Abstract
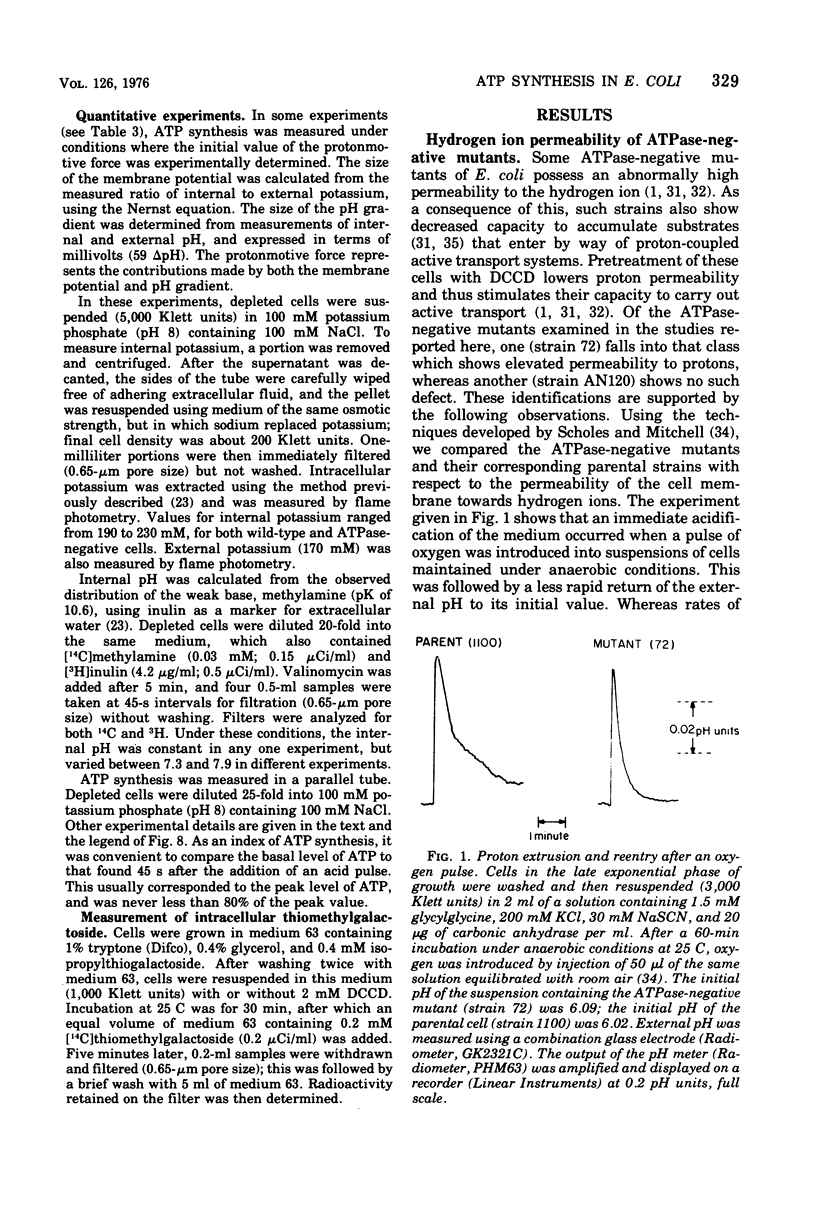
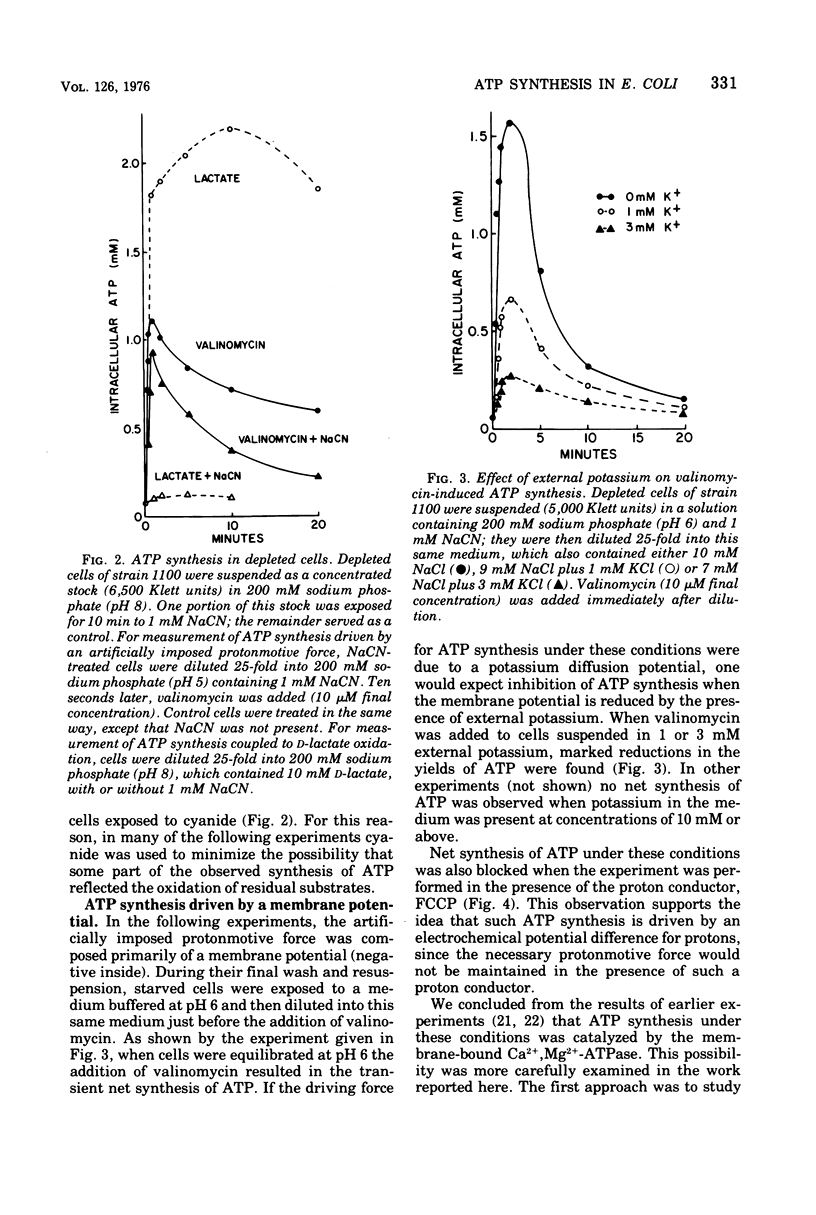
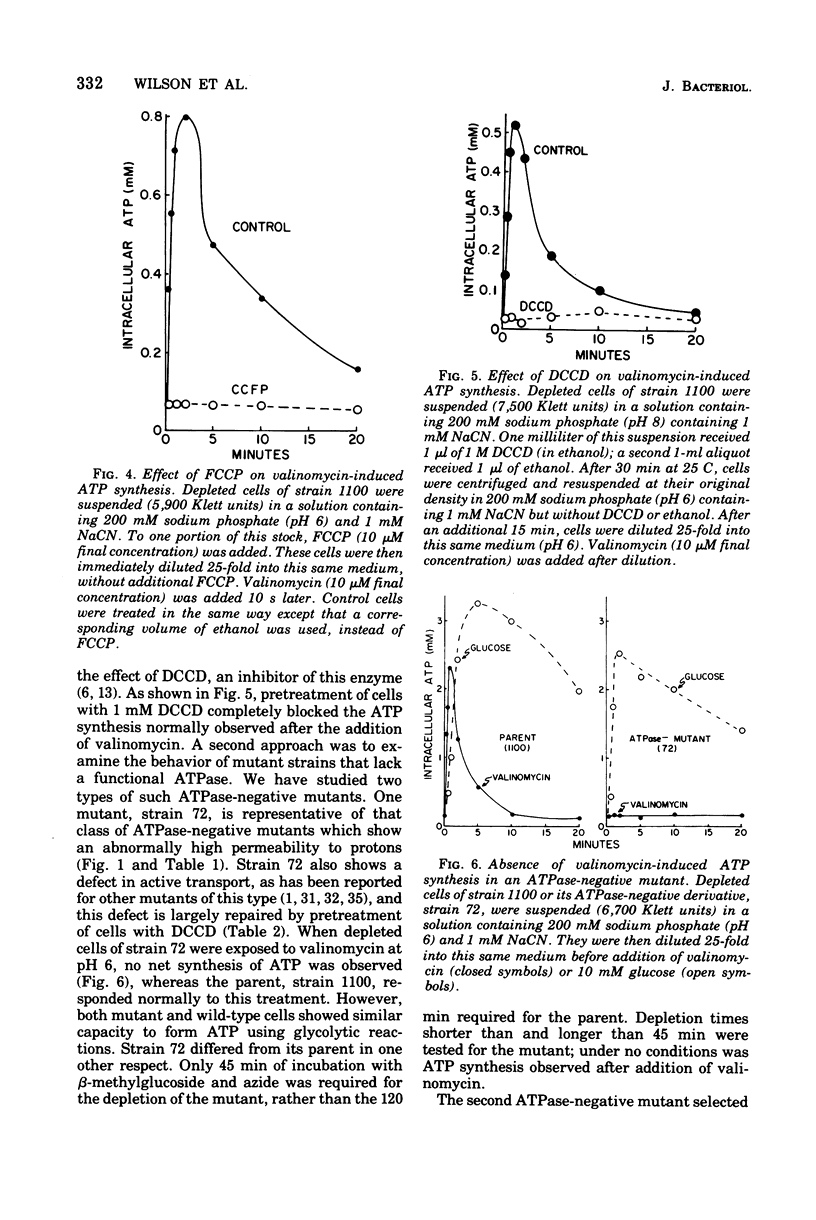
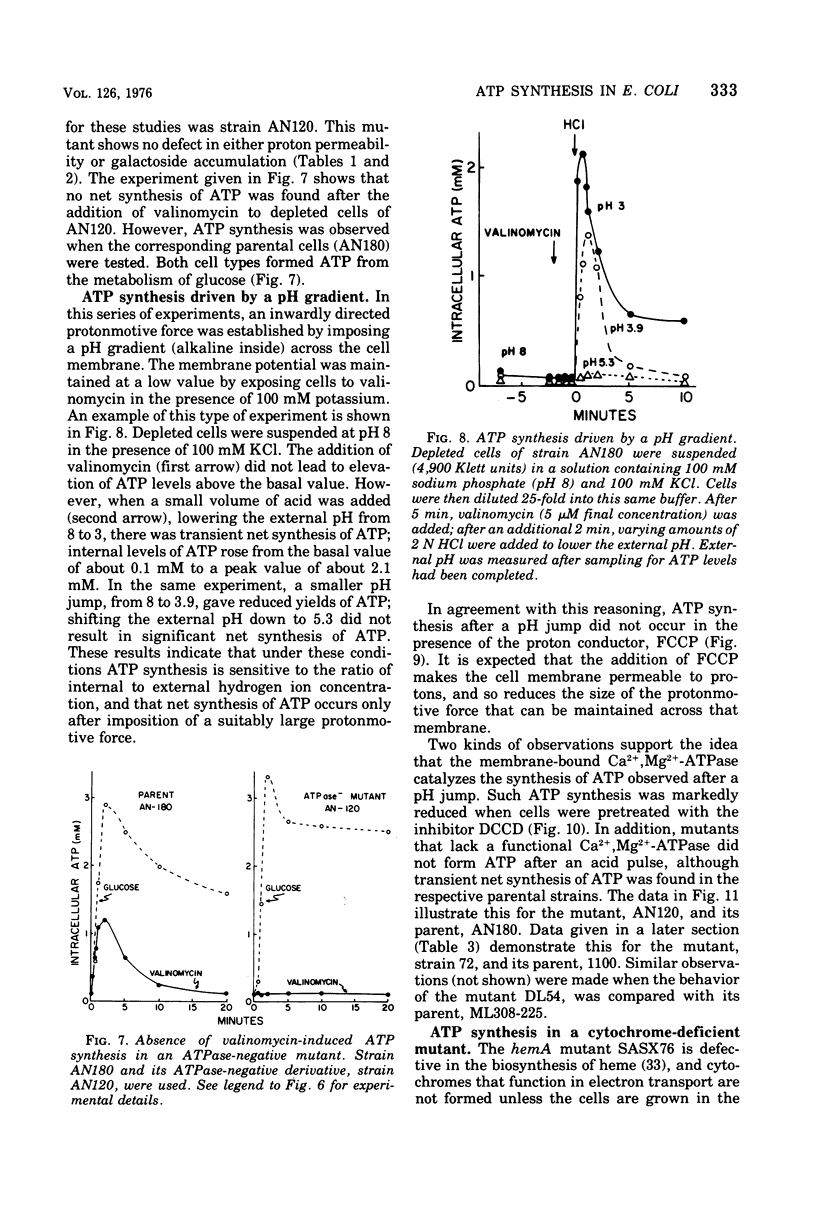
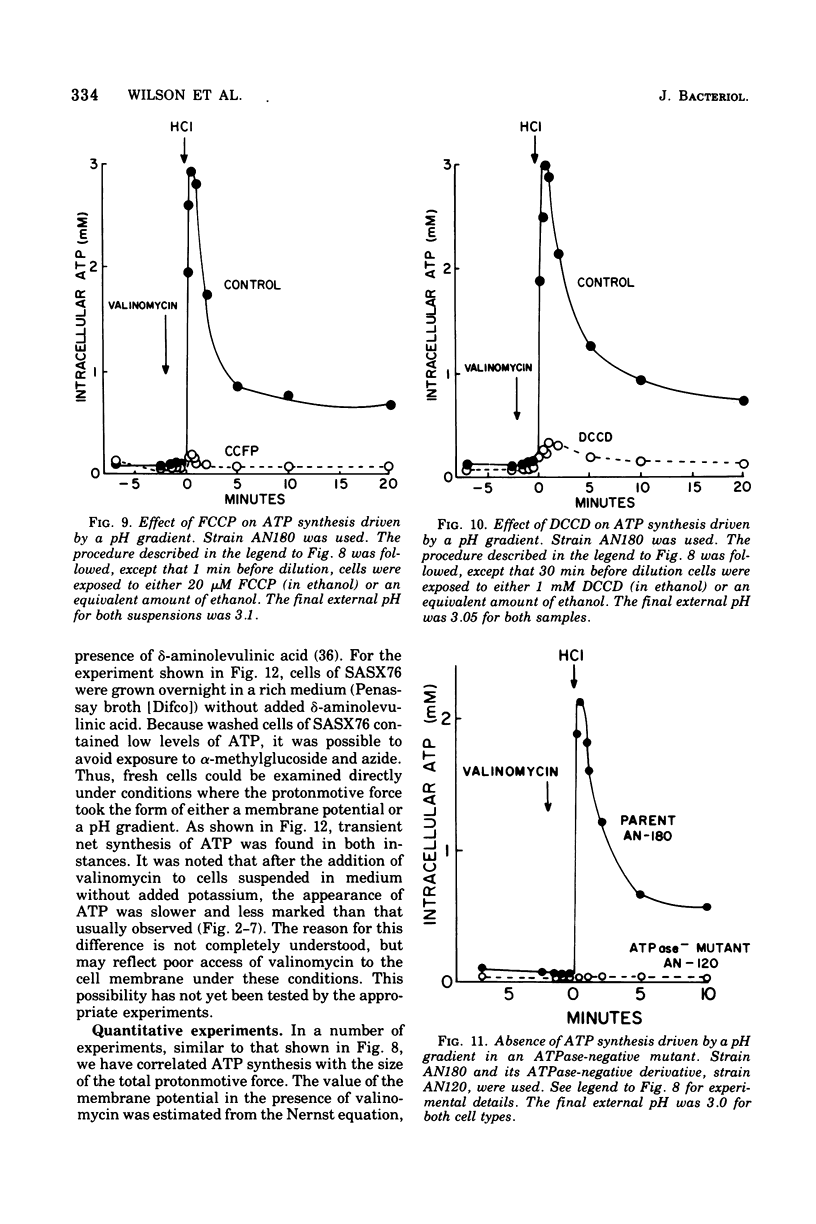
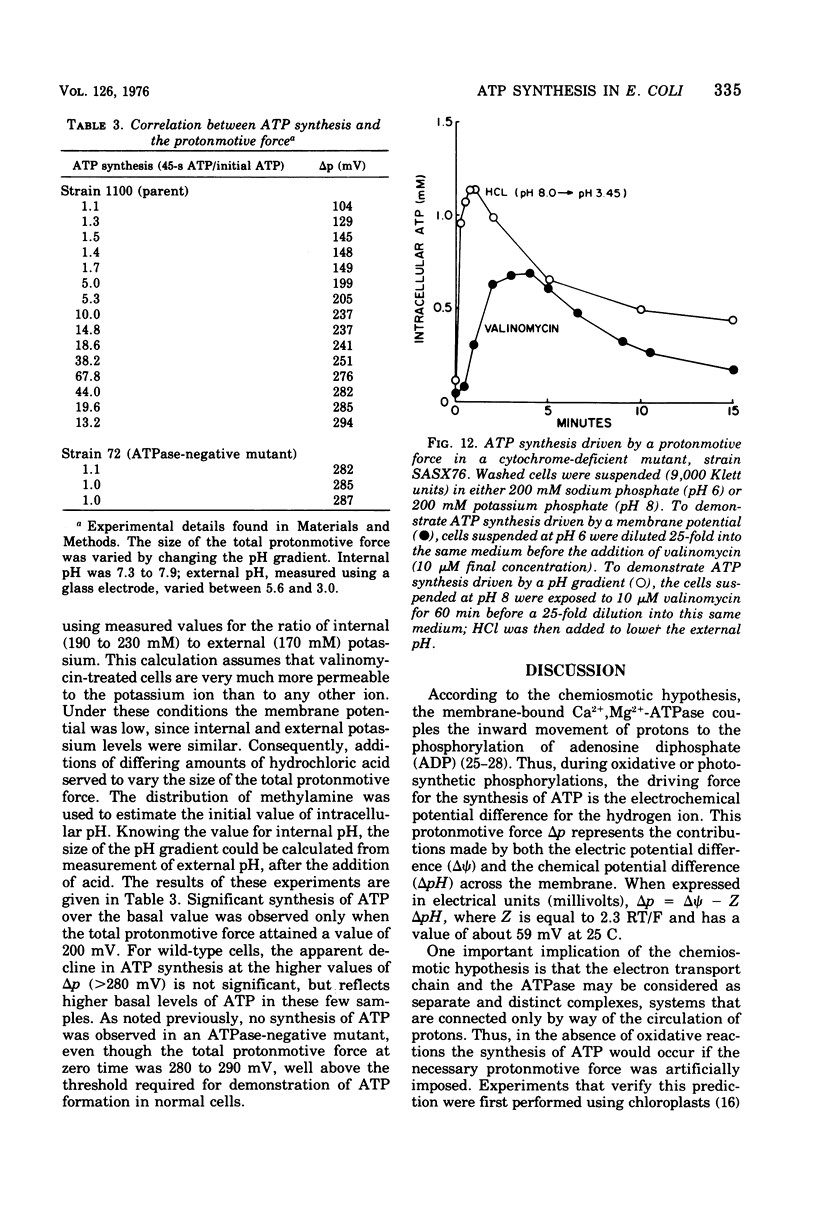
Net synthesis of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) in energy-depleted cells of Escherichia coli was observed when an inwardly directed protonmotive force was artificially imposed. In wild-type cells, ATP synthesis occurred whether the protonmotive force was dominated by the membrane potential (negative inside) or the pH gradient (alkaline inside). Formation of ATP did not occur unless the protonmotive force exceeded a value of 200 mV. Under these conditions, no ATP synthesis was found when cells were exposed to an inhibitor of the membrane-bound Ca2+- and Mg2+- stimulated adenosine triphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.3), dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, or to a proton conductor, carbonylcyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-hydrazone. Adenosine triphosphatase-negative mutants failed to show ATP synthesis in response to either a membrane potential or a pH gradient. ATP synthesis driven by a protonmotive force was observed in a cytochrome-deficient mutant. These observations are consistent with the chemiosmotic hypothesis of Mitchell (1961, 1966, 1974).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K., Harold F. M., Simoni R. D. Impairment and restoration of the energized state in membrane vesicles of a mutant of Escherichia coli lacking adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4587–4593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K12. Mutations affecting magnesium ion- or calcium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):75–81. doi: 10.1042/bj1240075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Wimpenny J. W., Hughes D. E. The ATP pool in Escherichia coli. I. Measurement of the pool using modified luciferase assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;143(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Gibson F. Studies on electron transport and energy-linked reactions using mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 30;346(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(74)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J. Membrane Mg-(Ca)-Activated Adenosine Triphosphatase of Escherichia coli: Characterization in the Membrane-Bound and Solubilized States. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1203–1212. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1203-1212.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L., Slusnyte R., Griniuviene B. ATP synthesis driven by protonmotive force imposed across Escherichia coli cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 1;57(3):290–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80319-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griniuviene B., Chmieliauskaite V., Grinius L. Energy-linked transport of permeant ions in Escherichia coli cells: evidence for membrane potential generation by proton-pump. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):206–213. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griniuviene B., Chmieliauskaite V., Melvydas V., Dzheja P., Grinius L. Conversion of Escherichia coli cell-produced metabolic energy into electric form. J Bioenerg. 1975 Mar;7(1):17–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01558460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R., Baron C., Abrams A. Inhibition of membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase and of cation transport in Streptococcus faecalis by N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2261–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Hinkle P. C. Oxidative phosphorylation and proton translocation in membrane vesicles prepared from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):178–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90908-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata H., Altendorf K., Harold F. M. Role of an electrical potential in the coupling of metabolic energy to active transport by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagendorf A. T., Uribe E. ATP formation caused by acid-base transition of spinach chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):170–177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeacocke R. E., Niven D. F., Hamilton W. A. The protonmotive force in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(3):57P–58P. doi: 10.1042/bj1270057p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John P., Whatley F. R. Paracoccus denitrificans and the evolutionary origin of the mitochondrion. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):495–498. doi: 10.1038/254495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Energy expenditure is obligatory for the downhill transport of galactosides. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):447–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawford H. G., Haddock B. A. Respiration-driven proton translocation in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):217–220. doi: 10.1042/bj1360217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 1961 Jul 8;191:144–148. doi: 10.1038/191144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. A protonmotive force drives ATP synthesis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Wilson T. H. ATP synthesis driven by a protonmotive force in Streptococcus lactis. J Membr Biol. 1975;25(3-4):285–310. doi: 10.1007/BF01868580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Jones C. W. Oxidative phosphorylation in bacteria which contain different cytochrome oxidases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):144–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. A chemiosmotic molecular mechanism for proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 15;43(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P. Transient pH changes during D-lactate oxidation by membrane vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov;45(4):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R. A., Moyle J., Mitchell P. Synthesis of adenosine triphosphate by a protonmotive force in rat liver mitochondria. Nature. 1966 Oct 15;212(5059):257–258. doi: 10.1038/212257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Beta-galactoside transport and proton movements in an adenosine triphosphatase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 21;53(4):1289–1296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90605-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Restoration of active transport in an Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1124-1129.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P., Mitchell P. Respiration-driven proton translocation in Micrococcus denitrificans. J Bioenerg. 1971 Sep;1(3):309–323. doi: 10.1007/BF01516290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Shallenberger M. K. Coupling of energy to active transport of amino acids in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. P., Bragg P. D. Energization of phenylalanine transport and energy-dependent transhydrogenase by ATP in cytochrome-deficient Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1200–1206. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90824-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Săsărman A., Surdeanu M., Horodniceanu T. Locus determining the synthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1882–1884. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1882-1884.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. The proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80880-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I., Mitchell P. Proton-coupled beta-galactoside translocation in non-metabolizing Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg. 1972 Aug;3(5):445–462. doi: 10.1007/BF01516082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T. H., Mével-Ninio M., Valentine R. C. Essential role of membrane ATPase or coupling factor for anaerobic growth and anaerobic active transport in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 26;314(3):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



