Abstract
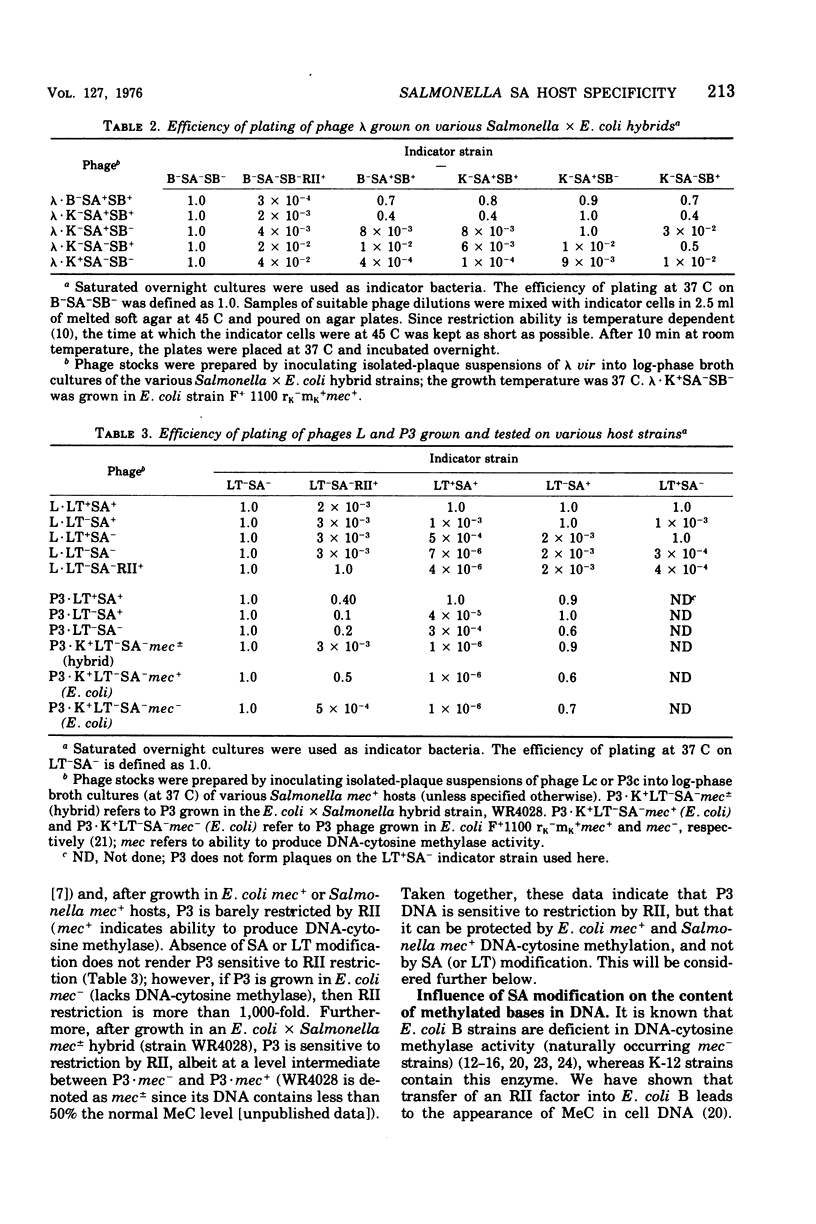
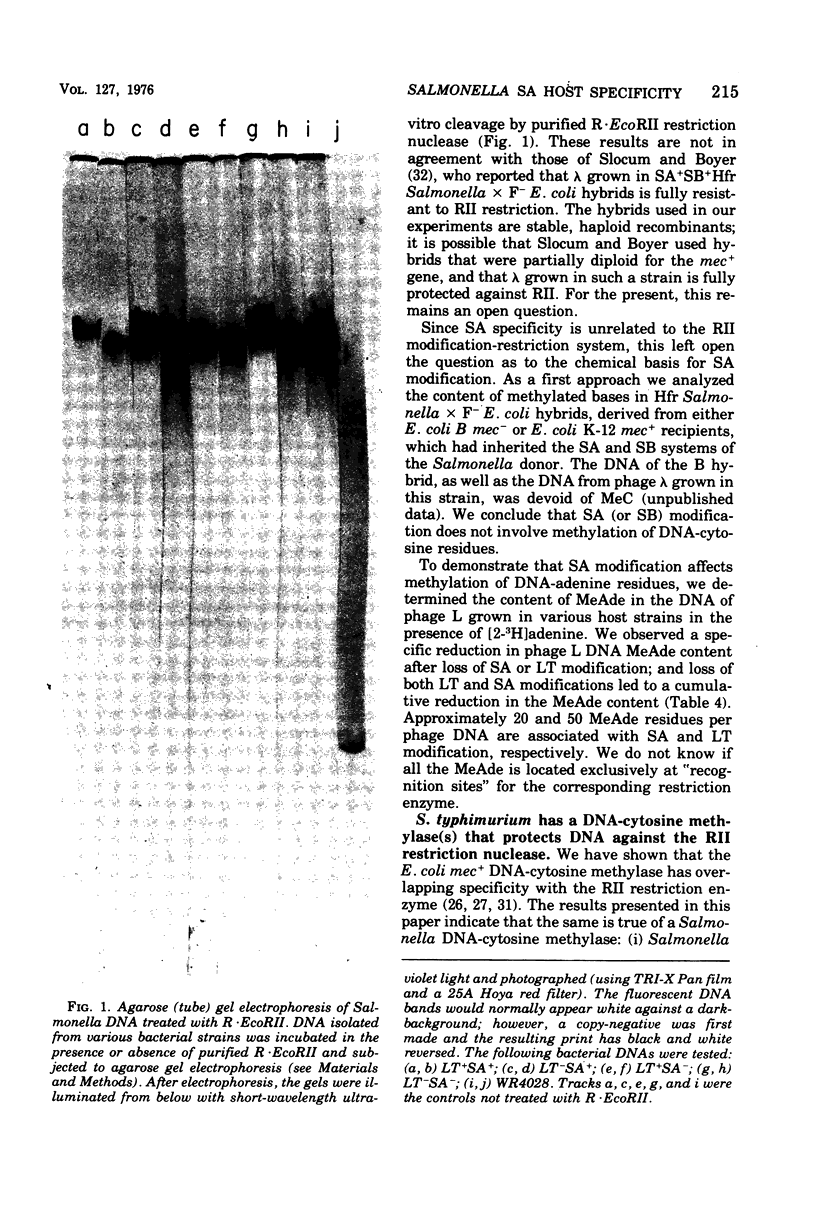
We have determined the nature of the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) modification governed by the SA host specificity system of Salmonella typhimurium. Two lines of evidence indicate that SA modification is based on methylation of DNA-adenine residues. (i) The SA+ locus of Salmonella was transferred into Escherichia coli B, a strain that does not contain 5-methylcytosine in its DNA; although the hybrid strain was able to confer SA modification, its DNA still did not contain 5-methylcytosine. (ii) the N6-methyladenine content of phage L DNA was measured after growth in various host strains; phage lacking SA modification contained fewer N6-methyladenine residues per DNA. We also investigated the possibility, suggested by others (32), that SA modification protects phage DNA against restriction by the RII host specificity system. Phages lambda, P3, and L were grown in various SA+ and SA- hosts and tested for their relative plating ability on strains containing or lacking RII restriction; the presence or absence of SA modification had no effect on RII restriation. In vitro studies revealed, however, that Salmonella DNA is protected against cleavage by purified RII restriction endonuclease (R-EcoRII). This protection is not dependent on SA modification; rather, it appears to be due to methylation by a DNA-cytosine methylase which has overlapping specificity with the RII modification enzyme, but which is not involved in any other known host specificity system.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber W. DNA modification and restriction. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1974;14(0):1–37. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arber W., Linn S. DNA modification and restriction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:467–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezdek M., Amati P. Properties of P22 and A related Salmonella typhimurium phage. I. General features and host specificity. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Chow L. T., Dugaiczyk A., Hedgpeth J., Goodman H. M. DNA substrate site for the EcoRII restriction endonuclease and modification methylase. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):40–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio244040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W. DNA restriction and modification mechanisms in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:153–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W. Restriction and modification of DNA: enzymes and substrates. Introductory remarks. Fed Proc. 1974 May;33(5):1125–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullas L. R., Colson C. DNA restriction and modification systems in Salmonella. III. SP, a Salmonella potsdam system allelic to the SB system in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Aug 27;139(3):177–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colson A. M., Colson C., Van Pel A. Host-controlled restriction mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Sep;58(1):57–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colson C., Colson A. M. A new Salmonella typhimurium DNA host specificity. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(3):345–351. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-3-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colson C., Colson A. M., Van Pel A. Chromosomal location of host specificity in Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):265–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colson C., Van Pel A. DNA restriction and modification systems in Salmonella. I. SA and SB, two Salmonella typhimurium systems determined by genes with a chromosomal location comparable to that of the Escherichia coli hsd genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Apr 3;129(4):325–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00265696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOSKOCIL J., SORMO'VA Z. THE OCCURRENCE OF 5-METHYLCYTOSINE IN BACTERIAL DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 15;95:513–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doskocil J., Sormová Z. The sequences of 5-methylcytosine in the DNA of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 26;20(3):334–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D., Srinivasan P. R., Borek E. On the nature of the deoxyribonucleic acid methylases. Biological evidence for the multiple nature of the enzymes. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2849–2855. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Baron L. S., Yamamoto N. Formation of hybrids between coliphage lambda and Salmonella phage P22 with a Salmonella typhimurium hybrid sensitive to these phages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3110–3114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough M., Lederberg S. Methylated bases in the host-modified deoxyribonucleic acid of Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1460-1468.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S. DNA methylation of T-even bacteriophages and of their nonglucosylated mutants: its role in P1-directed restriction. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Gold E., Plotnik A. Methylation of cytosine residues in DNA controlled by a drug resistance factor (host-induced modification-R factors-N 6 -methyladenine-5-methylcytosine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):187–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S. Plasmid-controlled variation in the content of methylated bases in bacteriophage lambda deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):356–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.356-361.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Schlagman S., Cousens L. Isolation of a mutant of Escherichia coli defective in cytosine-specific deoxyribonucleic acid methylase activity and in partial protection of bacteriophage lambda against restriction by cells containing the N-3 drug-resistance factor. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1103–1107. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1103-1107.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S. Variation of 6-methylaminopurine content in bacteriophage P22 deoxyribonucleic acid as a function of host specificity. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):690–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.690-691.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. G. The sensitivity of bacteriophage lambda DNA to restriction endonuclease RII. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):645–647. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg S. 5-Methylcytosine in the host-modified DNA of Escherichia coli and phage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):293–297. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamelak L., Boyer H. W. Genetic control of the secondary modification of deoxyribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):57–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.57-62.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G., Morris N. R. Isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid methylase mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1143–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1143-1150.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M. S., Hattaman S. Deoxyribonucleic acid-cytosine methylation by host- and plasmid-controlled enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):129–138. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.129-138.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M. S., Hattman S. Analysis of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid sequences methylated by host- and R-factor-controlled enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):768–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.768-770.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Yuan R., Heywood J. Restriction and modification of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:447–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutter R. L., Bullas L. R., Schultz R. L. Some properties of five new Salmonella bacteriophages. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):754–764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.754-764.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlagman S., Hattman S., May M. S., Berger L. In vivo methylation by Escherichia coli K-12 mec+ deoxyribonucleic acid-cytosine methylase protects against in vitro cleavage by the RII restriction endonuclease (R. Eco RII). J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):990–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.990-996.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlagman S., Hattman S. Mutants of the N-3 R-factor conditionally defective in hspII modification and deoxyribonucleic acid-cytosine methylase activity. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):234–239. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.234-239.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slocum H., Boyer H. W. Host specificity of Salmonella typhimurium deoxyribonucleic acid restriction and modification. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):724–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.724-726.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel A., Colson C. DNA restriction and modification systems in Salmonella. II. Genetic complementation between the K and B systems of Escherichia coli and the Salmonella typhimurium system SB, with the same chromosomal location. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;135(1):51–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00433901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




