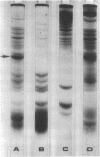
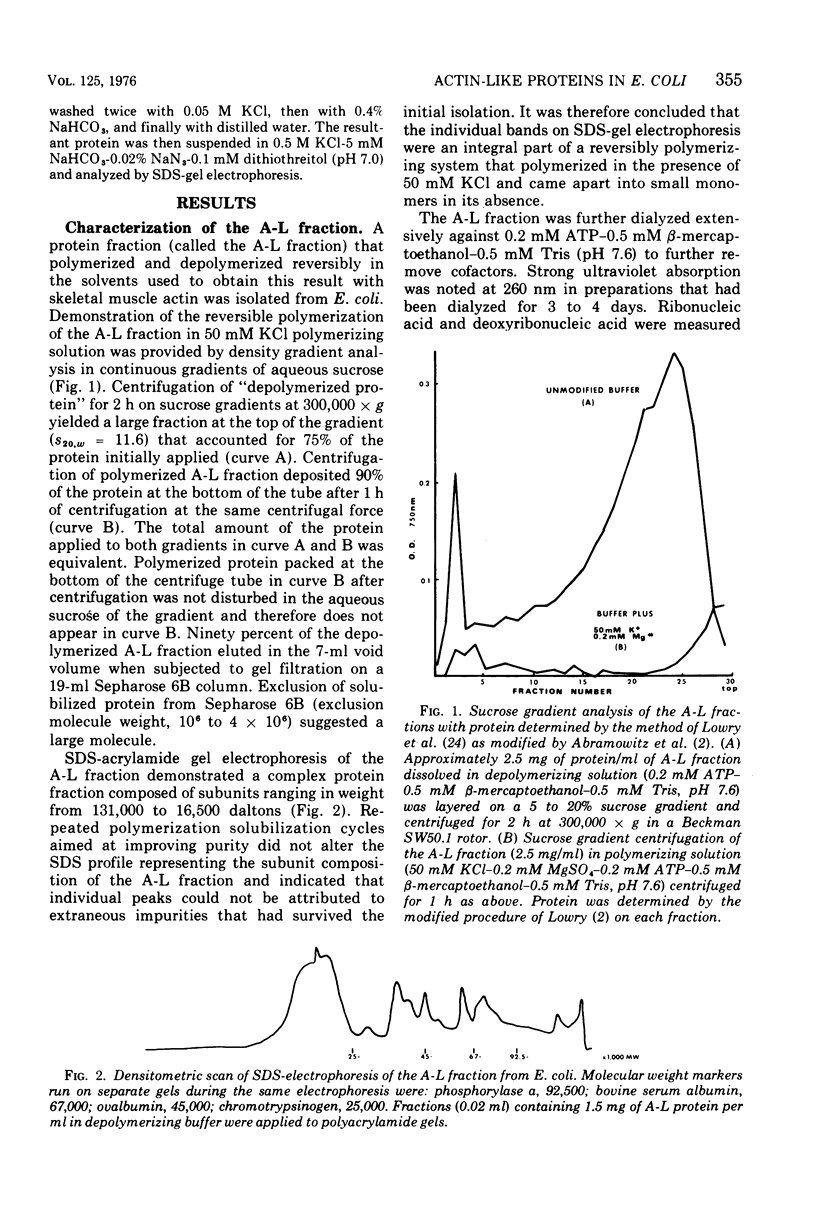
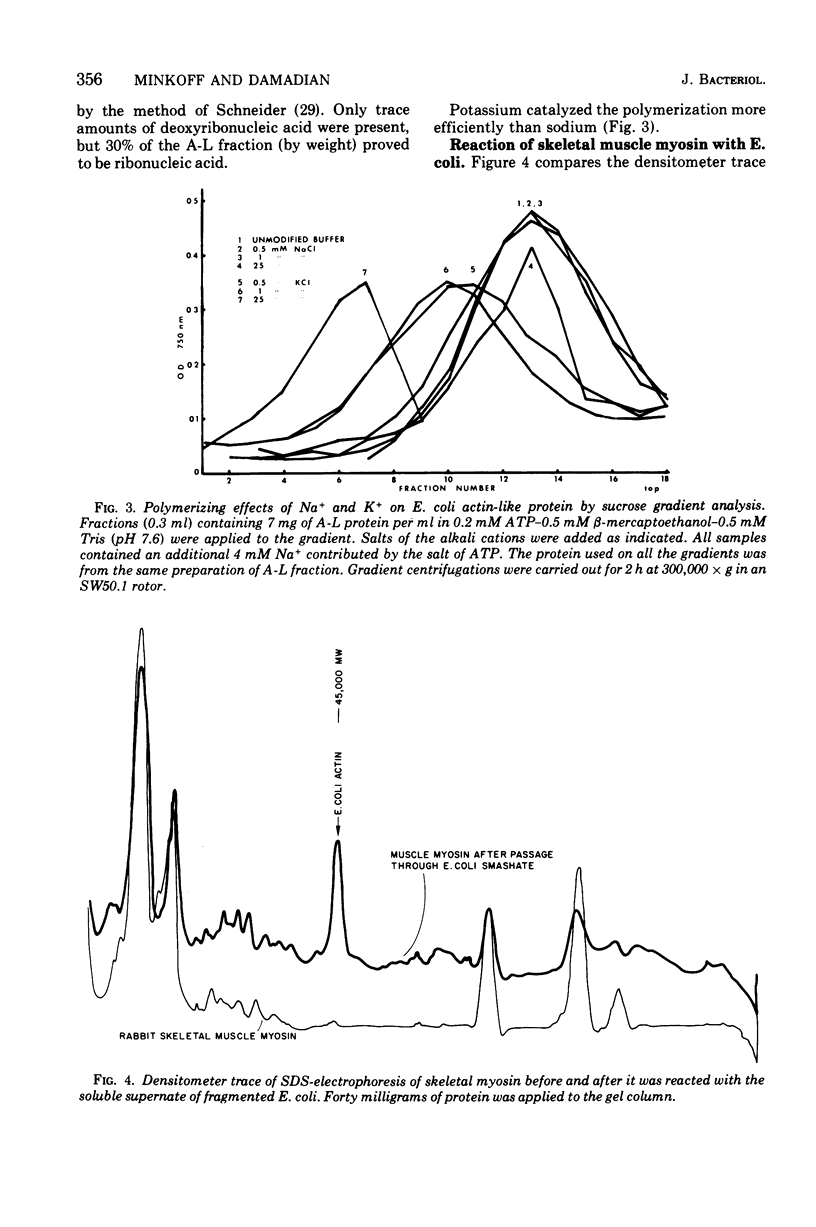
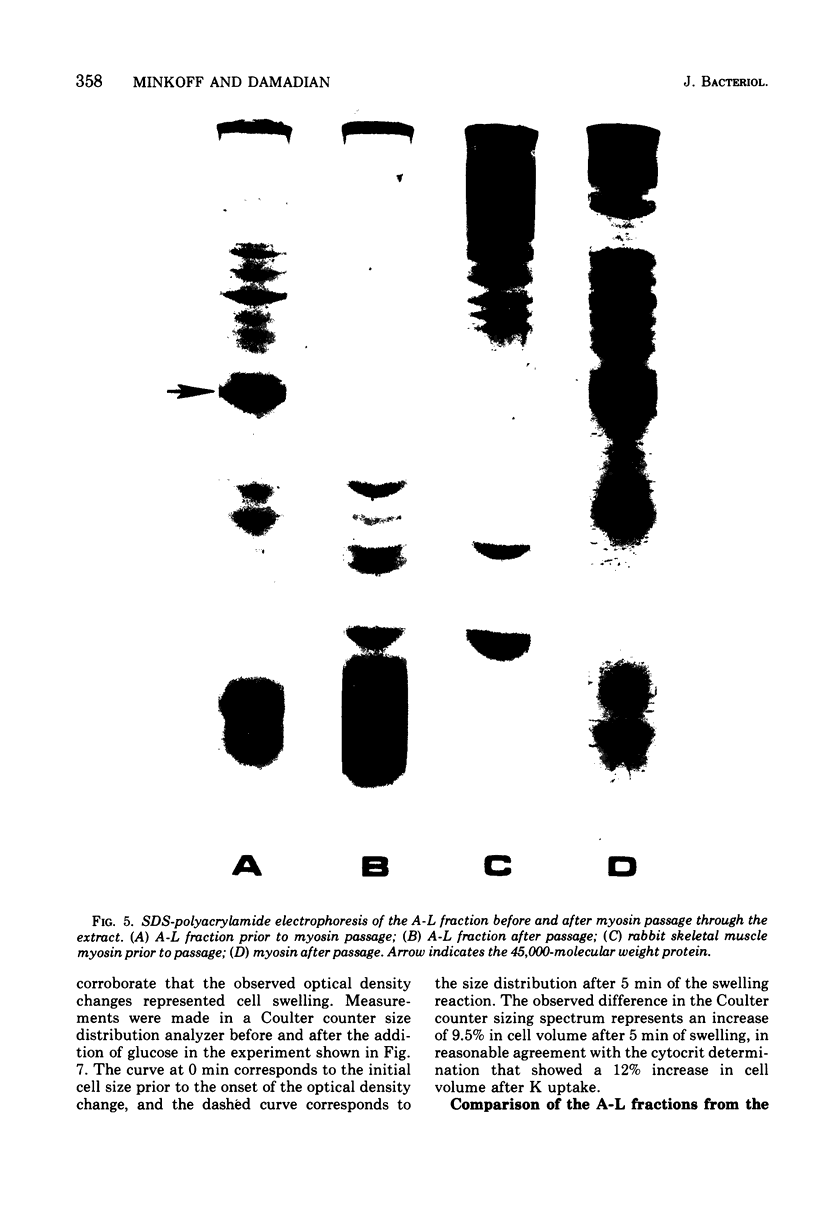
Abstract
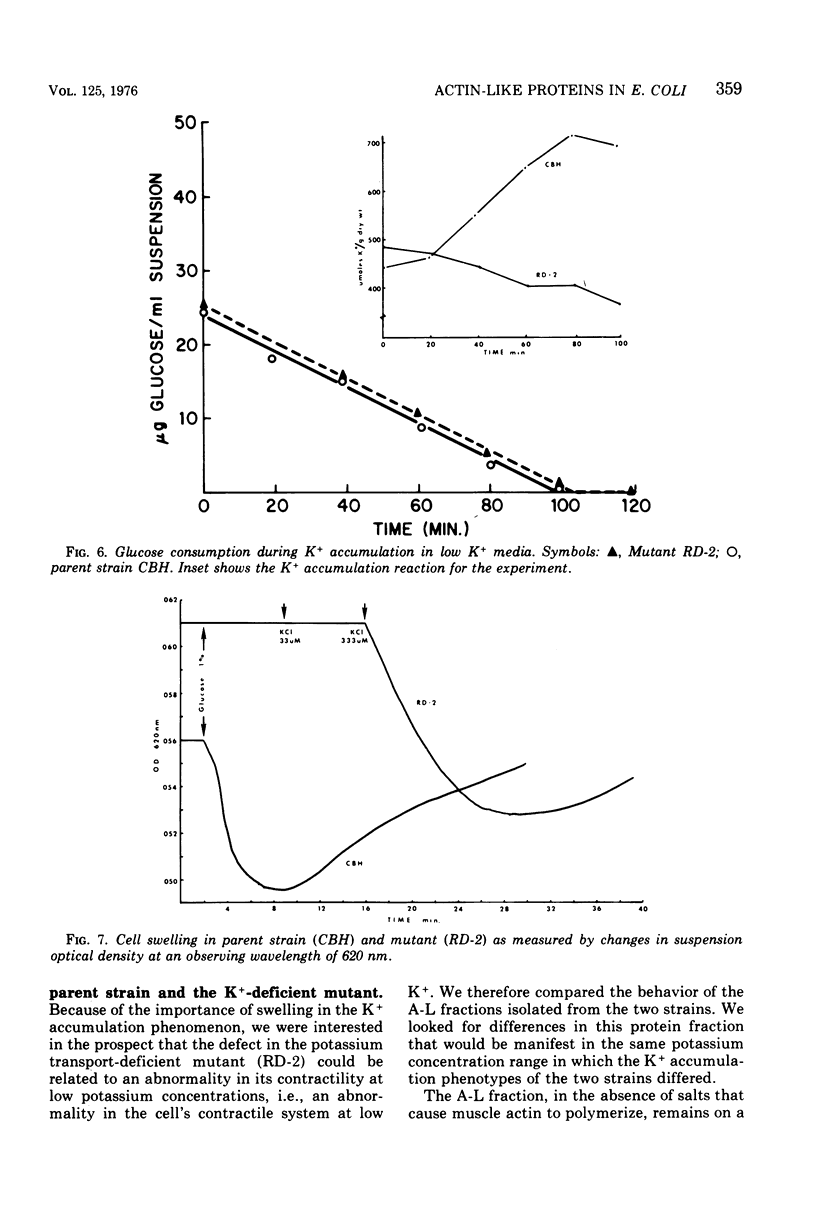
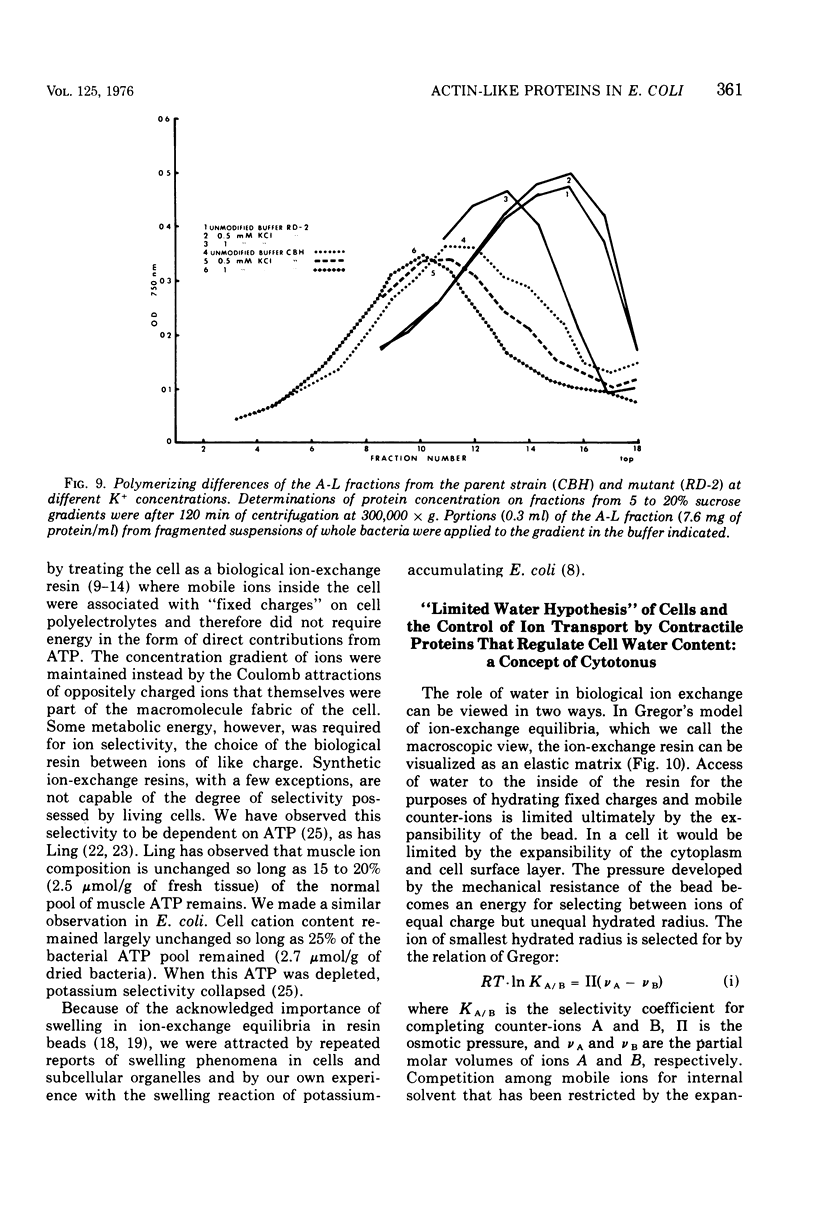
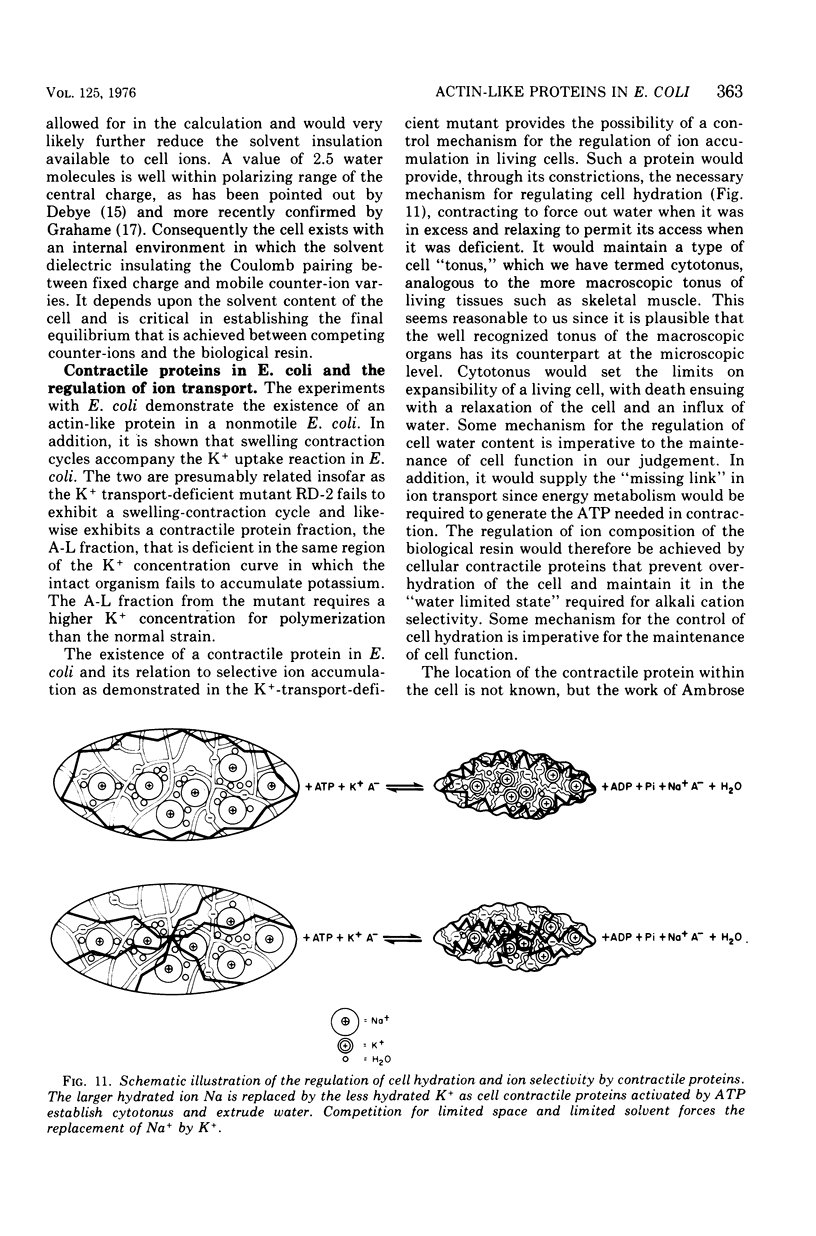
A protein fraction (A-L fraction) with characteristics reminiscent of muscle actin has been isolated from Escherichia coli. The A-L fraction undergoes reversible aggregation under the same conditions in which actin is polymerized and depends primarily on potassium for its polymerization. This fraction, upon electrophoresis on acrylamide gels in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate, exhibits a distinct peak at the characteristic molecular weight of 45,000. Passage of skeletal muscle myosin through the A-L fraction specifically removes this 45,000-molecular weight peak. Examination of the myosin by sodium dodecyl sulfate electrophoresis after the passage reveals a new band at the proper molecular weight. The A-L fraction from wild-type E. coli is compared with the protein from a potassium transport mutant. Important catalytic differences exist between the A-L fractions of the two strains. The A-L fraction from the mutant fails to polymerize in low-K media in the K+ concentration range in which the mutant fails to take up to K+. In low-K+ media, the parent strain accumulates potassium and the A-L fraction from this organism polymerizes. The cell swelling reaction of both strains has been studied. Parent cells swell during low-K+ uptake, whereas the mutant does not. It is construed from this that the differences in the characterization of the A-L fraction relative to that of the wild type are related to the loss of cell swelling in the mutant and hence to the loss in alkali cation selectivity. The possible role of contractile proteins in biological ion exchange is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMS A. Reversible metabolic swelling of bacterial protoplasts. J Biol Chem. 1959 Feb;234(2):383–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramowitz J., Stracher A., Detwiler T. The differential effect of Ca-ATP and Mg-ATP on platelet actomyosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):958–963. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adelman M. R., Taylor E. W. Isolation of an actomyosin-like protein complex from slime mold plasmodium and the separation of the complex into actin- and myosin-like fractions. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4964–4975. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose E. J., Batzdorf U., Osborn J. S., Stuart P. R. Sub-surface structures in normal and malignant cells. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):397–398. doi: 10.1038/227397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl S., Puszkin S., Nicklas W. J. Actomyosin-like protein in brain. Science. 1973 Feb 2;179(4072):441–446. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4072.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
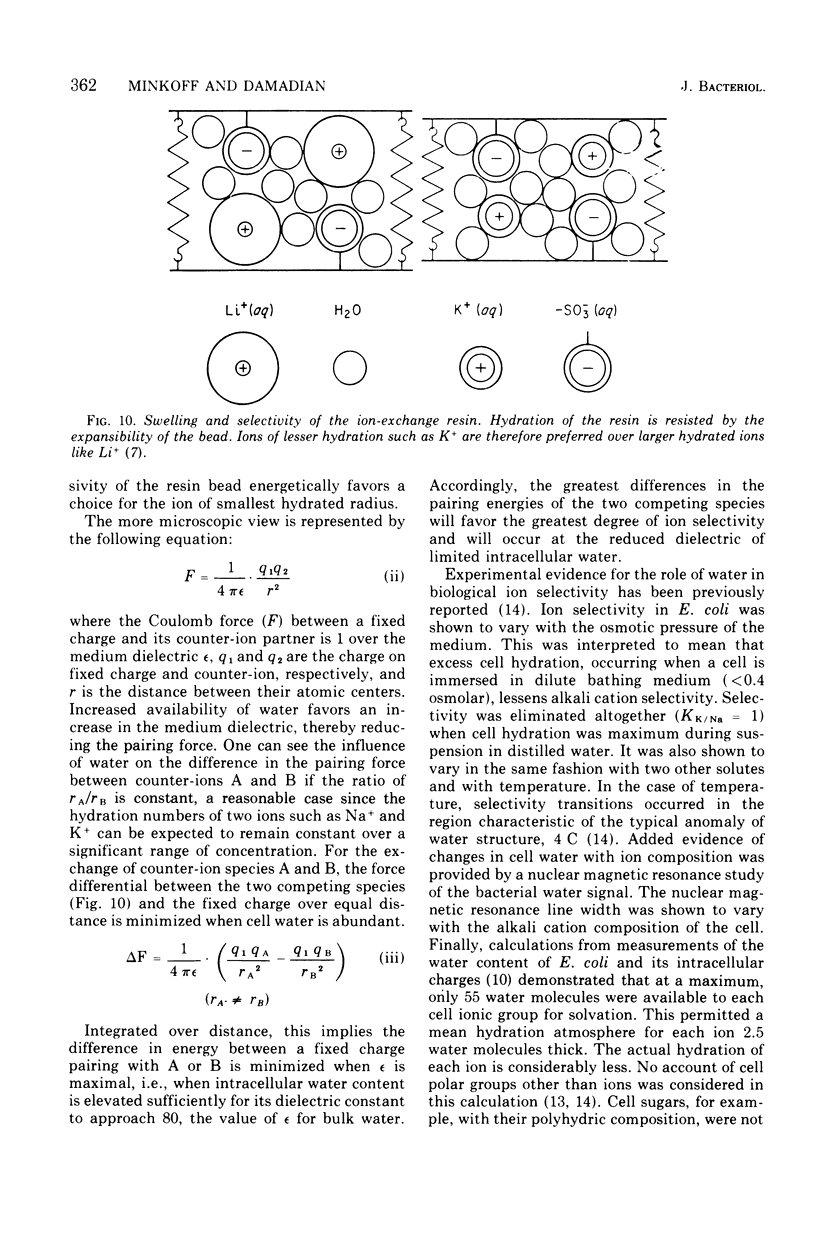
- Damadian R. Biological ion exchanger resins. 3. Molecular interpretation of cellular ion exchange. Biophys J. 1971 Sep;11(9):773–785. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(71)86253-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Biological ion exchanger resins. I. Quantitative electrostatic correspondence of fixed charge and mobile counter ion. Biophys J. 1971 Sep;11(9):739–760. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86251-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Biological ion exchanger resins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:211–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R., Goldsmith M., Zaner K. S. Biological ion exchanger resins. II. QUERP water and ion exchange selectivity. Biophys J. 1971 Sep;11(9):761–772. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86252-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Ion metabolism in a potassium accumulation mutant of Escherichia coli B. I. Potassium metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):113–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.113-122.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1971 Mar 19;171(3976):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3976.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreizen P., Hartshorne D. J., Stracher A. The subunit structure of myosin. I. Polydispersity in 5 M guanidine. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A. L. Some calculations on the turbidity of mitochondria and bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Aug 19;51:429–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90599-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. N. An answer to a reported apparent contradiction in the predicted relation between the concentration of ATP and K in living cells. Physiol Chem Phys. 1974;6(3):285–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. N., Ochsenfeld M. M. Control of cooperative adsorption of solutes and water in living cells by hormones, drugs, and metabolic products. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:325–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkoff L., Damadian R. Caloric catastrophe. Biophys J. 1973 Feb;13(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)85977-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palevitz B. A., Ash J. F., Hepler P. K. Actin in the green alga, Nitella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):363–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. I. Intracellular Na and K concentrations and net cation movement. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:355–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEDESCHI H., HARRIS D. L. Some observations on the photometric estimation of mitochondrial volume. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 May;28(2):392–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihing R. R., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba actin. Isolation and properties. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 16;10(4):590–600. doi: 10.1021/bi00780a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]