Abstract
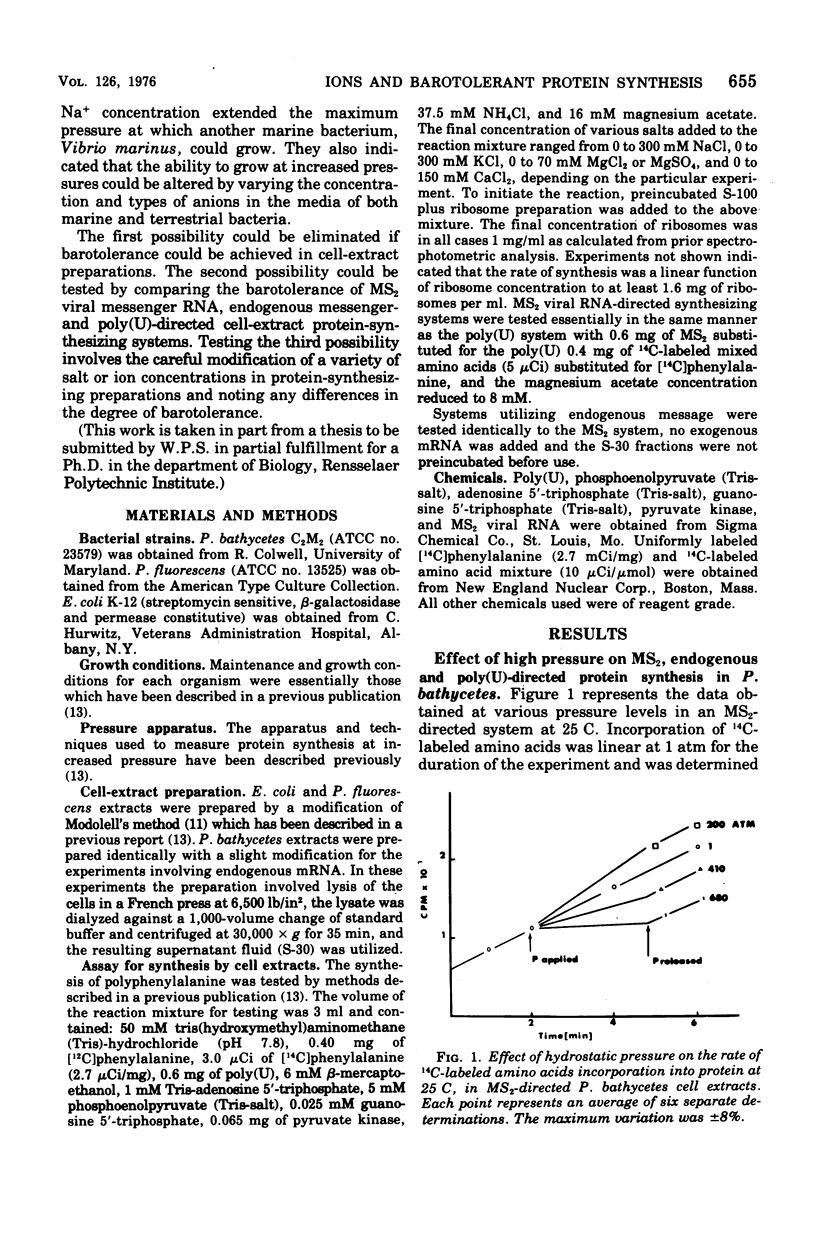
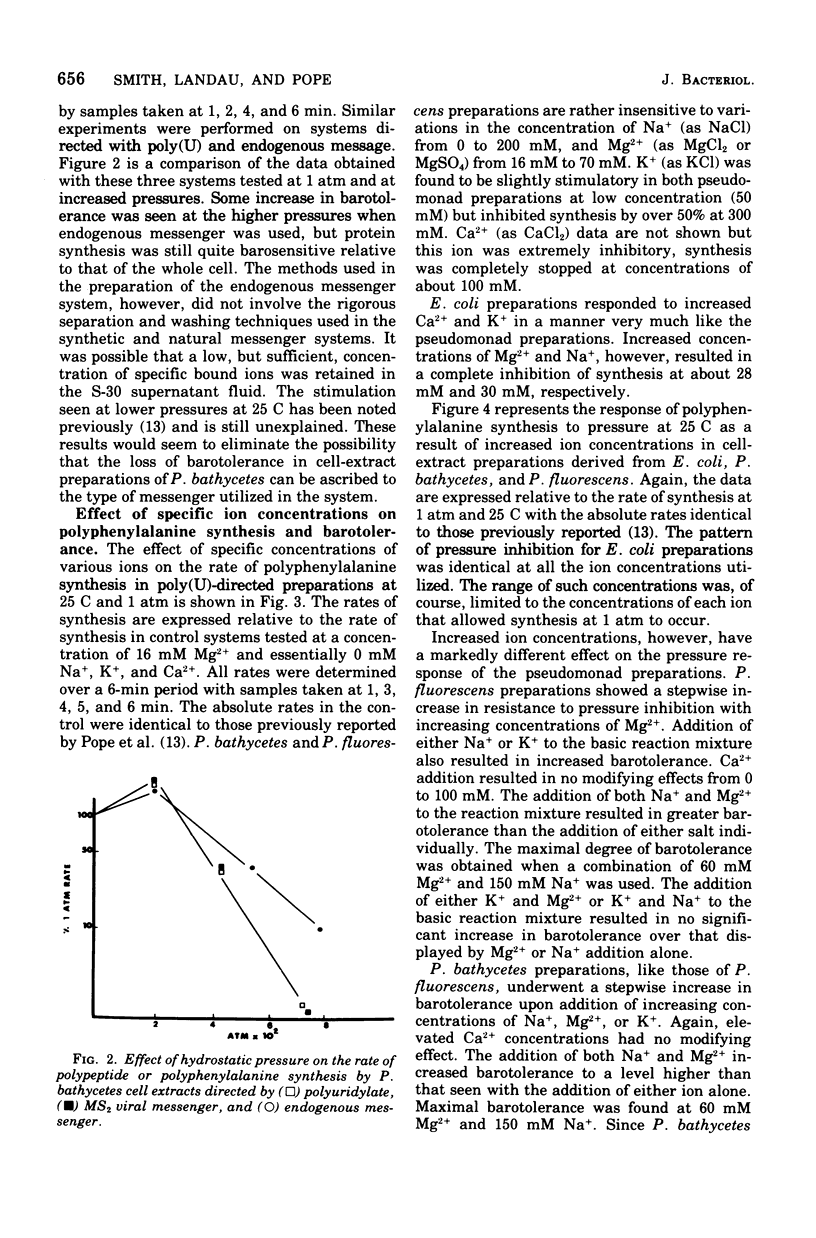
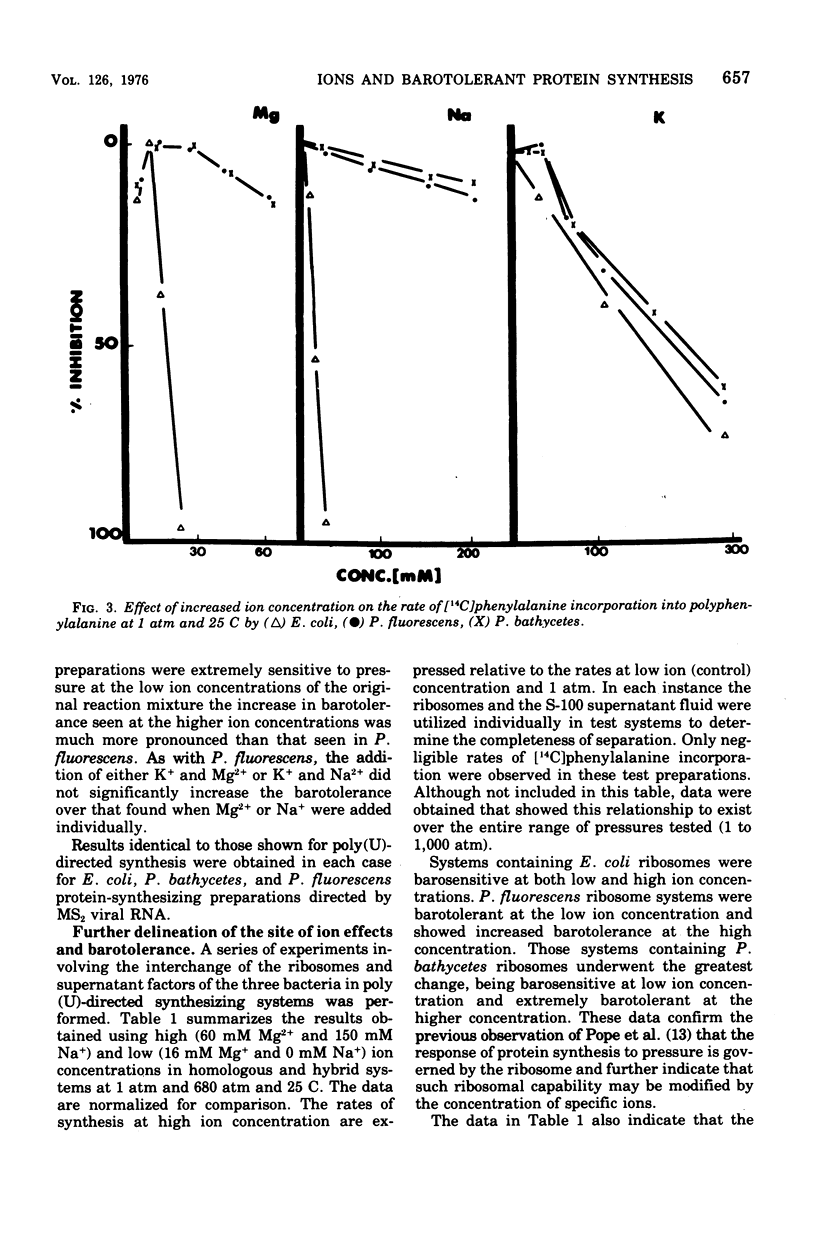
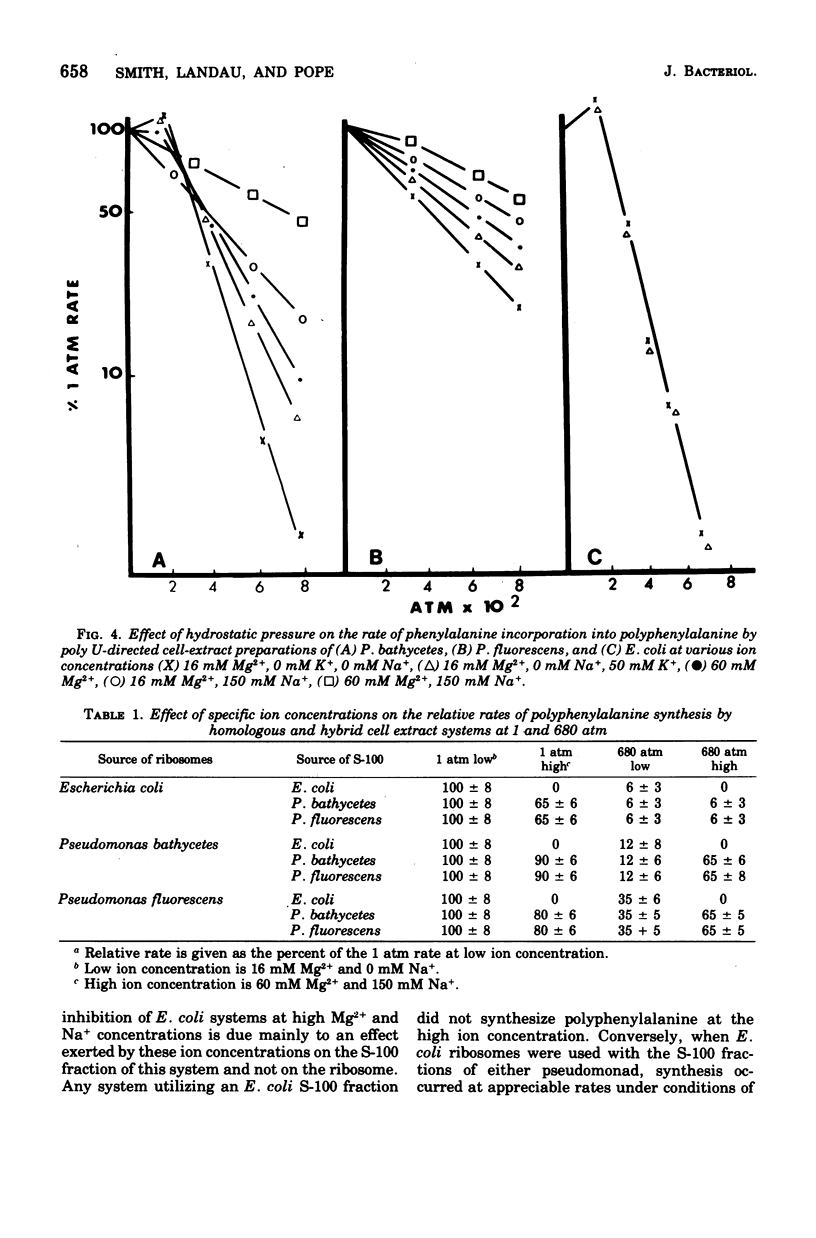
The degree of barotolerance exhibited by Pseudomonas fluorescens and Pseudomonas bathycetes in vitro polyphenylalanine-synthesizing systems can be modified by altering the concentrations of specific ions in the reaction mixture. Hybrid-protein-synthesizing systems, utilizing all the possible S-100 supernatant fluid and ribosome combinations from Escherichia coli, P. fluorescens, and P. bathycetes, were tested for barotolerance under conditions of low (16 mM Mg2+ plus 0 mM Na+) and high (150 mM Na+ plus 60 mM Mg2+) ion concentrations. The results reveal that barotolerant synthesis is a characteristic determined by the origin of the ribosome. Systems utilizing E. coli ribosomes are barosensitive at both low and high ion concentrations, P. fluorescens ribosomes barotolerant under both conditions, and P. bathycetes ribosomes barosensitive at low and barotolerant at high ion concentrations. Therefore, certain concentrations of specific ions will increase barotolerance, but only if the ribosomes are capable of functioning at high pressures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. J. Alternate pressurization-depressurization effects on growth and net protein, RNA and DNA synthesis by Escherichia coli and Vibrio marinus. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Oct;15(10):1237–1240. doi: 10.1139/m69-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. M., Albright L. J. Hydrostatic pressure effects on the translation stages of protein synthesis in a cell-free system from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 13;238(2):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSON D. A ribonucleic acid particle released from ribosomes by salt. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:232–234. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90818-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F. Unfolding of Escherichia coli ribosomes by removal of magnesium. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(2):356–371. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau J. V. Induction, transcription and translation in Escherichia coli: a hydrostatic pressure study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Dec 19;149(2):506–512. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftfield R. B. The mechanism of aminoacylation of transfer RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1972;12:87–128. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60660-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S., Somero G. N. Activation volumes in enzymic catalysis: their sources and modification by low-molecular-weight solutes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope D. H., Smith W. P., Swartz R. W., Landau J. V. Role of bacterial ribosomes in barotolerance. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):664–669. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.664-669.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. R., Landau J. V. Hydrostatic pressure effects on Escherichia coli: site of inhibition of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):945–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.945-948.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. R., Landau J. V. Inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis by hydrostatic pressure. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1222–1227. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1222-1227.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W., Pope D., Landau J. V. Role of bacterial ribosome subunits in barotolerance. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):582–584. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.582-584.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Davis B. D. Release of 70 S ribosomes from polysomes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 15;74(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



