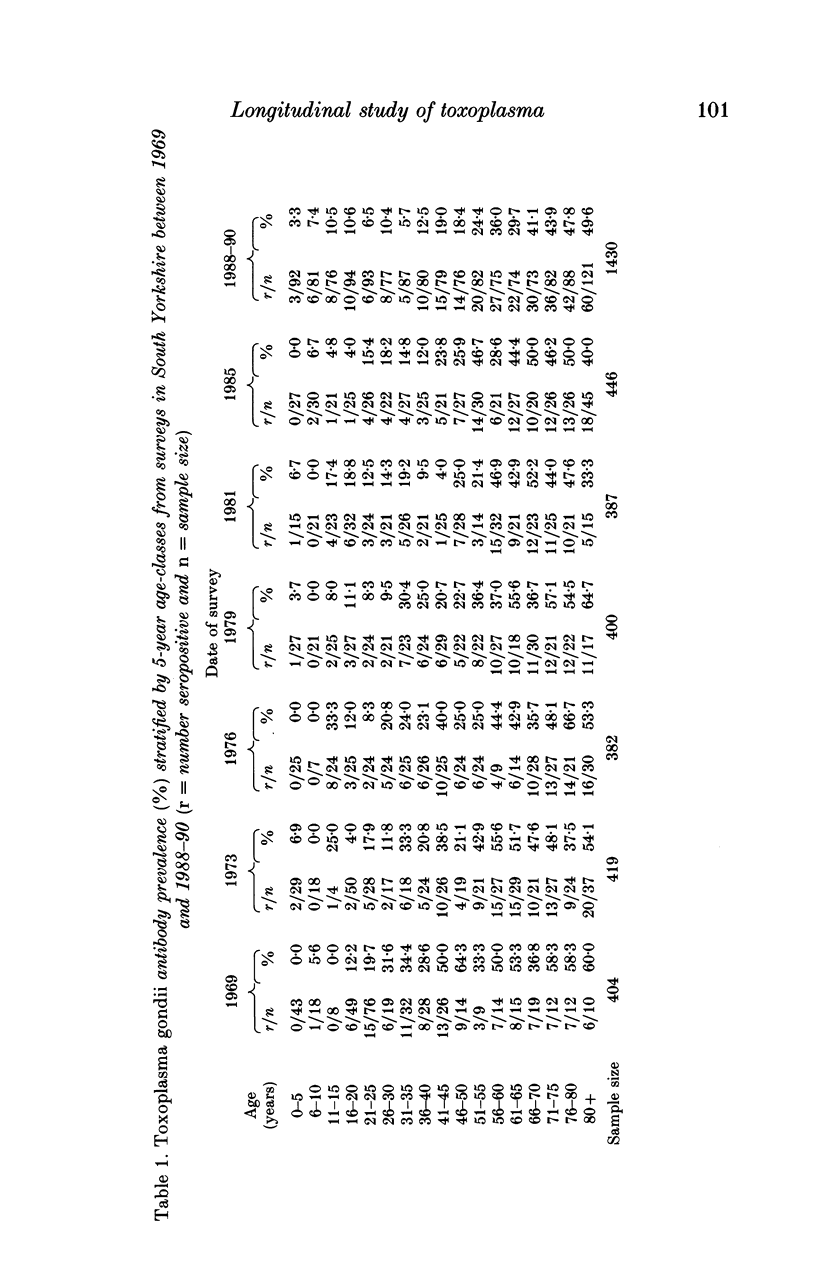
Abstract
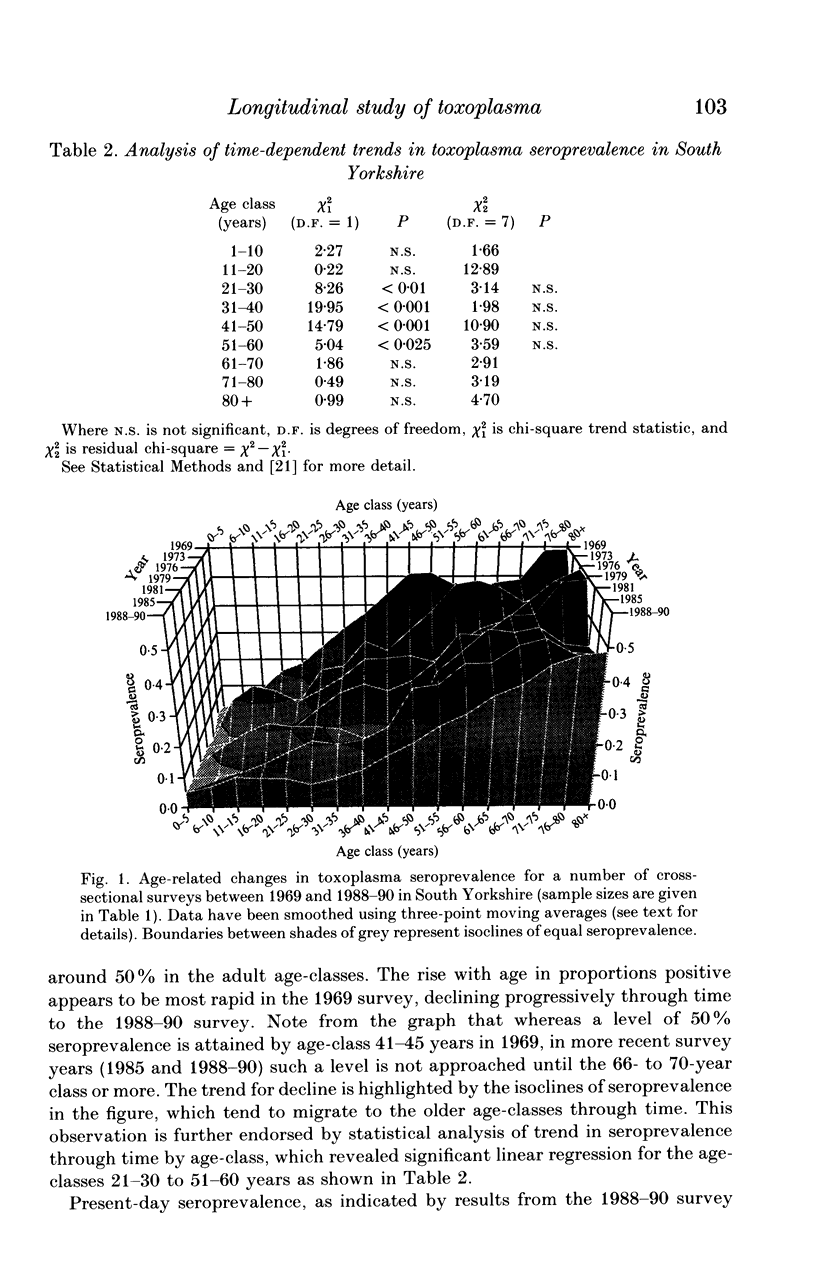
Serum samples collected from individuals of a wide range of ages in South Yorkshire between 1969 and 1990 provided the basis for a longitudinal seroprevalence survey of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies. Sera numbering 3868 were screened for T. gondii specific antibodies using a commercial latex agglutination test. The resultant temporal series of serological profiles revealed a rise, with age, in seroprevalence, the rate of which showed a decrease through time. A plateau of around 40-50% prevalence was attained by the 41- to 45-year age-class in 1969 which was not approached until the 66- to 70-year class in the 1988-90 data set. This trend for decline in seroprevalence was confirmed by statistical analysis for the age range 21-60 years. These results may be indicative of a decrease in the rate of toxoplasma exposure in this study community over the 20-year period. The survey of 1988-90 provides a base-line profile of present-day seroprevalence in which 11% of individuals in the age range 16-45 years (roughly corresponding to the childbearing age-range) show evidence of past infection. The representative nature of the serum collection and public-health implications of these results are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ades A. E., Peckham C. S., Dale G. E., Best J. M., Jeansson S. Prevalence of antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in pregnant women, and estimated rates of infection. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1989 Mar;43(1):53–60. doi: 10.1136/jech.43.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlfors K., Börjeson M., Huldt G., Forsberg E. Incidence of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women in the city of Malmö, Sweden. Scand J Infect Dis. 1989;21(3):315–321. doi: 10.3109/00365548909035702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balfour A. H., Fleck D. G., Hughes H. P., Sharp D. Comparative study of three tests (dye test, indirect haemagglutination test, latex agglutination test) for the detection of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in human sera. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Feb;35(2):228–232. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.2.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck D. G. Toxoplasmosis. Public Health. 1969 Mar;83(3):131–135. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(69)80103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuith L. C., Reibnegger G., Hönlinger M., Wachter H. Screening for toxoplasmosis in pregnancy. Lancet. 1988 Nov 19;2(8621):1196–1196. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90264-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall S. M. Congenital toxoplasmosis in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland: some epidemiological problems. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Aug 13;287(6390):453–455. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6390.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliman R. E. Serological study of the prevalence of toxoplasmosis in asymptomatic patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Oct;105(2):415–418. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J., Duffy K., New L., Holliman R. E., Chessum B. S., Fleck D. G. Direct agglutination test and other assays for measuring antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Pathol. 1989 May;42(5):536–541. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.5.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joss A. W., Chatterton J. M., Ho-Yen D. O. Congenital toxoplasmosis: to screen or not to screen? Public Health. 1990 Jan;104(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(05)80340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joss A. W., Skinner L. J., Chatterton J. M., Chisholm S. M., Williams H. D., Ho-Yen D. O. Simultaneous serological screening for congenital cytomegalovirus and toxoplasma infection. Public Health. 1988 Sep;102(5):409–417. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(88)80078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joss A. W., Skinner L. J., Chatterton J. M., Cubie H. A., Pryde J. F., Campbell J. D. Toxoplasmosis: effectiveness of enzyme immunoassay screening. Med Lab Sci. 1989 Apr;46(2):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joynson D. H., Payne R. Screening for toxoplasma in pregnancy. Lancet. 1988 Oct 1;2(8614):795–796. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92443-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppe J. G., Loewer-Sieger D. H., de Roever-Bonnet H. Results of 20-year follow-up of congenital toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):254–256. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90785-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Remington J. S. AIDS commentary. Toxoplasmic encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papoz L., Simondon F., Saurin W., Sarmini H. A simple model relevant to toxoplasmosis applied to epidemiologic results in France. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Jan;123(1):154–161. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenzle D., Dietz K., Frösner G. G. Antibody against hepatitis A in seven European countries. II. Statistical analysis of cross-sectional surveys. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Jul;110(1):70–76. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. A., Scott J. M., Macfarlane D. E., Williamson J. M., Elias-Jones T. F., Williams H. Congenital toxoplasmosis: a prospective survey in the West of Scotland. J Infect. 1981 Sep;3(3):219–229. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)90773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreghitt T. G., Gray J. J., Balfour A. H. Problems with serological diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infections in heart transplant recipients. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Oct;39(10):1135–1139. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.10.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


