Abstract
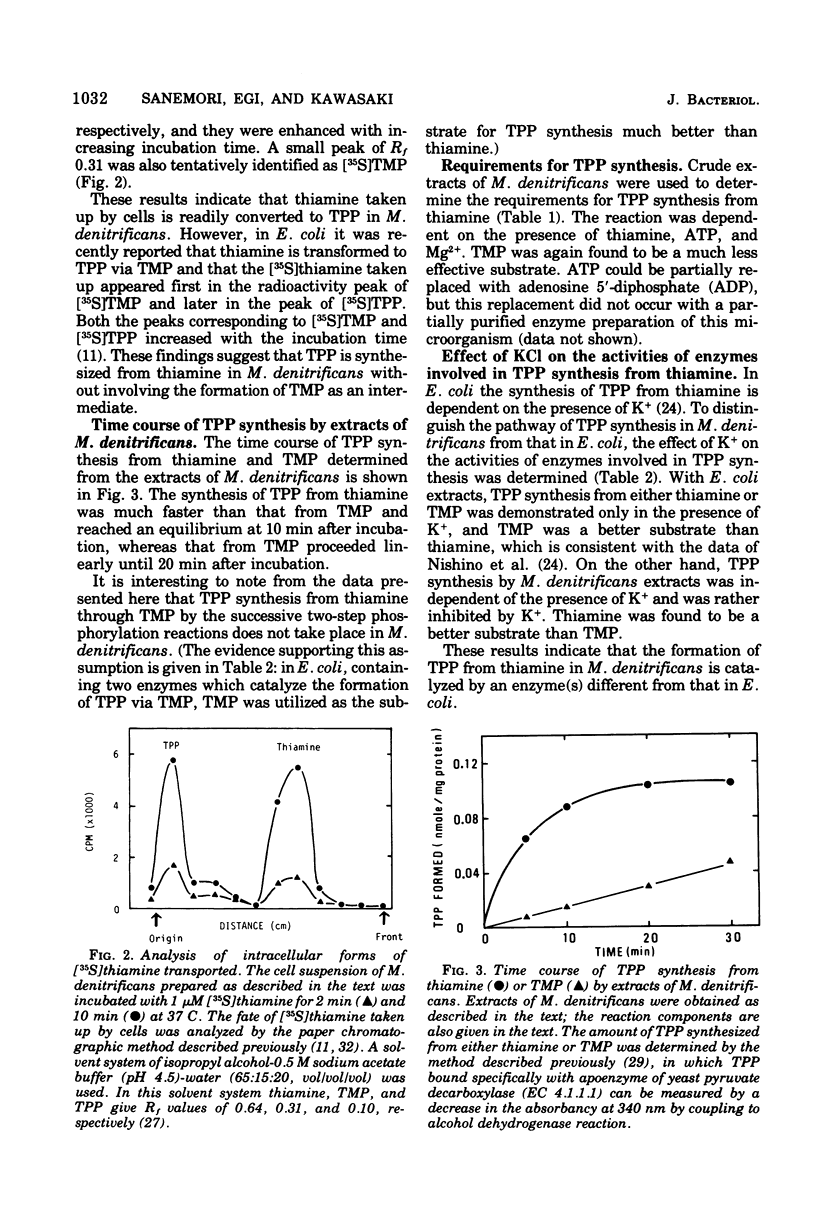
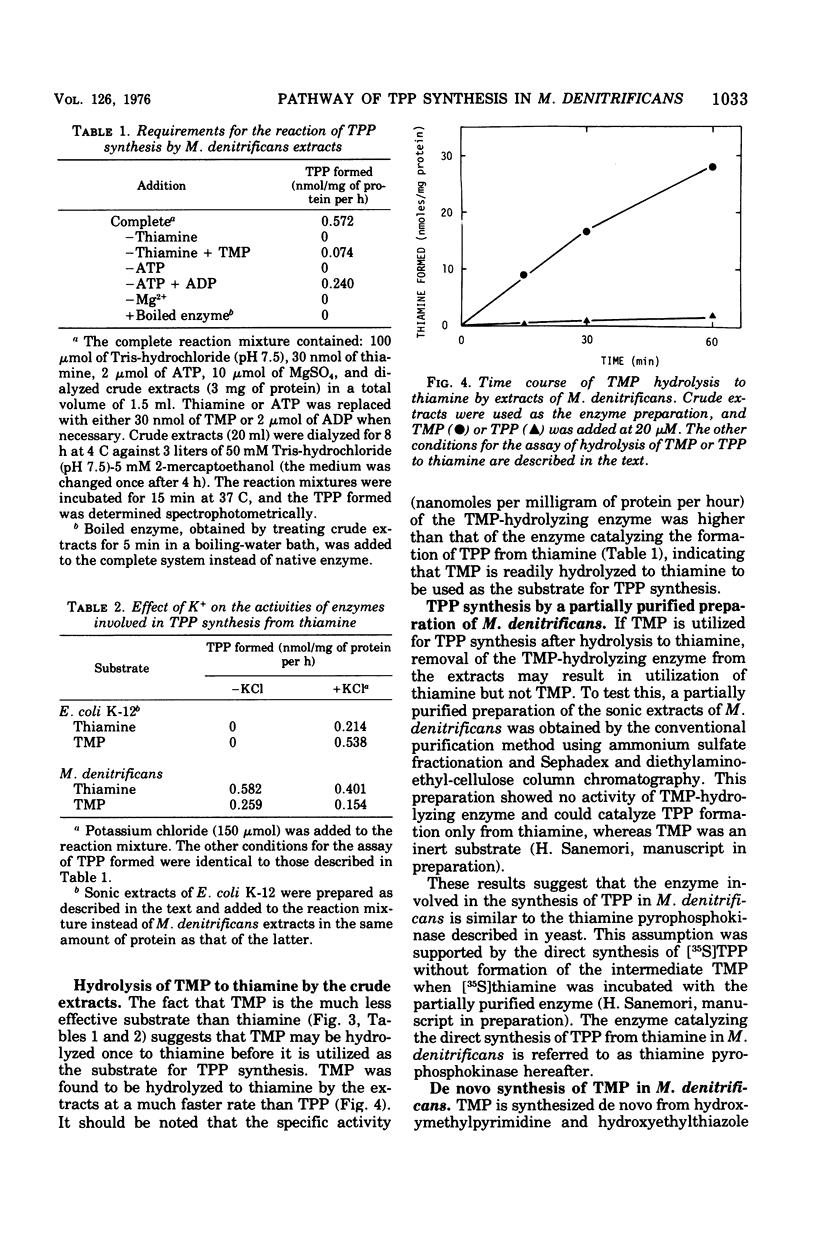
The pathway of thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) biosynthesis, which is formed either from exogeneously added thiamine or from the pyrimidine and thiazole moieties of thiamine, in Micrococcus denitrificans was investigated. The following indirect evidence shows that thiamine pyrophosphokinase (EC 2.7.6.2) catalyzes the synthesis of TPP from thiamine: (i) [35S]thiamine incubated with cells of this microorganism was detected in the form of [35S]thiamine; (ii) thiamine gave a much faster rate of TPP synthesis than thiamine monophosphate (TMP) when determined with the extracts; and (iii) a partially purified preparation of the extracts can use thiamine, but not TMP, as the substrate. The activities of the four enzymes involved in TMP synthesis from pyrimidine and thiazole moieties of thiamine were detected in the extracts of M. denitrificans. The extracts contained a high activity of the phosphatase, probably specific for TMP. After M. denitrificans cells were grown on a minimal medium containing 3 mM adenosine, which causes derepression of de novo thiamine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli, the activities of the four enzymes involved with TMP synthesis, the TMP phosphatase, and the thiamine pyrophosphokinase were enhanced two- to threefold. These results indicate that TPP is synthesized directly from thiamine without forming TMP as an intermediate and that de novo synthesis of TPP from the pyrimidine and thiazole moieties involves the formation of TMP, followed by hydrolysis to thiamine, which is then converted to TPP directly. Thus, the pathway of TPP synthesis from TMP synthesized de novo in M. denitrificans is different from that found in E. coli, in which TMP synthesized de novo is converted directly to TPP without producing thiamine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMIENER G. W., BROWN G. M. The biosynthesis of thiamine. 1. Enzymatic formation of thiamine and phosphate esters of the pyrimidine moiety of thiamine. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2404–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMIENER G. W., BROWN G. M. The biosynthesis of thiamine. 2. Fractionation of enzyme system and identification of thiazole monophosphate and thiamine monophosphate as intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2411–2417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG J. P., MORRIS J. G. Studies on the utilization of nitrate by Micrococcus denitrificans. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Oct;29:301–310. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-2-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashima A., Nishino H., Nose Y. Conversion of thiamine to thiamine monophosphate by cell-free extracts of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90991-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAZIRO Y., TANAKA R., MANO Y., SHIMAZONO N. On the mechanism of transpyrophosphorylation in the biosynthesis of thiamine diphosphate. J Biochem. 1961 Jun;49:472–476. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Nakata T., Nose Y. Genetic mapping with a thiamine-requiring auxotroph of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in thiamine phosphate pyrophosphorylase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1483–1485. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1483-1485.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Yamada K. The uptake system of free thiamine in mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Apr 28;47(2):465–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90737-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasi T., Iwashima A., Nose Y. Regulation of thiamine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1969 Mar;65(3):407–416. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayama Y., Kawasaki T. Purification and properties of thiaminephosphate pyrophosphorylase of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Sep;158(1):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90618-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDER I. G. The enzymatic synthesis of thiamine monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:3066–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuda H., Takii Y., Iwami K., Yasumoto K. Purification and properties of thiamine pyrophosphokinase from parsely leaf. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 1975;21(2):103–115. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.21.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOSE Y., TOKUDA Y., HIRABAYASHI M., IWASHIMA A. THIAMINE BIOSYNTHESIS FROM HYDROXYMETHYLPYRIMIDINE AND THIAZOLE BY WASHED CELLS AND CELL EXTRACTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND ITS MUTANTS. J Vitaminol (Kyoto) 1964 Jun 10;10:105–110. doi: 10.5925/jnsv1954.10.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOSE Y., UEDA K., KAWASAKI T. Enzymic synthesis of thiamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:277–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOSE Y., UEDA K., KAWASAKI T., IWASHIMA A., FUJITA T. Enzymatic synthesis of thiamine. II. The thiamine synthesis from pyrimidine and thiazole phosphates and the enzymatic synthesis of pyrimidine mono- and diphosphate and thiazole monophosphate. J Vitaminol (Kyoto) 1961 Jun 10;7:98–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama H., Hayashi R. Biosynthesis of thiamine pyrophosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):936–938. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.936-938.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama H., Hayashi R. Biosynthetic pathway of thiamine pyrophosphate: a special reference to the thiamine monophosphate-requiring mutant and the thiamine pyrophosphate-requiring mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1118–1126. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1118-1126.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell P. C., Tucker R. G. The de-repression of thiamine biosynthesis by adenosine a tool for investigating this biosynthetic pathway. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):512–516. doi: 10.1042/bj1000512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino H. Biogenesis of cocarboxylase in Escherichia coli. Partial purification and some properties of thiamine monophosphate kinase. J Biochem. 1972 Nov;72(5):1093–1100. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino H., Iwashima A., Nose Y. Biogenesis of cocarboxylase in Escherichia coli: a novel enzyme catalyzing the formation of thiamine pyrophosphate from thiamine monophosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90827-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEYN-PARVE E. P. Partial purification and properties of thiaminokinase from yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Mar;8(3):310–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanemori H., Yoshida S., Kawasaki T. Studies on the binding of thiamine pyrophosphate to apoenzyme of yeast pyruvate decarboxylase. J Biochem. 1974 Jan;75(1):123–129. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Sanemori H., Yamada K., Kawasaki T. Hydroxyethylthiazole uptake in Escherichia coli: general properties and relationship between uptake and thiamine biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1280–1286. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1280-1286.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



