Abstract
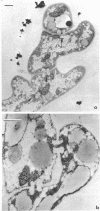
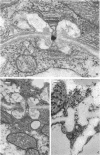
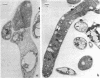
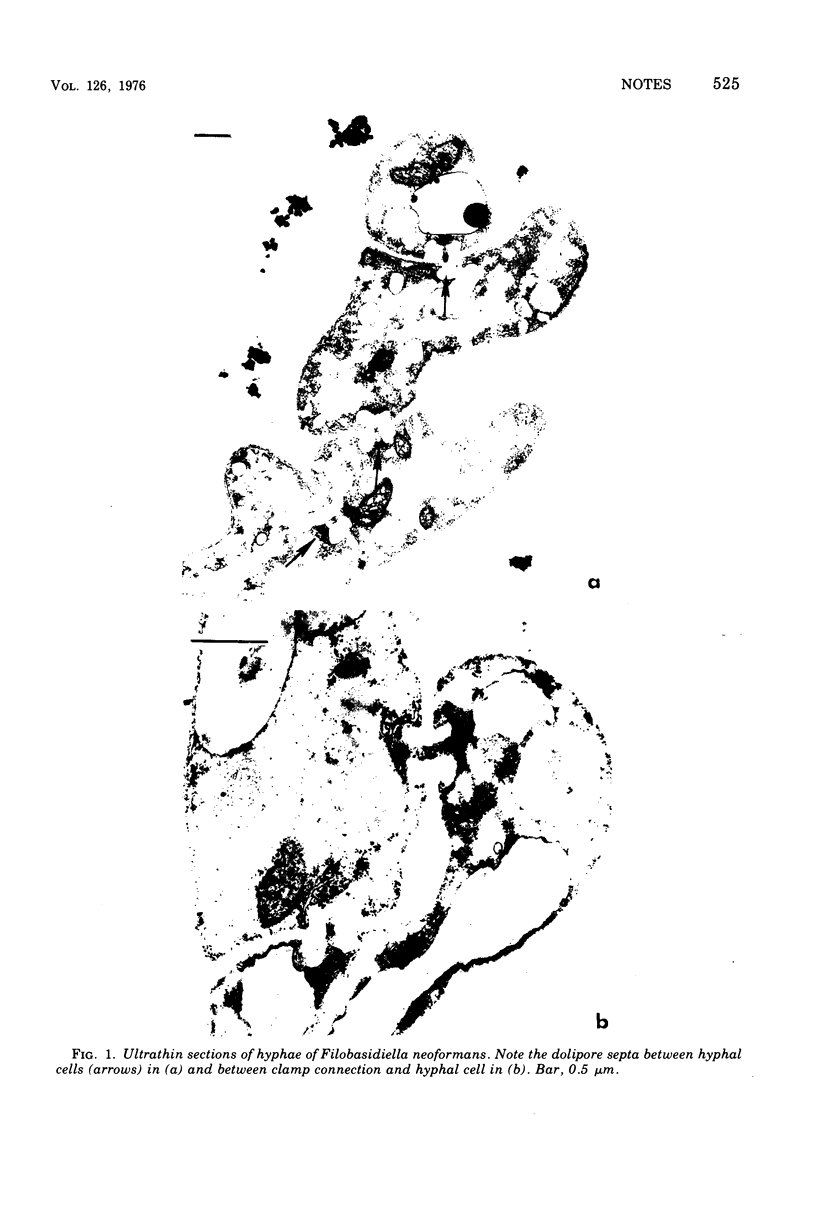
Electron microscopy of Filobasidiella neoformans, the perfect state of Cryptococcus neoformans, revealed basidiomycete doliporesepta between hyphal cells and also between clamp connections and adjacent cells. The pore-occluding material was a heterogeneous flattened plate with dark margins and a lighter center, as seen in the species of Filobasidium. Representative basidiomycete parenthesomes were lacking, and endoplasmic reticulum was seen in the dolipore region.
Full text
PDF
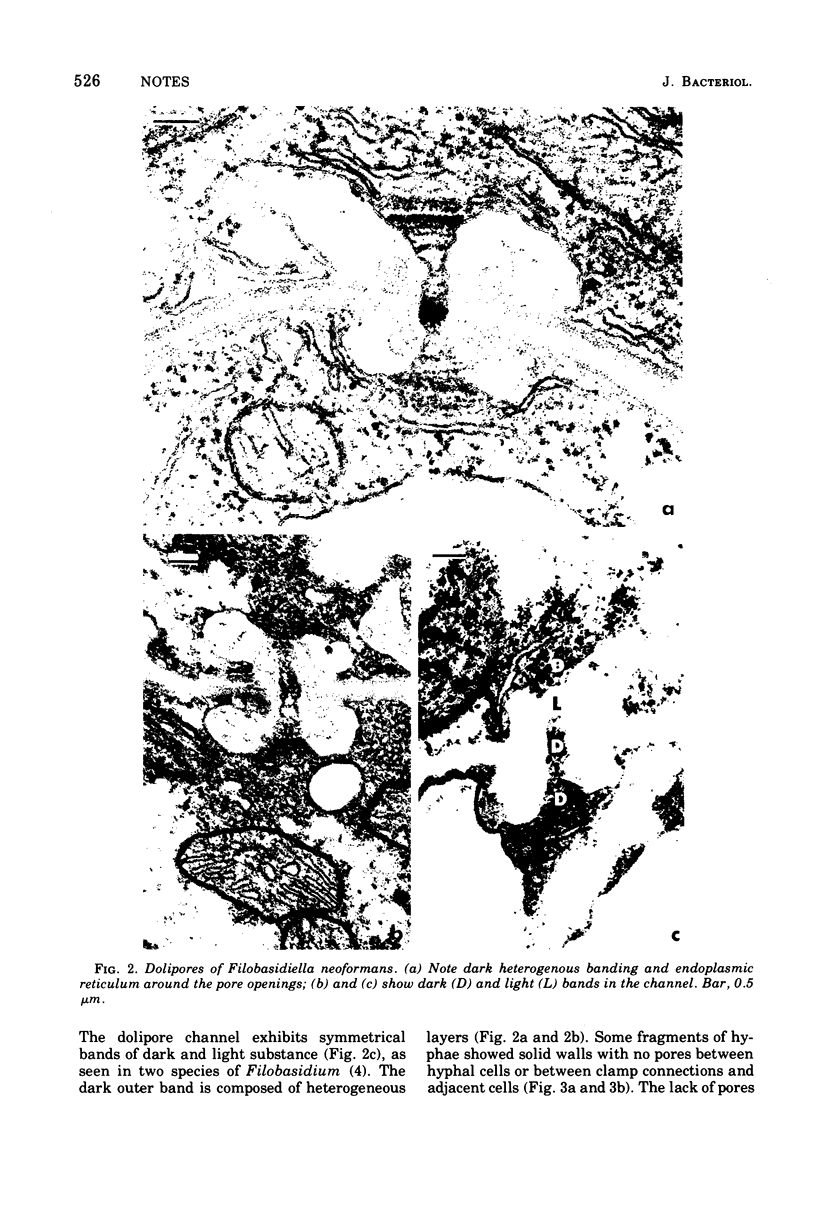
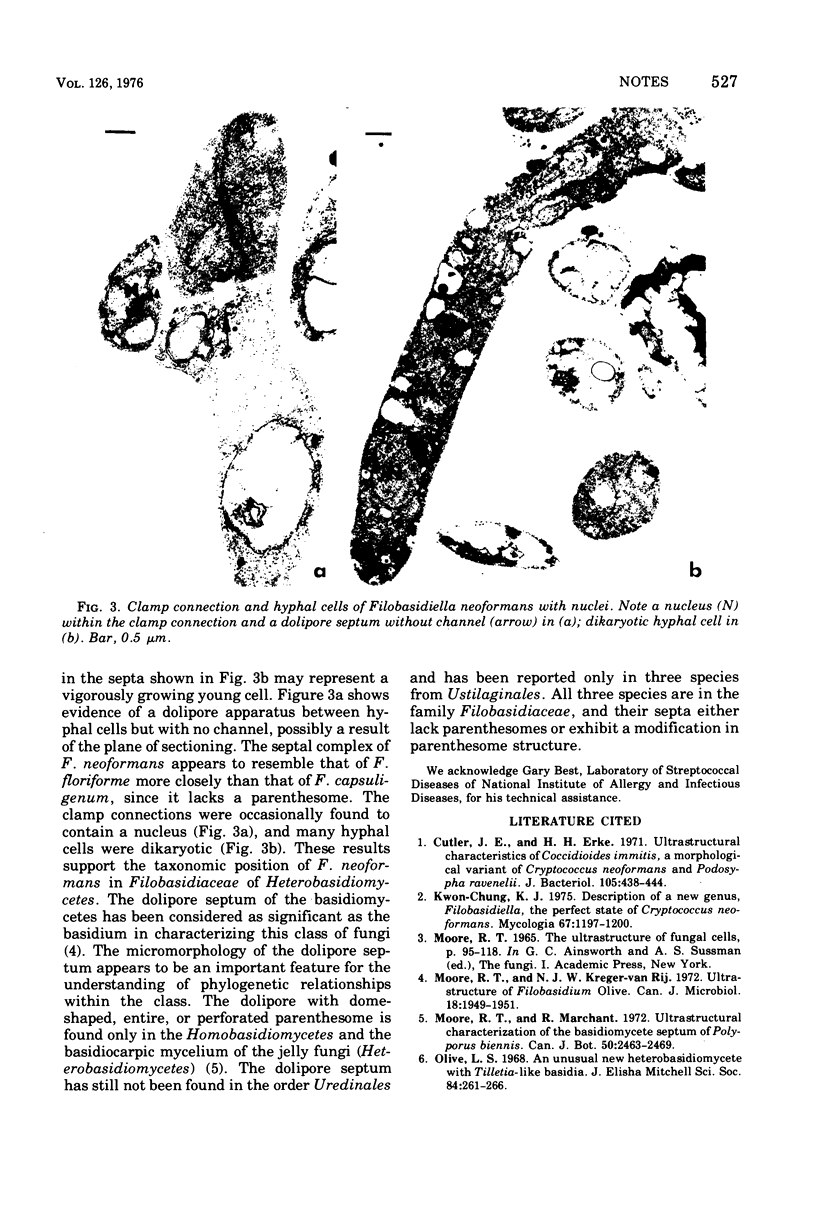

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cutler J. E., Erke K. H. Ultrastructural characteristics of Coccidioides immitis, a morphological variant of Cryptococcus neoformans and Podosypha ravenelii. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):438–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.438-444.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. A new genus, filobasidiella, the perfect state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1975 Nov-Dec;67(6):1197–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. T., Kreger-Van Rij N. J. Ultrastructure of Filobasidium Olive. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Dec;18(12):1949–1951. doi: 10.1139/m72-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popkin T. J., Theodore T. S., Cole R. M. Electron microscopy during release and purification of mesosomal vesicles and protoplast membranes from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):907–917. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.907-917.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues de Miranda L. Filobasidum capsuligenum nov. comb. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1972;38(1):91–99. doi: 10.1007/BF02328080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]