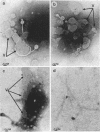
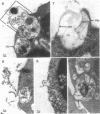
Abstract
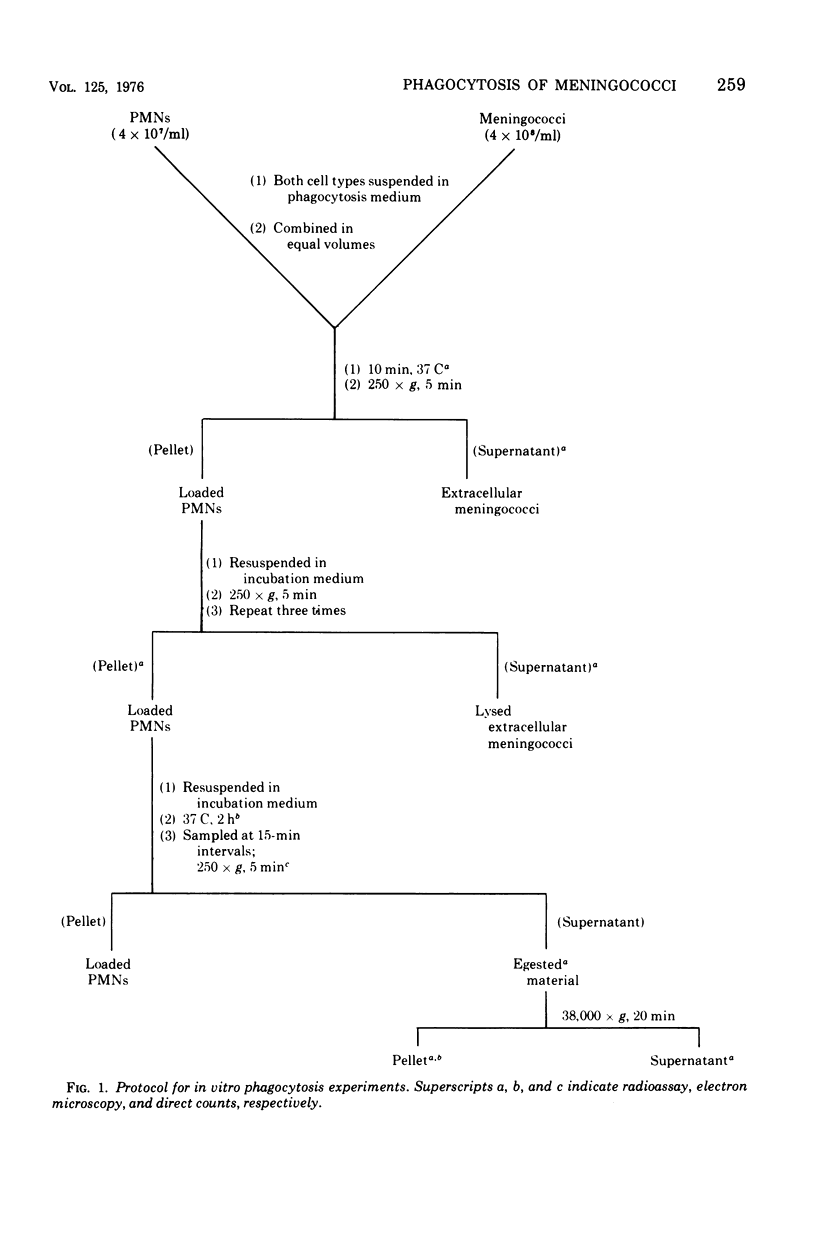
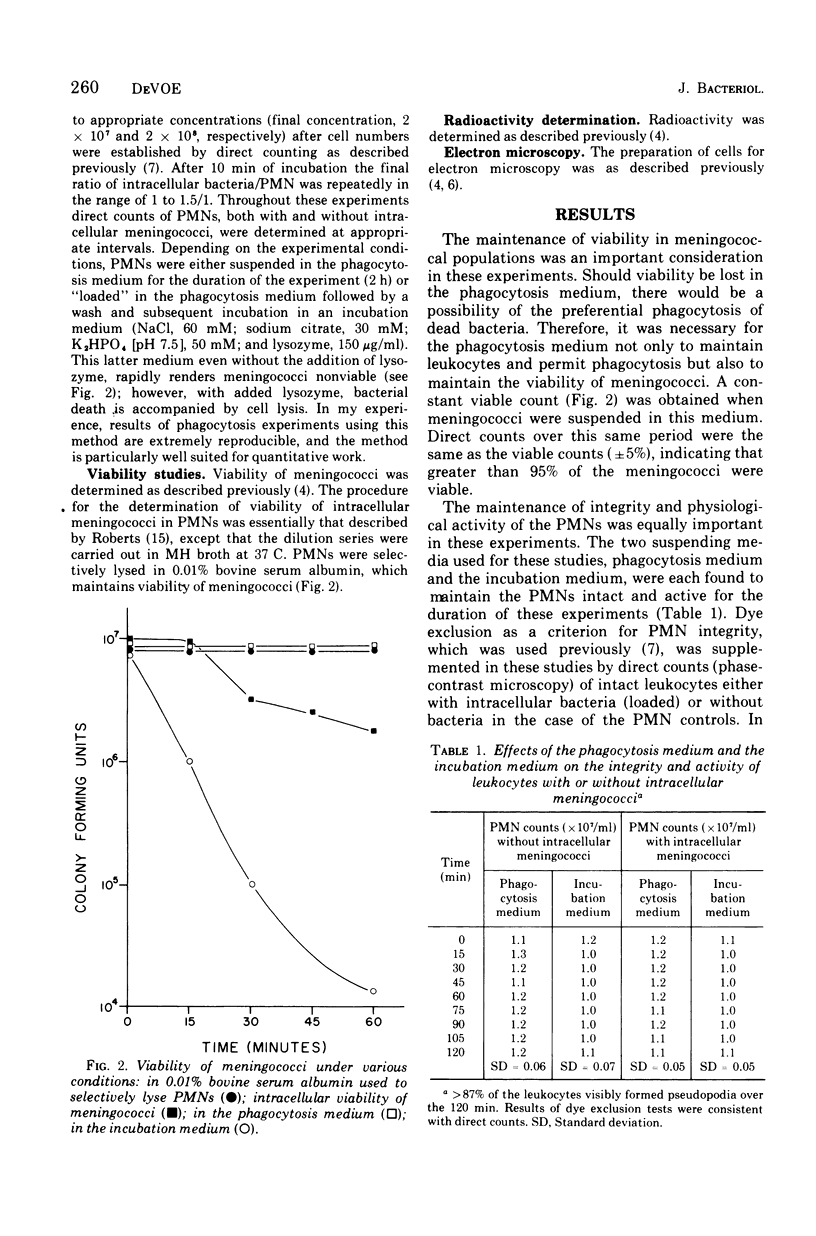
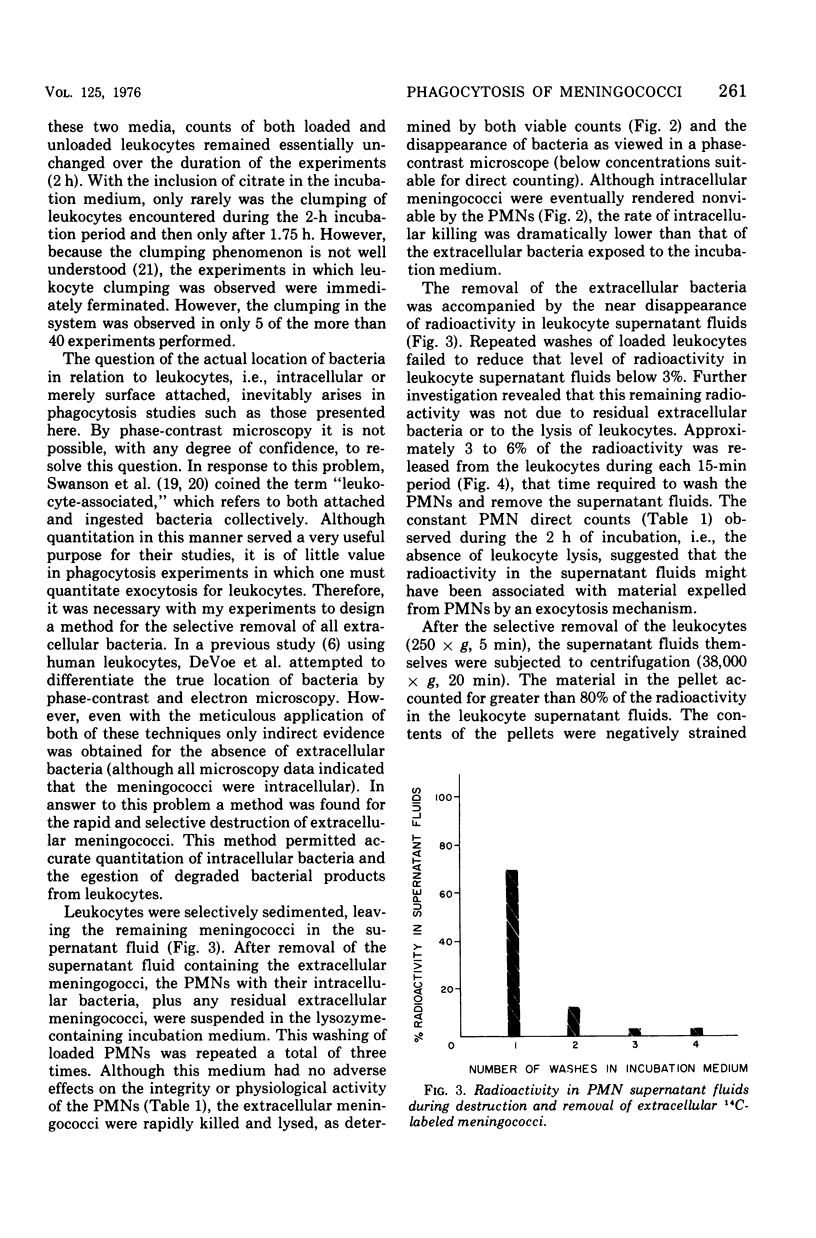
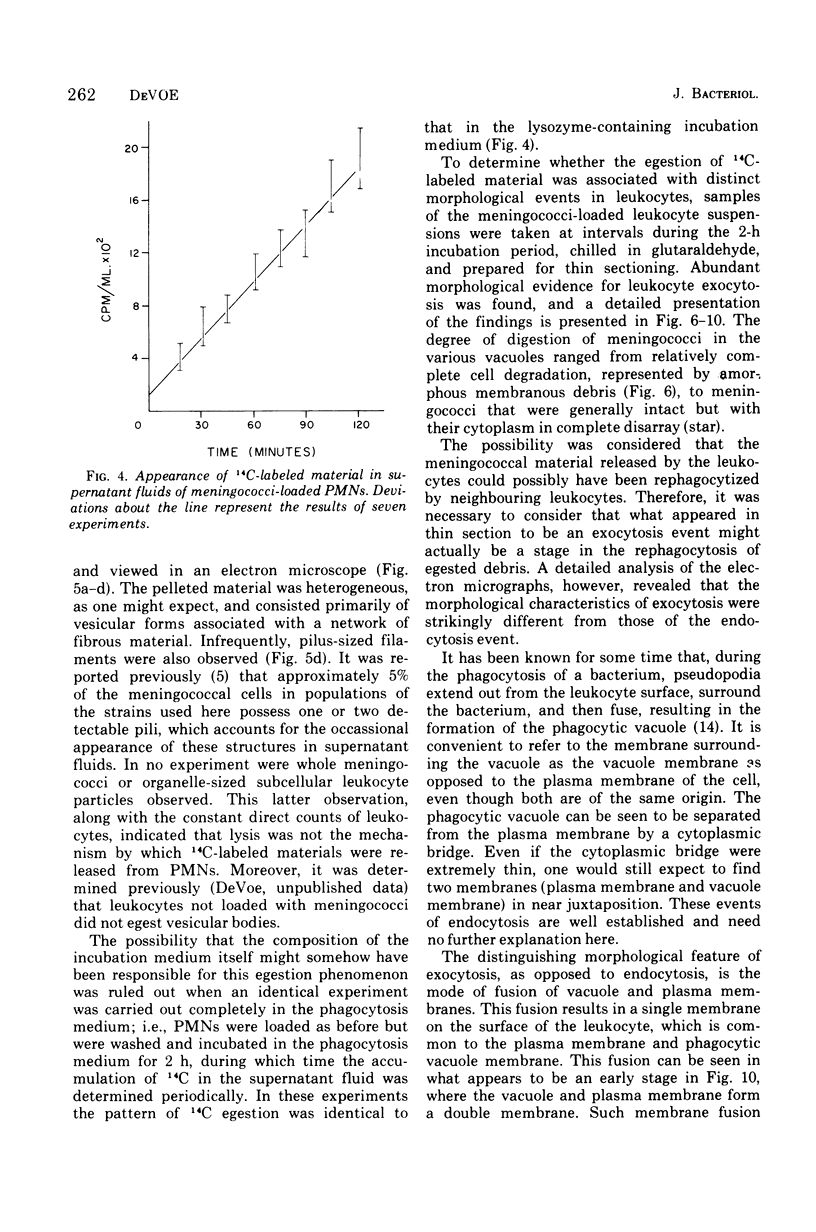
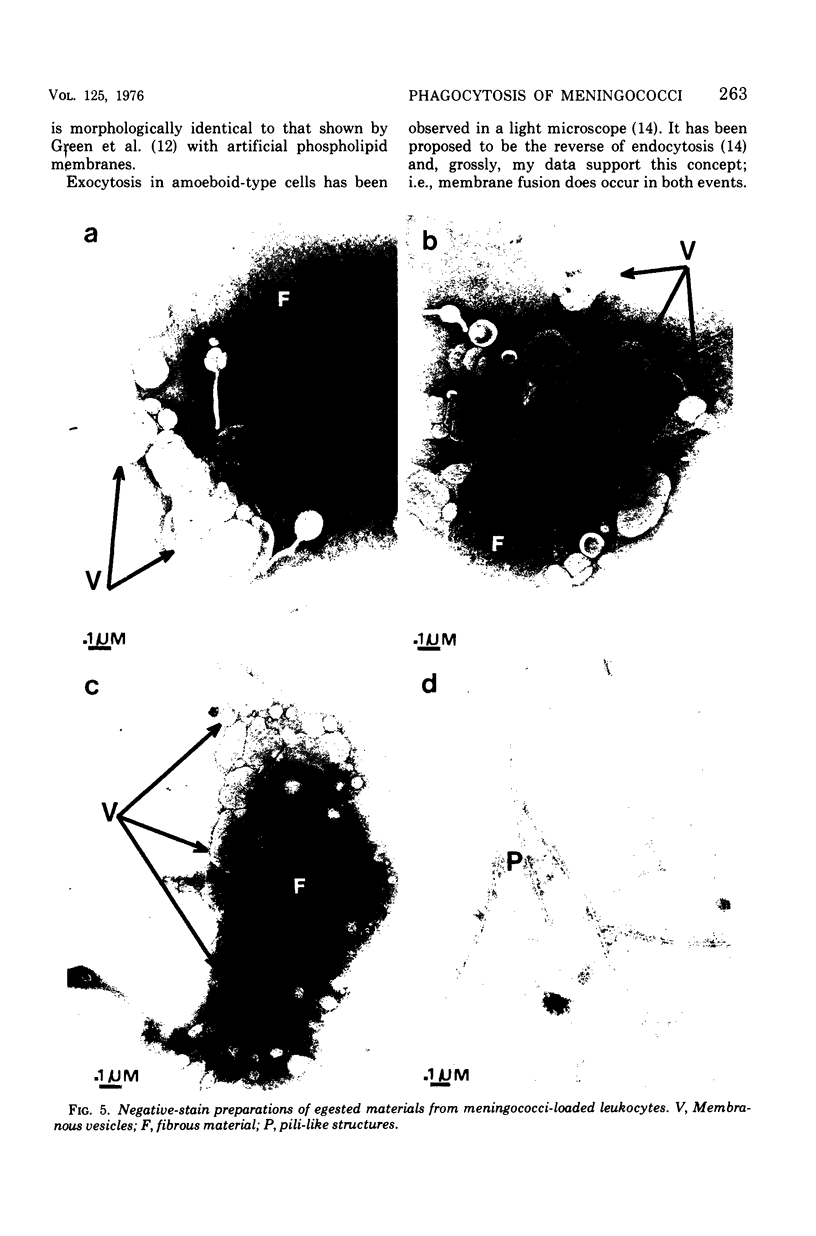
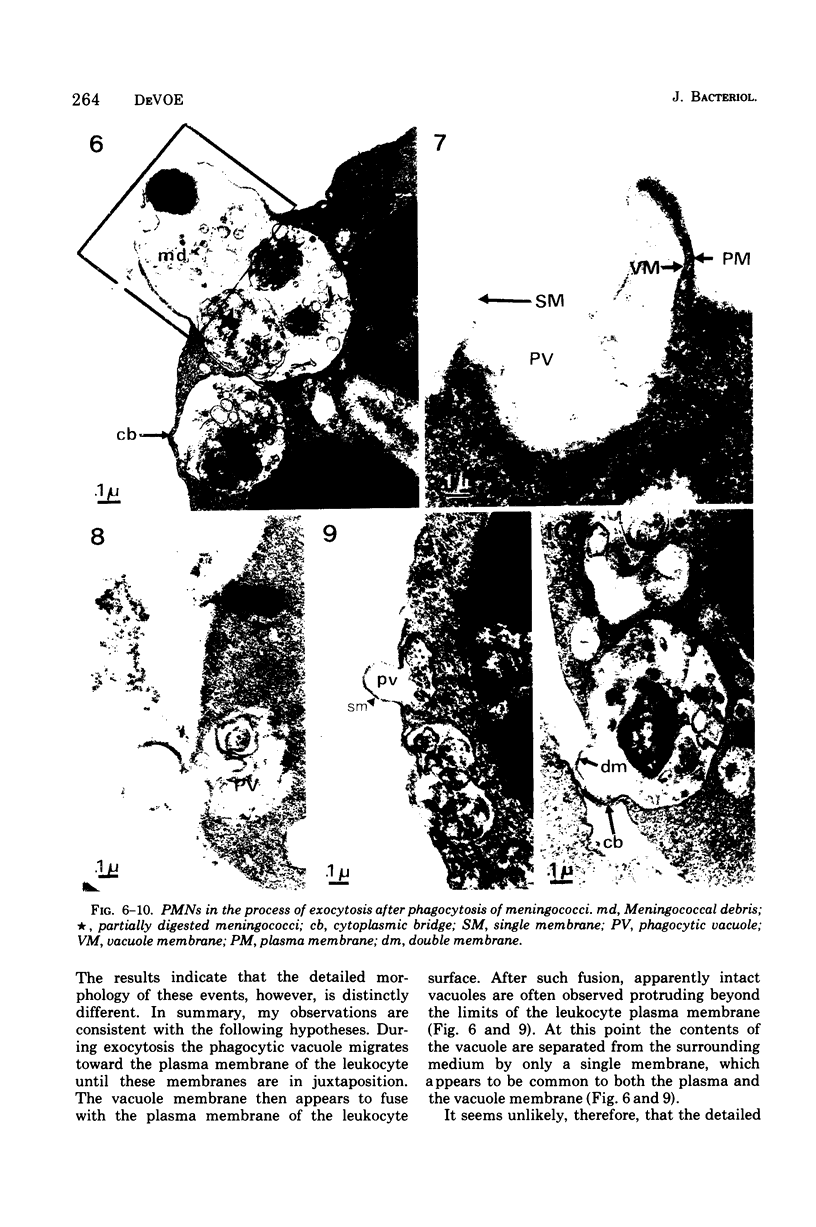
Quantitative studies were carried out on the in vitro phagocytosis of 14C-labeled Neisseria meningitidis by mouse polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Intact, "loaded" leukocytes were found to excrete radioactive bacterial products back into supernatant fluids. Morphological events associated with the exocytosis events revealed a fusion between the phagocytic vacuole and plasma membranes of the leukocyte followed by an emptying of the vacuole contents. Egested materials were free from whole meningococci and consisted mainly of membranous vesicles.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHN Z. A. The fate of bacteria within phagocytic cells. I. The degradation of isotopically labeled bacteria by polymorphonuclear leucocytes and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1963 Jan 1;117:27–42. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS R. D., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. VI. The interaction of leucocytes and endotoxin in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Dec 1;110:1005–1016. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.6.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Thompson J., Costerton J. W., MacLeod R. A. Stability and comparative transport capacity of cells, mureinoplasts, and true protoplasts of a gram-negative bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1014–1026. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1014-1026.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E., Storm D. W. Ultrastructural studies on the fate of group B meningococci in human peripheral blood leukocytes. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1355–1359. doi: 10.1139/m73-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W., Storm D. W., Gilchrist J. E. A study of phagocytosis of radio-labeled Staphylococcus epidermidis and on structural events during intracellular degradation. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Apr;19(4):525–530. doi: 10.1139/m73-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Release of endotoxin in the form of cell wall blebs during in vitro growth of Neisseria meningitidis. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1156–1167. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Ultrastructure of pili and annular structures on the cell wall surface of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):872–876. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.872-876.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducker T. B., Simmons R. L. The pathogenesis of meningitis. Systemic effect of meningococcal endotoxin within the cerebrospinal fluid. Arch Neurol. 1968 Feb;18(2):123–128. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470320025002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON J. H., CHAPMAN O. D. Fulminating meningococcic infections and the so-called Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1948 Jul;24(4):763–795. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P. Comparison of endotoxin detoxification by leukocytes and macrophages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1396–1400. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., COHN Z. A. Degranulation of polymorphonuclear leucocytes following phagocytosis of microorganisms. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1005–1014. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. B. The interaction in vitro between group B meningococci and rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Demonstration of type specific opsonins and bactericidins. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):795–818. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERP H. W. Neisseria and neisserial infections. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1955;9:319–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.09.100155.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahama T., Cohen A. S. Ultrastructural evidence for leakage of lysosomal contents after phagocytosis of monosodium urate crystals. A mechanism of gouty inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1974 Sep;76(3):501–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Biochemical challenge of microbial pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Sep;32(3):164–184. doi: 10.1128/br.32.3.164-184.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Zeligs B., Siam M. A., Parrott C. Studies on gonococcus infection. V. Observations on in vitro interactions of gonococci and human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):633–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.633-644.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Zeligs B. Studies on gonococcus infection. VI. Electron microscopic study on in vitro phagocytosis of gonococci by human leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):645–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.645-656.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talstad I. The relationship between phagocytosis of polystyrene latex particles by polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PML) and aggregation of PML. Scand J Haematol. 1972;9(5):516–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1972.tb00978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]