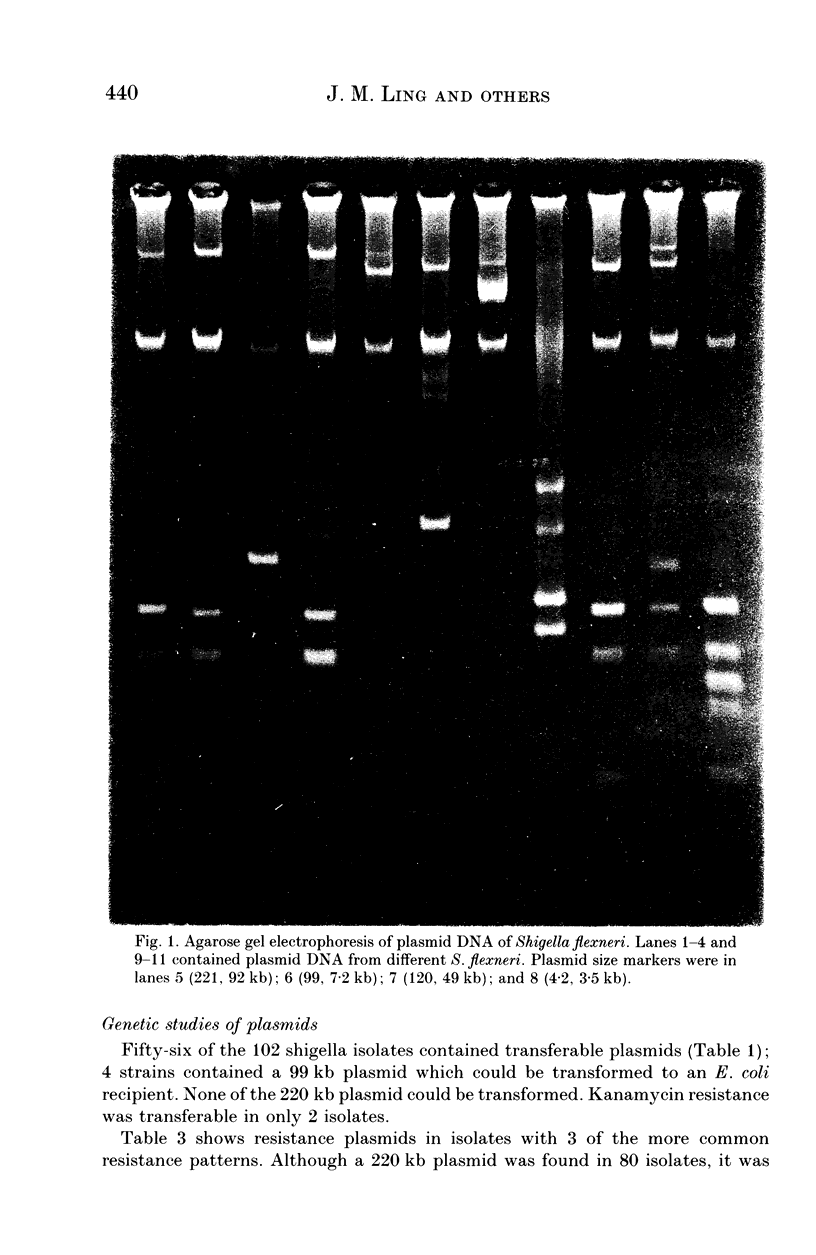
Abstract
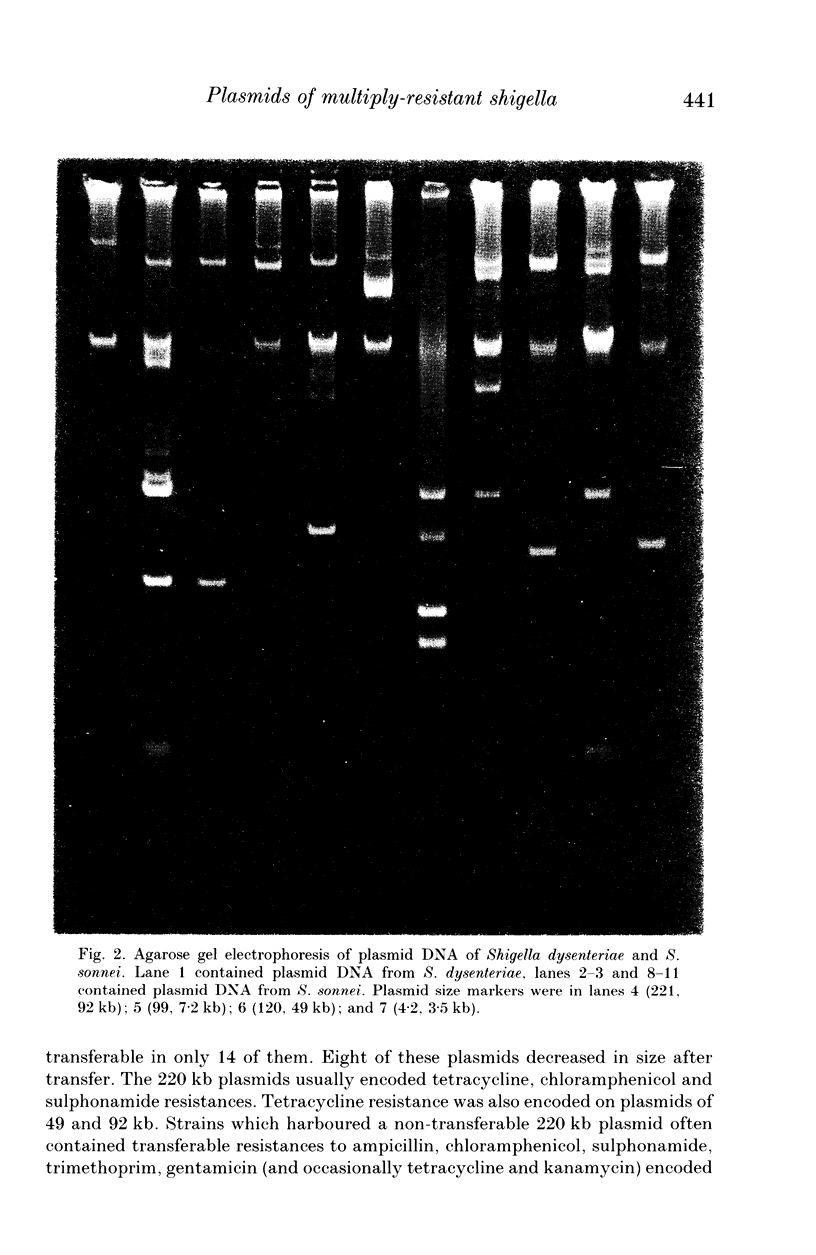
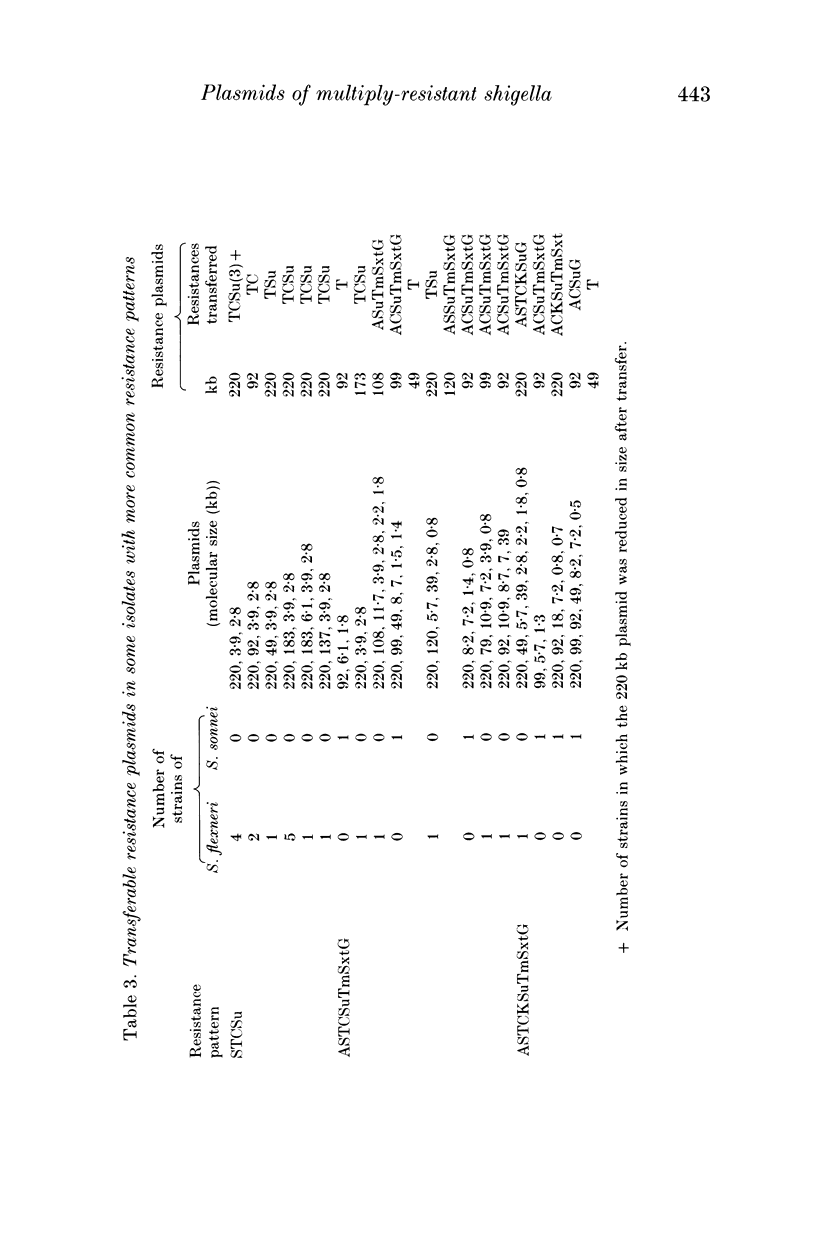
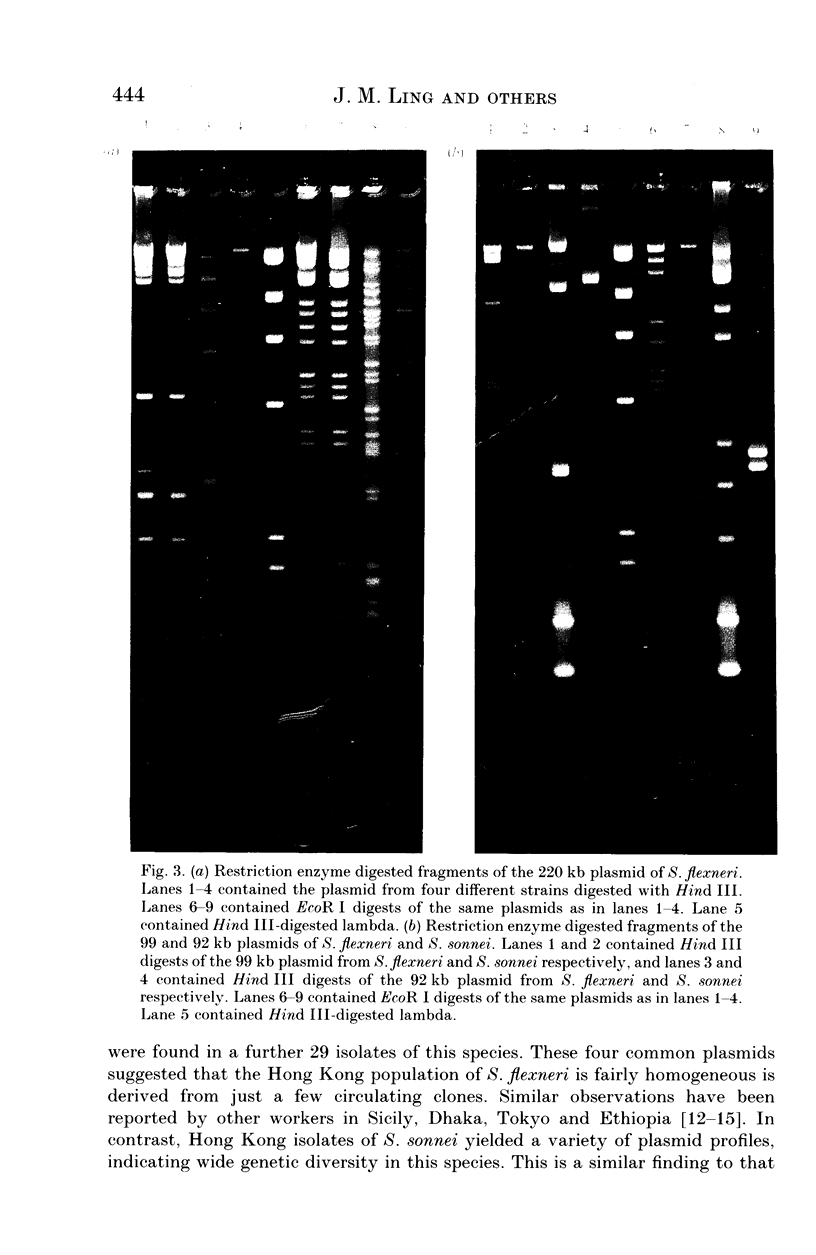
One hundred and two Shigella spp. isolated in two hospitals in Hong Kong were analysed for antibiotic resistances, resistance plasmids and plasmid profiles. Three quarters of the isolates were S. flexneri. All isolates harboured plasmids, up to a maximum of ten within one strain. Plasmids of 220 kb encoding resistances to tetracycline, chloramphenicol and sulphonamide and probably also associated with invasiveness in the Sereny test were found in 80 strains and were transferable in 18% of cases. Resistance plasmids of 92 and 99 kb were found in 27 and 15 strains respectively and encoded resistances to ampicillin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, kanamycin, sulphonamide, trimethoprim, cotrimoxazole and gentamicin; these plasmids were usually transferable. Four plasmids of 3.9, 2.8, 2.2 and 1.8 kb were commonly found in S. flexneri strains, but were rare in other species. In contrast, there was no predominant plasmid profile in S. sonnei. S. flexneri is endemic in Hong Kong and these plasmid studies suggest that the strains in circulation are derived from only a few clones.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. J., Singh K. V., Murray B. E., Erlich J. Molecular epidemiology of Shigella infection in Central Australia. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Aug;105(1):51–57. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun D., Cho D. T., Seol S. Y., Suh M. H., Lee Y. C. R plasmids conferring multiple drug resistance from shigella isolated in Korea. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Apr;92(2):153–160. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400064160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost J. A., Rowe B. Plasmid-determined antibiotic resistance in Shigella flexneri isolated in England and Wales between 1974 and 1978. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Feb;90(1):27–32. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebre-Yohannes A., Drasar B. S. Molecular epidemiology of plasmid patterns in Shigella flexneri types 1-6. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Oct;107(2):321–334. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider K., Huq M. I., Samadi A. R., Ahmad K. Plasmid characterization of Shigella spp. isolated from children with shigellosis and asymptomatic excretors. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Dec;16(6):691–698. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.6.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. F., Bremner D. A., Bergquist P. L., Lane H. E. Characterization of plasmids from antibiotic-resistant Shigella isolates by agarose gell electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jul;113(1):73–81. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling J. M., Zhou G. M., Woo T. H., French G. L. Antimicrobial susceptibilities and beta-lactamase production of Hong Kong isolates of gastroenteric salmonellae and Salmonella typhi. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Dec;28(6):877–885. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.6.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling J., Kam K. M., Lam A. W., French G. L. Susceptibilities of Hong Kong isolates of multiply resistant Shigella spp. to 25 antimicrobial agents, including ampicillin plus sulbactam and new 4-quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):20–23. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling J., Ling K. L., Chan K. W., French G. L. Computer programs for accurate determination of size of DNA fragments in agarose gels. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jun;40(6):692–695. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.6.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marranzano M., Giammanco G., d'Hauteville H., Sansonetti P. Epidemiological markers of Shigella sonnei infections: R-plasmid fingerprinting, phage-typing and biotyping. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 May-Jun;136A(3):339–345. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi S., Sakaguchi T., Arai T. A survey of plasmids in the clinically isolated Shigella strains and their invasive ability and antibiotic resistances. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1986 Jun;59(1-2):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva R. M., Toledo M. R., Trabulsi L. R. Correlation of invasiveness with plasmid in enteroinvasive strains of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Nov;146(5):706–706. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.5.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]