Abstract
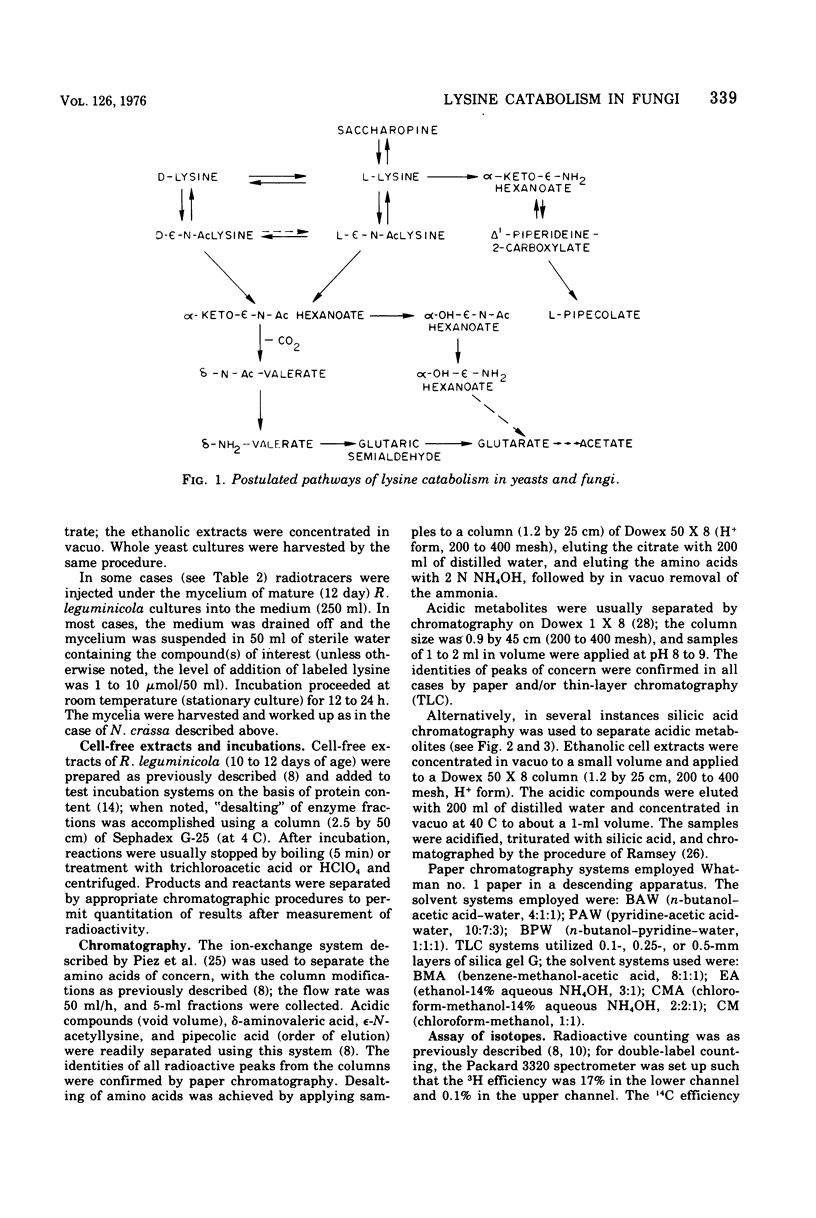
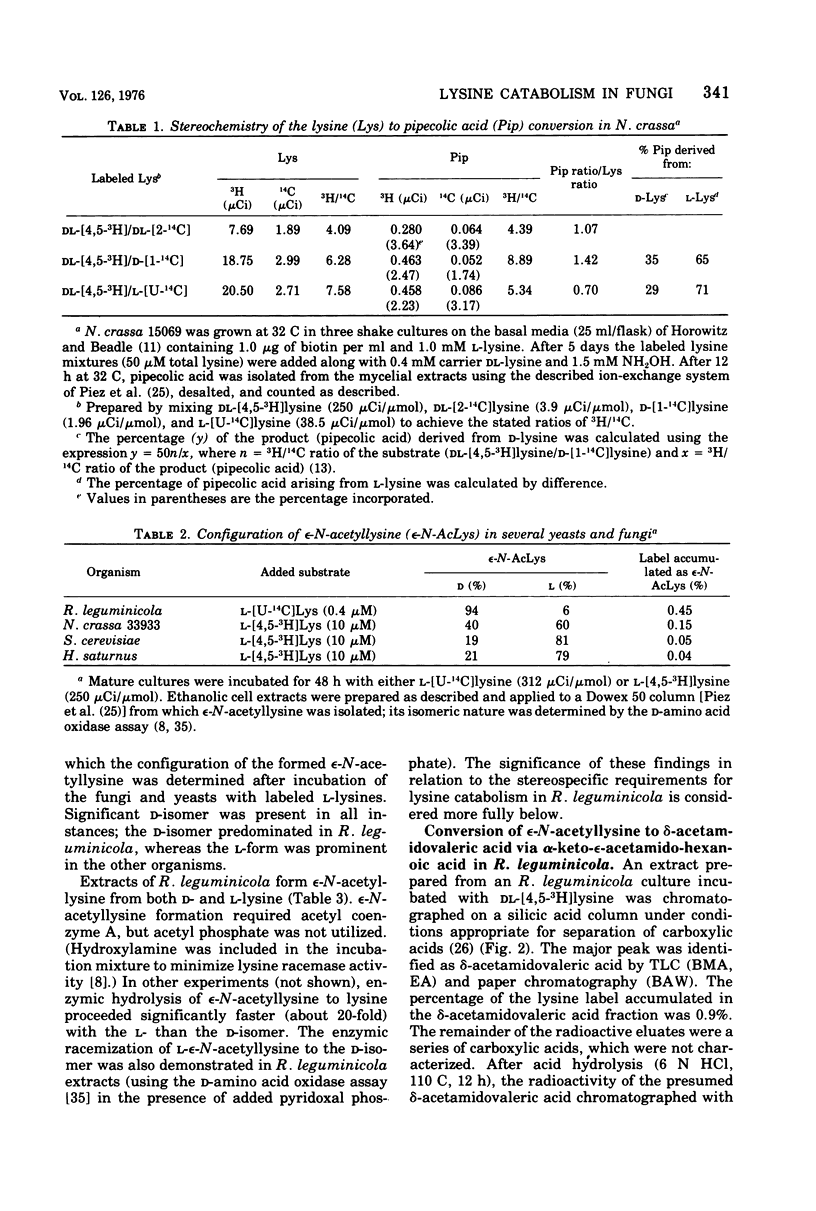
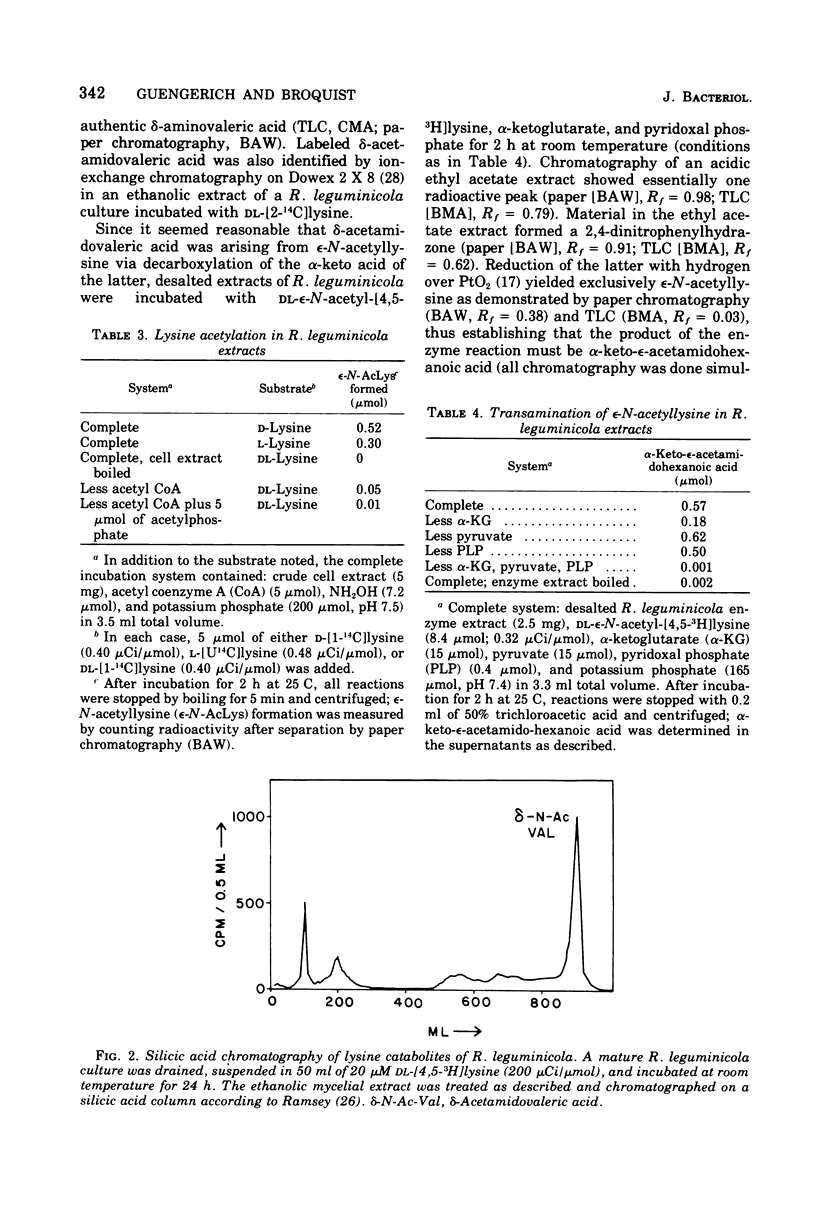
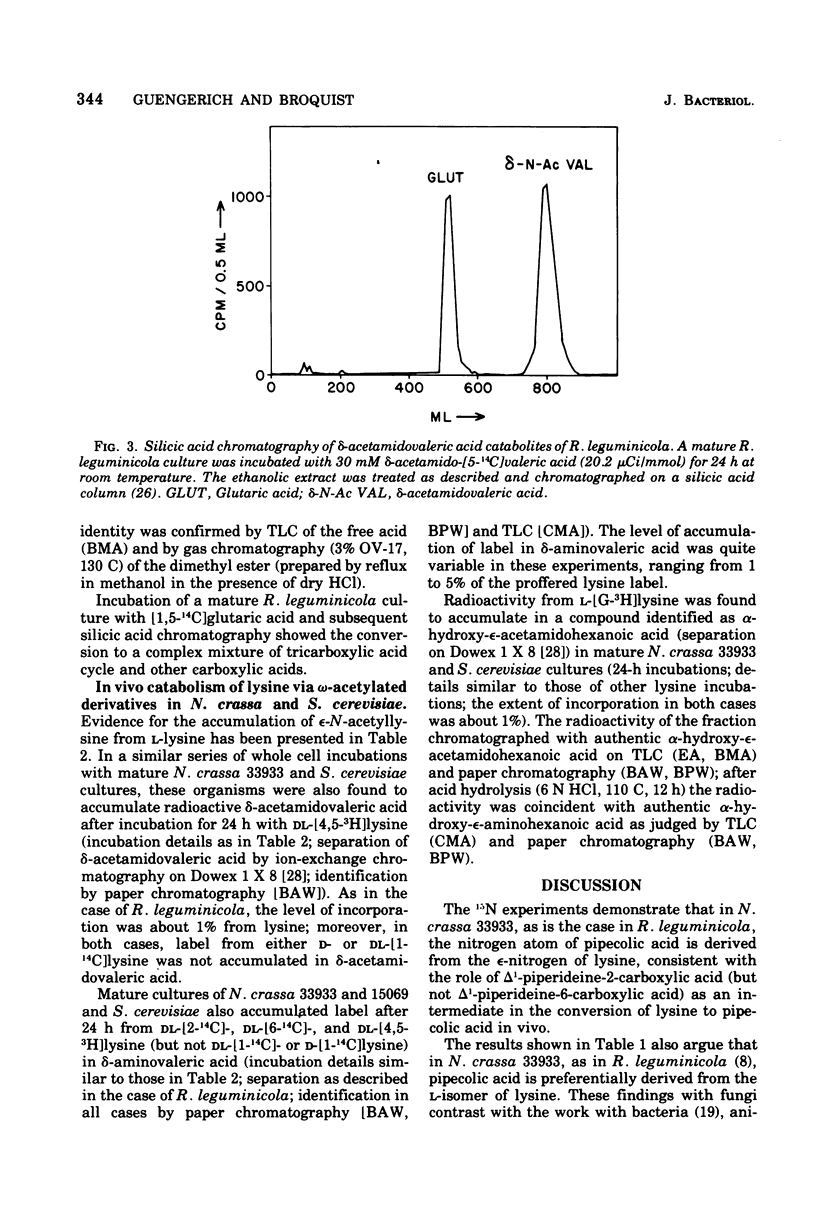
The catabolism of lysine was studied in several yeasts and fungi. Results with cell-free extracts of Rhizoctonia leguminicola support a proposed pathway involving (D- and L-) EPSILON-N-acetyllysine, alpha-keto-epsilon-acetamidohexanoic acid, delta-acetamidovaleric acid, and delta-aminovaleric acid in the conversion of L-lysine to shortchain organic acids. Label from radioactive L-lysine was found to accumulate in D- and L-epsilon-N-acetyllysine, delta-acetamidovaleric acid, delta-aminovaleric acid, and glutaric acid in cultures of R. leguminicola, Neurospora crassa, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Hansenula saturnus, suggesting that the proposed omega-acetyl pathway of lysine catabolism is generalized among yeasts and fungi. In N. crassa, as is the case in R. leguminicola, the major precursor of L-pipecolic acid was the L-isomer of lysine; 15N experiments were consistent with delta1-piperideine-2-carboxylic acid as an intermediate in the transformation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calvert A. F., Rodwell V. W. Metabolism of pipecolic acid in a Pseudomonas species. 3. L-alpha-aminoadipate delta-semialdehyde:nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidoreductase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. A., Gilbertson T. J., Hammerstedt R. H., Henderson L. M. The metabolism of D- and L-lysine specifically labeled with 15N. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 30;184(2):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Broquist H. P. Biosynthesis of slaframine, (1S,6S,8aS)-1-acetoxy-6-aminooctahydroindolizine, a parasympathomimetic alkaloid of fungal origin. II. The origin of pipecolic acid. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 9;12(21):4270–4274. doi: 10.1021/bi00745a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Snyder J. J., Broquist H. P. Biosynthesis of slaframine, (1S,6S,8aS)-1-acetoxy-6-aminooctahydroindolizine, a parasympathomimetic alkaloid of fungal origin. I. Pipecolic acid and slaframine biogenesis. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 9;12(21):4264–4269. doi: 10.1021/bi00745a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRREVERRE F., PIEZ K. A., WOLFF H. L. The separation and determination of cyclic imino acids. J Biol Chem. 1956 Dec;223(2):687–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUO M. H., SAUNDERS P. P., BROQUIST H. P. LYSINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN YEAST: A NEW METABOLITE OF ALPHA-AMINOADIPIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:508–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leistner E., Gupta R. N., Spenser I. D. A general method for the determination of precursor configuration in biosynthetic precursor-product relationships. Derivation of pipecolic acid from D-lysine, and of piperidine alkaloids from L-lysine. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Jun 13;95(12):4040–4047. doi: 10.1021/ja00793a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTOON J. R., HAIGHT R. D. Glutaric acid accumulation by a lysine-requiring yeast mutant. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3486–3490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEISTER A., RADHAKRISHNAN A. N., BUCKLEY S. D. Enzymatic synthesis of L-pipecolic acid and L-proline. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):789–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEISTER A. The alpha-keto analogues of arginine, ornithine, and lysine. J Biol Chem. 1954 Feb;206(2):577–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Rodwell V. W. Metabolism of basic amino acids in Pseudomonas putida. Catabolism of lysine by cyclic and acyclic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2758–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. U., Leistner E. Conversion of D-lysine via L-pepecolic acid in Neurospora crassa. Z Naturforsch C. 1975 Mar-Apr;30(2):253–262. doi: 10.1515/znc-1975-3-419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUMA S., ISHIMURA Y., NAKAZAWA T., OKAZAKI T., HAYAISHI O. ENZYMIC STUDIES ON THE METABOLISM OF GLUTARATE IN PSEUDOMONAS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3915–3926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger A., Sanger F. The availability of the acetyl derivatives of lysine for growth. Biochem J. 1943 Oct;37(4):515–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0370515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfetti R., Campbell R. J., Titus J., Hartline R. A. Catabolism of pipecolate to glutamate in Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4089–4095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSTEIN M., COOKSEY K. E., GREENBERG D. M. Metabolic conversion of pipecolic acid to alpha-aminoadipic acid. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2828–2830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSTEIN M., HART J. L. PRODUCTS OF LYSINE METABOLISM IN YEAST. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 8;93:439–441. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein M. Intermediates of lysine dissimilation in the yeast, Hansenula saturnus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Aug;111(2):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGISAKA S., SHIMURA K. Studies in lysine biosynthesis. II. Metabolic fate of DL-alpha-aminoadipic acid-6-C14 in T. utilis. J Biochem. 1961 May;49:392–396. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWEET R. S., HOLDEN J. T., LOWY P. H. The metabolism of lysine in Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):517–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda H., Hayaishi O. Crystalline L-lysine oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 10;241(11):2733–2736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



