Abstract
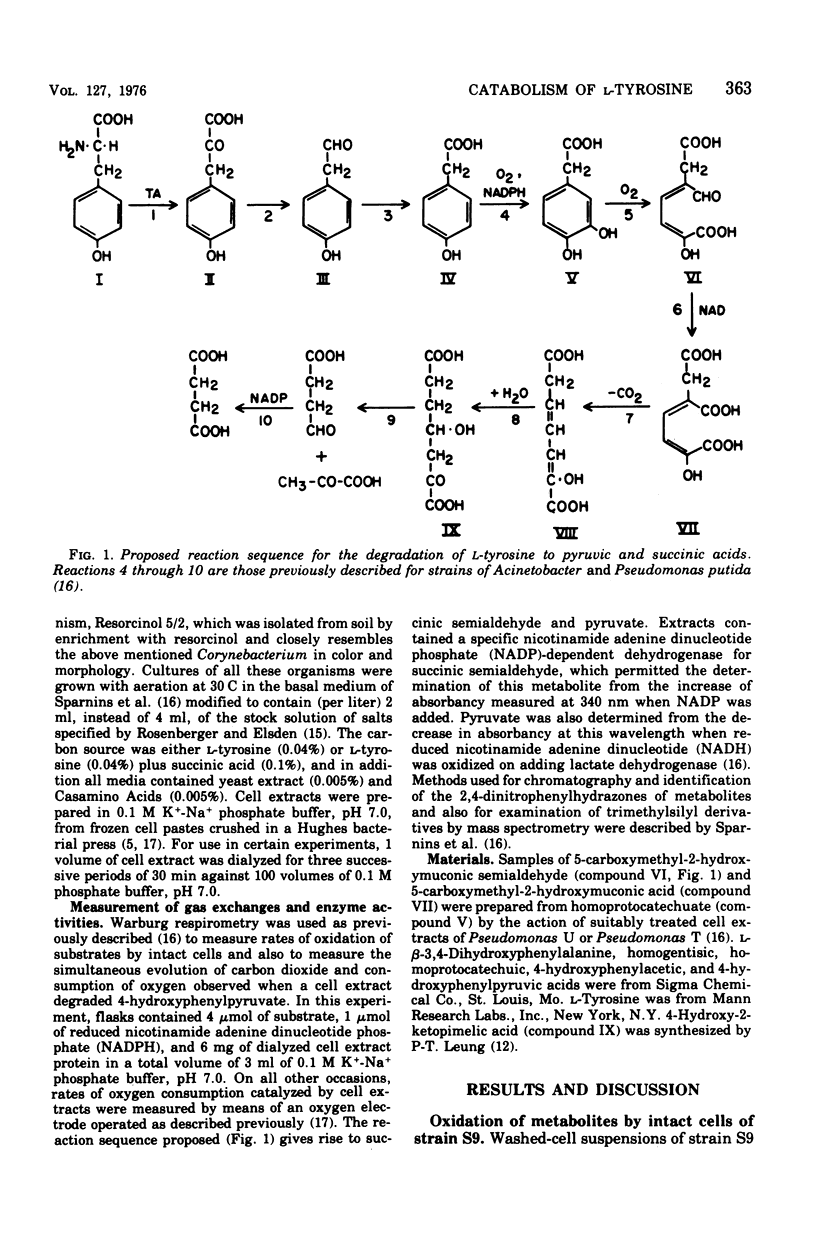
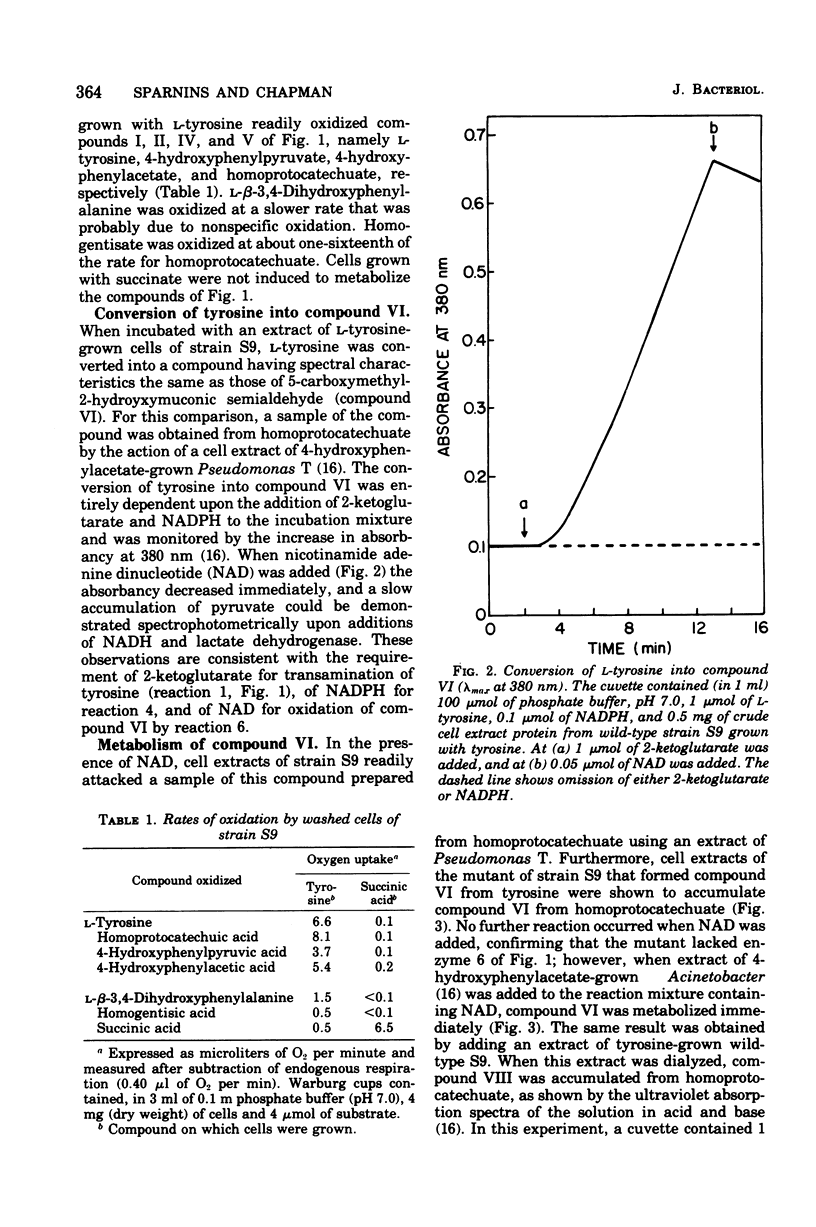
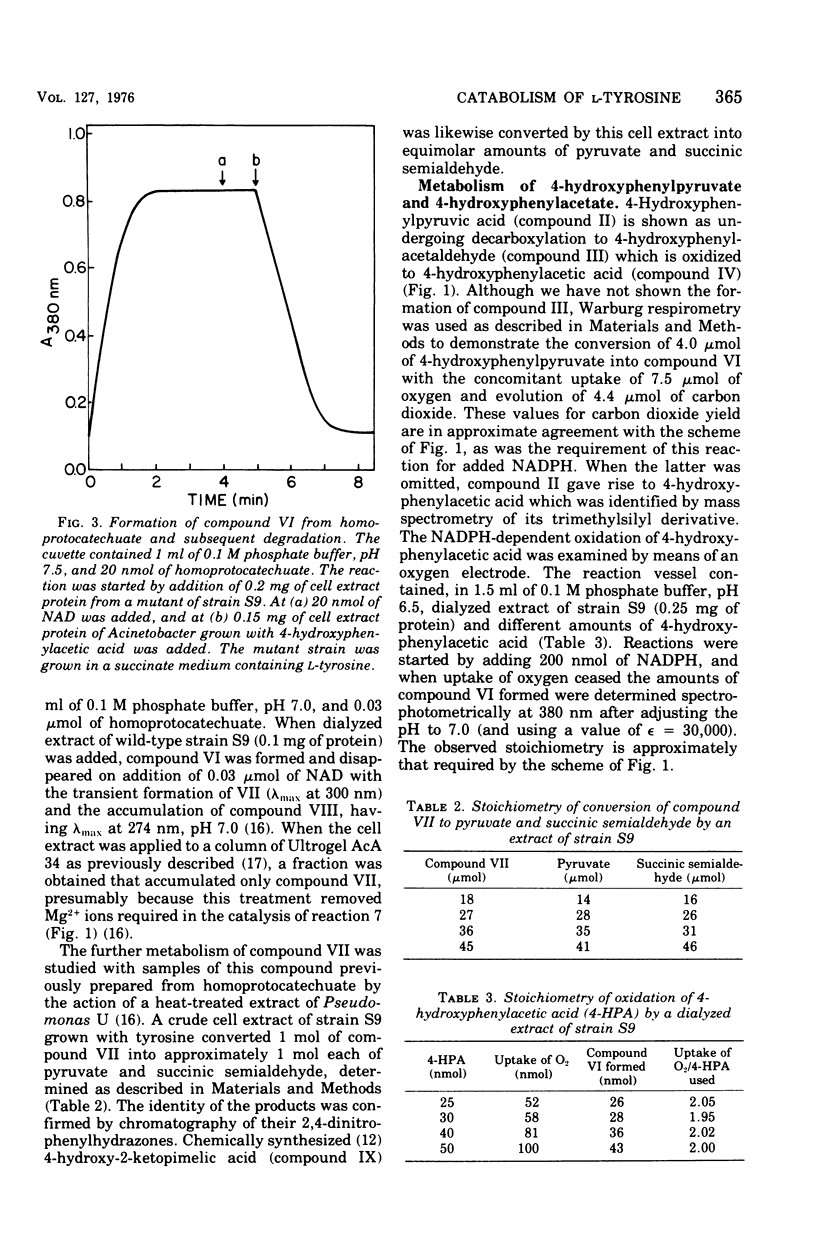
A metabolic pathway for L-tyrosine catabolism involves 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (homoprotocatechuic acid) as substrate for fission of the benzene nucleus. Cell extracts of an organism tentatively identified as a Micrococcus possessed the enzymes required for degrading homoprotocatechuate to succinate and pyruvate, and stoichiometry was established for several of these reactions. When the required coenzymes were added, cell extracts degraded L-tyrosine to the ring-fission product of homoprotocatechuate 2,3-dioxygenase and also converted 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid into 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid. This compound, in turn, gave stoichiometric amounts of the ring-fission product of homoprotocatechuate by the action of a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent 3-hydroxylase coupled with homoprotocatechuate 2,3-dioxygenase. Evidence is presented that this route for L-tyrosine catabolism is taken by five other gram-positive strains, including Micrococcus lysodeikticus and a species of Bacillus. Five other gram-positive bacteria from other genera employed the alternative homogentisate pathway.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi K., Iwayama Y., Tanioka H., Takeda Y. Purification and properties of homogentisate oxygenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 12;118(1):88–97. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi T., Murooka Y., Harada T. Derepression of arylsulfatase synthesis in Aerobacter aerogenes by tyramine. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.19-24.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN P. J., DAGLEY S. Oxidation of homogentistic acid by cell-free extracts of a vibrio. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jun;28:251–256. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., GIBSON D. T. THE BACTERIAL DEGRADATION OF CATECHOL. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0950466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi N. A., Kutty R. K., Vasantharajan V. N., Subba RAO P. V. Microbial metabolism of phenolic amines: degradation of dl-synephrine by an unidentified arthrobacter. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):866–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.866-873.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hareland W. A., Crawford R. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Metabolic function and properties of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 1-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):272–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.272-285.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Enzymic formation of D-malate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):798–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1100798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Metabolism of l-Malate and d-Malate by a Species of Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1197–1202. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1197-1202.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. The enzymic degradation of alkyl-substituted gentisates, maleates and malates. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):29–40. doi: 10.1042/bj1220029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung P. T., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Purification and properties of 4-hydroxy-2-ketopimelate aldolase from Acinetobacter. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):168–172. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.168-172.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris D. B., Trudgill P. W. The metabolism of cyclohexanol by Nocardia globerula CL1. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):363–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1210363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG E., HOLMES P. OXIDATION OF SECONDARY ALCOHOLS BY EXTRACTS OF A CORYNEBACTERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1212–1216. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1212-1216.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERGER R. F., ELSDEN S. R. The yields of Streptococcus faecalis grown in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:726–739. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparnins V. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Bacterial degradation of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and homoprotocatechuic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.159-167.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparnins V. L., Dagley S. Alternative routes of aromatic catabolism in Pseudomonas acidovorans and Pseudomonas putida: gallic acid as a substrate and inhibitor of dioxygenases. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1374–1381. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1374-1381.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


