Abstract
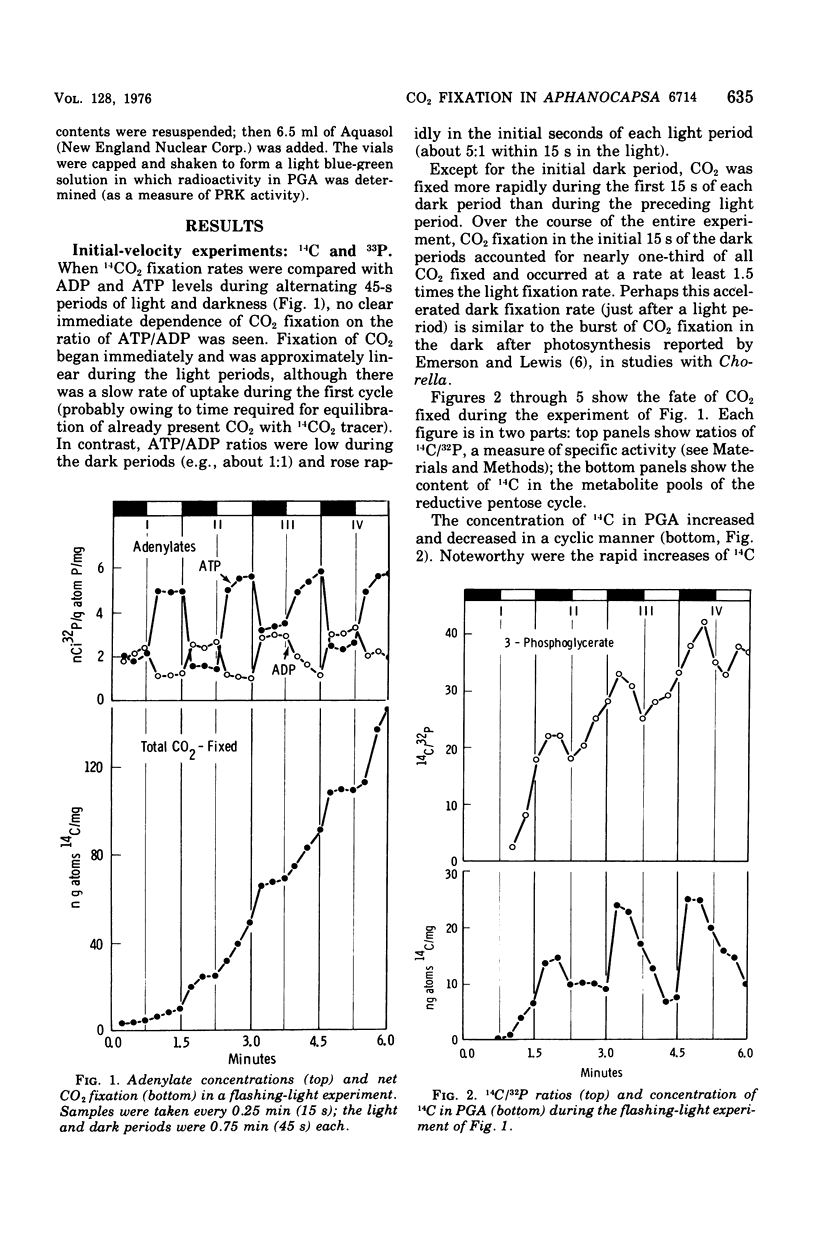
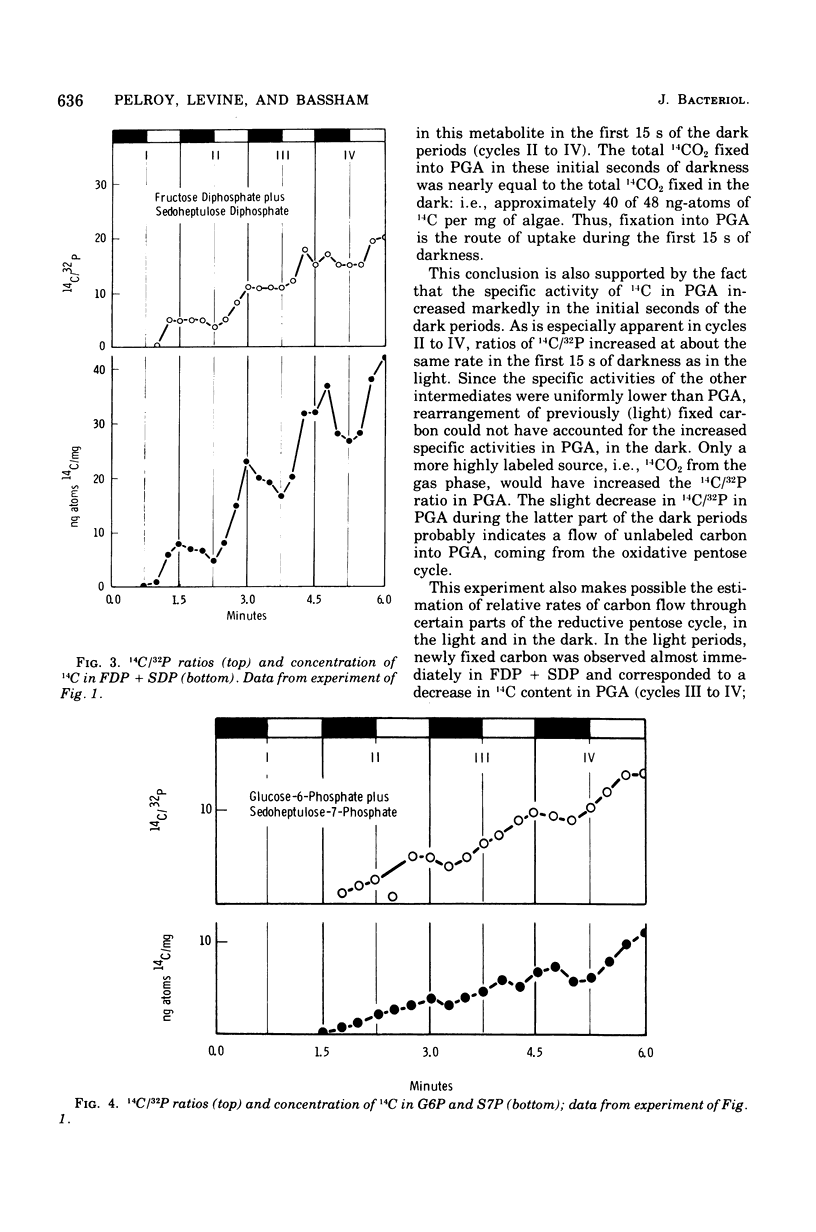
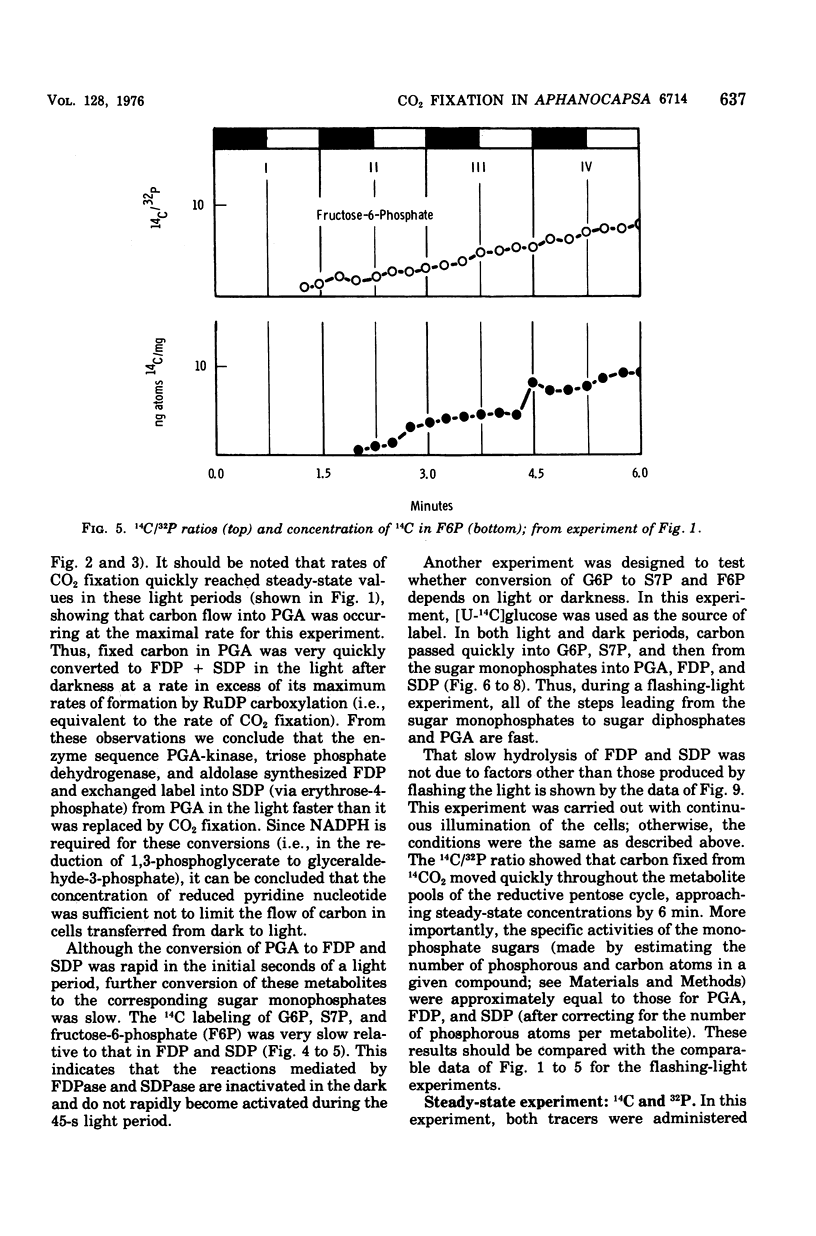
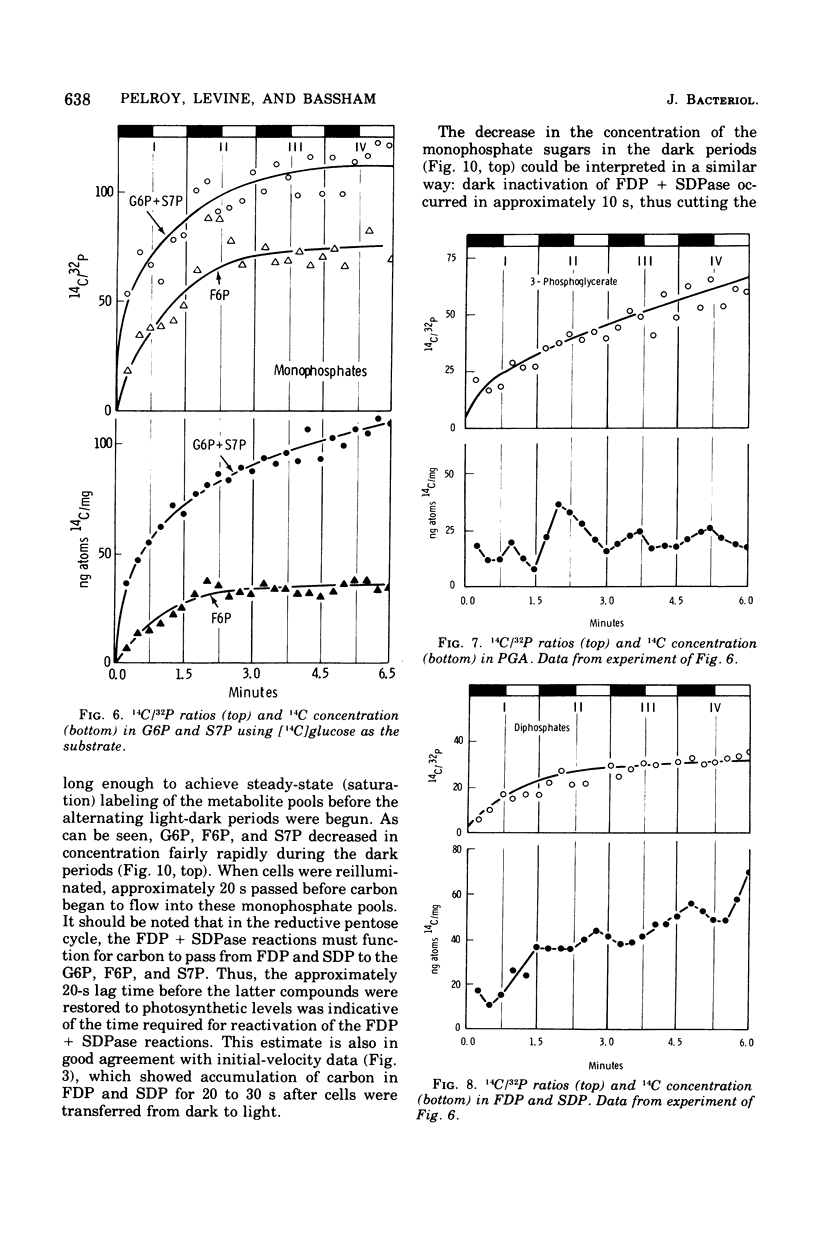
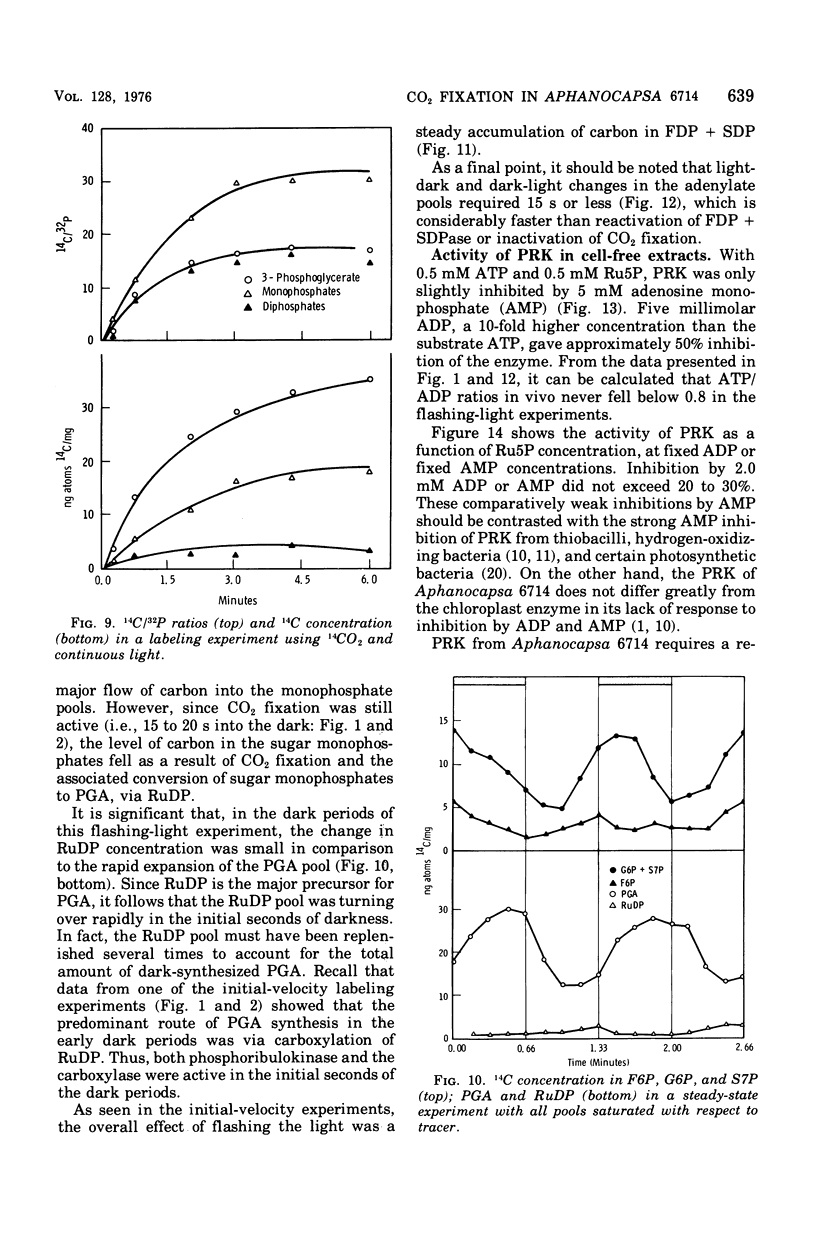
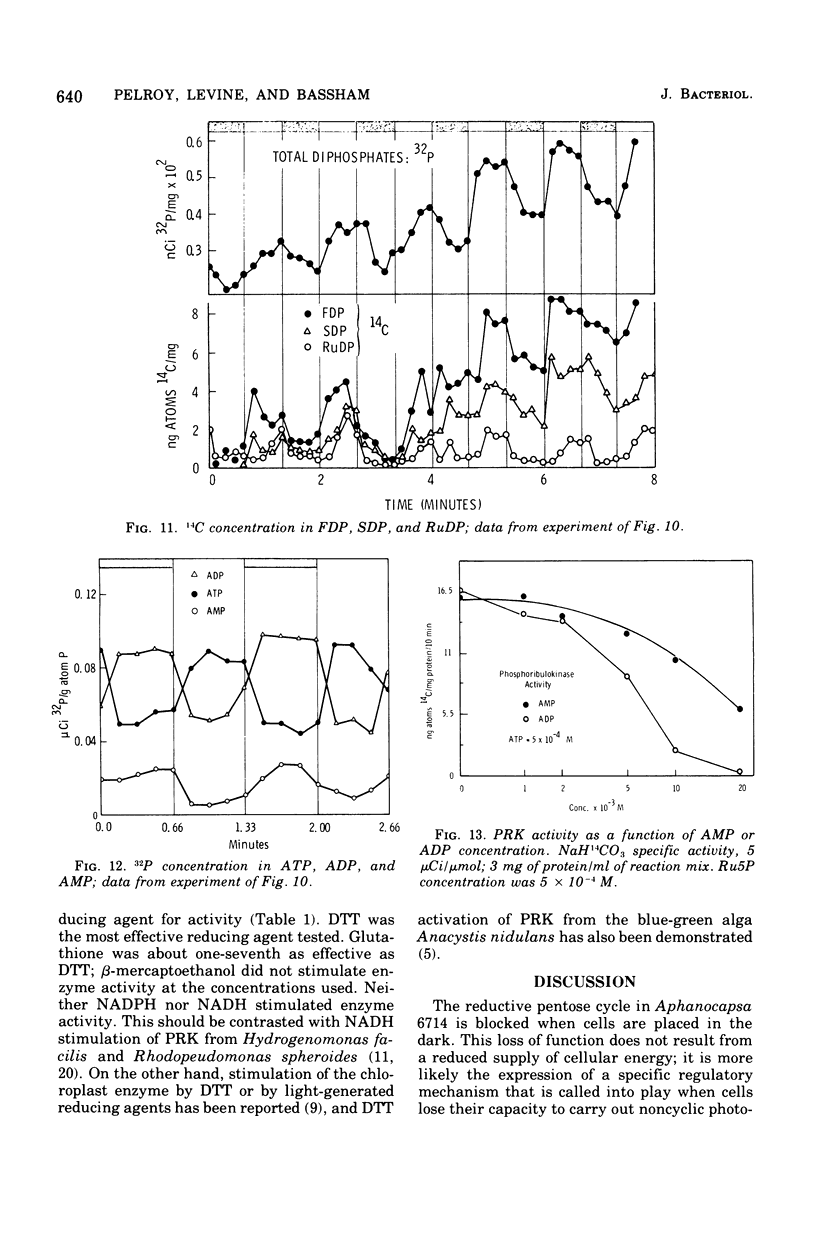
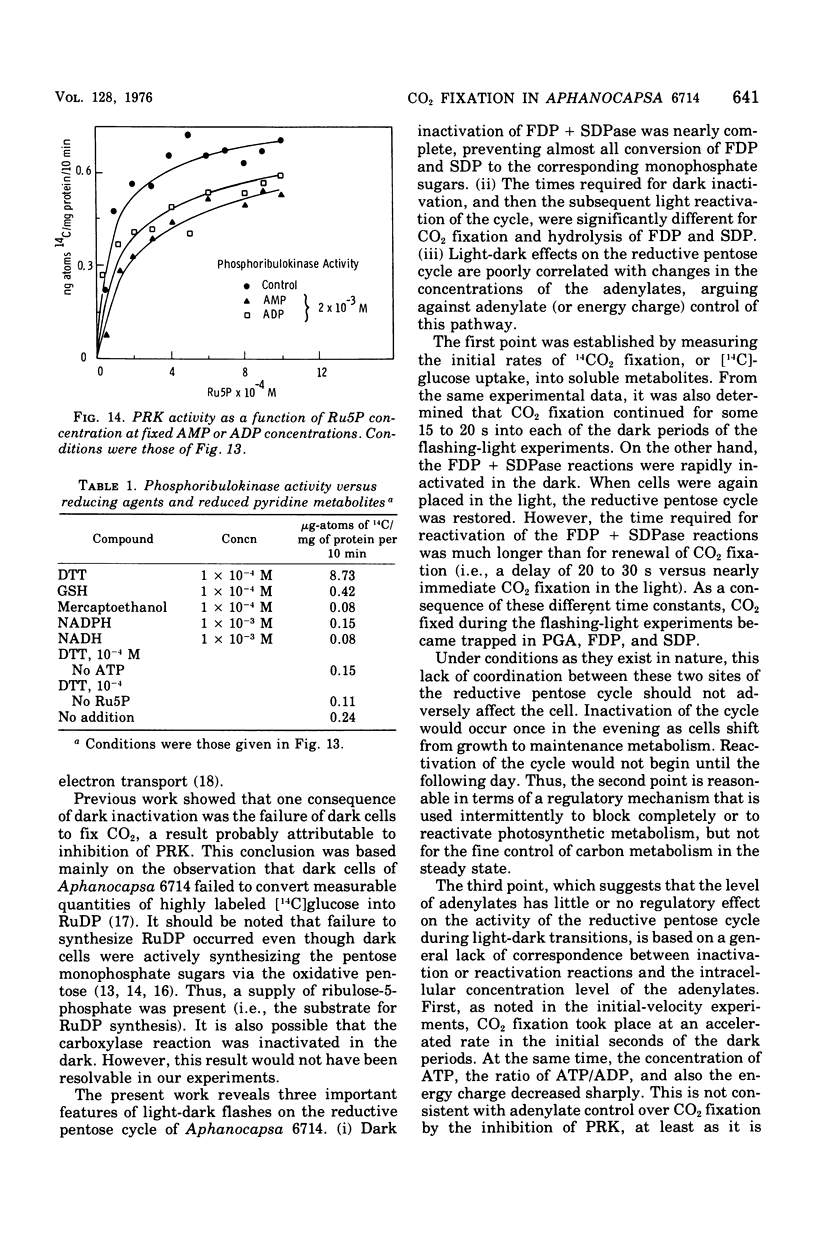
Cells of Aphanocapsa 6714 were subjected to alternating ligh-dark periods (flashing-light experiments). The corresponding activation (in the light) and inactivation (in the dark) of the reductive pentose cycle was measured, in vivo, from initial rates of 14CO2 incorporation and also by changes in the total concentration of 14C and 32P in soluble metabolites. Two principle sites of metabolic regulation were detected: (i) CO2 fixation was inactivated 15 to 20 s after removal of the light source, but reactivated rapidly on reentering the light; (ii) hydrolysis of fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) and sedoheptulose-1,7-diphosphate (SDP) by their respective phosphatase(s) (FDP + SDPase) was rapidly inhibited in the dark but only slowly reactivated in the light. The time required for reactivation of FDP + SDPase, in the light, was on the order of 20 to 30 s. As a consequence of the timing of these inactivation-reactivation reactions, newly fixed CO2 accumulated in the FDP and SDP pools during the flashing-light experiments. Changes in the concentrations of the adenylate pools (mainly in the levels of adenosine 5'-triphosphate and adenosine diphosphate) were fast in comparison to the inactivation-reactivation reactions in the reductive pentose cycle. Thus, these regulatory effects may not be under the control of the adenylates in this organism. The activation of CO2 fixation in the light is at least in part due to activation of phosphoribulokinase, which is required for formation of ribulose-1,5-diphoshate, the carboxylation substrate. Phosphoribulokinase activity in crude extracts was found to be dependent on the presence of strong reducing agents such as dithiothreitol, but not significantly dependent on adenylate levels, although adenosine 5'-triphosphate is a substrate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. E., Avron M. Light Modulation of Enzyme Activity in Chloroplasts: Generation of Membrane-bound Vicinal-Dithiol Groups by Photosynthetic Electron Transport. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):209–213. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E. Regulation of pea leaf ribulose-5-phosphate kinase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 10;321(2):484–488. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avron M., Gibbs M. Properties of phosphoribulokinase of whole chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1974 Feb;53(2):136–139. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Schürmann P., Kalberer P. P. Ferredoxin-activated fructose diphosphatase of spinach chloroplasts. Resolution of the system, properties of the alkaline fructose diphosphatase component, and physiological significance of the ferredoxin-linked activation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5952–5959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. A., Gibson J. Ribulose-5-phosphate kinase from Chromatium sp. strain D. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):308–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90483-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihlenfeldt M. J., Gibson J. CO2 fixation and its regulation in Anacystis nidulans (Synechococcus). Arch Microbiol. 1975;102(1):13–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00428339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latzko E., von Garnier R., Gibbs M. Effect of photosynthesis, photosynthetic inhibitors and oxygen on the activity of ribulose 5-phosphate kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970;39(6):1140–1144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90678-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSES V., LONBERG-HOLM K. K. A semiautomatic device for measuring radioactivity on two-dimensional paper chromatograms. Anal Biochem. 1963 Jan;5:11–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacElroy R. D., Johnson E. J., Johnson M. K. Allosteric regulation of phosphoribulokinase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 27;30(6):678–682. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90566-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacElroy R. D., Johnson E. J., Johnson M. K. Control of ATP-dependent CO2 fixation in extracts of Hydrogenomonas facilis: NADH regulation of phosphoribulokinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Apr;131(1):272–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miginiac-Maslow M., Champigny M. L. Relationship between the Level of Adenine Nucleotides and the Carboxylation Activity of Illuminated Isolated Spinach Chloroplasts: A Study with Antimycin A. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jun;53(6):856–862. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.6.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miović M. L., Gibson J. Nucleotide pools and adenylate energy charge in balanced and unbalanced growth of Chromatium. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):86–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.86-95.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Bassham J. A. Kinetics of glucose incorporation by Aphanocapsa 6714. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):943–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.943-948.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Bassham J. A. Photosynthetic and dark carbon metabolism in unicellular blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;86(1):25–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00412397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Kirk M. R., Bassham J. A. Photosystem II regulation of macromolecule synthesis in the blue-green alga Aphanocapsa 6714. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):623–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.623-632.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Rippka R., Stanier R. Y. Metabolism of glucose by unicellular blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;87(4):303–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00409131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindt K. P., Ohmann E. NADH and AMP as allosteric effectors of ribulose-5-phosphate kinase in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 7;36(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90572-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



