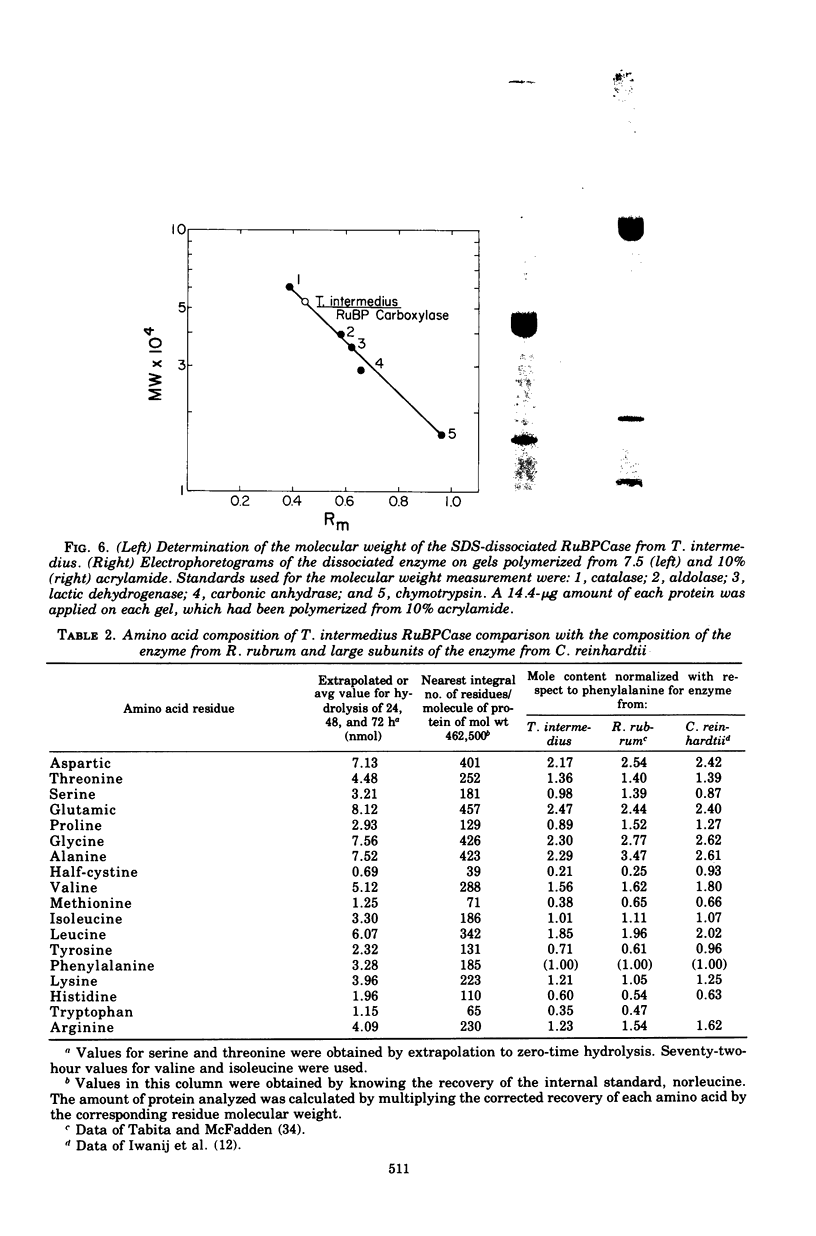
Abstract
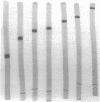
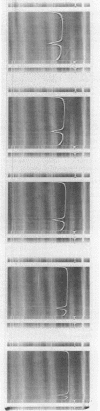
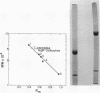
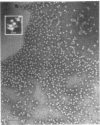
D-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) carboxylase has been purified from glutamate-CO2-S2O3(2)-grown Thiobacillus intermedius by pelleting the enzyme from the high-speed supernatant and by intermediary crystallization followed by sedimentation into a discontinuous 0.2 to 0.8 M sucrose gradient. The enzyme was homogeneous by the criteria of electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels of several acrylamide concentrations, sedimentation velocity and equilibrium measurements, and electron microscopic observations of negatively stained preparations. The molecular weights of the enzyme determined by sedimentation equilibrium and light-scattering measurements averaged 462,500 +/- 13,000. The enzyme consisted of closely similar or identical polypeptide chains of a molecular weight of 54,500 +/- 5,450 determined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. The S(0)20,w of the enzyme was 18.07S +/- 0.22. Electron microscopic examination suggested that the octomeric enzyme (inferred from the molecular measurements mentioned) had a cubical structure. The specific activity of the enzyme was 2.76 mumol of RuBP-dependent CO2 fixed/min per mg of protein (at pH 8 and 30 C), and the turnover number in terms of moles of CO2 fixed per mole of catalytic site per second was 2.6. The enzyme was stable for 3 months at -20 C and at least 4 weeks at 0 C. The apparent Km for CO2 was 0.75 mM, and Km values for RuBP and Mg2+ were 0.076 and 3.6 mM, respectively. Dialyzed enzyme could be fully reactivated by the addition of 20 mM Mg2+ and partially reactivated by 20 mM Co2+, but Cd2+, Mn2+, Ca2+, and Zn2+ had no effect. The compound 6-phosphogluconate was a linear competitive inhibitor with respect to RuBP when it had been preincubated with enzyme, Mg2+, and HCO3-.
Full text
PDF


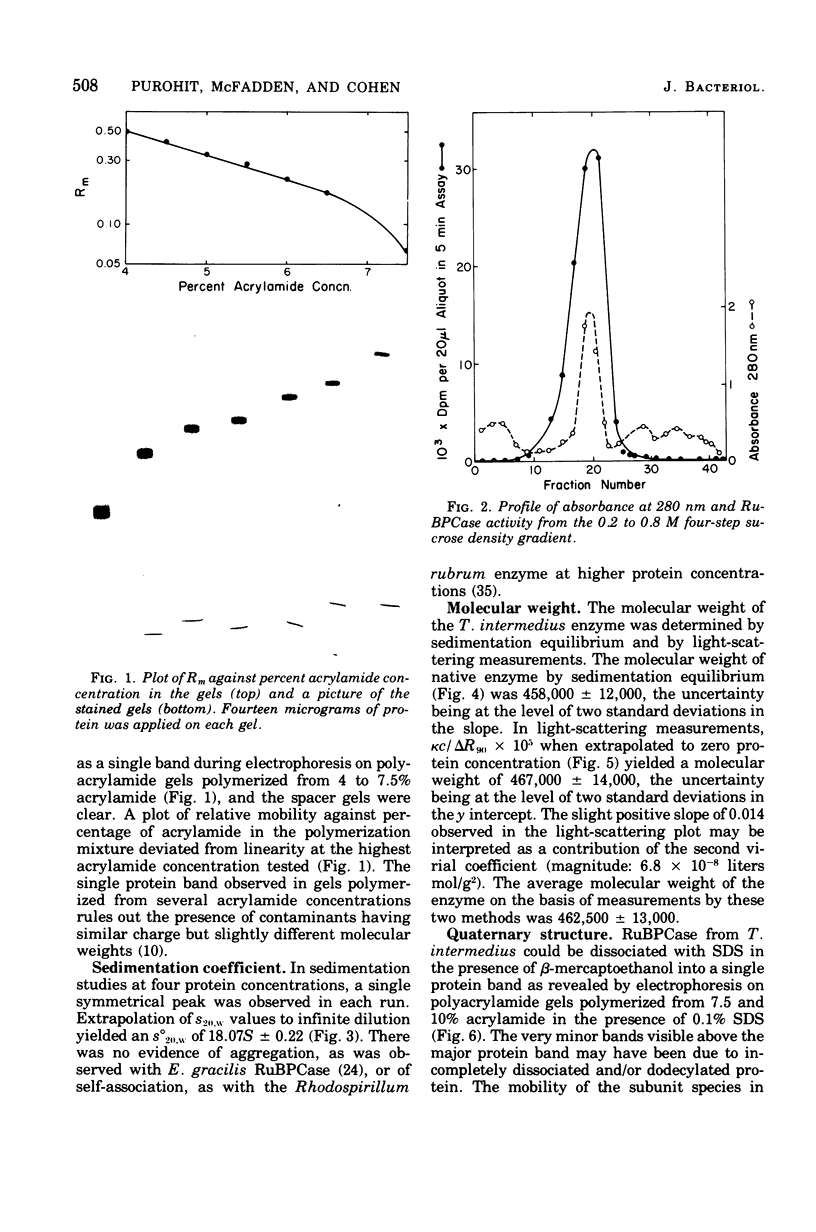
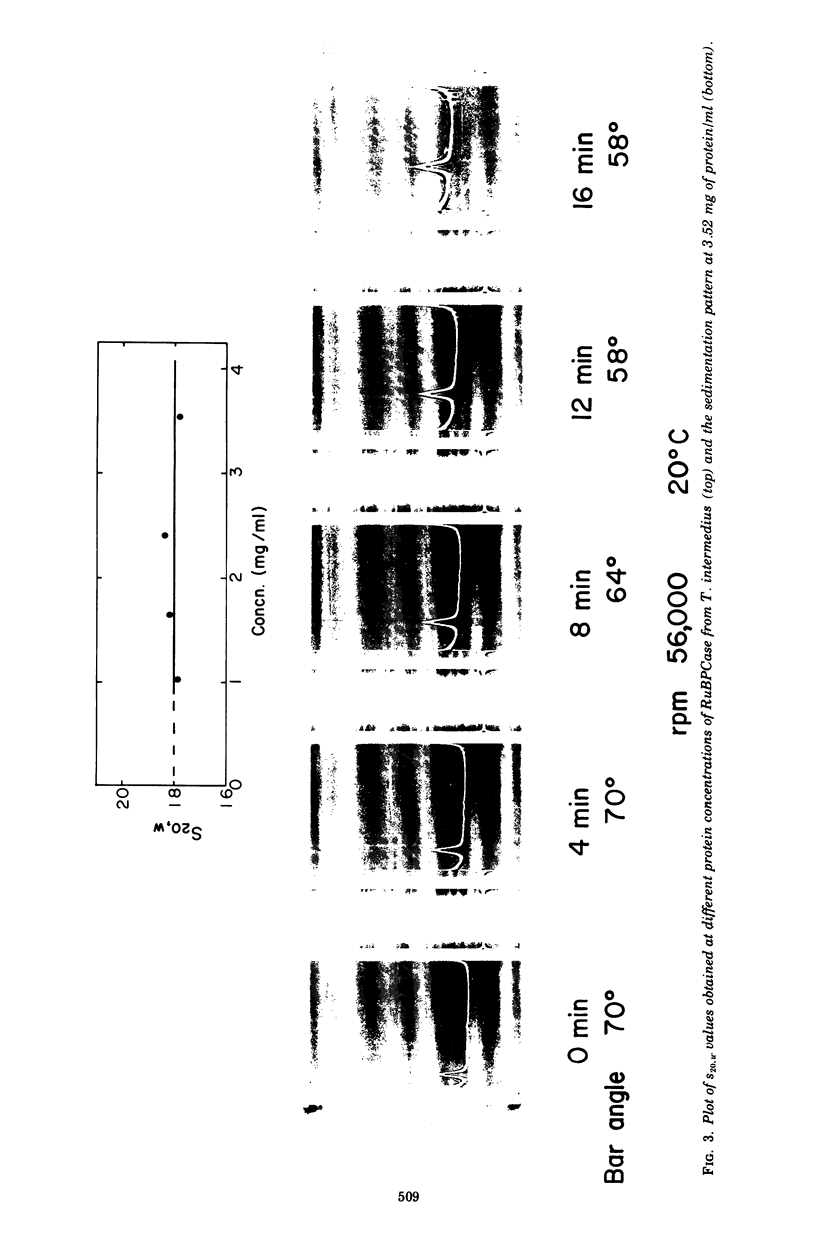
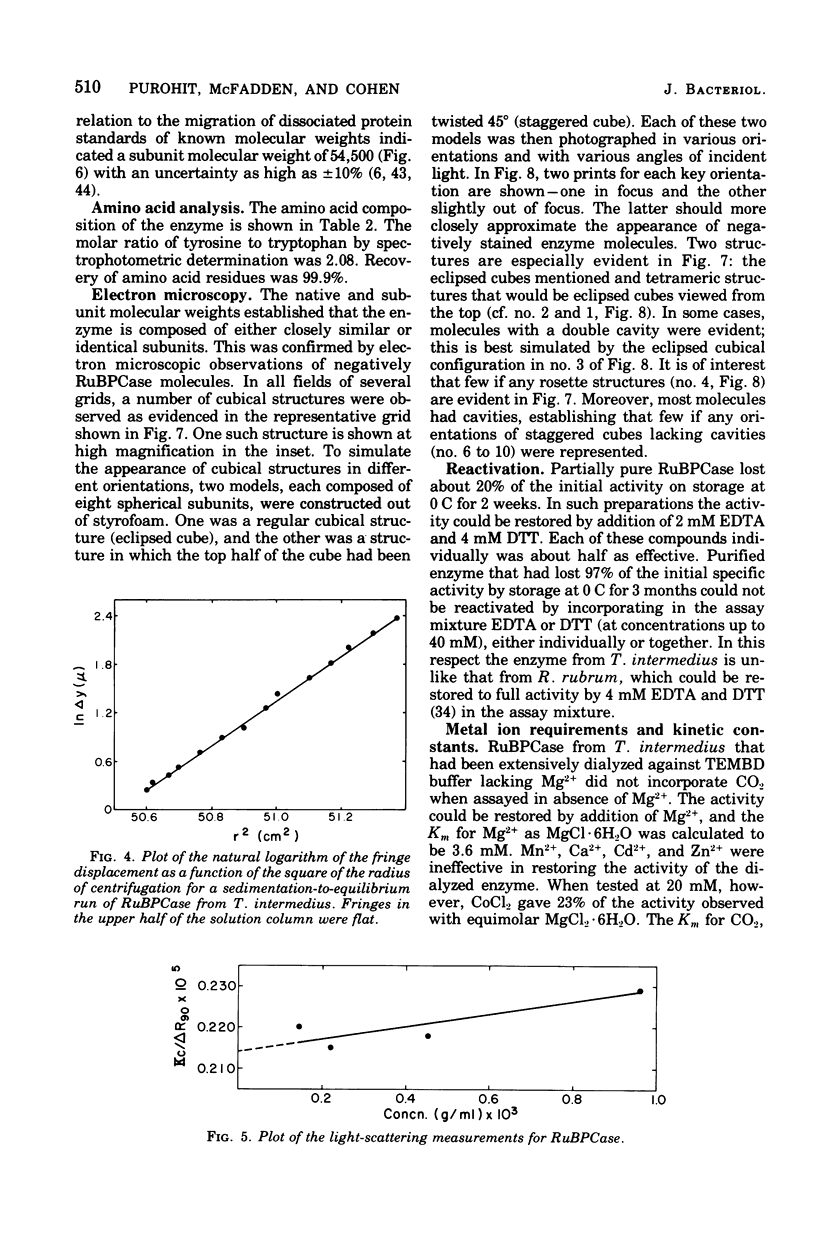



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleem M. I., Huang E. Carbon dioxide fixation and carboxydismutase in Thiobacillus novellus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90610-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. II. Inhibition: nomenclature and theory. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:173–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91815-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Activation and inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):373–379. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Filmer D. The active species of "CO2" utilized by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1081–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite J. J., Bogorad L. A one-step method for the isolation and determination of leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1971 May;41(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn G. D., McFadden B. A. Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha and Hydrogenomonas facilis. I. Purification, metallic ion requirements, inhibition, and kinetic constants. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2394–2402. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn G. D., McFadden B. A. Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha and Hydrogenomonas facilis. II. Molecular weight, subunits, composition, and sulfhydryl groups. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2403–2408. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J., Rittenberg S. C. Effects of organic matter on the growth of Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1062–1069. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1062-1069.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacElroy R. D., Johnson E. J., Johnson M. K. Characterization of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase and phosphoribulokinase from Thiobacillus thioparus and Thiobacillus neapolitanus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):310–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. T., Charles A. M. Properties and regulation of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus novellus. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Sep 30;105(1):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00447113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. T., Charles A. M. Purification and purine nucleotide regulation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus novellus. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):329–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A. Autotrophic CO2 assimilation and the evolution of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):289–319. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.289-319.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Denend A. R. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from autotrophic microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):633–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.633-642.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Lord J. M., Rowe A., Dilks S. Composition, quaternary structure, and catalytic properties of D-ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Euglena gracilis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):195–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R. D-ribulose-1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase and the evolution of autotrophy. Biosystems. 1974 Oct;6(2):93–112. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(74)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R., Kuehn G. D. Ribulose-diphosphate carboxylase from the hydrogen bacteria and Rhodospirillum rubrum. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:461–472. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A., Shaykh M. M. D-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and polyhedral inclusion bodies in Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):516–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.516-522.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao G. S., Berger L. R. Basis of pyruvate inhibition in Thiobacillus thiooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):462–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.462-466.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTER M., VISHNIAC W. CO2 incorporation by extracts of Thiobacillus thioparus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Sep;18(1):157–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI I., WERKMAN C. H. Chemoautotrophic carbon dioxide fixation by extracts of Thiobacillus thiooxidans. I. Formation of oxalacetic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Jul;76(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel M. I., Lane M. D. Chemical and enzymatic evidence for the participation of a 2-carboxy-3-ketoribitol-1,5-diphosphate intermediate in the carboxylation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5486–5498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. I. Levels, purification, and effects of metallic ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3453–3458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Quaternary structure, composition, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3459–3464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. One-step isolation of microbial ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(3):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00696237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A., Pfennig N. D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum Tassajara. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 21;341(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Regulation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phospho-D-gluconate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Stevens S. E., Jr, Gibson J. L. Carbon dioxide assimilation in blue-green algae: initial studies on the structure of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.531-539.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita R. F., Stevens S. E., Jr, Quijano R. D-ribulose 1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase from blue-green algae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. F., Hoare D. S. Thiobacillus denitrificans as an obligate chemolithotroph. II. Cell suspension and enzymic studies. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;80(3):262–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00410127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]