Abstract
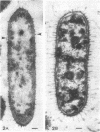
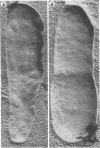
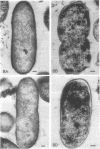
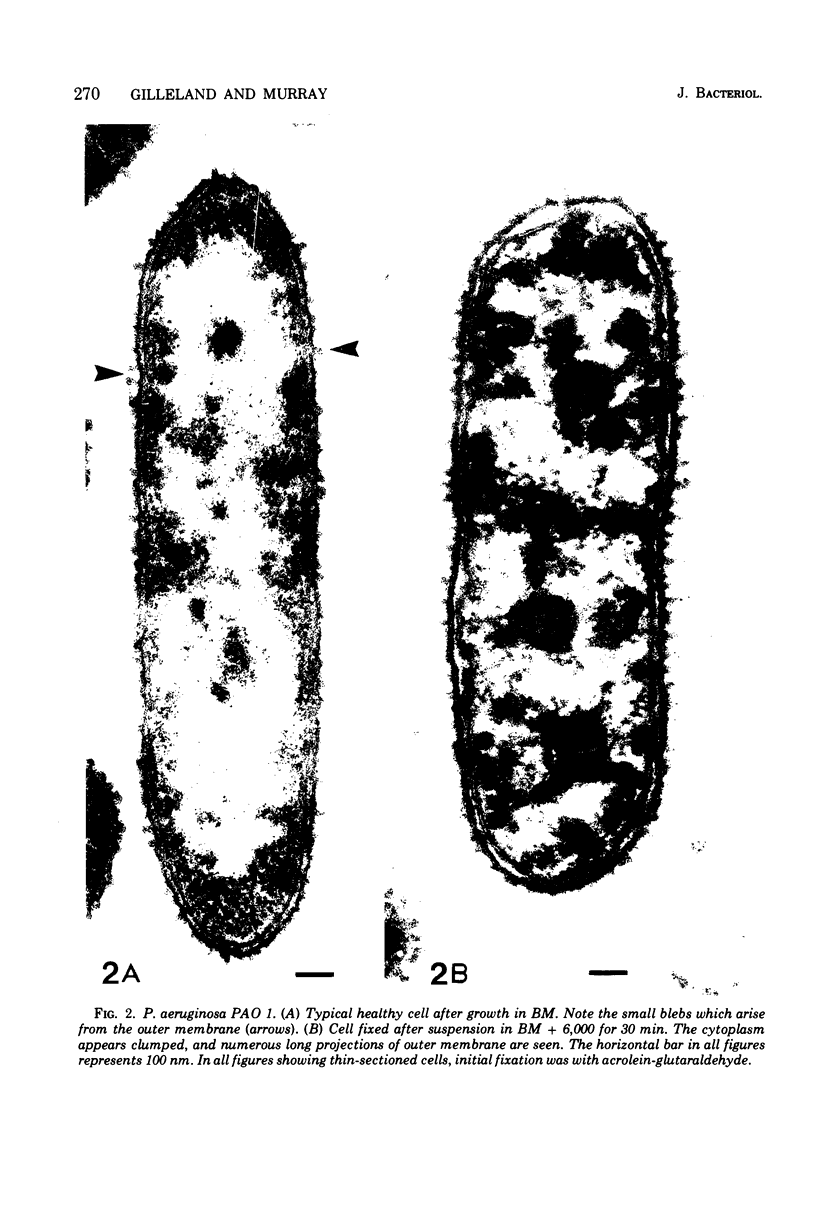
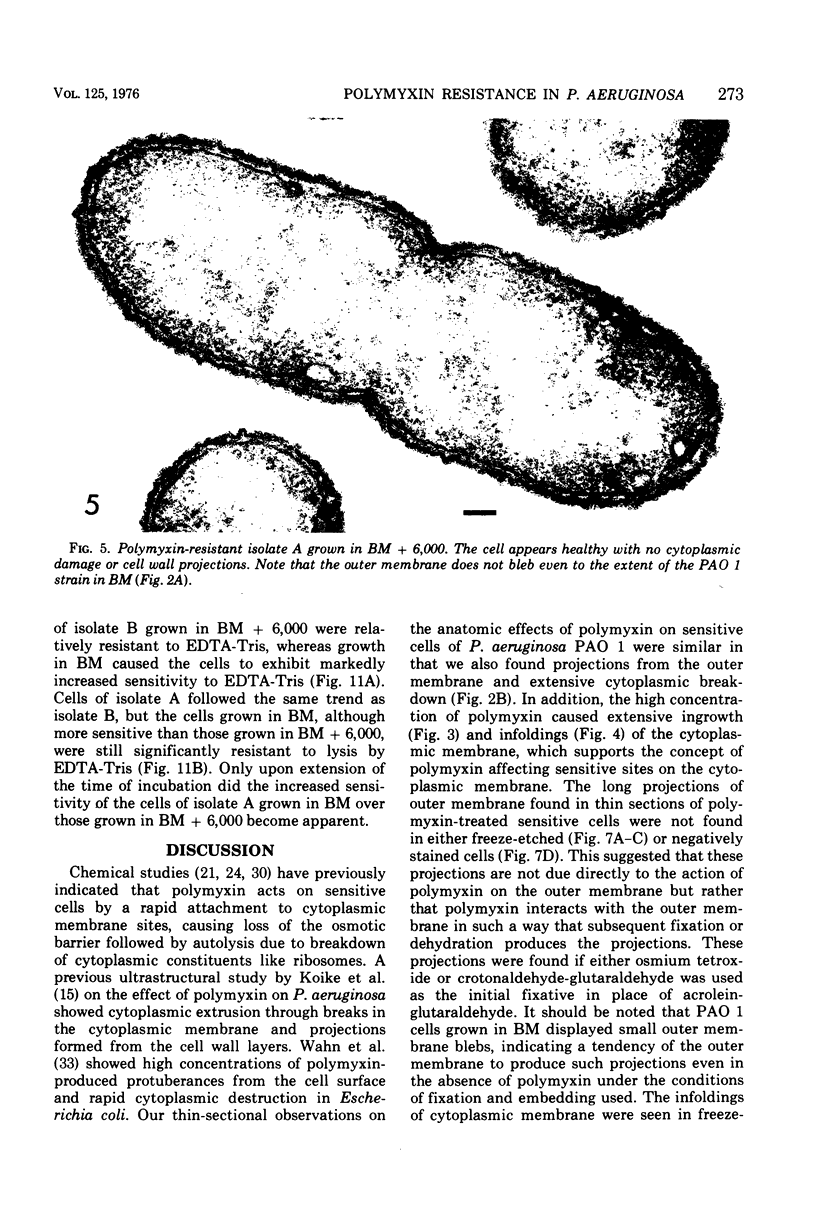
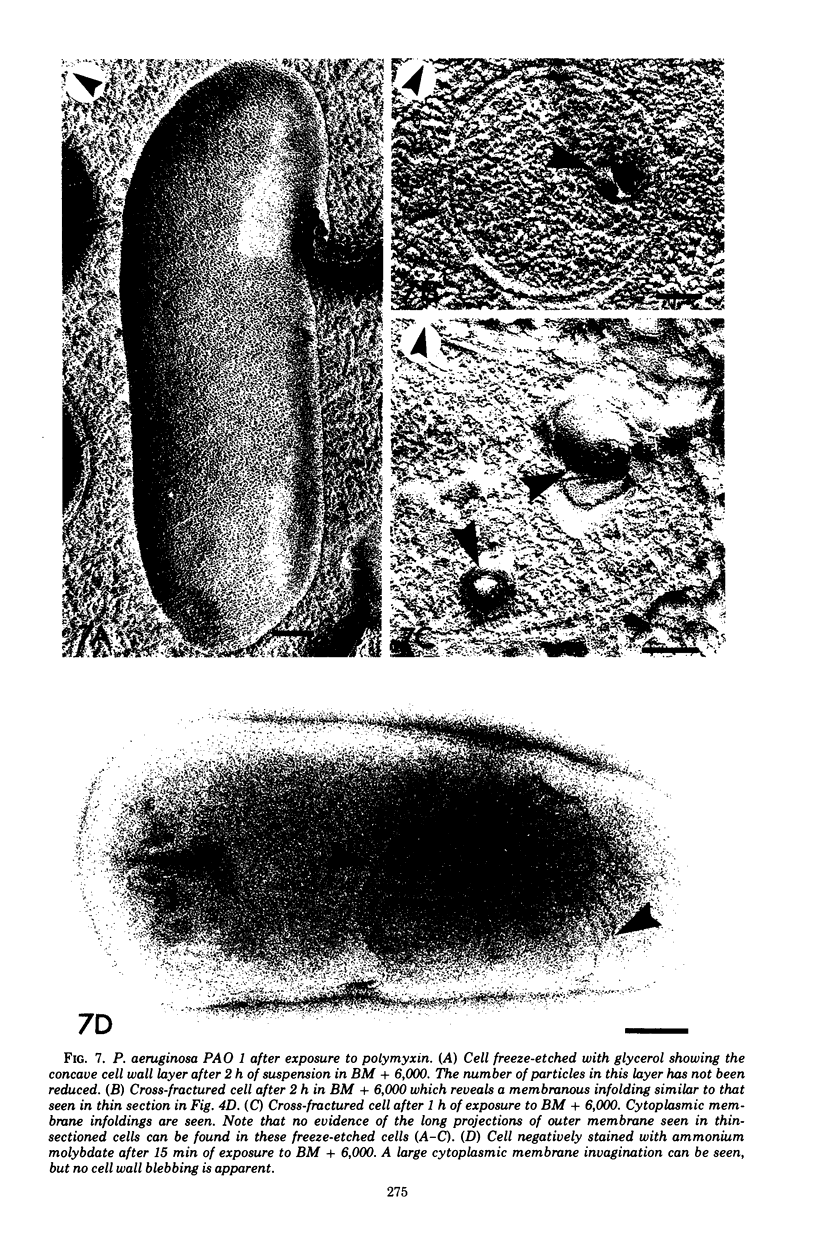
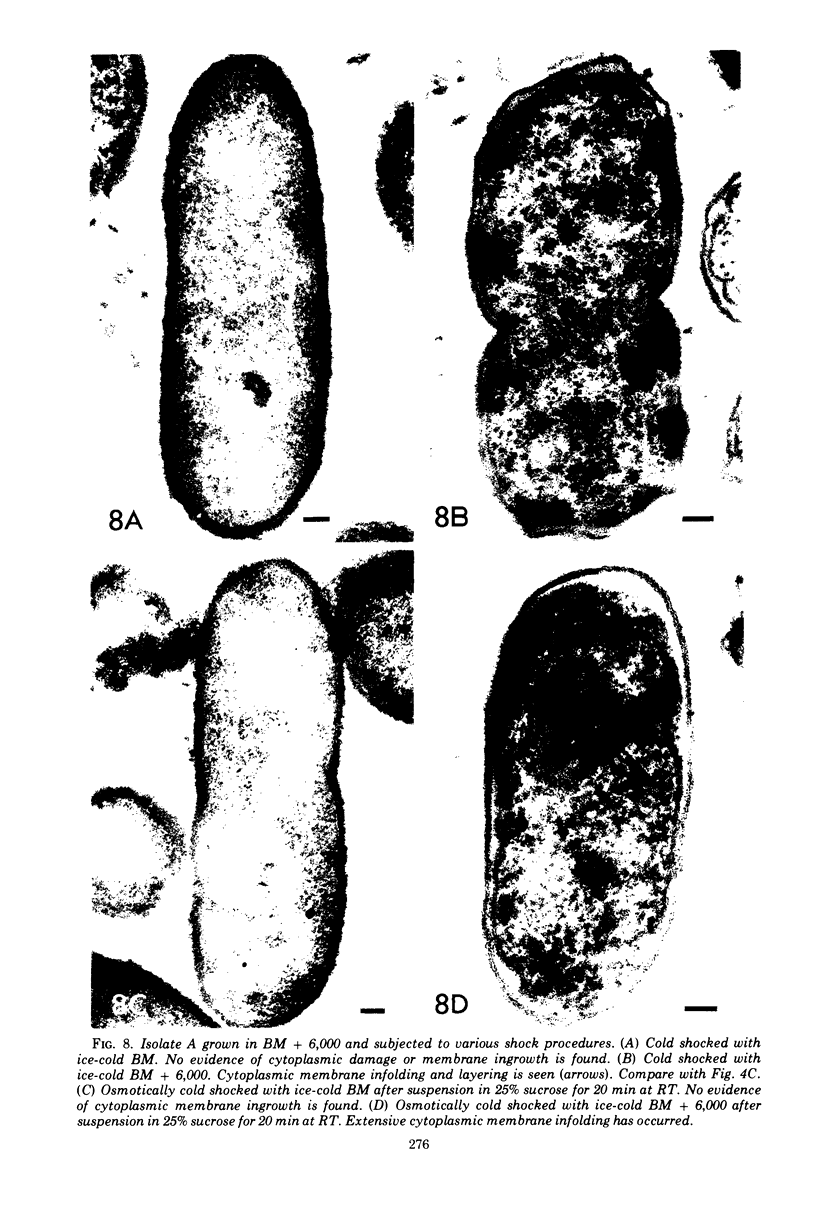
Upon exposure to 6,000 U of polymyxin B sulfate per ml, cells of the polymyxin-sensitive PAO 1 strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa displayed in thin sections long projections arising from the outer membrane of the cell wall and extensive cytoplasmic degradation with accumulation of cytoplasmic membrane infoldings. Polymyxin-resistant isolates derived from the PAO 1 strain, however, grew well in the presence of 6,000 U of polymyxin per ml and exhibited none of these effects, having instead the appearance of a typically healthy cell. Freeze-etching of cells of the sensitive strain grown in basal medium without polymyxin revealed a concave cell wall layer studded with numerous particles. Freeze-etching of cells of the resistant isolates grown in basal medium containing 6,000 U of polymyxin per ml revealed a concave cell wall layer (i.e., the outer half of the outer membrane) in which most of these particles were absent. Thus, acquisition of resistance to polymyxin was correlated with an alteration in the architecture of the outer membrane. When the resistant isolates were grown in the basal medium lacking polymyxin and then freeze-etched, the particle distribution in the concave cell wall layer resembled that of the sensitive parent strain. The cells had regained sensitivity to polymyxin upon suspension in medium containing 6,000 U/ml as determined by their failure to grow and by internal damages seen in thin sections. These cells also had acquired increased sensitivity to ethylenediaminetetraacetate, whereas the polymyxin-resistant cells grown in the presence of polymyxin were resistant to lysis by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. The polymyxin-resistant isolates were not stable mutants but instead represented an adaptive response to the presence of polymyxin in the medium.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Spudich E. N., Nikaido H. Protein composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):406–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.406-416.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E., Asscher A. W. Action of ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid (EDTA) on carbenicillin-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):355–359. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Jonsson S., Monner D., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Cell-surface alterations in Escherichia coli K-12 with chromosmal mutations changing ampicillin resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:342–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Melling J. Role of divalent cations in the action of polymyxin B and EDTA on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(2):263–274. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Watkins W. M. Low magnesium and phospholipid content of cell wals of Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to polymyxin. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1360–1361. doi: 10.1038/2271360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Wood S. M. Relation between cation and lipid content of cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus vulgaris and Klebsiella aerogenes and their sensitivity to polymyxin B and other antibacterial agents. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;24(3):215–218. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Murray R. G. Demonstration of cell division by septation in a variety of gram-negative rods. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):721–725. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.721-725.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Stinnett J. D., Eagon R. G. Ultrastructural and chemical alteration of the cell envelope of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, associated with resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate resulting from growth in a Mg2+-deficient medium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):302–311. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.302-311.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Stinnett J. D., Roth I. L., Eagon R. G. Freeze-etch study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: localization within the cell wall of an ethylenediaminetetraacetate-extractable. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):417–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.417-432.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. A. The mechanism of the bacteriostatic action of tetrachlorosalicylanilide: a Membrane-active antibacterial compound. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):441–458. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Genetics of Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Sep;33(3):419–443. doi: 10.1128/br.33.3.419-443.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M. A three-dimensional molecular assembly model of a lipoprotein from the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K. Effect of polymyxin on the bacteriophage receptors of the cell walls of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1402–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1402-1411.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Iida K., Matsuo T. Electron microscopic studies on mode of action of polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):448–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.448-452.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koplow J., Goldfine H. Alterations in the outer membrane of the cell envelope of heptose-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):527–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.527-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder I. G. Interrelated effects of cold shock and osmotic pressure on the permeability of the Escherichia coli membrane to permease accumulated substrates. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):211–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.211-219.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley M., Dawes E. A. The regulation of transport of glucose and methyl alpha-glucoside in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):141–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1320141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monner D. A., Jonsson S., Boman H. G. Ampicillin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 with lipopolysaccharide alterations affecting mating ability and susceptibility to sex-specific bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1971 Aug;107(2):420–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.2.420-432.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):14–27. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.14-27.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. W., Gilleland H. E., Jr, Eagon R. G. Characterization of a protein-lipopolysaccharide complex released from cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):743–748. doi: 10.1139/m69-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., MacAlister T., Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J. Permeability of lipopolysaccharide-deficient (rough) mutants of Salmonella typhimurium to antibiotics, lysozyme, and other agents. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Aug;20(8):1135–1145. doi: 10.1139/m74-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Thornley M. J., Glauert A. M. Location of the fracture faces within the cell envelope of Acinetobacter species strain MJT-F5-5. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):693–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.693-707.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinnett J. D., Gilleland H. E., Jr, Eagon R. G. Proteins released from cell envelopes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on exposure to ethylenediaminetetraacetate: comparison with dimethylformamide-extractable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):399–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.399-407.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Matsuhashi M. Increase in sensitivity to antibiotics and lysozyme on deletion of lipopolysaccharides in Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):453–454. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.453-454.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Sato T., Matsuhashi M. Role of lipopolysaccharides in antibiotic resistance and bacteriophage adsorption of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):968–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.968-975.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. H., Broadbridge R. A. The nature of carbenicillin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(2):231–241. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-2-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahn K., Lutsch G., Rockstroh T., Zapf K. Morphological and physiological investigations on the action of polymyxin B on Escherichia coli. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;63(2):103–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00412165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]