Abstract
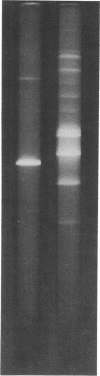
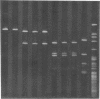
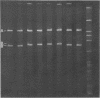
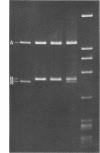
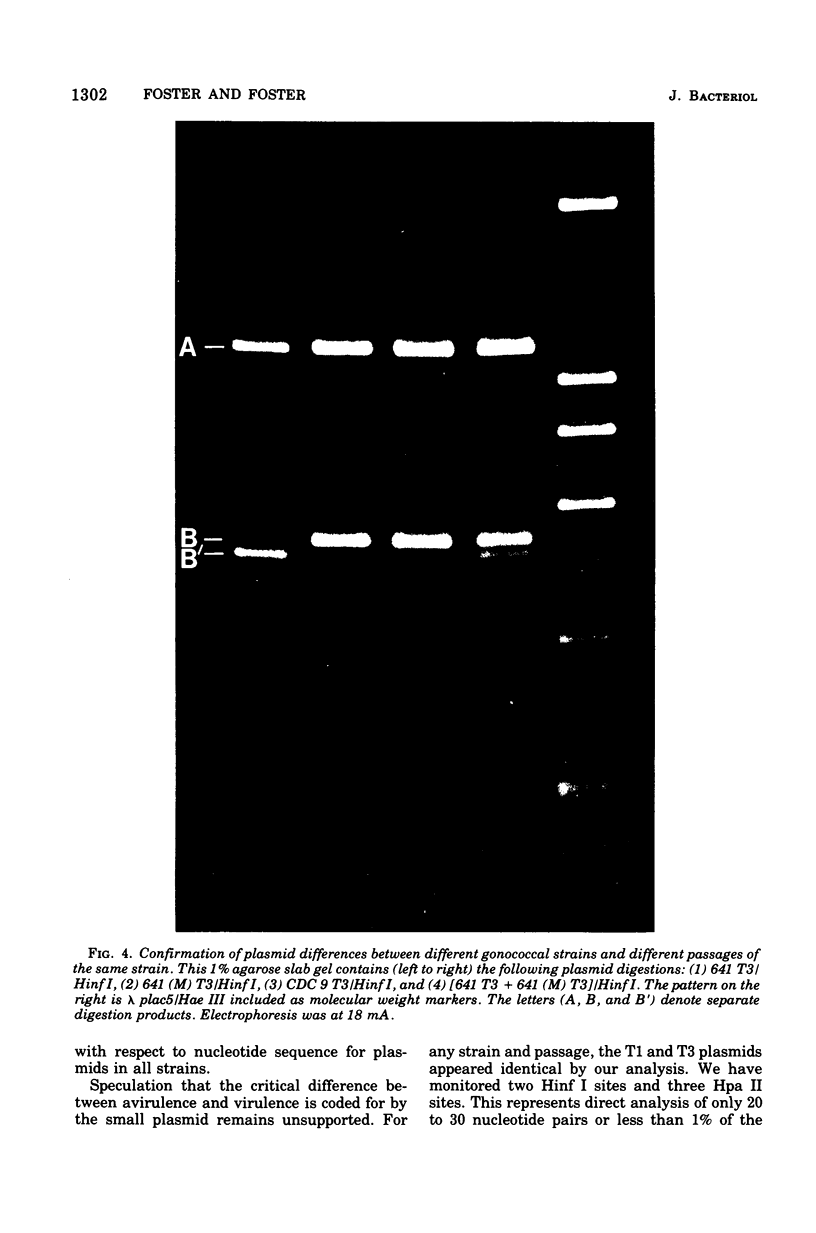
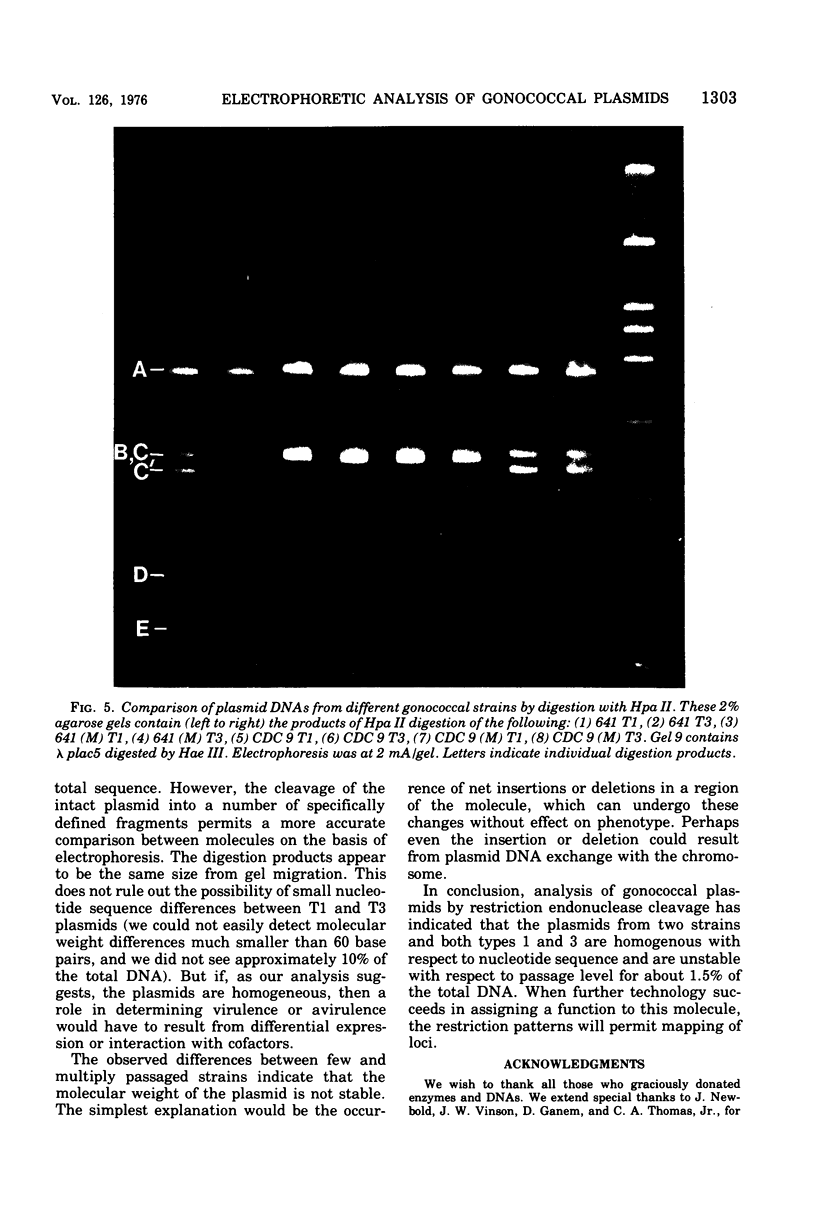
In order to associate virulence in Neisseria gonorrhoeae with an alteration of the nucleotide sequence of its small covalently closed plasmid, plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid was isolated from both virulent (T1) and avirulent (T3) morphological types for two strains. Electrophoretic and contour length measurements of intact plasmids indicated a homogeneous population with a molecular weight of approximately 2.6 x 10(6). Digestion with two restriction endonucleases. Hinf I and Hpa II, generated distinct fragment patterns which in each case were identical for T1 and T3 plasmid molecules from the same strain. The analysis suggests no sequence differences between the plasmids from virulent and avirulent types. For both strains, however, a deletion or addition of about 1.5% of the total deoxyribonucleic acid appeared in the Hpa II C digestion fragment when patterns for gonococci serially passaged 300 times were compared to those for bacteria freshly established from frozen stocks. The significance of the plasmid instability remains undetermined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bode V. C. Single-strand scissions induced in circular and linear lambda DNA by the presence of dithiothreitol and other reducing agents. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):125–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelkirk P. G., Schoenhard D. E. Physical evidence of a plasmid in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):197–200. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in tissue cultures: cellular attachment, entry, and survival. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1141–1146. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1141-1146.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield V., Boyer H. W., Yanofsky C., Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Plasmid ColEl as a molecular vehicle for cloning and amplification of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Reyn A., Birch-Andersen A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae 3. Demonstration of presumed appendages to cells from different colony types. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):437–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness M. J., Sparling P. F. Multiple antibiotic resistance due to a single mutation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):321–330. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manteuil S., Hamer D. H., Thomas C. A., Jr Regular arrangement of restriction sites in Drosophila DNA. Cell. 1975 Aug;5(4):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W., Holmes K. K., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):712–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.712-717.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Bartenstein L. Factors affecting autolysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Apr;145(4):1418–1421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-38025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Genetic transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1364–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1364-1371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Yobs A. R. Colonial morphology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from males and females. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):513–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.513-.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiffler P. W., Lerner S. A., Bohnhoff M., Morello J. A. Plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in clinical isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1293–1300. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1293-1300.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]