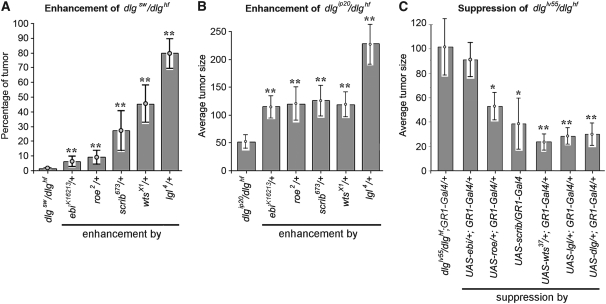
Figure 3.—
Quantitative analysis of dlg enhancement and suppression. (A) Frequency of dlgsw/dlghf; enhancer/+ tumor invasion. lgl causes the highest frequency, scrib and wts an intermediate frequency, and ebi and rn the lowest frequency of invasion. All enhancements were significant (**P < 0.01). (B) For all dlgip20/dlghf; enhancer/+ genotypes invasion occurs in 100% of ovarioles (Figure 2). To compare the strengths of enhancement we determined the average tumor size (materials and methods). Removal of one copy of lgl (dlgip20/dlghf; lgl/+) causes tumors that are four to five times the size of dlgip20/dlghf tumors, while removal of one copy of ebi, rn, scrib, or wts causes tumors that are roughly twice larger (**P < 0.01). (C) Suppression of dlglv55/dlghf tumorigenesis by dlg enhancer overexpression. The Gal4-UAS system (Brand and Perrimon 1993) was used to drive overexpression of each UAS-dlg enhancer transgene with GR1-Gal4, which is expressed in all follicle cells throughout oogenesis (Szafranski and Goode 2007). dlglv55/dlghf tumorigenesis was most significantly suppressed by dlg, lgl, and wts (**P < 0.01) and to a lesser but still significant degree by scrib and roe (*P < 0.05). ebi showed no significant suppression.