Abstract
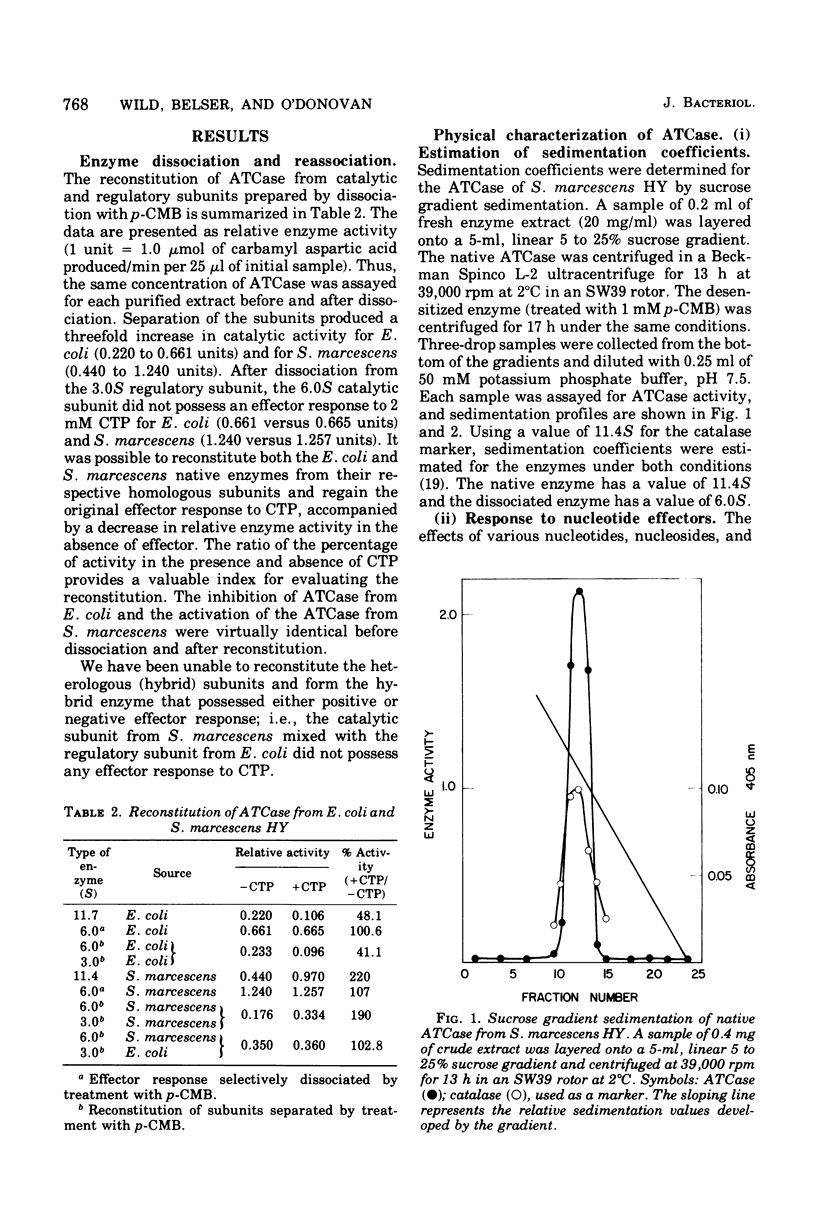
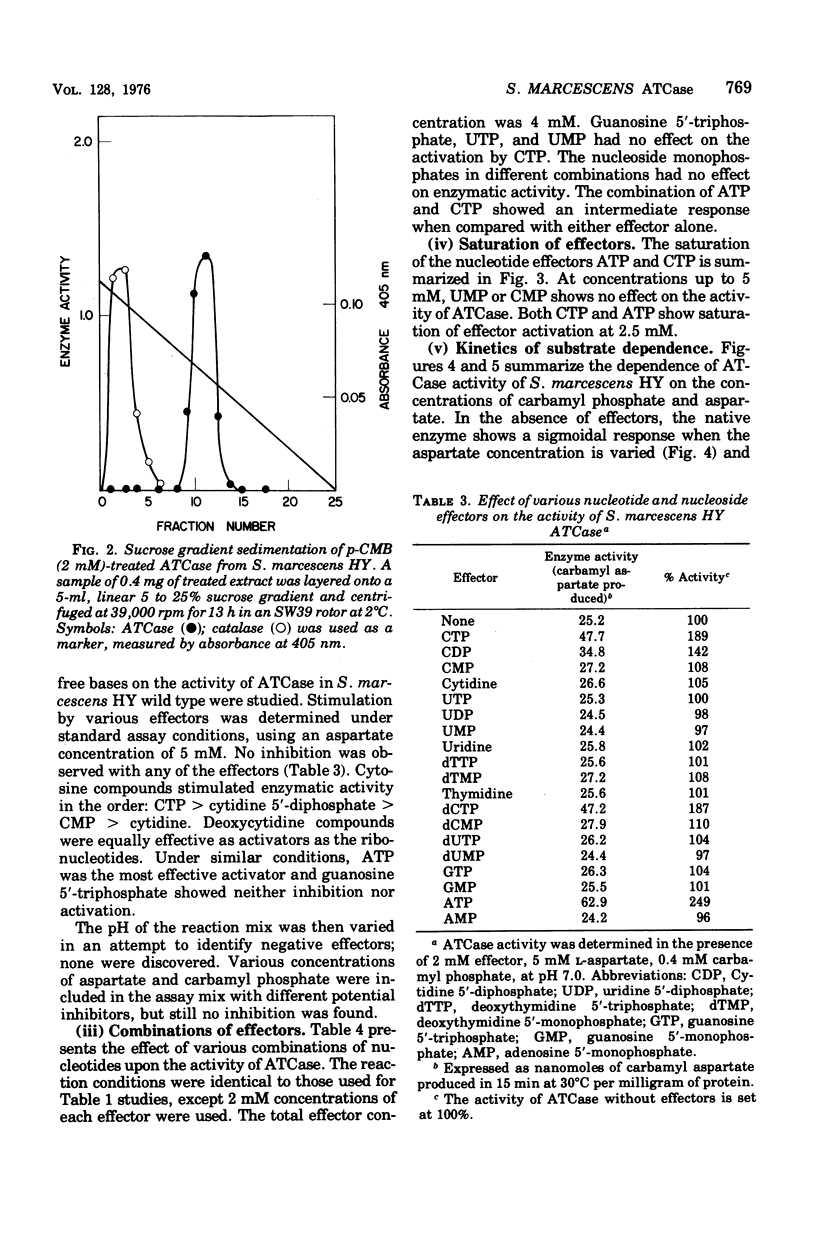
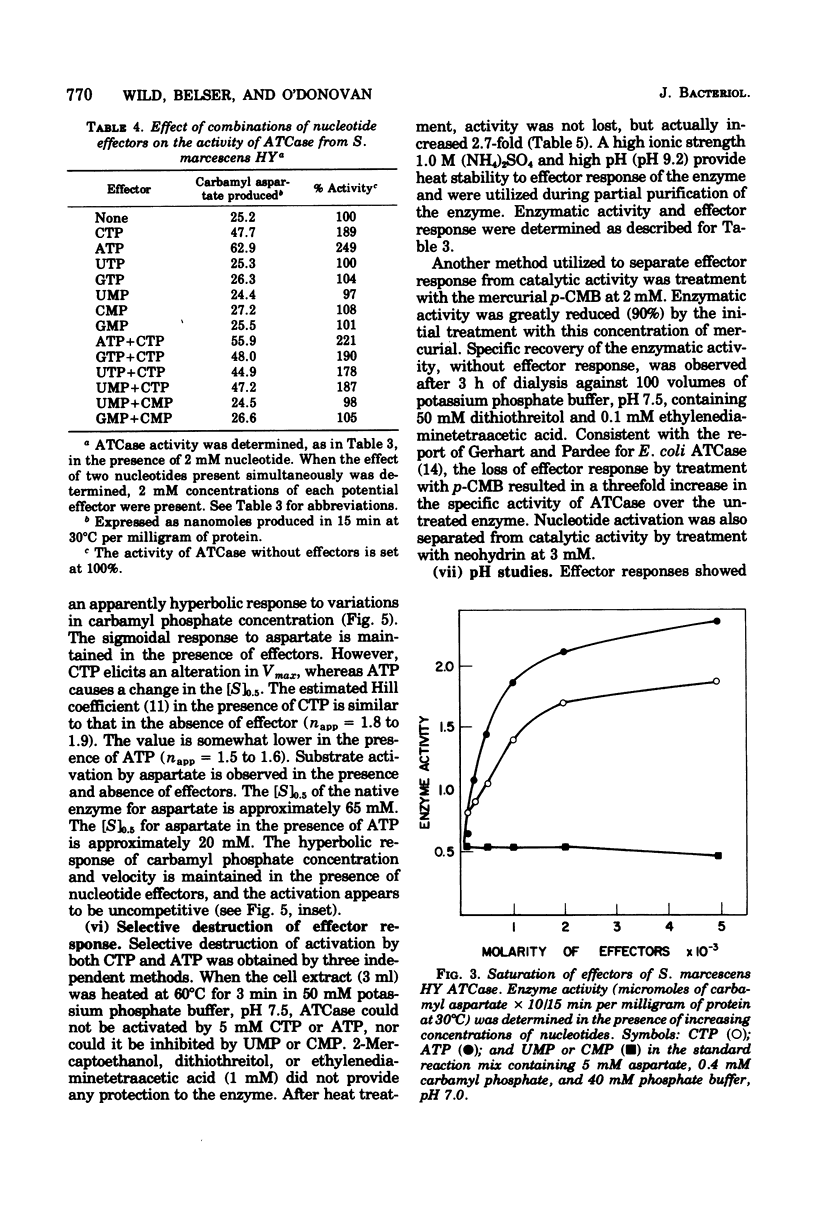
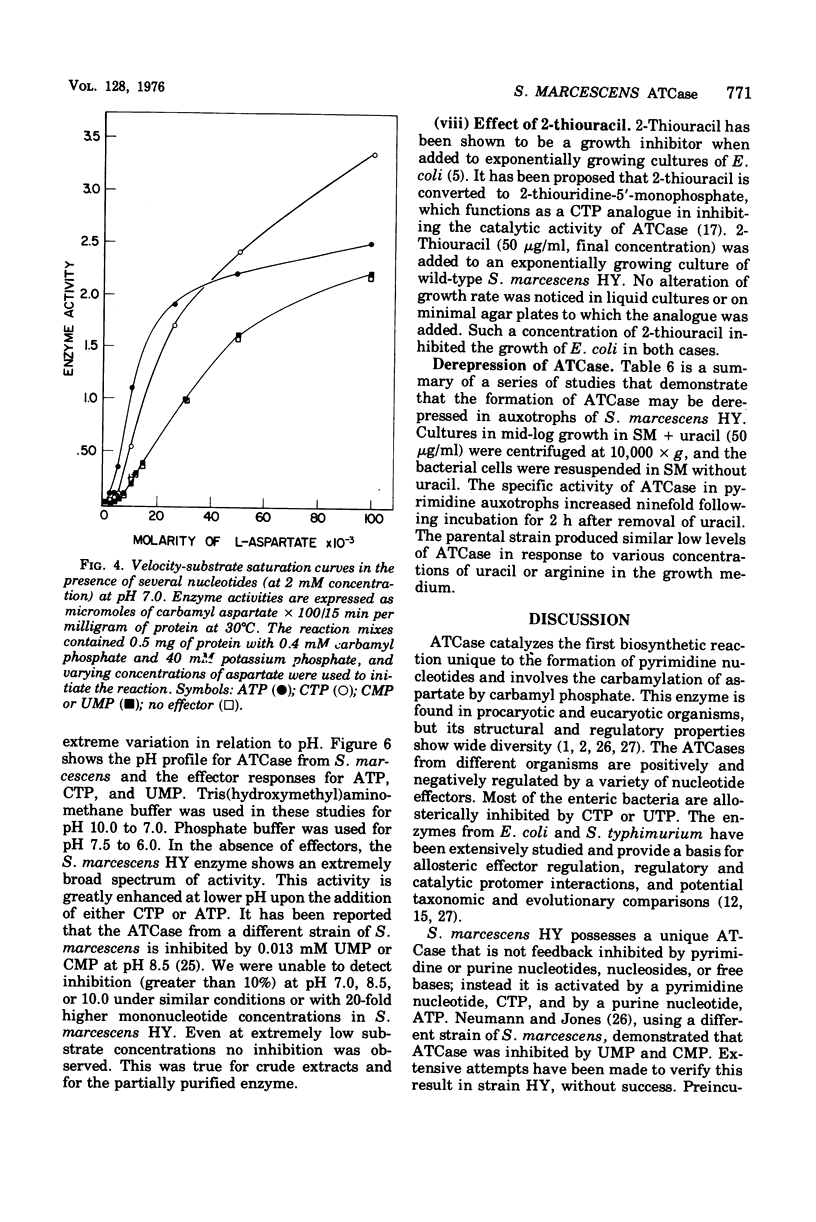
Aspartate trancarbamylase (ATC ase; EC 2.1.3.2) from Serratia marcescens HY has been purified 134-fold. Its properties are unique. Unlike the ATCase from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, the S. marcescens HY enzyme activity is not feedback inhibited by any purine or pyrimidine nucleotide effectors; instead, the enzyme is activated by both cytidine 5'-triphosphate and adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Like the ATCase from E. coli and S. typhimurium, adenosine 5'-triphosphate alters the [S]0.5 of the enzyme and, in contrast, cytidine 5'-triphosphate does not alter the [S]0.5 but, instead, alters the Vmax. As has been shown for both E. coli and S . typhimurium, effector sensitivity may be selectively dissociated form catalytic activity by treatment with heat, parachloromercuribenzoate, or neohydrin. This dissociated enzyme possesses threefold higher specific activity than the native enzyme. The sedimentation coefficient of the native enzyme is approximately 11.4S, whereas the dissociated enzyme has a value of 6.0S. Whereas it has been possible to reconstitute the E. coli and the S. marcescens ATCase enzymes from their own homologous subunits, it has not been possible to make hybrid enzymes of catalytic and regulatory heterologous subunits from each other. It was not possible to detect repression of ATCase formation after growth of prototrophic strains of S. marcescens HY supplemented with 200 mug of uracil per ml, but eightfold derepression was observed after uracil withdrawal in pyrimidine auxotrophs.
Full text
PDF

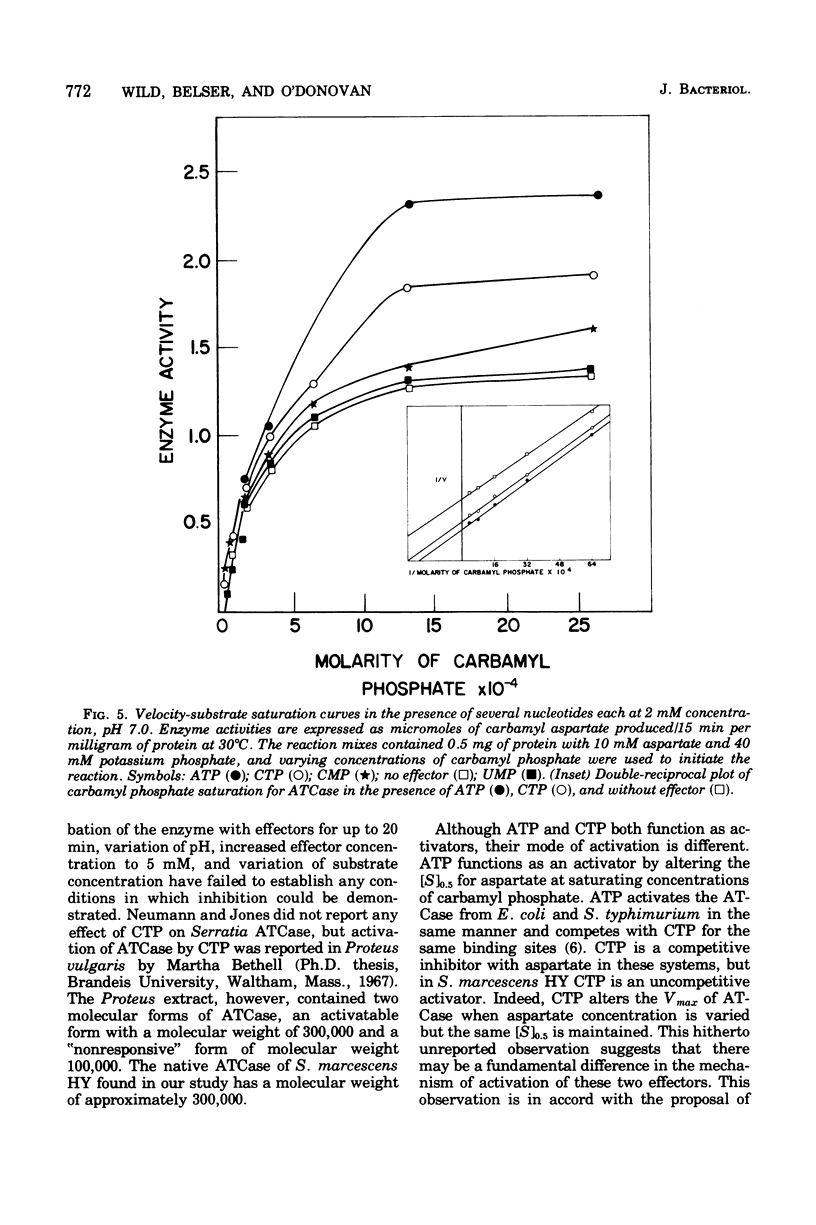
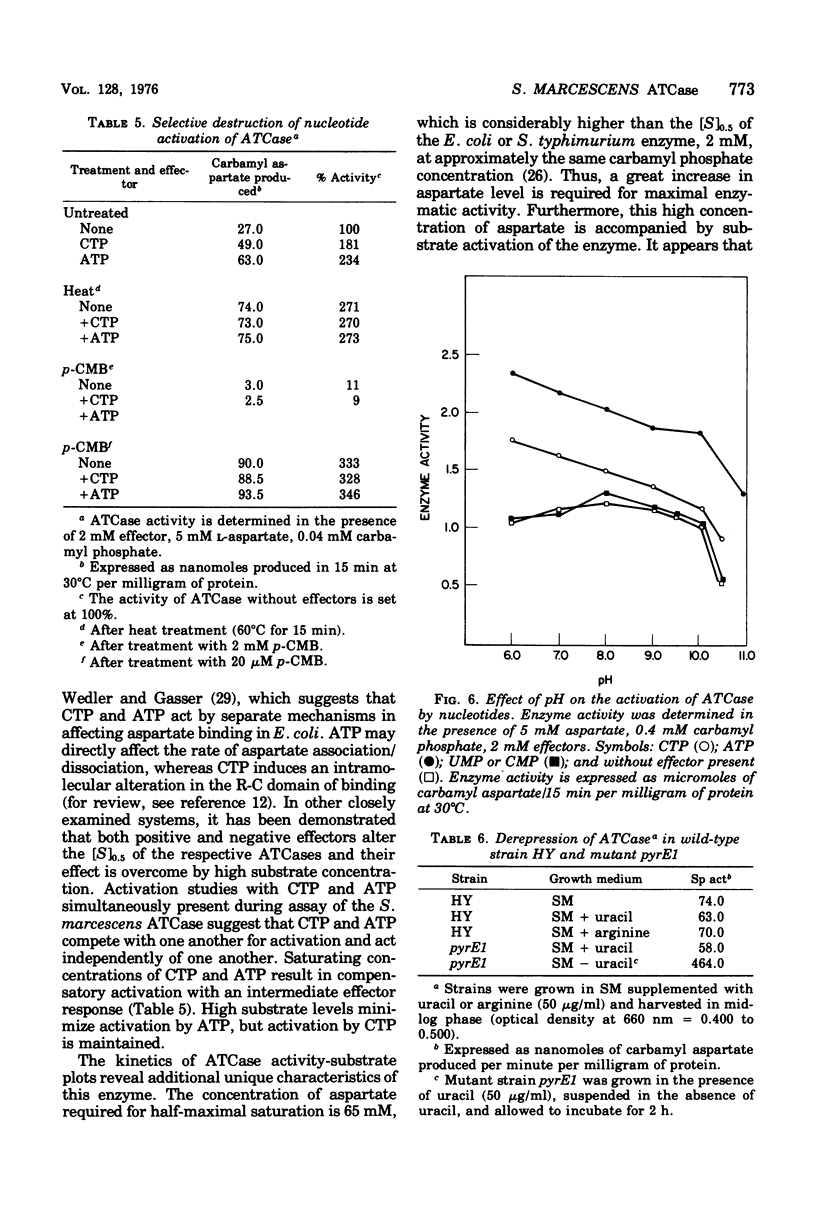


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair L. B., Jones M. E. Purification and characteristics of aspartate transcarbamylase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2308–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethell M. R., Jones M. E. Molecular size and feedback-regulation characteristics of bacterial asartate transcarbamulases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):352–365. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethell M. R., Smith K. E., White J. S., Jones M. E. Carbamyl phosphate: an allosteric substrate for aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1442–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Citarella R. V., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among members of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):637–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.637-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardeilhac P. T. A toxic effect of 2-thiouracil on pyrimidine metabolism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jul;125(3):692–696. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Allosteric interactions in aspartate transcarbamylase. I. Binding of specific ligands to the native enzyme and its isolated subunits. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):531–538. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks G. T., Wilson A. C. Enzyme evolution in the Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):793–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.793-802.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M. S., Jones M. E. Aspartate transcarbamylases of Citrobacter freundii. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3390–3396. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condon S., Collins J. K., O'donovan G. A. Regulation of arginine and pyrimidine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas putida. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Feb;92(2):375–383. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-2-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P. Gene rearrangements in the evolution of the tryptophan synthetic pathway. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):87–120. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.87-120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endrenyi L., Fajszi C., Kwong F. H. Evaluation of Hill slopes and Hill coefficients when the saturation binding or velocity is not known. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 21;51(2):317–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHART J. C., PARDEE A. B. The enzymology of control by feedback inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Holoubek H. The purification of aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli and separation of its protein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2886–2892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Allosteric interactions in aspartate transcarbamylase. II. Evidence for different conformational states of the protein in the presence and absence of specific ligands. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):538–552. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Distinct subunits for the regulation and catalytic activity of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1054–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich M. E., Cardeilhac P. 2-thiouridine 5'-phosphate and its inhibition of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 29;222(3):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Belser W. L. Regulation of pyrimidine biosynthesis in Serratia marcescens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1483–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M. A., Belser W. L. Enzymes of tryptophan biosynthesis in Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.109-115.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac J. H., Holloway B. W. Control of pyrimidine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1732–1741. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1732-1741.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABRUM E. L., BUNTING M. I. Spontaneous and induced color-variation of the HY strain of Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1953 Apr;65(4):394–404. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.4.394-404.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., FALKOW S., MANDEL M. NEW APPROACHES TO BACTERIAL TAXONOMY. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1963;17:329–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.17.100163.001553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. M., Mills S. E. Immunochemical and enzymatic comparisons of the tryptophan synthase alpha subunits from five species of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1310–1320. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1310-1320.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUMANN J., JONES M. E. END-PRODUCT INHIBITION OF ASPARTATE TRANSCARBAMYLASE IN VARIOUS SPECIES. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Mar;104:438–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan G. A., Holoubek H., Gerhart J. C. Regulatory properties of intergeneric hybrids of aspartate transcarbamylase. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 30;238(87):264–266. doi: 10.1038/newbio238264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan G. A., Neuhard J. Pyrimidine metabolism in microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Sep;34(3):278–343. doi: 10.1128/br.34.3.278-343.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha V., Crawford I. P., Mills S. E. Comparative immunological and enzymatic study of the tryptophan synthetase beta 2 subunit in the Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.163-168.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedler F. C., Gasser F. J. Modes of modifier action in E. coli aspartate transcarbamylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



