Abstract
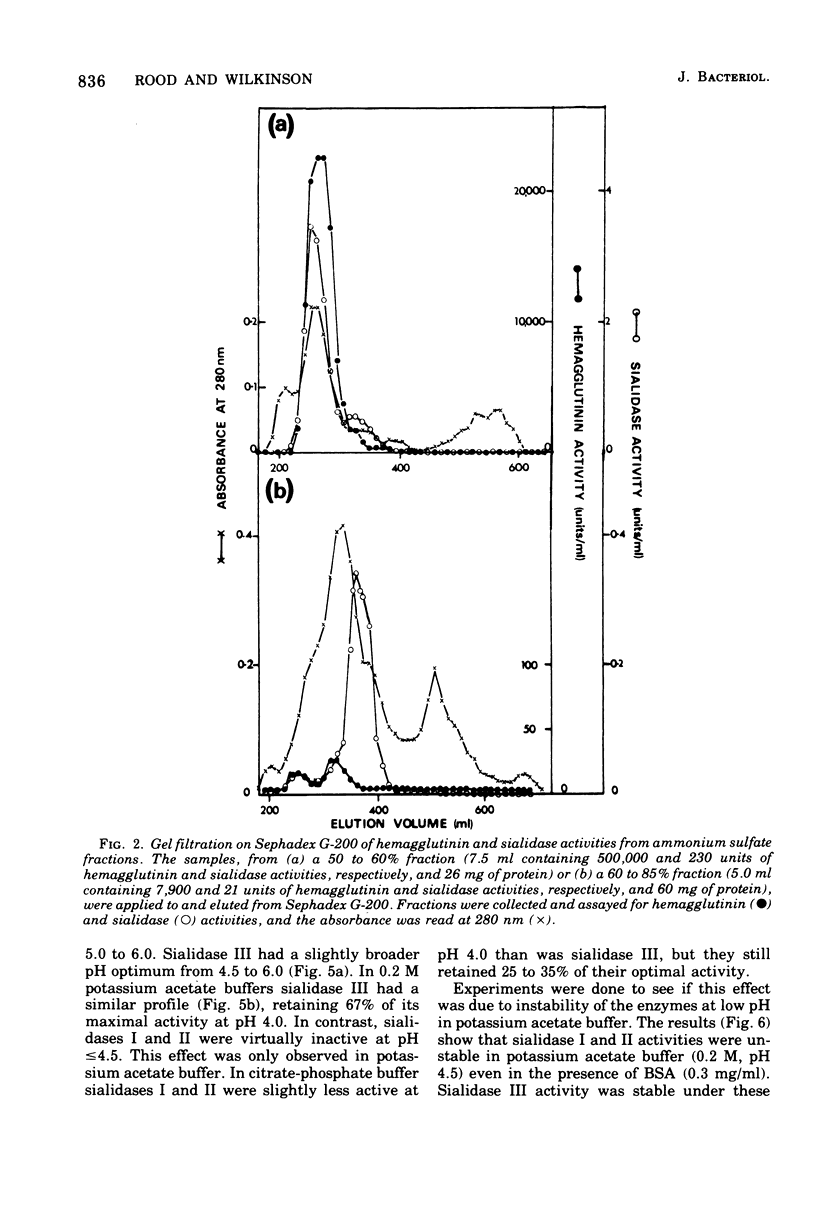
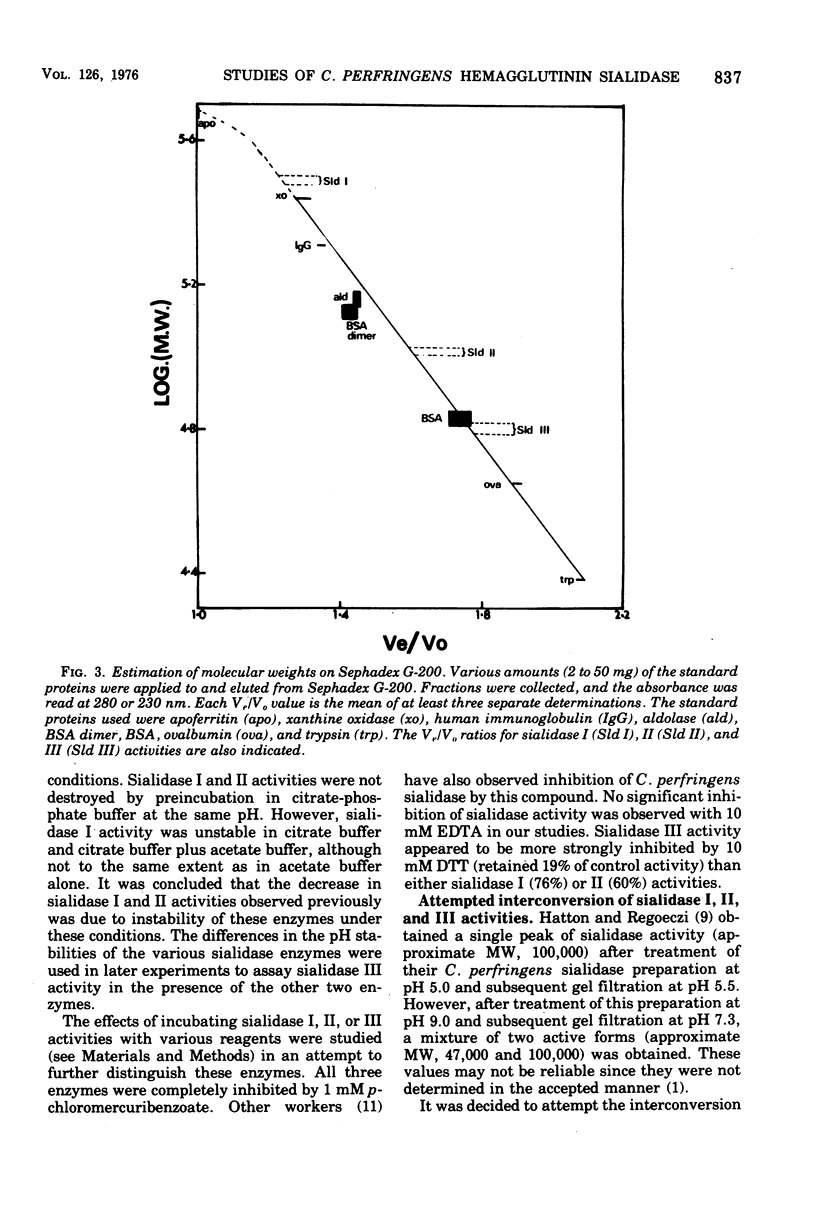
Biochemical characterization of hemagglutinin and sialidase activities from Clostridium perfringens strain CN3870 revealed that this strain produced three sialidase enzymes that were separable to gel filtration, ion exchange chromatography, and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The molecular weights of sialidase I, II, and III activities were 310,000 +/- 10,000, 105,000 +/- 4,000 and 64,000 +/- 2,000, respectively, the first figure being an approximate value only.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke E., Drzeniek R. Untersuchungen über die Clostridium perfringens-Neuraminidase. Z Naturforsch B. 1969 May;24(5):599–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke E., Scharmann W., Drzeniek R. Die Bestimmung des Molekulargewichtes bakterieller Neuraminidasen mit Hilfe der Gel-Filtration. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974;229(1):55–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy J. T., Jourdian G. W., Roseman S. The sialic acids. VI. Purification and properties of sialidase from Clostridium perfringens. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3501–3506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collee J. G. The relationship of the haemagglutinin of Clostridium welchii to the neuraminidase and other soluble products of the organism. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):13–30. doi: 10.1002/path.1700900103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. A simple method for the purification of commercial neuraminidase preparations free from proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 15;327(1):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ispolatovskaia M. V., Tokinova T. N., Cherikovskaia E. N., Borishpolets Z. I. Neiraminidaza v kletkakh i toksinakh Cl. perfringens. Vopr Med Khim. 1973 Jan-Feb;19(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunimoto S., Aoyagi T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Purification and characterization of Streptomyces sialidases. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):394–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.394-400.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meindl P., Bodo G., Palese P., Schulman J., Tuppy H. Inhibition of neuraminidase activity by derivatives of 2-deoxy-2,3-dehydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nees S., Veh R. W., Schauer R. Purification and characterization of neuraminidase from Clostridium perfringens. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Jun;356(6):1027–1042. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.s1.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rood J. I., Wilkinson R. G. Isolation and characterization of Clostridium perfringens mutants altered in both hemagglutinin and sialidase production. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):419–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.419-427.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rood J. I., Wilkinson R. G. Relationship between hemagglutinin and sialidase from Clostridium perfringens CN3870: gel filtration of mutant and reverant activities. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):845–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.845-851.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Isolation of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Association of both hemagglutinating and neuraminidase activities with the larger SV5 glycoprotein. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):640–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Isolation and purification of the envelope proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.263-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. The hemagglutinating and neuraminidase protein of a paramyxovirus: interaction with neuraminic acid in affinity chromatography. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90308-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozawa H., Watanabe M., Ishida N. Structural components of Sendai virus. Serological and physicochemical characterization of hemagglutinin subunit associated with neuraminidase activity. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):242–253. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICKHAM N. The relationship of the haemagglutinin of Cl. welchii to other soluble antigens of the organism. J Comp Pathol. 1956 Jan;66(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(56)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


