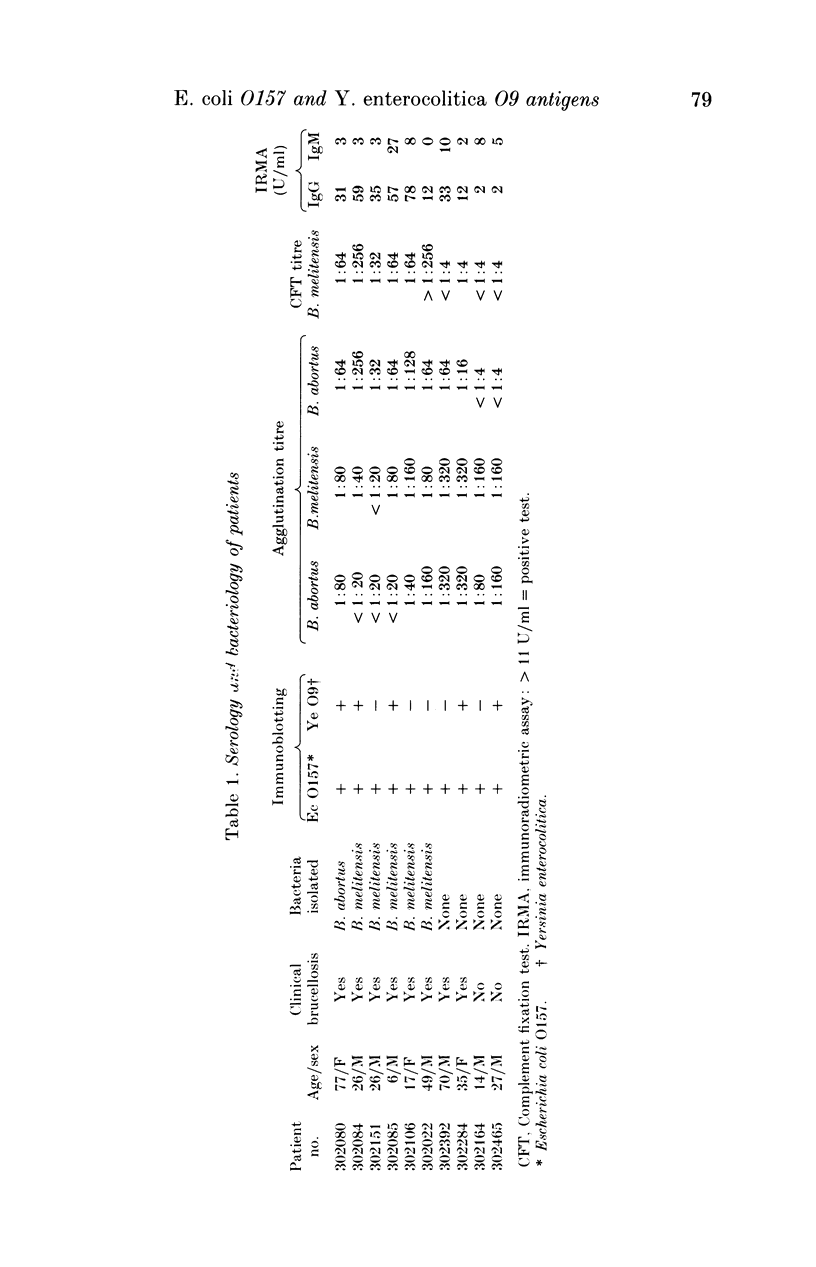
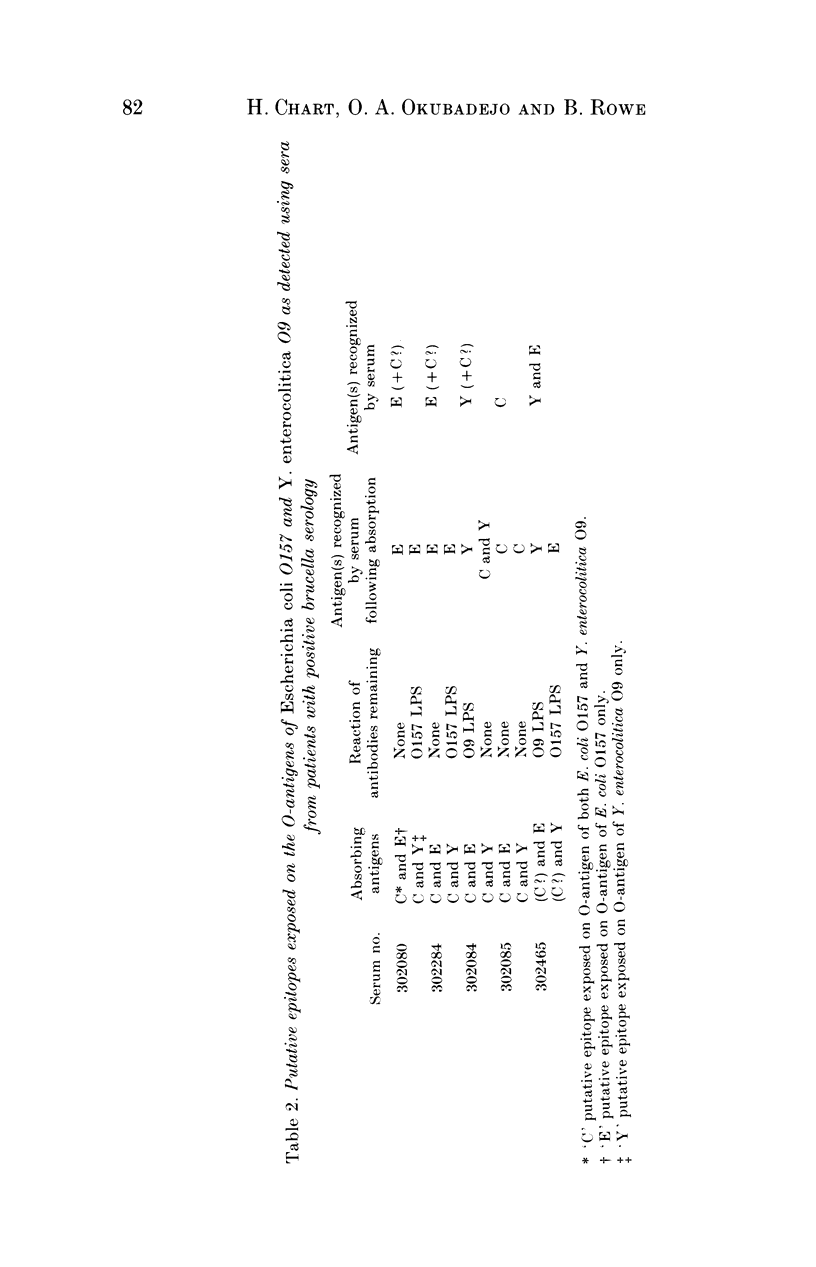
Sera from ten patients with positive brucella serology were used to investigate antibody cross-reactions between the O-antigens of Escherichia coli O157 and Yersinia enterocolitica O9. SDS-PAGE profiles of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), purified from strains of E. coli O157 and Y. enterocolitica O9, were reacted with sera by immunoblotting. All ten sera contained antibodies which bound to the LPS of E. coli O157, and five of these sera also contained antibodies which bound to the LPS of Y. enterocolitica O9. Absorption studies using these five cross-reacting sera indicated the existence of at least three epitopes exposed on the O-antigens of E. coli O157 and Y. enterocolitica O9. One antigen binding site appeared to be exposed on the LPS of both organisms, while one epitope was exposed on the LPS of E. coli O157 only, and another on the LPS of Y. enterocolitica O9 only.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bundle D. R., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Caroff M., Perry M. B. The lipopolysaccharides of Brucella abortus and B. melitensis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B. Structure of the O-chain of the phenol-phase soluble cellular lipopolysaccharide of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 15;139(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Rowe B. Purification of lipopolysaccharide from strains of Yersinia enterocolitica belonging to serogroups 03 and 09. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):341–345. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90577-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. Serum antibodies to Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 in patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):285–290. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.285-290.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Rowe B. Antibodies to Escherichia coli O157 in patients with haemorrhagic colitis and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Sep;42(9):973–976. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.9.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Smith H. R., Scotland S. M., Rowe B., Milford D. V., Taylor C. M. Serological identification of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet. 1991 Jan 19;337(8734):138–140. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90801-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbell M. J. The serological relationship between Brucella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica serotype IX and Salmonella serotypes of Kauffmann-White group N. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):151–171. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Stevenson P., Thorpe R., Chart H. Naturally occurring antibodies in human sera that react with the iron-regulated outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):808–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.808-813.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Walters M. D., Barratt T. M. Hemolytic uremic syndrome. Adv Pediatr Infect Dis. 1989;4:51–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Haeggman S., Karlson K., Carlsson H. E., Mair N. S. Enzyme immunoassay of the antibody response to Brucella and Yersinia enterocolitica 09 infections in humans. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):295–307. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notenboom R. H., Borczyk A., Karmali M. A., Duncan L. M. Clinical relevance of a serological cross-reaction between Escherichia coli O157 and Brucella abortus. Lancet. 1987 Sep 26;2(8561):745–745. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., MacLean L., Griffith D. W. Structure of the O-chain polysaccharide of the phenol-phase soluble lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli 0:157:H7. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;64(1):21–28. doi: 10.1139/o86-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandulache R., Marx A. Immunochemical studies on a Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 lipopolysaccharide cross-reacting with Brucella abortus and Vibrio cholerae extracts. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Oct;129 B(3):425–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart F. A., Corbel M. J. Identification of a serological cross-reaction between Brucella abortus and Escherichia coli 0:157. Vet Rec. 1982 Feb 27;110(9):202–203. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.9.202-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]