Abstract
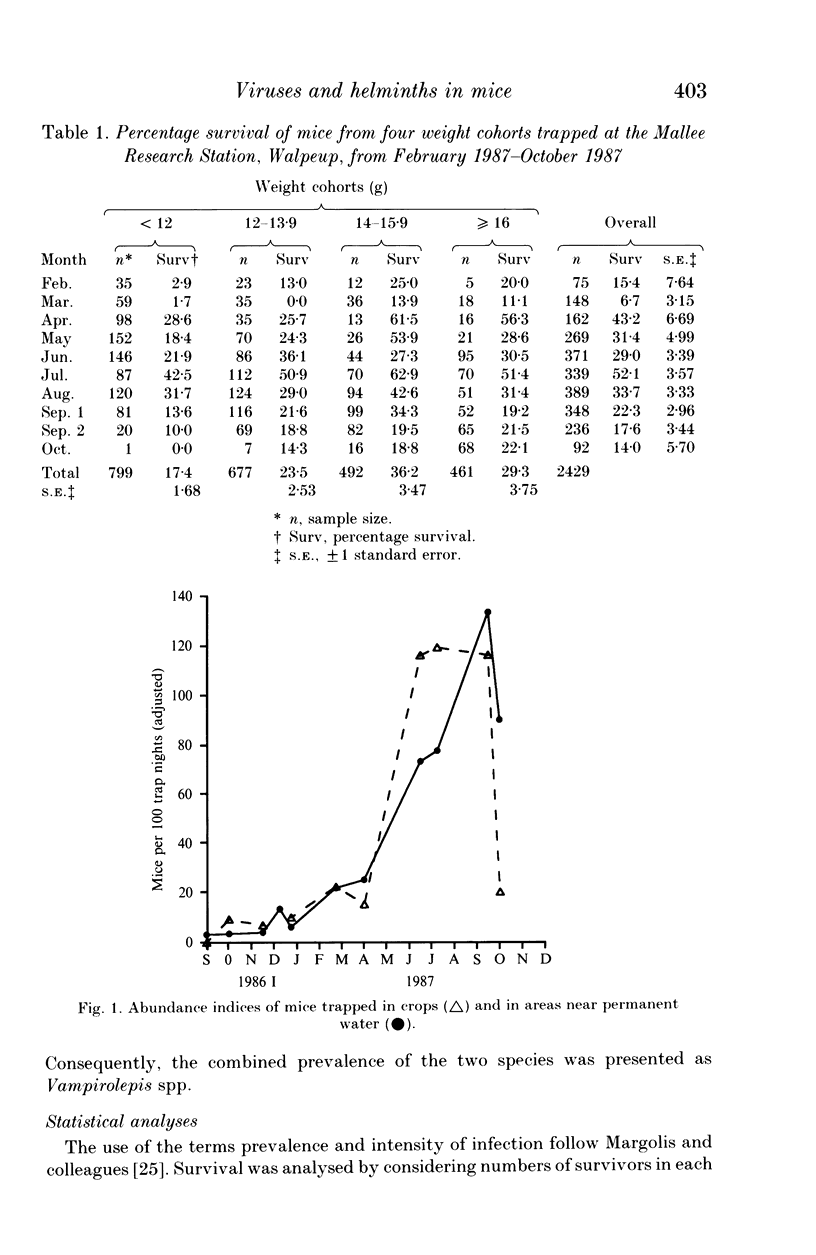
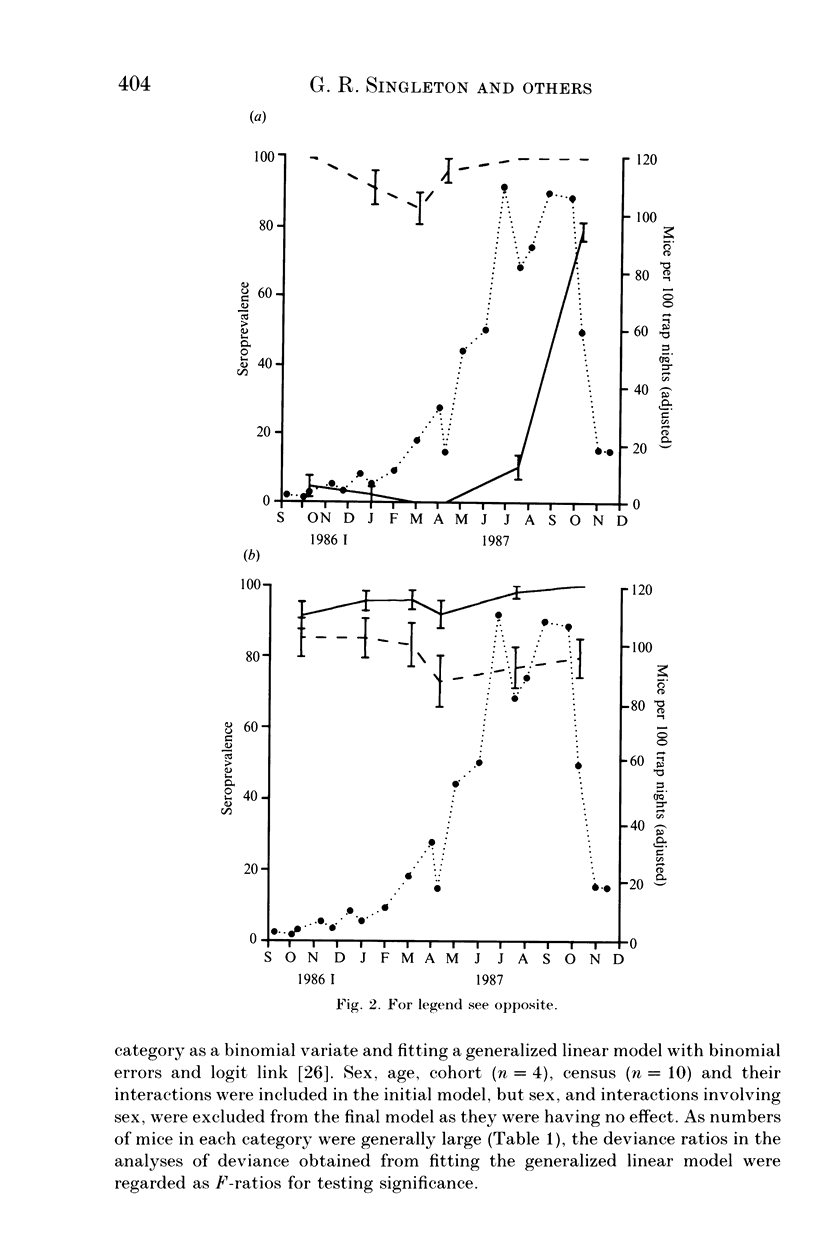
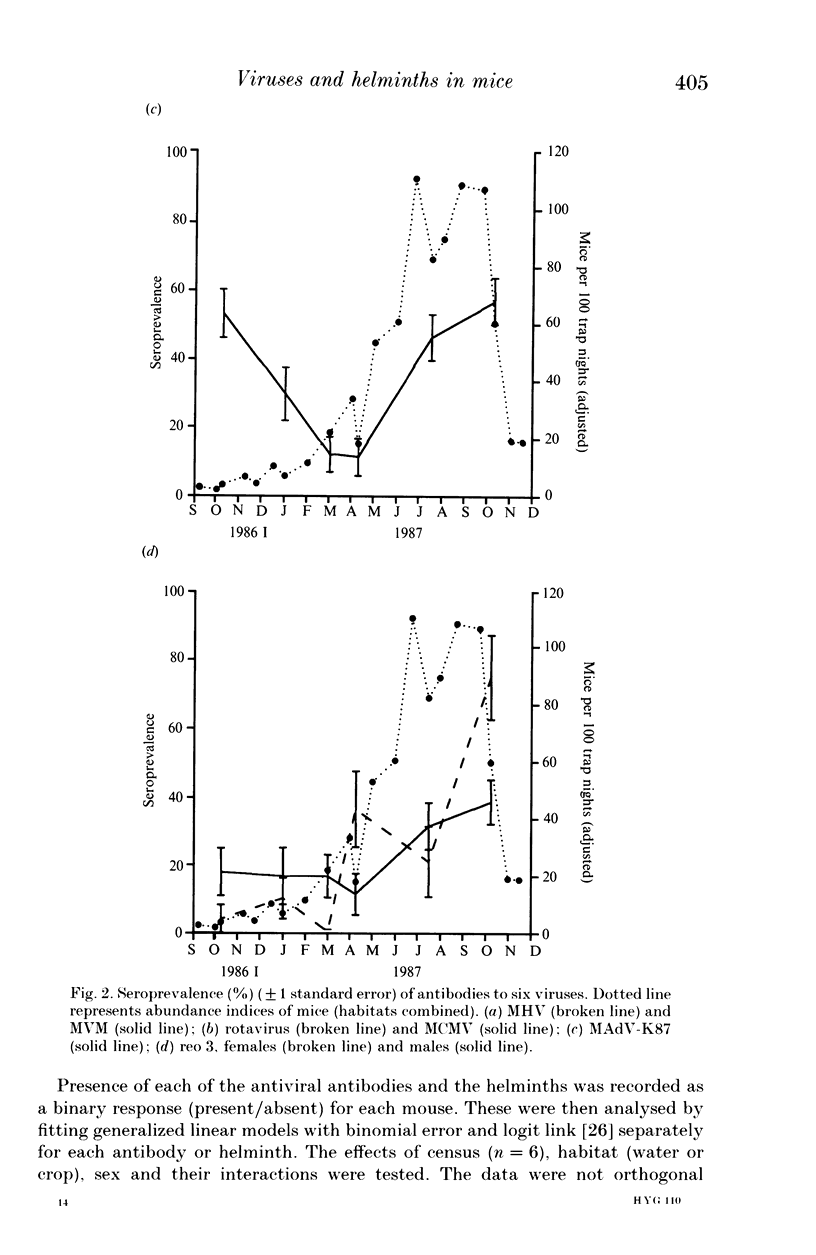
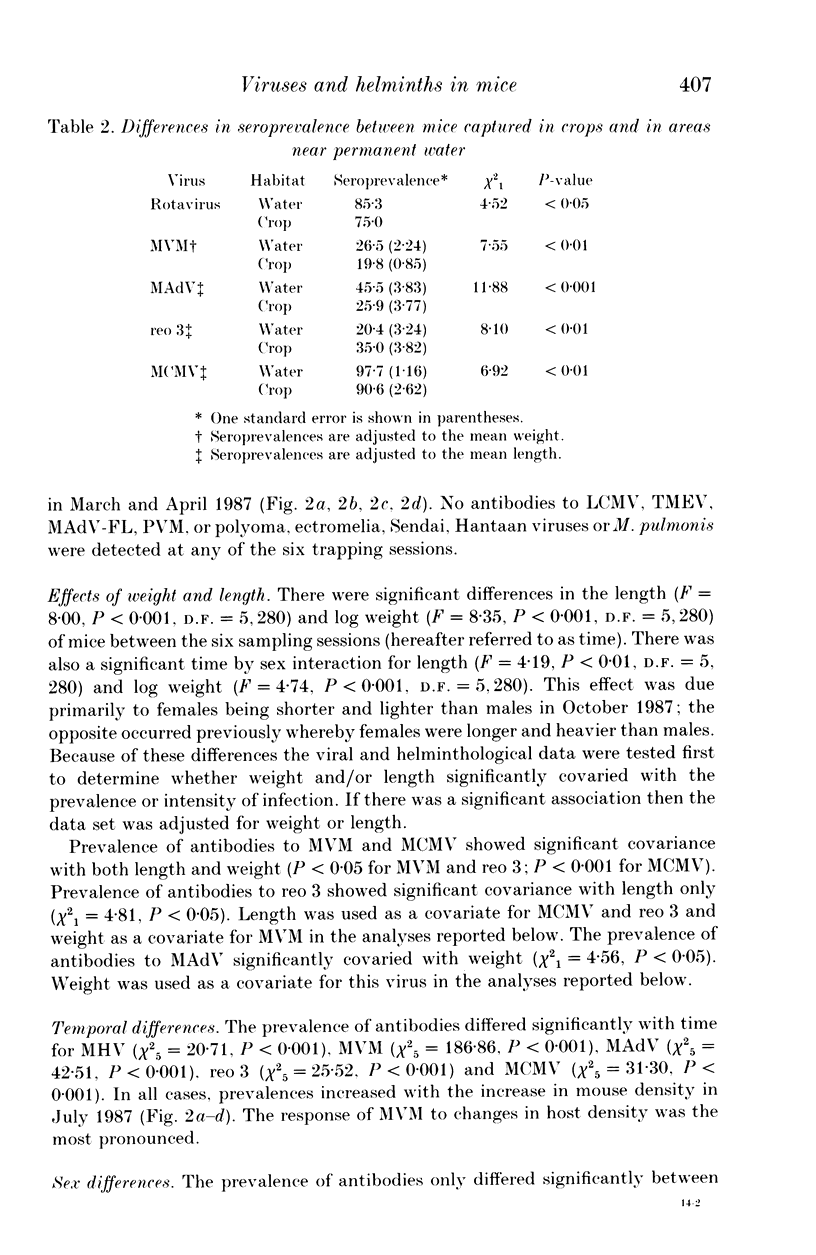
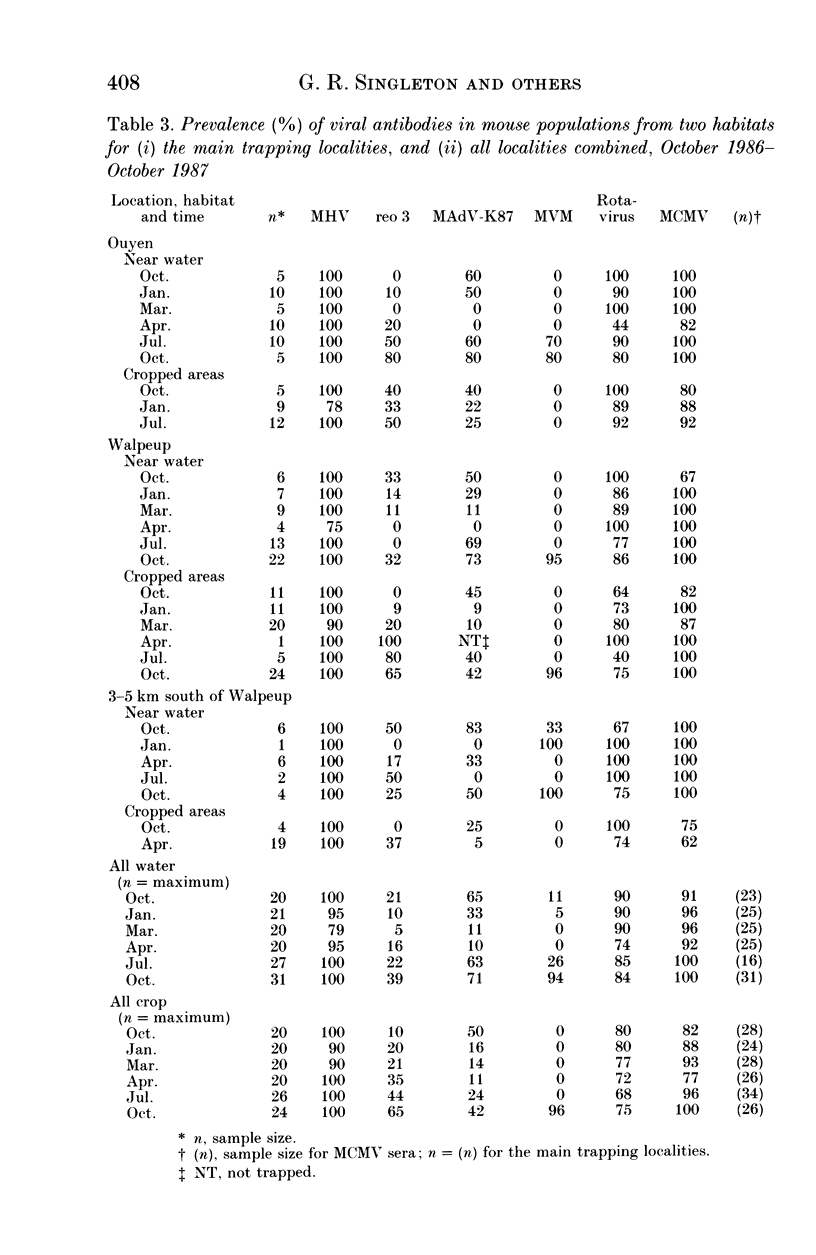
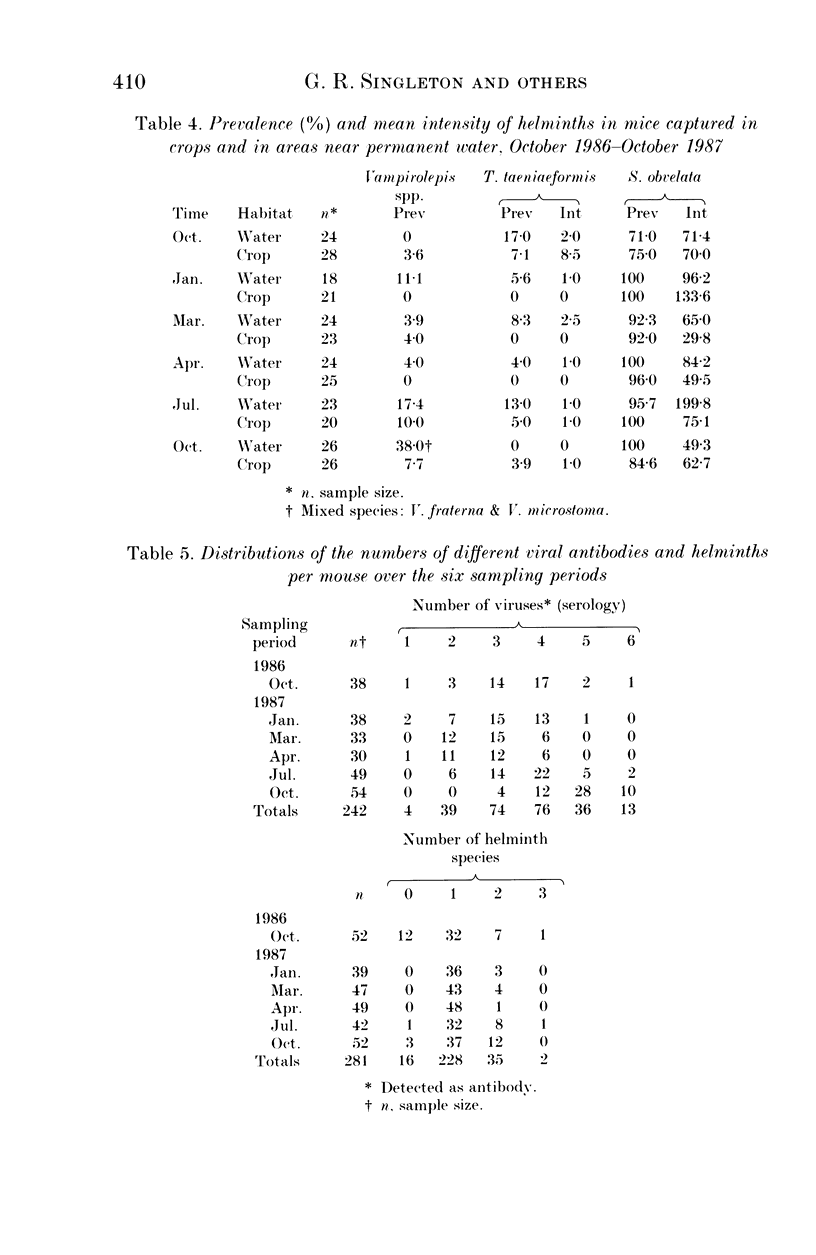
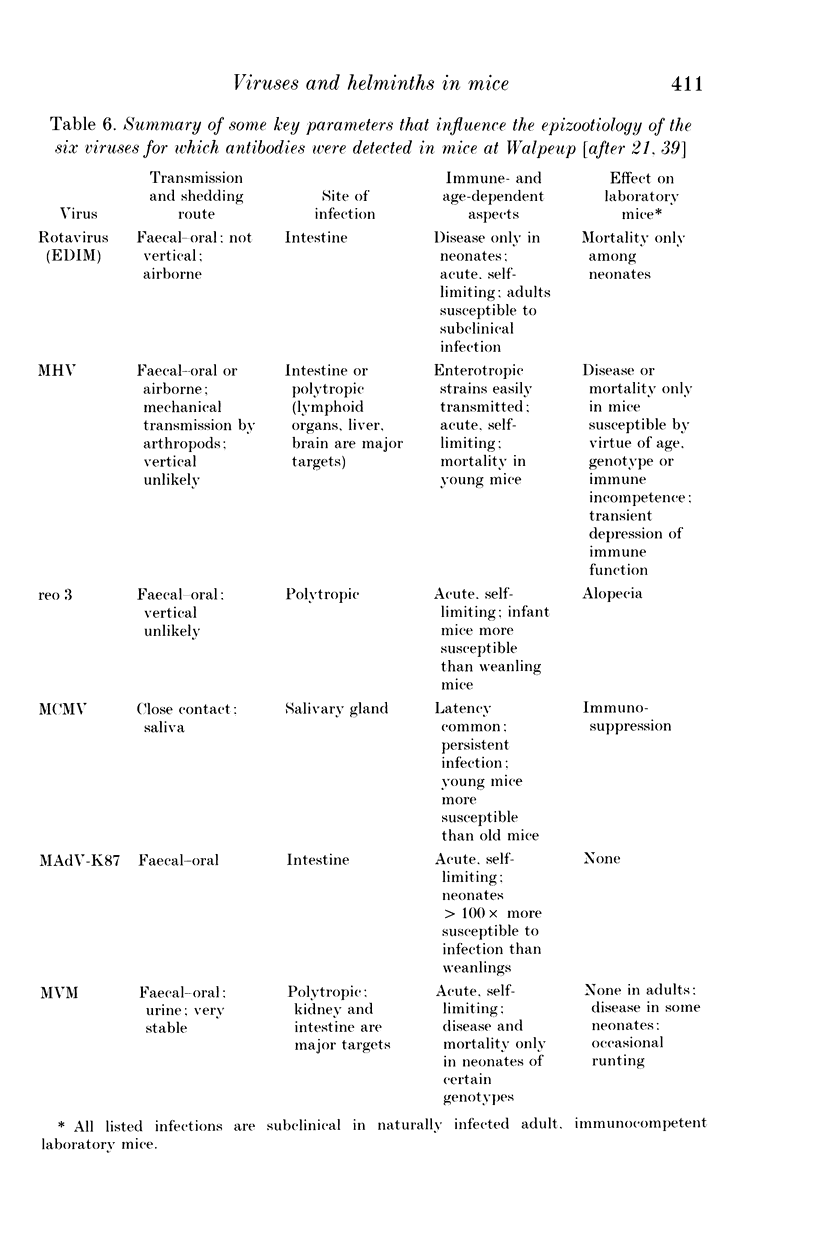
A 13-month study of wild mice (Mus domesticus) in wheatlands in southeastern Australia contrasted changes in the seroprevalence of antibody to 13 viruses and the occurrence of helminths with changes in their population dynamics. Mice were seropositive for mouse hepatitis virus (MHV), rotavirus, minute virus of mice (MVM), mouse adenovirus (MAdV), reovirus (reo 3), and murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV). The seroprevalences of all but rotavirus varied significantly with time and increased with host density. Near the end of the study, host density declined rapidly and the seroprevalence of MVM and reo 3 increased significantly. These two viruses had low seroprevalence when host survival was high and high seroprevalence when host survival was low, indicating they may play a role in regulating mouse populations. In the case of MVM, there was evidence of a viral epizootic during the decline in mouse abundance. The prevalence of four helminths (Taenia taeniaeformis, Syphacia obvelata, and Vampirolepis spp.) differed significantly with time but showed no apparent association with host density. These findings highlight the need for further study on the effect of viruses on the population dynamics of mice.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker S. C., Singleton G. R., Spratt D. M. Can the nematode Capillaria hepatica regulate abundance in wild house mice? Results of enclosure experiments in southeastern Australia. Parasitology. 1991 Dec;103(Pt 3):439–449. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000059965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Smith A. L. Viremic dissemination of mouse hepatitis virus-JHM following intranasal inoculation of mice. Arch Virol. 1992;122(1-2):35–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01321116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrano V. A., Barthold S. W., Beck D. S., Smith A. L. Alteration of viral respiratory infections of mice by prior infection with mouse hepatitis virus. Lab Anim Sci. 1984 Dec;34(6):573–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlinghouse L. E., Jr, Smith A. L. Responses of mice susceptible or resistant to lethal infection with mouse hepatitis virus, strain JHM, after exposure by a natural route. Lab Anim Sci. 1985 Oct;35(5):469–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum H. I., Singleton G. R. Models to assess the potential of Capillaria hepatica to control population outbreaks of house mice. Parasitology. 1989 Jun;98(Pt 3):425–437. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000061515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pena-Cruz V., Reiss C. S., McIntosh K. Sendai virus infection of mice with protein malnutrition. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3541–3544. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3541-3544.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeb T. R., Kervin K. C., Lindsey J. R. Exacerbation of murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in gnotobiotic F344/N rats by Sendai virus infection. Vet Pathol. 1985 May;22(3):272–282. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeb T. R., Lindsey J. R. Exacerbation of murine respiratory mycoplasmosis by sialodacryoadenitis virus infection in gnotobiotic F344 rats. Vet Pathol. 1987 Sep;24(5):392–399. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. E. An experimental and theoretical study of the dynamics of a mouse-nematode (Heligmosomoides polygyrus) interaction. Parasitology. 1990 Aug;101(Pt 1):75–92. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000079786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. E., Dobson A. The role of parasites in regulating host abundance. Parasitol Today. 1989 Jun;5(6):176–183. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(89)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton G. R., McCallum H. I. The potential of Capillaria hepatica to control mouse plagues. Parasitol Today. 1990 Jun;6(6):190–193. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90354-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo H. K., Price P., Papadimitriou J. M. The effects of protein malnutrition on the pathogenesis of murine cytomegalovirus disease. Int J Exp Pathol. 1991 Feb;72(1):67–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


