Abstract
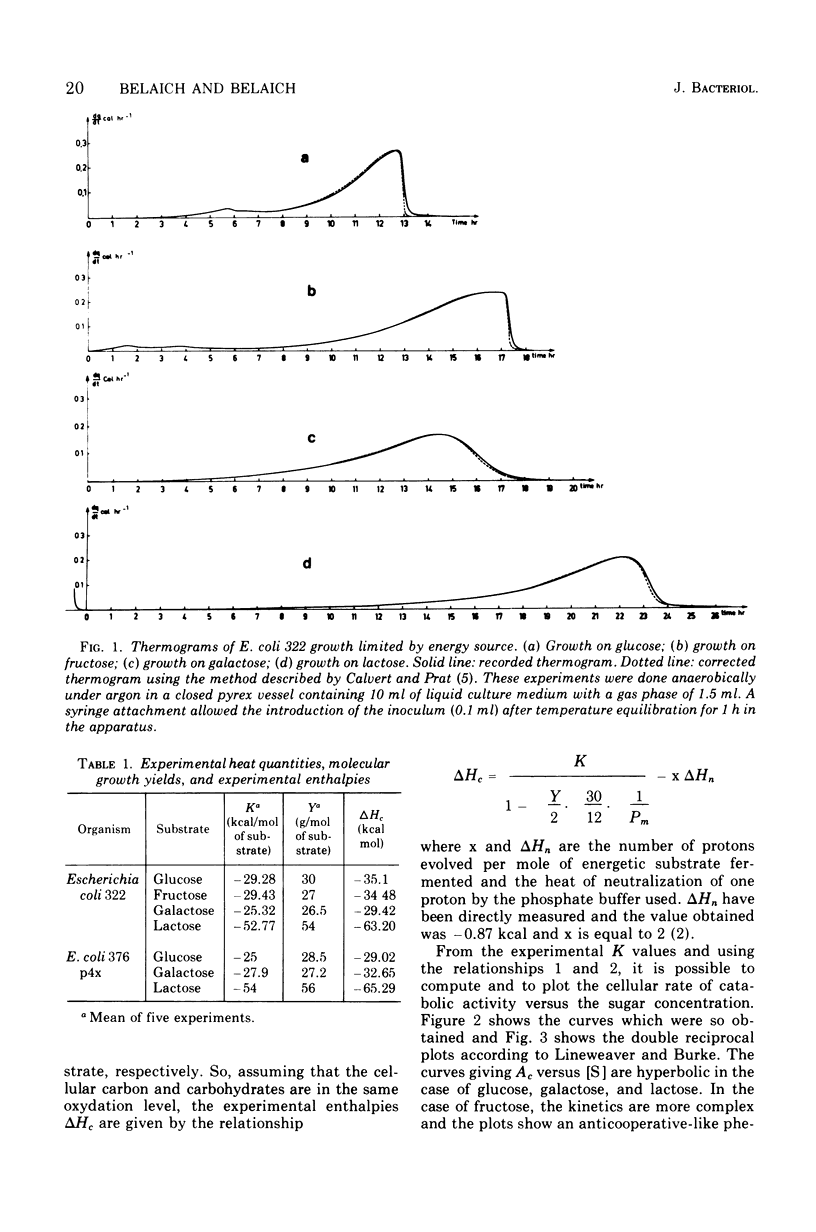
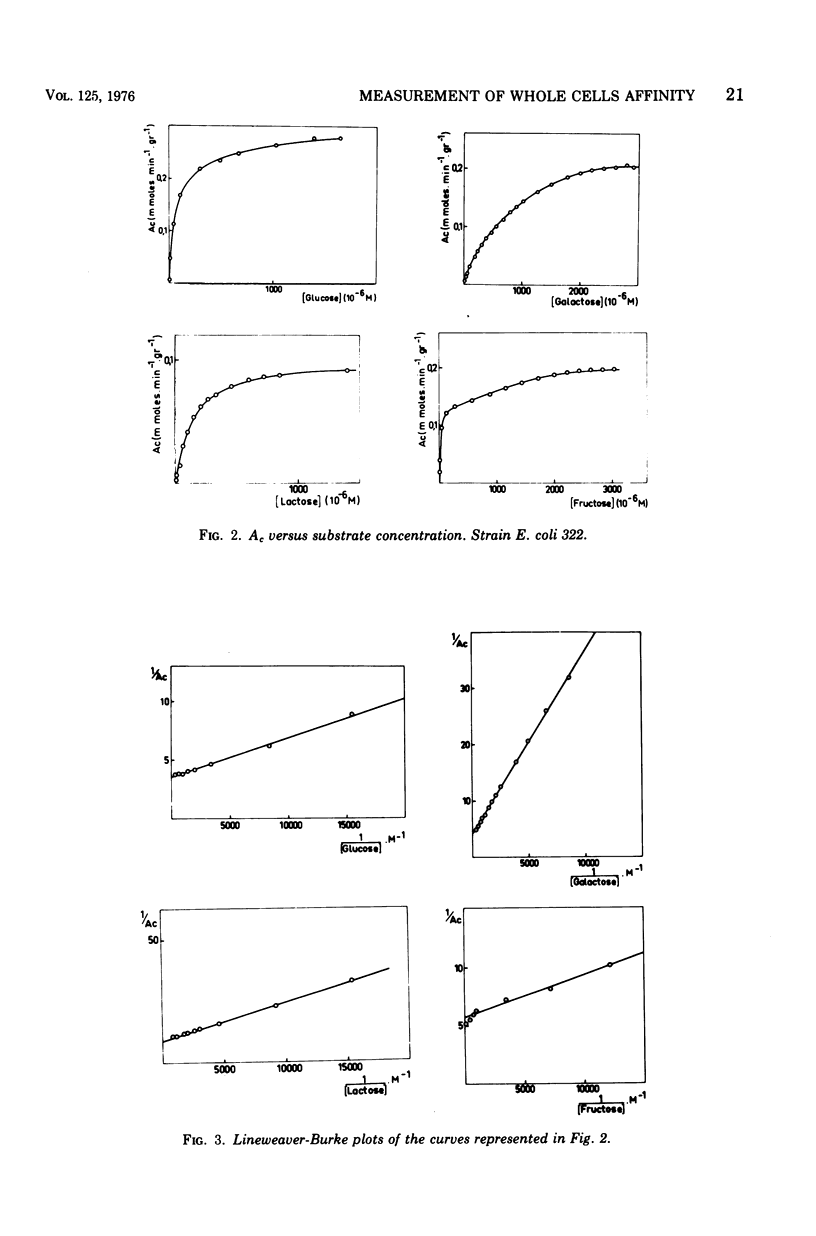
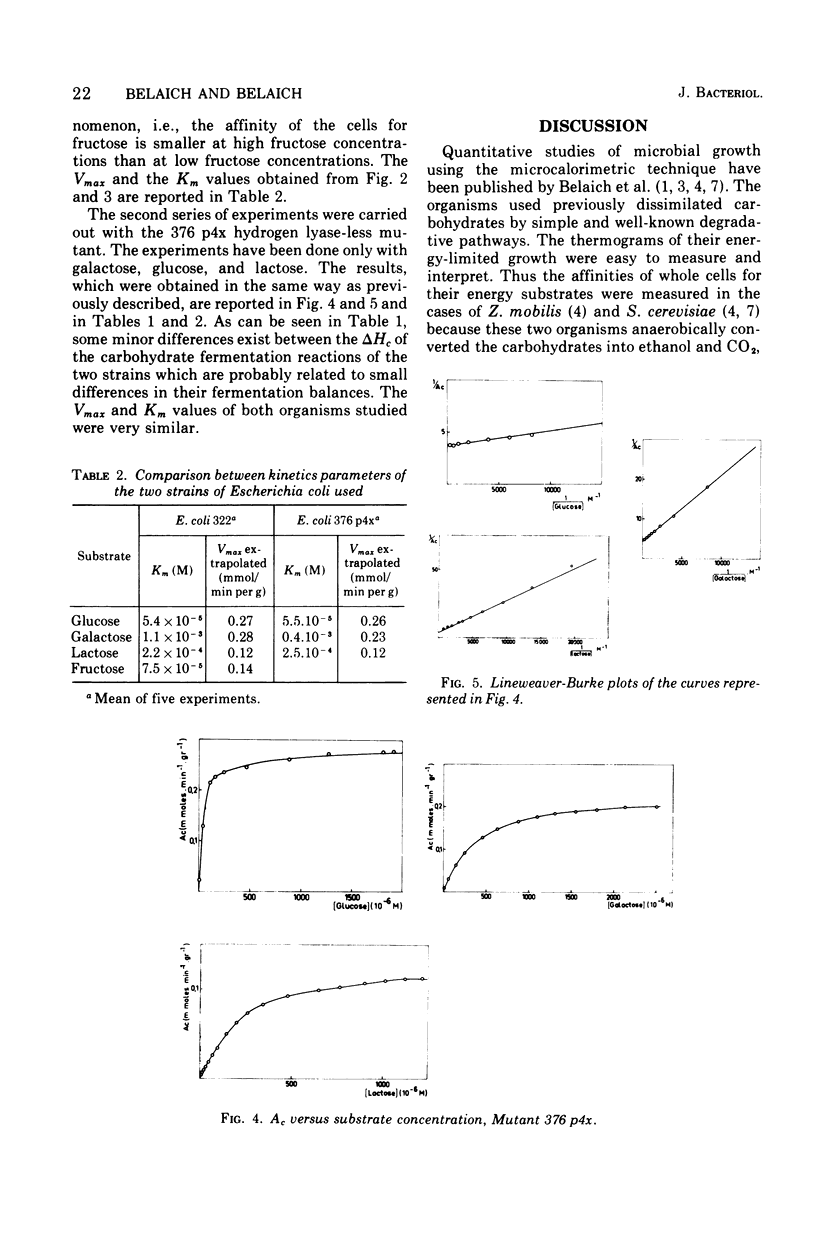
Microcalorimetry has been used to determine the affinity of whole cells of Escherichia coli for glucose, galactose, fructose, and lactose. Anaerobic growth thermograms were analyzed, and the Km and Vmax values for these energy substrates were measured at pH 7.8. Results obtained with this technique using various organisms growing anaerobically on different sugars are compared. This comparison shows that in practically all cases the cellular rate of catabolic activity is a hyperbolic function of the energy substrate concentrations at low sugar concentrations. In some cases this technique also allows determination of kinetics at high sugar concentrations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELAICH J. P., PRAT H. [Glucose-limiting thermogenesis and growth of Pseudomonas lindneri]. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1963 Jun 10;157:316–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belaich A., Belaich J. P. Microcalorimetric study of the anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli: growth thermograms in a synthetic medium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.14-18.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belaich J. P., Senez J. C., Murgier M. Microcalorimetric study of glucose permeation in microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1750–1757. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1750-1757.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgier M., Belaich J. P. Microcalorimetric determination of the affinity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for some carbohydrate growth substrates. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):573–579. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.573-579.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


