Abstract
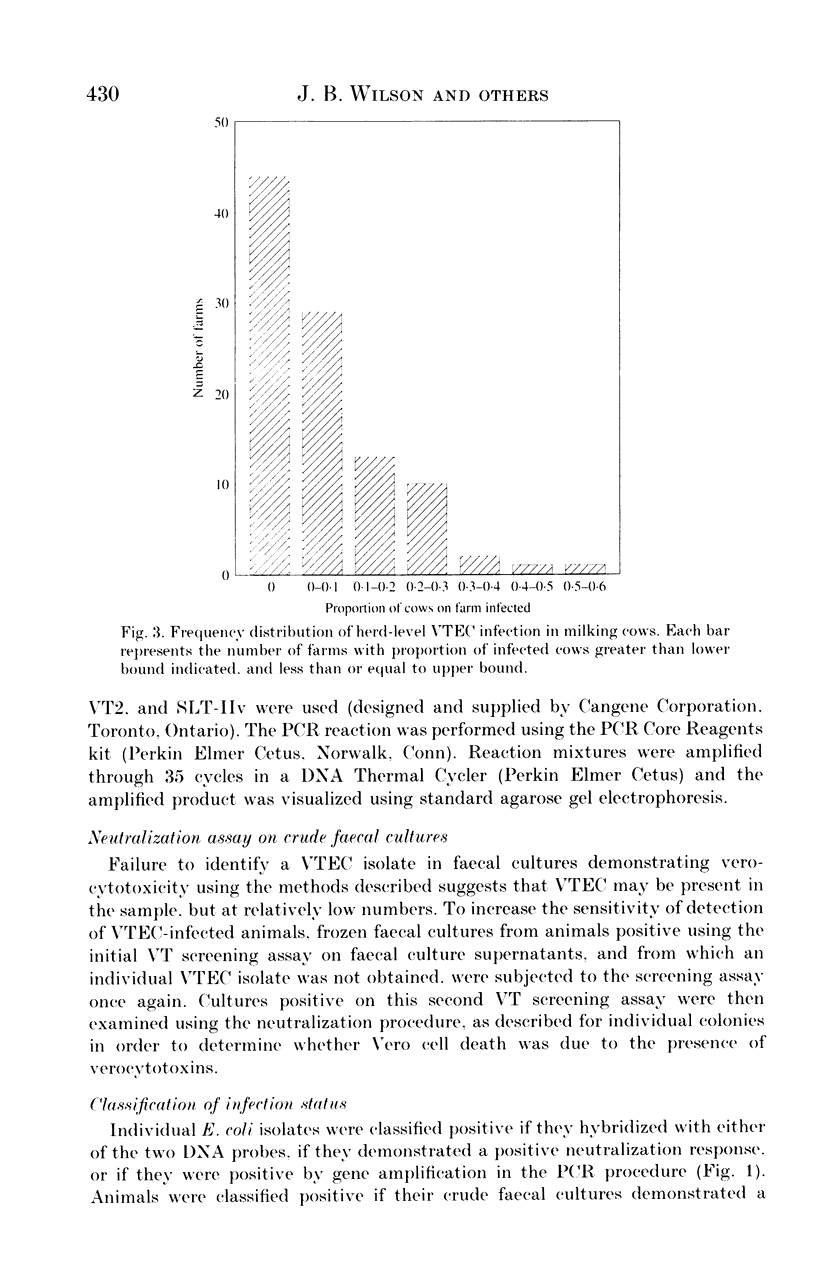
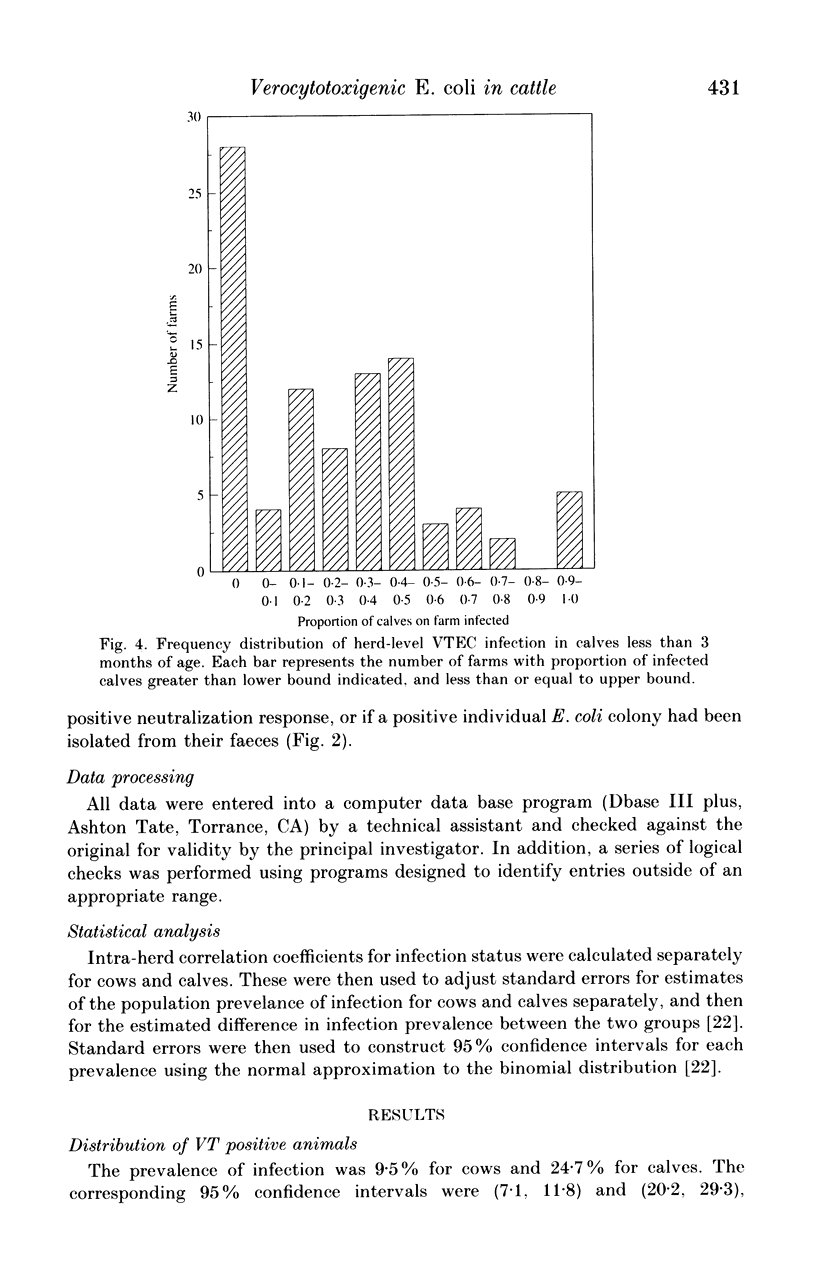
Faecal swabs obtained from a random sample of 1131 cows and 659 calves on 100 southern Ontario dairy farms were examined for verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli (VTEC) using a Vero cell assay. Five isolates from each positive culture were tested similarly. Positive colonies were examined with DNA probes for Shiga-like toxin I (SLT-I) and SLT-II sequences. Probe-negative colonies were tested for neutralization of verocytotoxicity using anti-SLT-I and anti-SLT-IIv antisera. Colonies showing no neutralization response were examined in a polymerase chain reaction procedure. Colonies positive by any test were confirmed to be E. coli biochemically, serotyped, biotyped and tested for antimicrobial resistance. Faecal culture supernatants which were positive in the Vero cell assay, but culture negative, were examined using the neutralization assay. Animals were classified positive by faecal culture supernatant or by positive VTEC isolate. The prevalence rates of VTEC infection in cows and calves were estimated to be 9.5 and 24.7%, respectively. The proportion of animals infected on each farm ranged from 0 to 60% for cows and 0 to 100% for calves. Of 206 VTEC isolates identified, few were of serotypes which have been isolated from humans and none were E. coli O 157.H7.
Full text
PDF


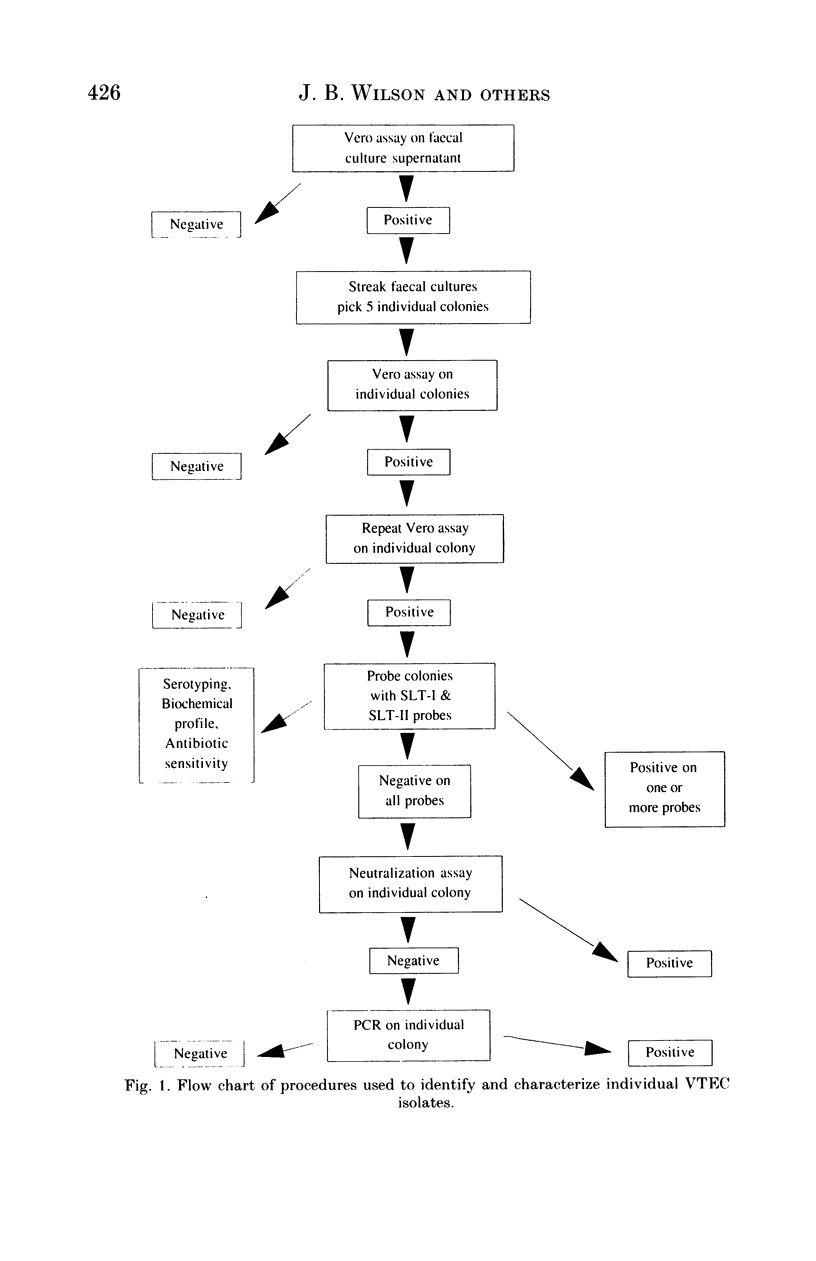
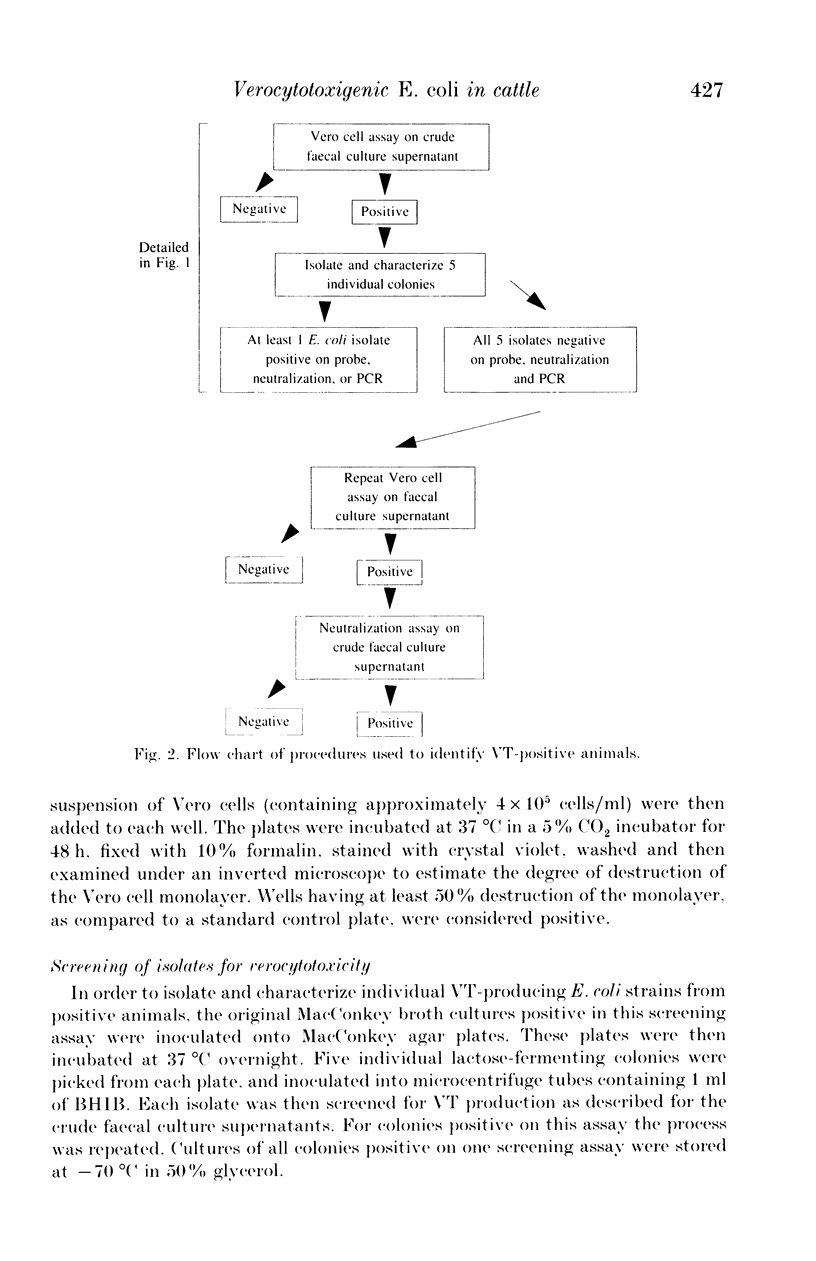








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borczyk A. A., Karmali M. A., Lior H., Duncan L. M. Bovine reservoir for verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet. 1987 Jan 10;1(8524):98–98. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91928-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. C., McEwen S. A., Gannon V. P., Lior H., Gyles C. L. Isolation of verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli from milk filters in south-western Ontario. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Apr;102(2):253–260. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes F. P., Green J. H., Greene K., Strockbine N., Wells J. G., Wachsmuth I. K. Development and evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detection of shiga-like toxin I and shiga-like toxin II. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1292–1297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1292-1297.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from retail fresh meats and poultry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2394–2396. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2394-2396.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod D. L., Gyles C. L. Purification and characterization of an Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin II variant. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1232–1239. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1232-1239.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek A. H., Martin S. W., Stone J. B., McMillan I., Britney J. B., Grieve D. G. The relationship among current management systems, production, disease and drug usage on Ontario dairy farms. Can J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;50(1):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read S. C., Gyles C. L., Clarke R. C., Lior H., McEwen S. Prevalence of verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli in ground beef, pork, and chicken in southwestern Ontario. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Aug;105(1):11–20. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthienkul O., Brown J. E., Seriwatana J., Tienthongdee S., Sastravaha S., Echeverria P. Shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in retail meats and cattle in Thailand. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1135–1139. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1135-1139.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Shipman L. D., Greene K. D., Sowers E. G., Green J. H., Cameron D. N., Downes F. P., Martin M. L., Griffin P. M., Ostroff S. M. Isolation of Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 and other Shiga-like-toxin-producing E. coli from dairy cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):985–989. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.985-989.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


