Abstract
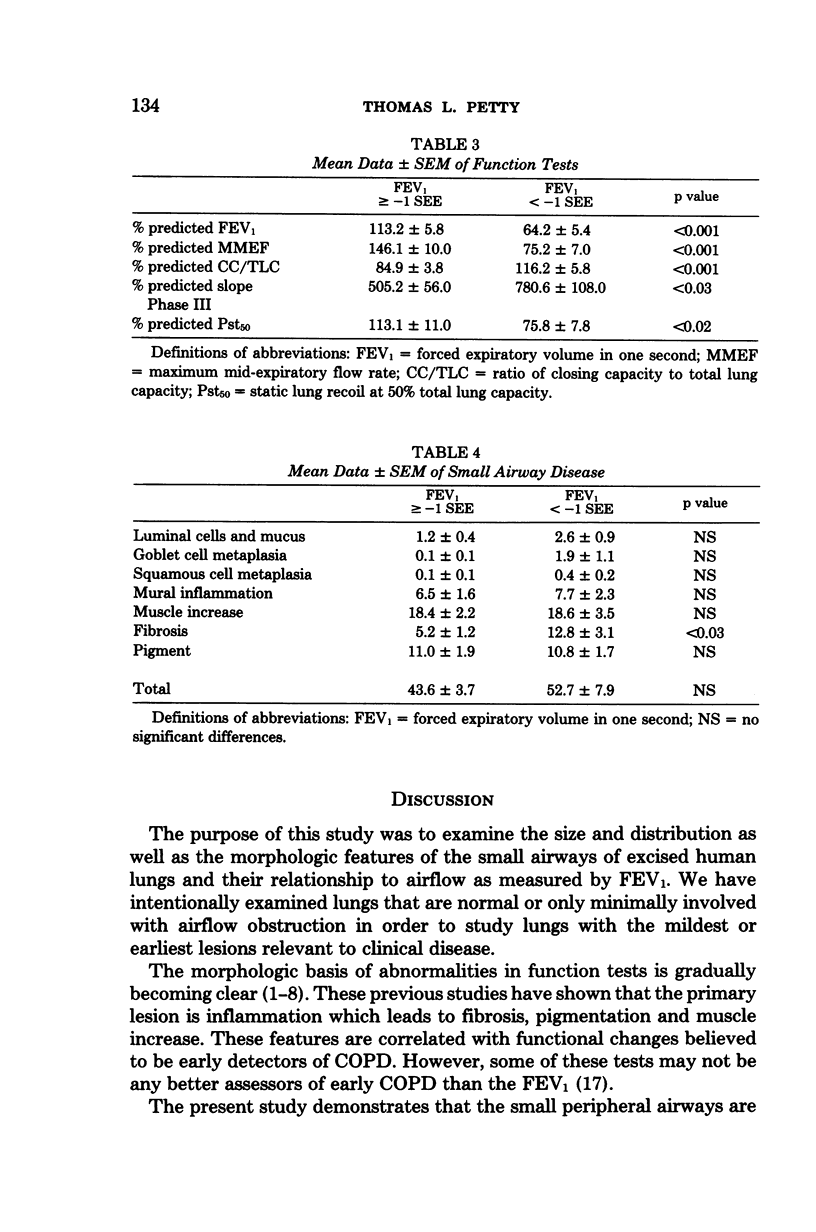
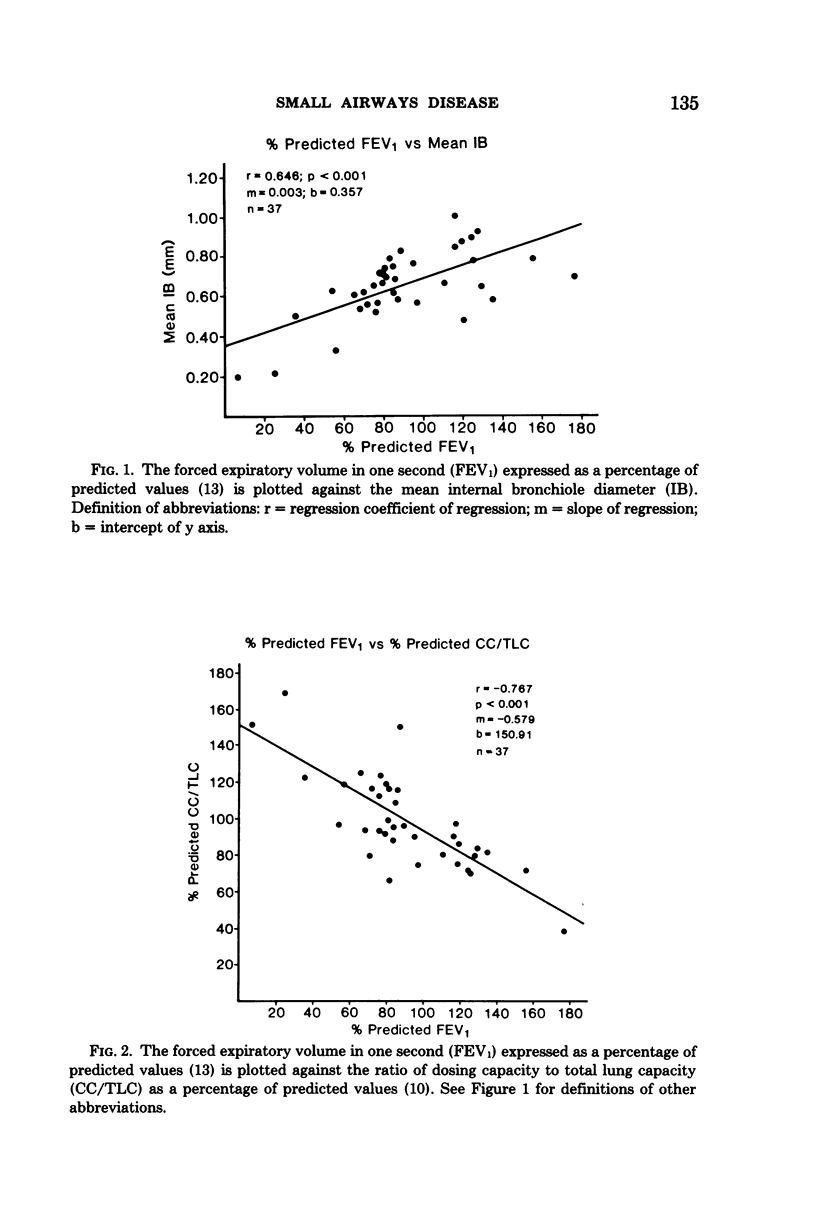
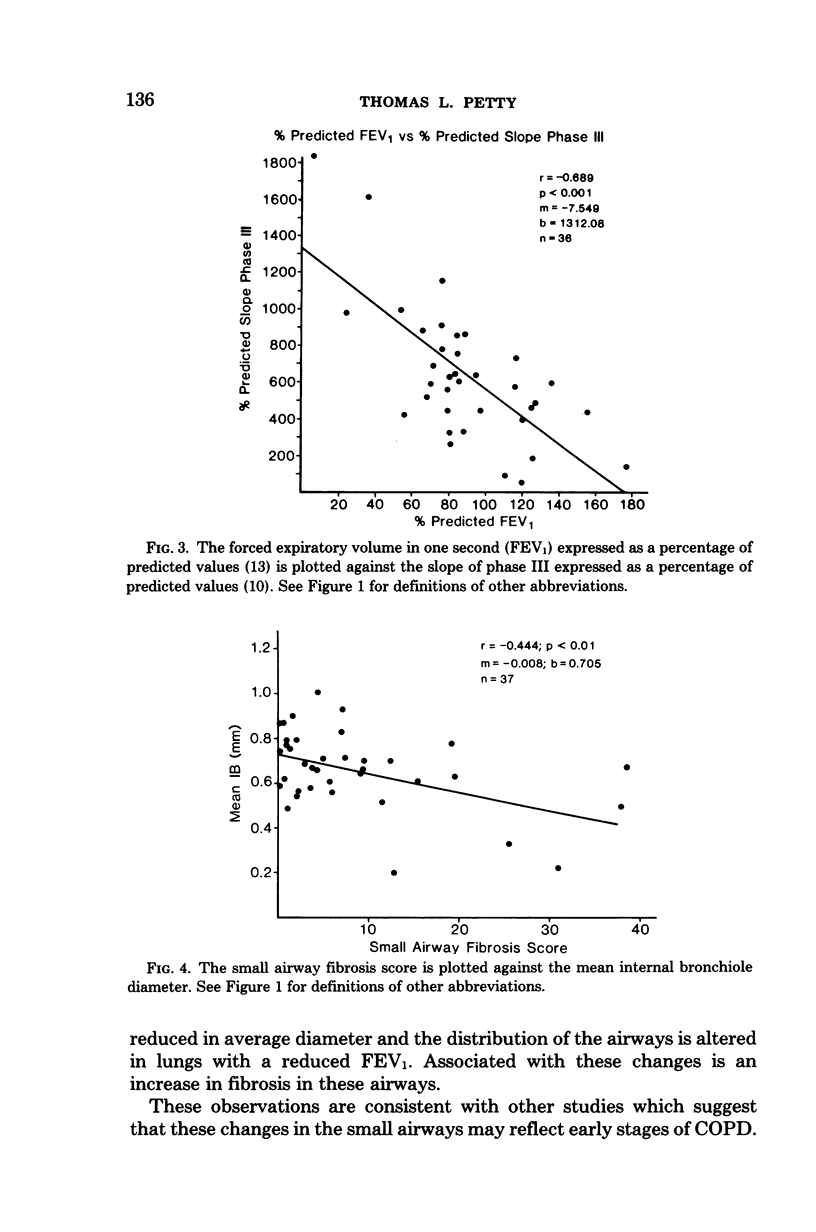
The morphologic and morphometric characteristics of the small airways of the lung and their relationship to airflow as measured by forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) were determined in 37 excised human lungs. After fixation the lungs were graded as to the degree of emphysema and the degree of small airway pathology. The internal diameters of the small airways were measured and corrected for shrinkage during processing. The mean bronchiolar diameter was positively correlated with the % predicted FEV1 (p less than 0.001) and negatively correlated with the small airway fibrosis (p less than 0.01). We conclude that fibrosis of the small airways of the lung is associated with a decrease in airway dimension which is in turn correlated with decreased FEV1 in excised human lungs.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berend N., Woolcock A. J., Marlin G. E. Correlation between the function and structure of the lung in smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 May;119(5):695–705. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berend N., Wright J. L., Thurlbeck W. M., Marlin G. E., Woolcock A. J. Small airways disease: reproducibility of measurements and correlation with lung function. Chest. 1981 Mar;79(3):263–268. doi: 10.1378/chest.79.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buist A. S., Ross B. B. Predicted values for closing volumes using a modified single breath nitrogen test. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 May;107(5):744–752. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.5.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
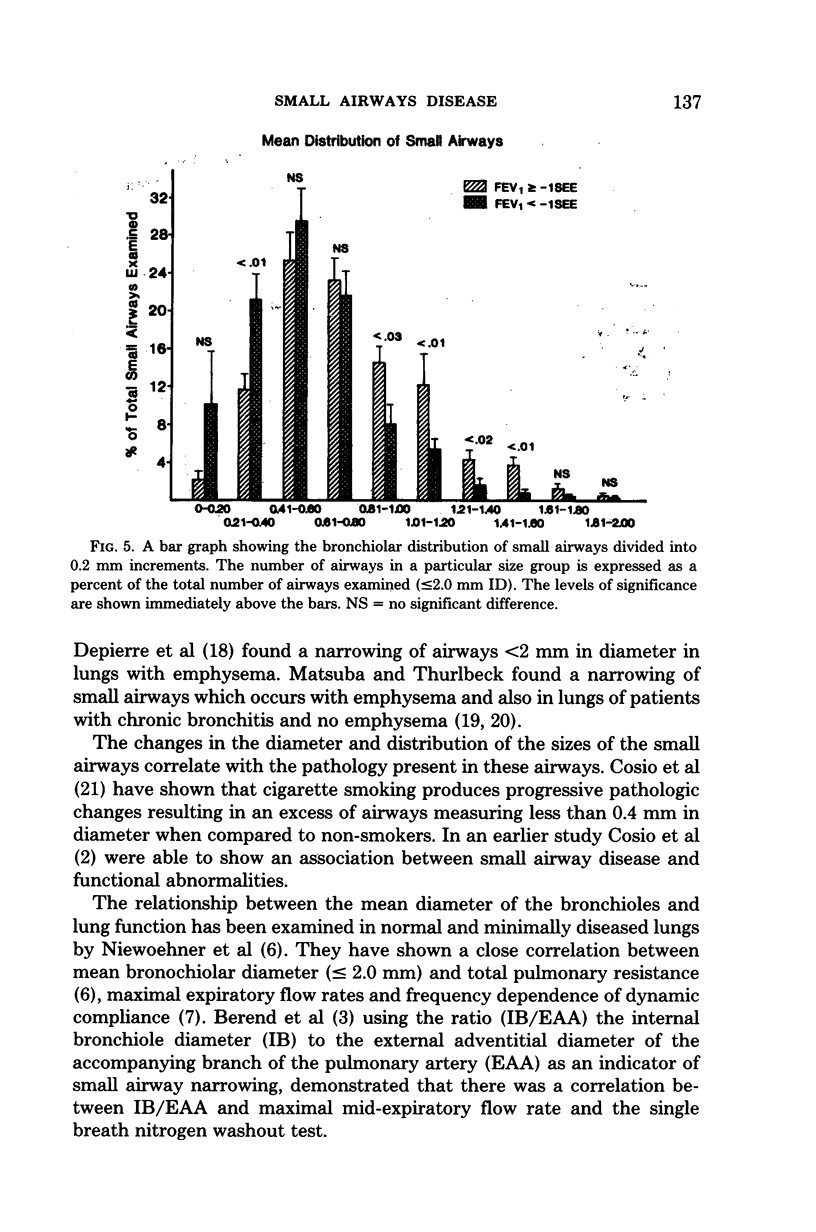
- Cosio M. G., Hale K. A., Niewoehner D. E. Morphologic and morphometric effects of prolonged cigarette smoking on the small airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Aug;122(2):265–221. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosio M., Ghezzo H., Hogg J. C., Corbin R., Loveland M., Dosman J., Macklem P. T. The relations between structural changes in small airways and pulmonary-function tests. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 8;298(23):1277–1281. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806082982303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depierre A., Bignon J., Lebeau A., Brouet G. Quantitative study of parenchyma and small conductive airways in chronic nonspecific lung disease. Use of histologic stereology and bronchial casts. Chest. 1972 Dec;62(6):699–708. doi: 10.1378/chest.62.6.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. I., BECKLAKE M. R. Respiratory function tests; normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Apr;79(4):457–467. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg J. C., Macklem P. T., Thurlbeck W. M. Site and nature of airway obstruction in chronic obstructive lung disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jun 20;278(25):1355–1360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196806202782501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson R. J., Lebowiz M. D. Comparison of flow-volume and closing volume variables in a random population. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Dec;116(6):1039–1045. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.6.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuba K., Thurlbeck W. M. Disease of the small airways in chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Apr;107(4):552–558. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuba K., Thurlbeck W. M. The number and dimensions of small airways in emphysematous lungs. Am J Pathol. 1972 May;67(2):265–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuba K., Thurlbeck W. M. The number and dimensions of small airways in nonemphysematous lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Oct;104(4):516–524. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.4.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. F., Koski A., Johnson L. C. Spirometric standards for healthy nonsmoking adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Jan;103(1):57–67. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewoehner D. E., Kleinerman J. Morphologic basis of pulmonary resistance in the human lung and effects of aging. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Apr;36(4):412–418. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewoehner D. E., Knoke J. D., Kleinerman J. Peripheral airways as a determinant of ventilatory function in the human lung. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):139–151. doi: 10.1172/JCI108750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L., Silvers G. W., Stanford R. E., Baird M. D., Mitchell R. S. Small airway pathology is related to increased closing capacity and abnormal slope of phase III in excised human lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Mar;121(3):449–456. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L., Silvers G. W., Stanford R. E. Small airway dimension and size distribution in human lungs with an increased closing capacity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 May;125(5):535–539. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.5.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvers G. W., Fine R., Paul G. W., Stanford R. E., Petty T. L., Filley G. F. Effect of increased static lung recoil on ventilation distribution in excised human lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Mar;115(3):435–442. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M., Dunnill M. S., Hartung W., Heard B. E., Heppleston A. G., Ryder R. C. A comparison of three methods of measuring emphysema. Hum Pathol. 1970 Jun;1(2):215–226. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



