Abstract
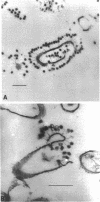
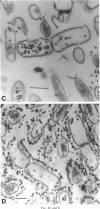
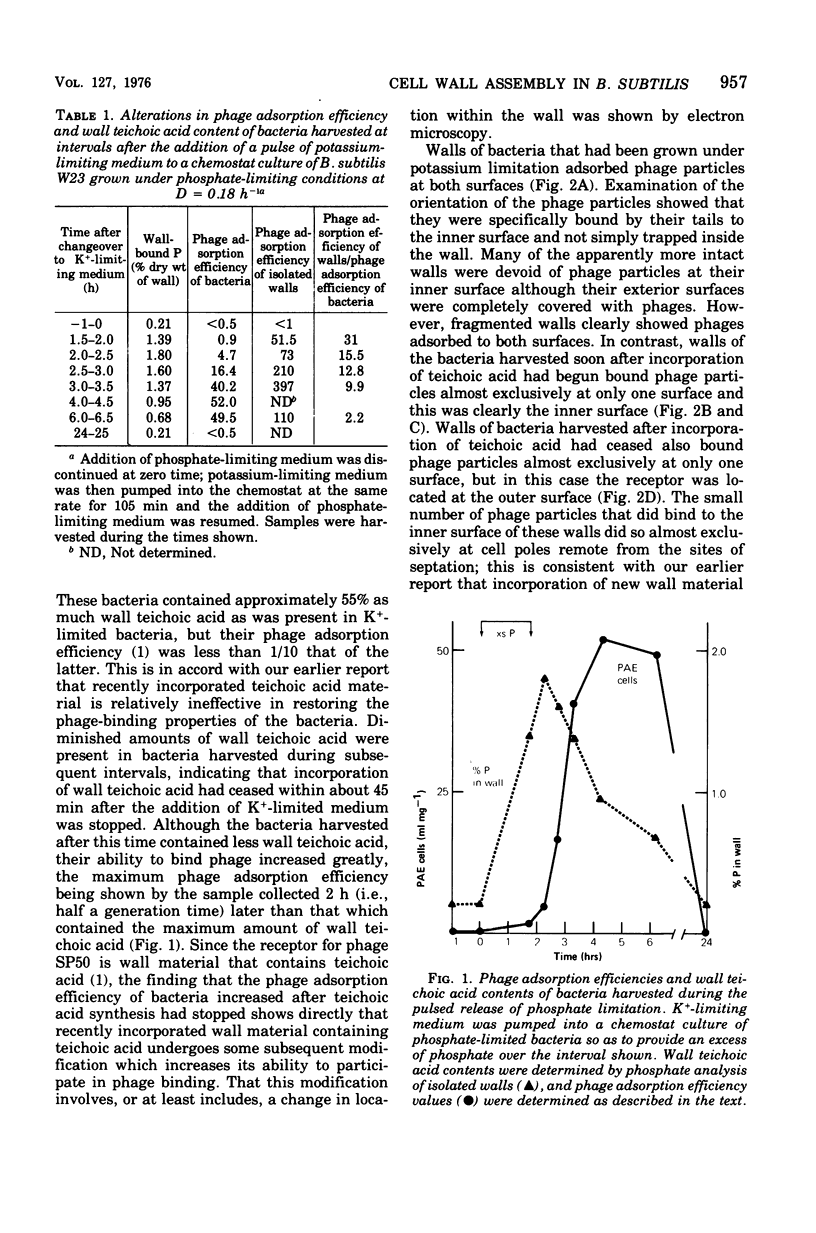
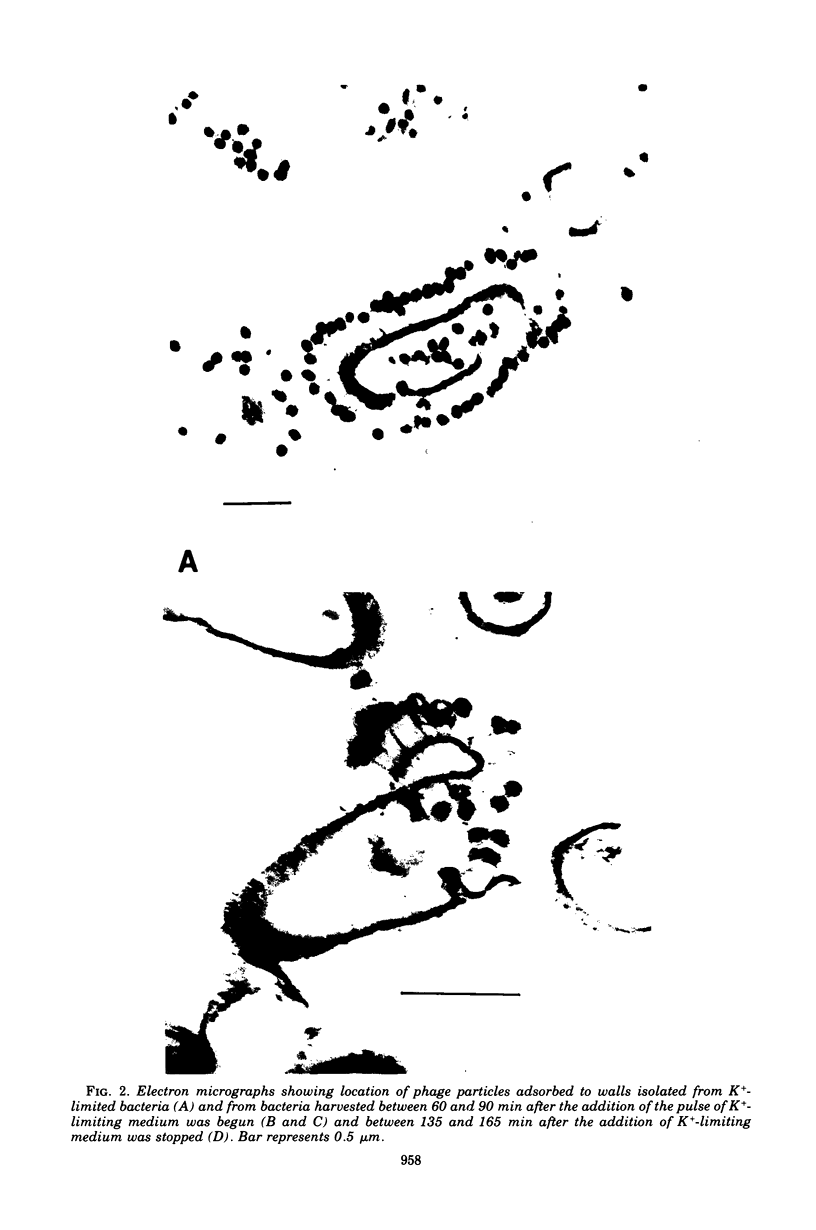
Addition of a pulse of excess phosphate to a phosphate-limited culture of Bacillus subtilis W23 resulted in the synthesis and incorporation of wall material that contained teichoic acid. Consequently, the bacteria regained the ability to bind phage SP50 although maximum phage-binding properties did not develop until approximately half a generation time after incorporation of teichoic acid had ceased. The present findings strongly support our earlier suggestion that newly synthesized receptor material is incorporated at the inner surface of the wall and becomes exposed at the outer surface only during subsequent growth.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. R., Coapes H. E. Bacteriophage SP50 as a marker for cell wall growth in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1195-1206.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P., Beckman B. E., Gardner-Eckstrom H. L. Mode of cell wall synthesis in gram-positive bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1157–1162. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1157-1162.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland J. M., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. An electron microscopic study of the location of teichoic acid and its contribution to staining reactions in walls of Streptococcus faecalis 8191. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):73–86. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Chan L., Glaser L. Turnover of the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1820–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M. Layered distribution, according to age, within the cell wall of bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1139–1147. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1139-1147.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M. Turnover and spreading of old wall during surface growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1127–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1127-1138.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]