Abstract
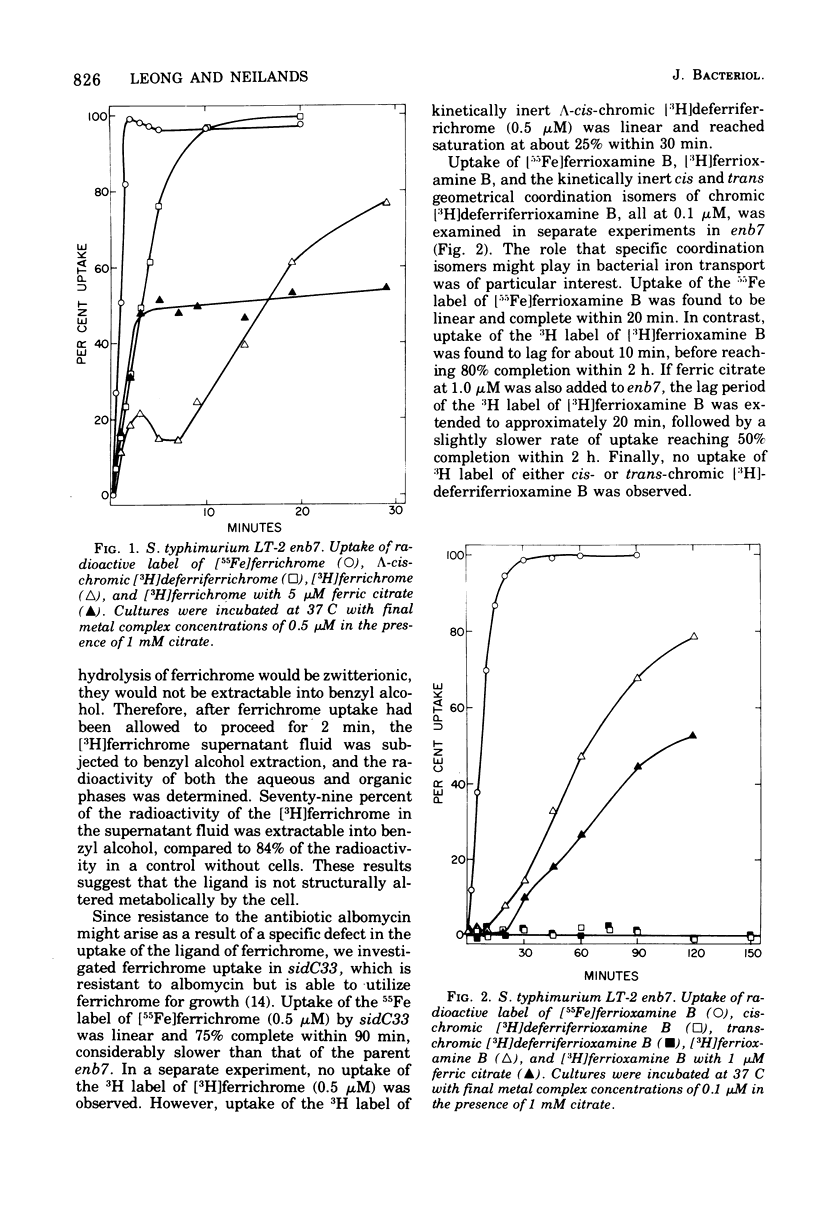
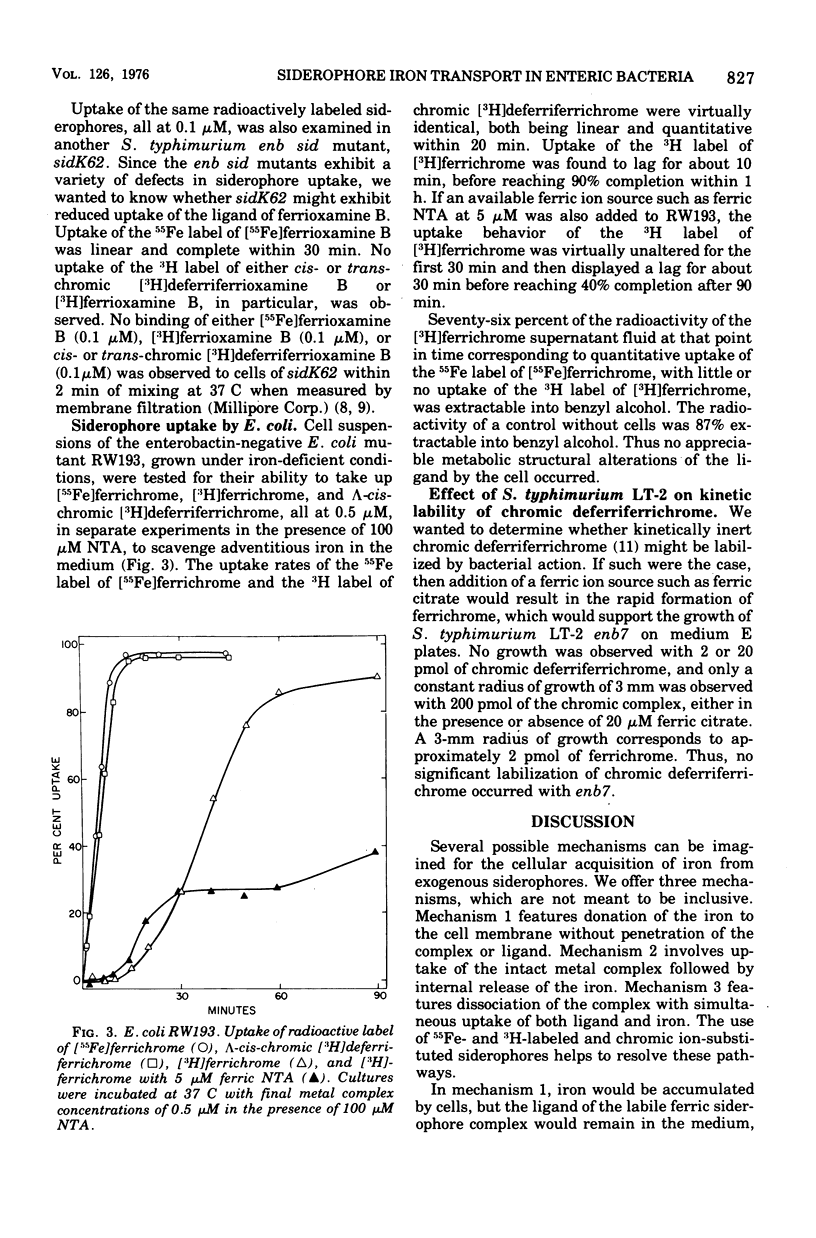
Uptake of 55Fe- and 3H-labeled siderophores and their chronic analogues have been studied in Salmonella typhimurium LT-2 and Escherichia coli K-12. In S. typhimurium LT-2, at least two different mechanisms for siderophore iron transport may be operative. Uptake of 55Fe- and 3H-labeled ferrichrome and kinetically inert lambda-cis-chromic [3H]deferriferrichrome by the S. typhimurium LT-2 enb7 mutant, which is defective in the production of its native siderophore, enterobactin, appears to occur by two concurrent mechanisms. The first mechanism is postulated to involve either rapid uptake of iron released from the ferric complex by cellular reduction without penetration of the complex or ligand or dissociation of the complex and simultaneous uptake of both ligand and iron coupled with simultaneous expulsion of the ligand. The second mechanism appears to consist of slower uptake of the intact ferric complex.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arceneaux J. E., Davis W. B., Downer D. N., Haydon A. H., Byers B. R. Fate of labeled hydroxamates during iron transport from hydroxamate-ion chelates. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):919–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.919-927.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer D. N., Davis W. B., Byers B. R. Repression of phenolic acid-synthesizing enzymes and its relation to iron uptake in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):181–187. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.181-187.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. T., Spiro R. G. The alpha 2-macroglobulin of human plasma. I. Isolation and composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5549–5555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T. Role of ferrichrome as a ferric ionophore in Ustilago sphaerogena. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1483–1488. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatmark T., Romslo I. Energy-dependent accumulation of iron by isolated rat liver mitochondria. Requirement of reducing equivalents and evidence for a unidirectional flux of Fe(II) across the inner membrane. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6433–6438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost G. E., Rosenberg H. The inducible citrate-dependent iron transport system in Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 30;330(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guterman S. K. Colicin B: mode of action and inhibition by enterochelin. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1217–1224. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1217-1224.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVENBERG W., BUCHANAN B. B., RABINOWITZ J. C. STUDIES ON THE CHEMICAL NATURE OF CLOSTRIDIAL FERREDOXIN. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3899–3913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman L., Young I. G., Frost G. E., Rosenberg H., Gibson F. Enterochelin system of iron transport in Escherichia coli: mutations affecting ferric-enterochelin esterase. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1142–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1142-1149.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Neilands J. B., Raymond K. N. Coordination isomers of biological iron transport compounds. III. (1) Transport of lambda-cis-chromic desferriferrichrome by Ustilago sphaerogena. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):1066–1071. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Raymond K. N. Coordination isomers of biological iron transport compounds, IV, Giometrical isomers of chromic desferriferrioxamine B. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jan 22;97(2):293–296. doi: 10.1021/ja00835a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Raymond K. N. Coordination isomers of biological iron transport compounds. II. The optical isomers of chromic desferriferrichrome and desferriferrichrysin. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Oct 16;96(21):6628–6630. doi: 10.1021/ja00828a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey M., Pollack J. R., Wayne R., Ames B. N., Neilands J. B. Iron uptake in Salmonella typhimurium: utilization of exogenous siderochromes as iron carriers. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):731–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.731-738.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. R., Ames B. N., Neilands J. B. Iron transport in Salmonella typhimurium: mutants blocked in the biosynthesis of enterobactin. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.635-639.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



