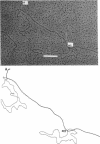
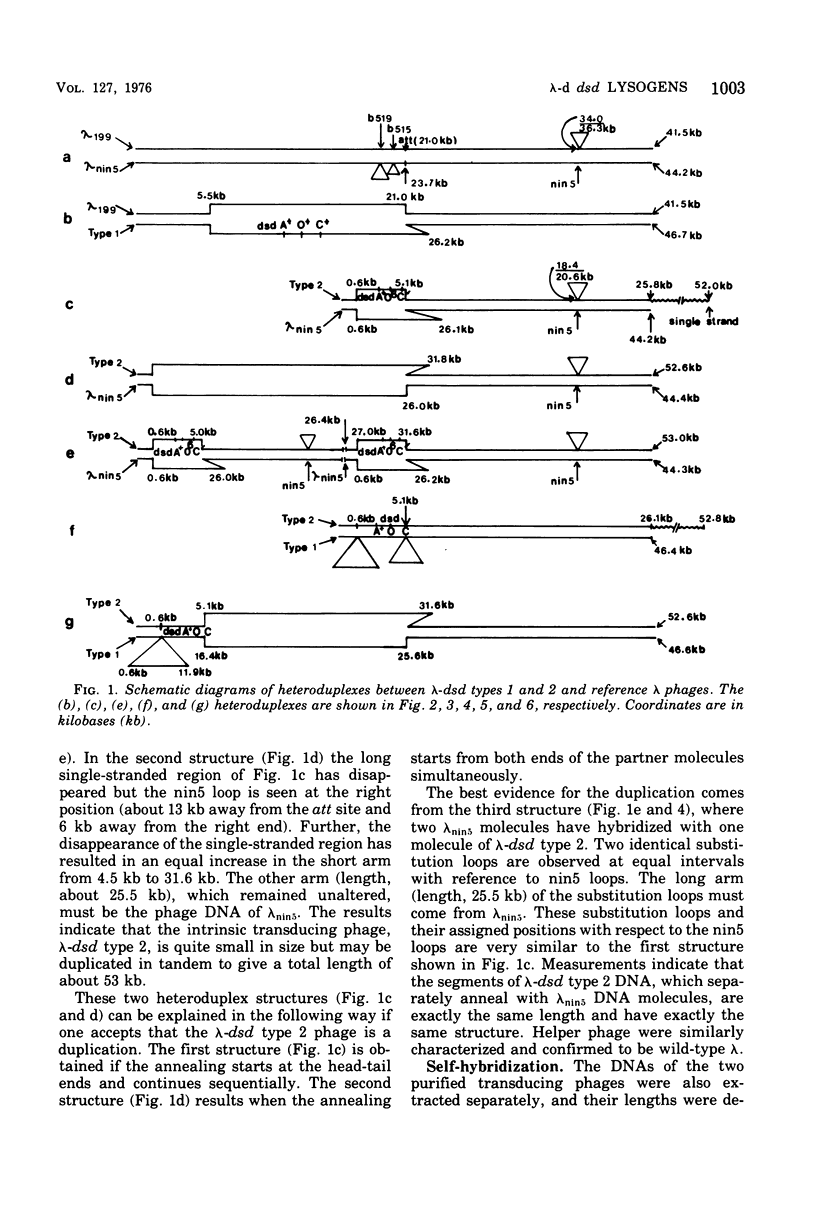
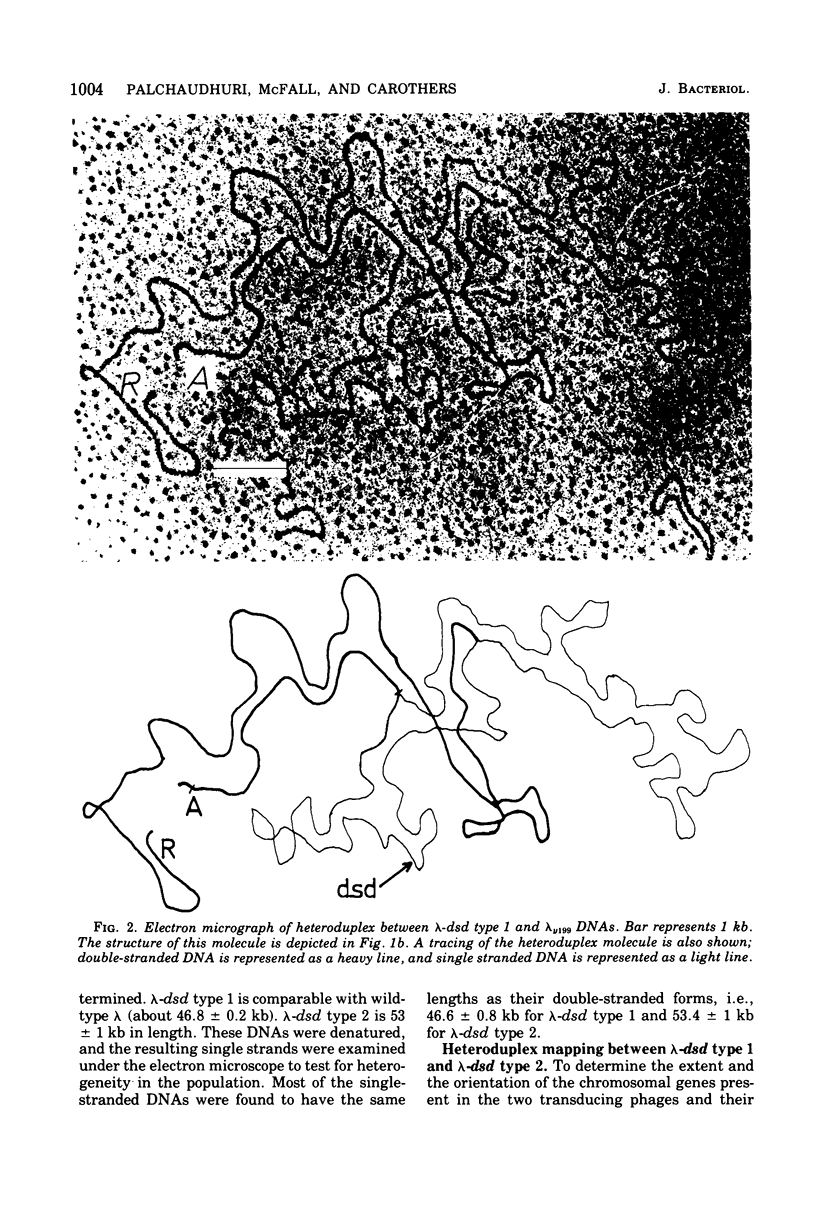
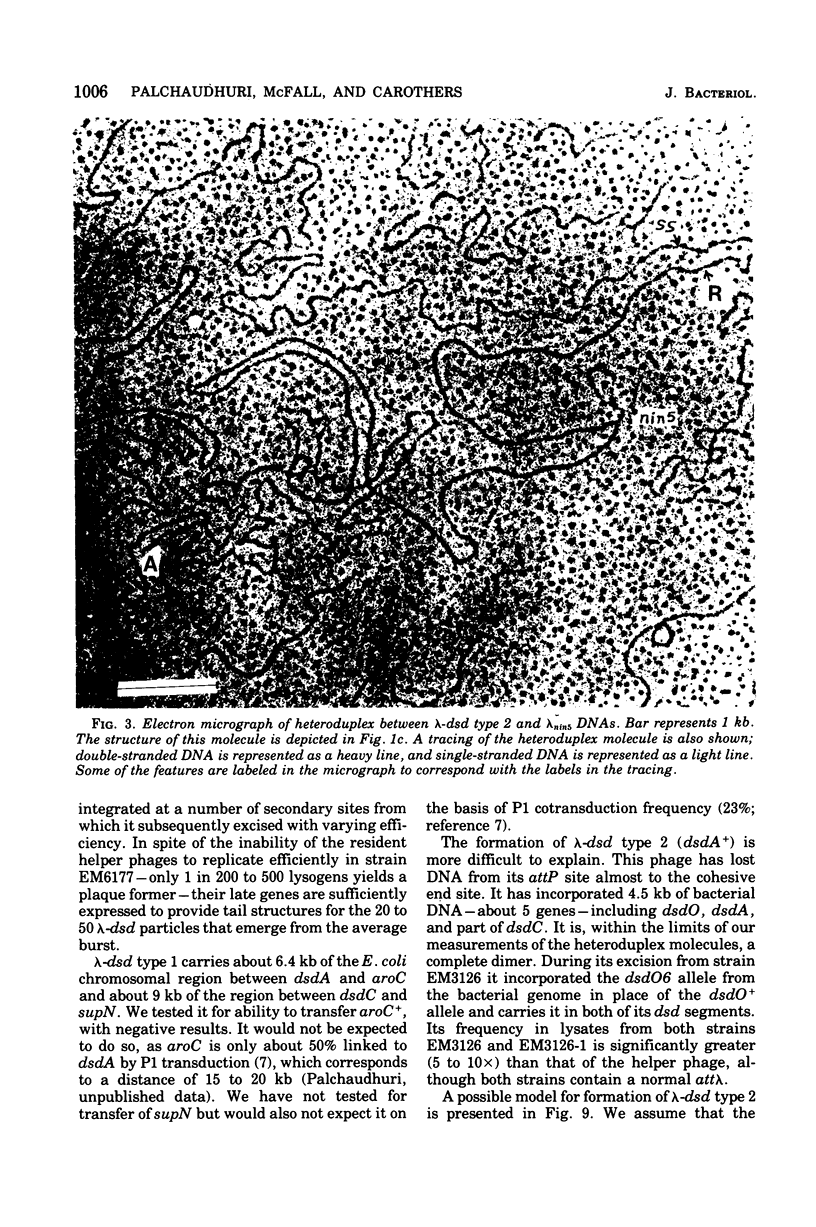
Abstract
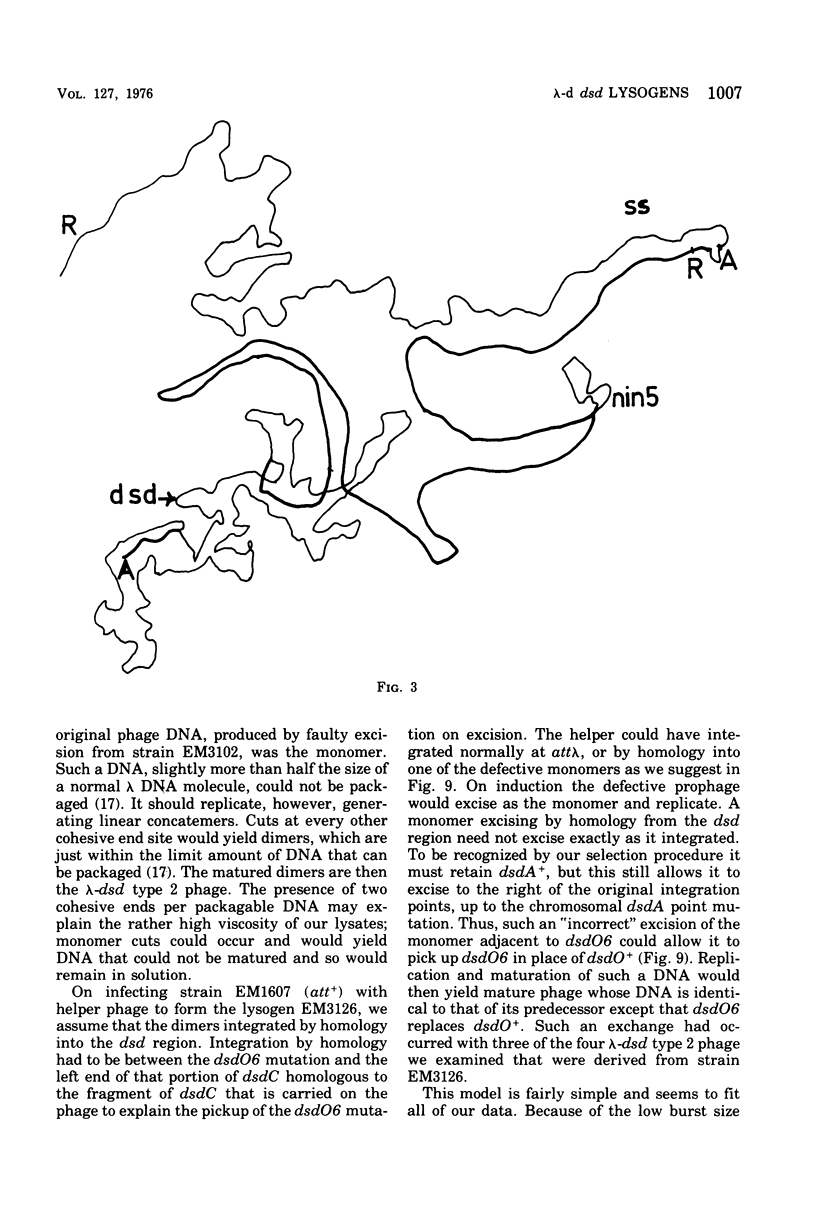
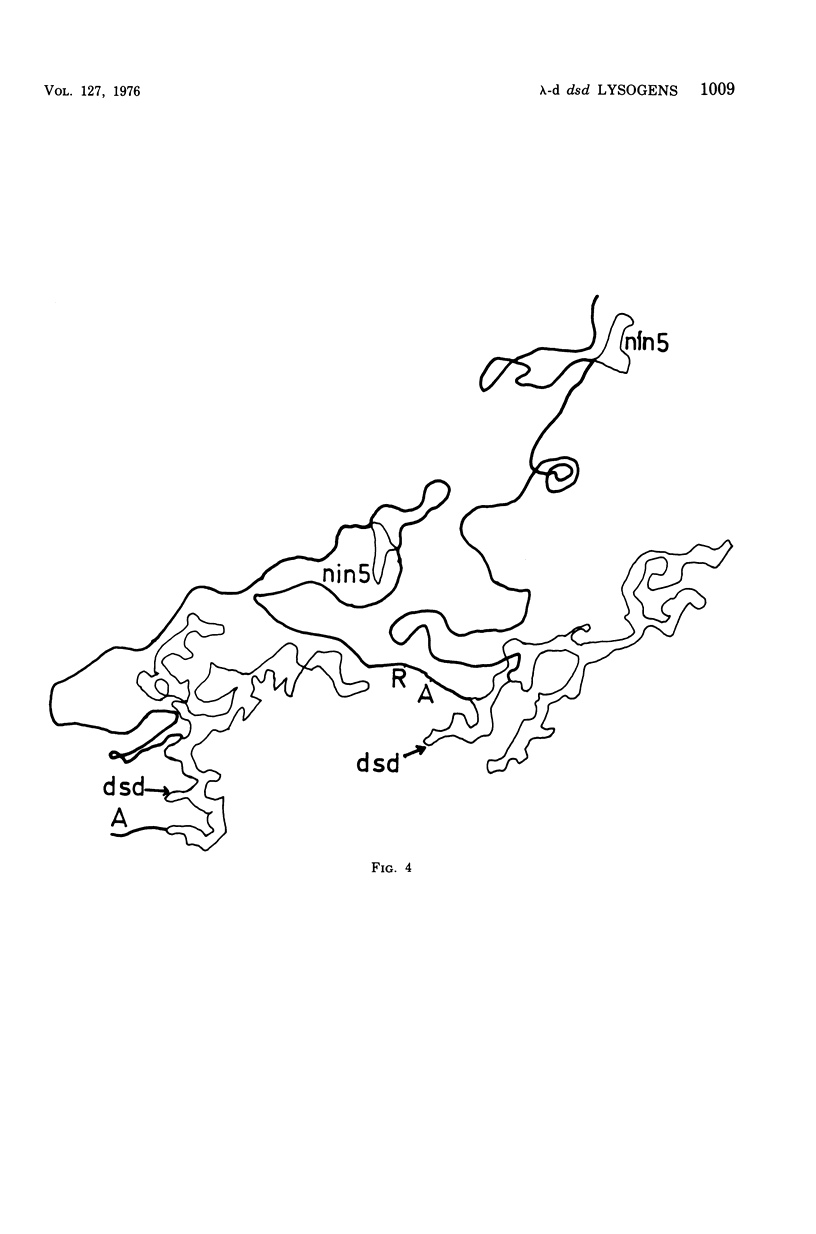
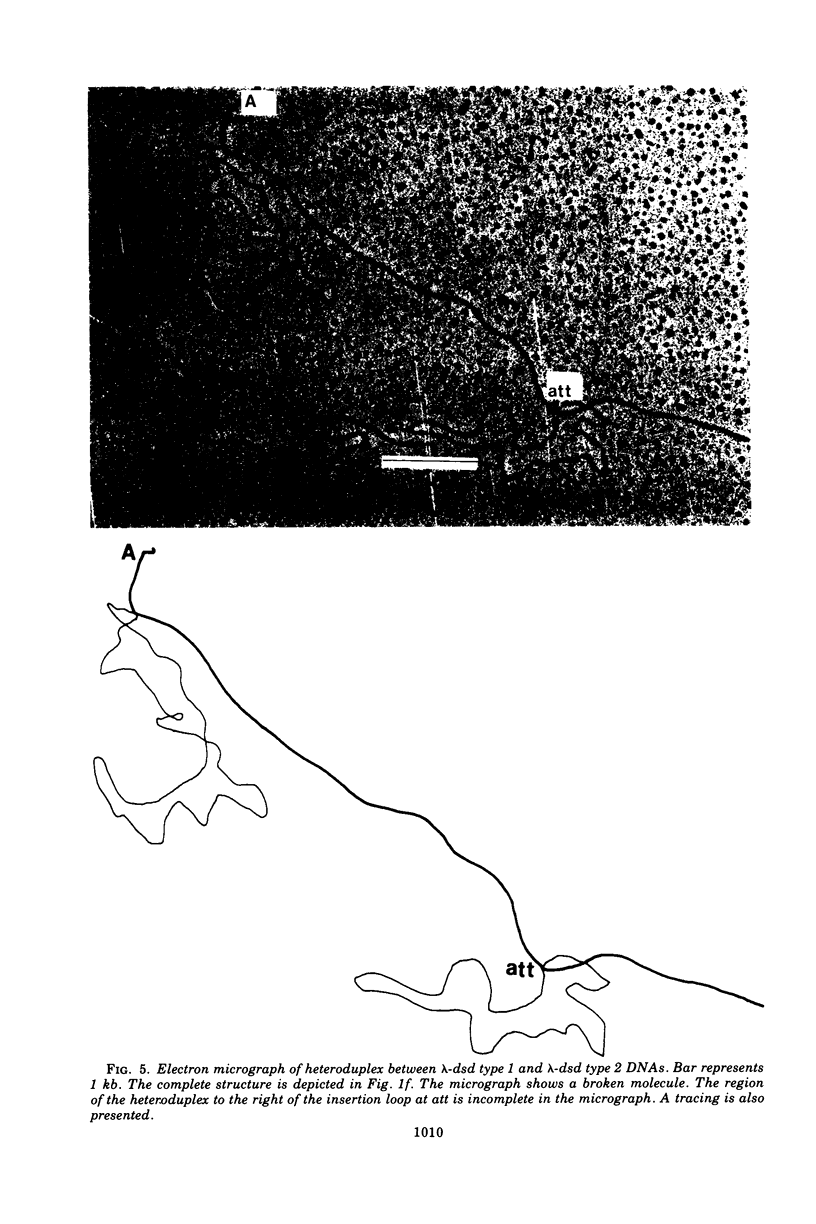
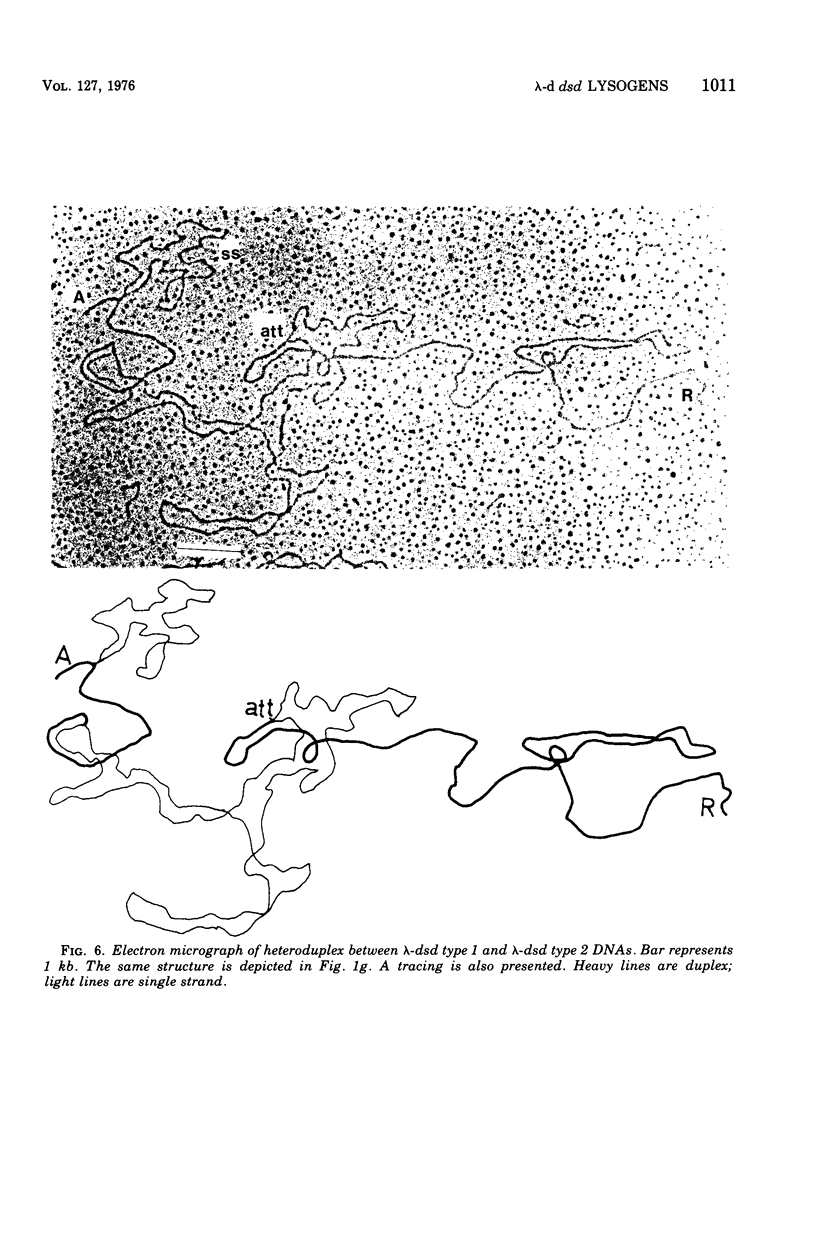
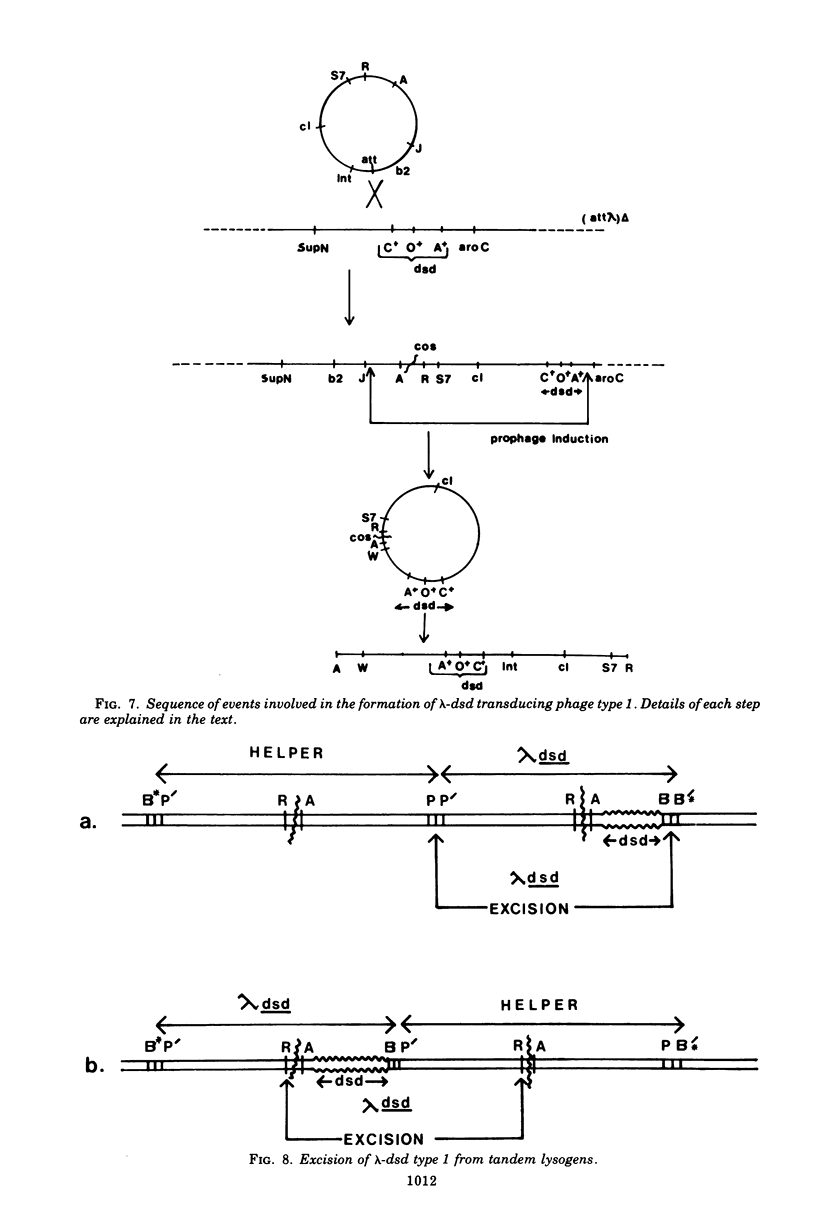
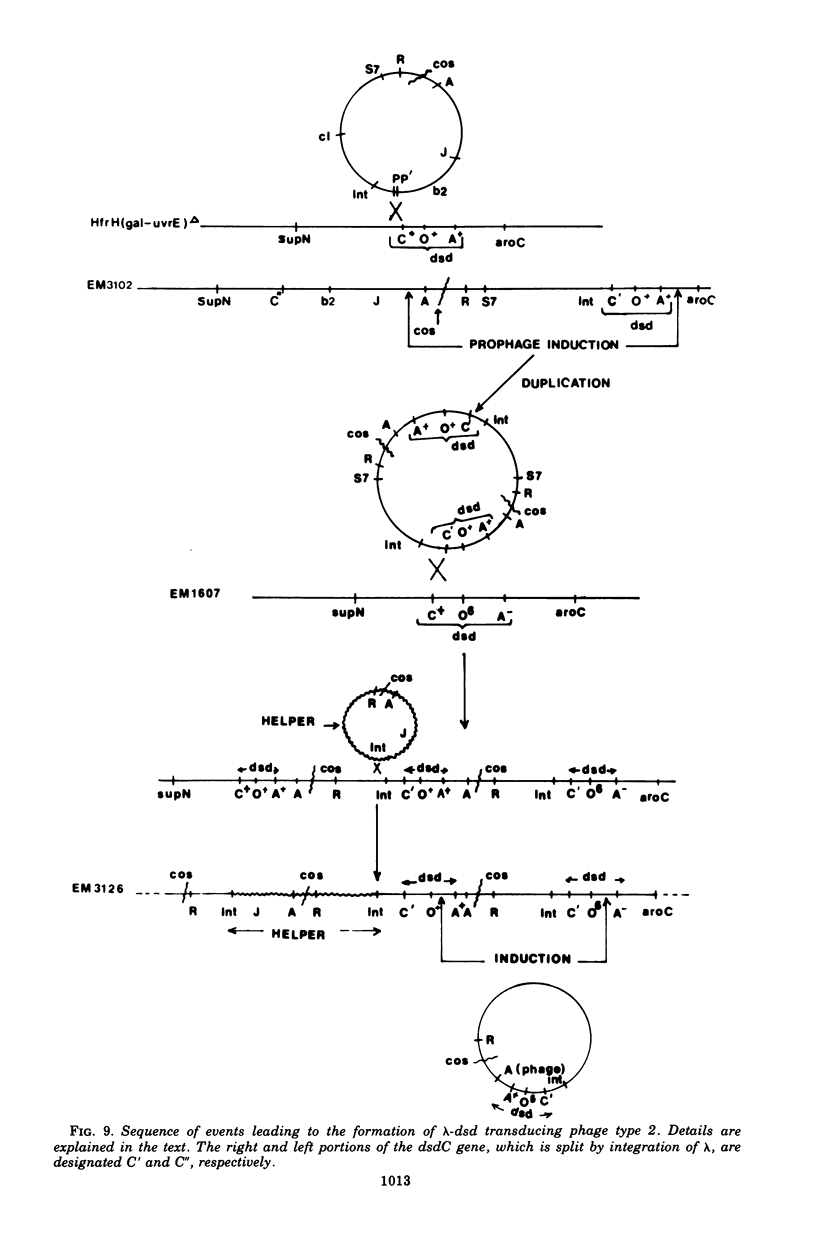
We have obtained two classes of double lysogens that on induction yield higher titers of lambda-d dsd transducing phage than of helper phage. One class was obtained by lysogenization of strain EM6116 (dsddelta attlambdadelta HfrC) with lambda-dsd type 2 (dsdC+ dsdO+ dsdA+, head-tail substitution). In the absence of either a normal attlambda or the homology of a chromosomal dsd region, the transducing phage integrated at other sites, at least one of which, in strain EM6177, is near the origin of HfrC. On induction, strain EM6177 yields a phage burst of 20 to 50 with a lambdadsd:lambda ratio of 10(4):1. The asnychronously high yield of lambda dsd is attributed to an efficiency of excision greater than that of lambda. The other class was obtained by lysogenization of strain EM1407 (dsdA attlambda+) with lambda-dsd type 2 (dsdO6 dsdA, partial deletion of dsdC). The DNA of mature lambda-dsd type 2 is a complete dimer. It lacks nearly all the phage late genes and b2 and carries about five bacterial genes. It could not be packaged as a monomer but is just within the packaging size limit as a dimer. Models for the derivation of these lambda dsd phages and the high-yielding lysogens are presented.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom F. R., McFall E., Young M. C., Carothers A. M. Positive control in the D-serine deaminase system of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1092–1101. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1092-1101.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in tissue cultures: cellular attachment, entry, and survival. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1141–1146. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1141-1146.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KAUFMAN H. Selecting bacterial mutants by the penicillin method. Science. 1960 Feb 26;131(3400):604–605. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3400.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Otsubo E., Deonier R. C., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex studies of sequence relations among plasmids of Escherichia coli. V. ilv+ Deletion mutants of F14. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):585–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall E. Dominance studies with stable merodiploids in the D-serine deaminase system of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1982–1988. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1982-1988.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall E. Escherichia coli K-12 mutant forming a temperature-sensitive D-serine deaminase. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1074–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1074-1077.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall E. Mapping of the d-serine deaminase region in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1967 Jan;55(1):91–99. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palchoudhury S. R., Iyer V. N. Compatibility between two F' factors in an Escherichia coli strain bearing a chromosomal mutation affecting DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):319–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90349-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press R., Glansdorff N., Miner P., De Vries J., Kadner R., Maas W. K. Isolation of transducing particles of phi-80 bacteriophage that carry different regions of the Escherichia coli genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):795–798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrenk W. J., Weisberg R. A. A simple method for making new transducing lines of coliphage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;137(2):101–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00341676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Hsu M. T., Otsubo E., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex studies of sequence relations among plasmids of Escherichia coli. I. Structure of F-prime factors. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):471–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Prophage lambda at unusual chromosomal locations. I. Location of the secondary attachment sites and the properties of the lysogens. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):483–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Prophage lambda at unusual chromosomal locations. II. Mutations induced by bacteriophage lambda in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):297–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Weisberg R. Packaging of prophage and host DNA by coliphage lambda. Nature. 1975 Jul 10;256(5513):97–103. doi: 10.1038/256097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]