Abstract
SPK-843, a new polyene antifungal, possessed efficacy in a murine model of systemic infection caused by Cryptococcus neoformans. The administration of 4.0 mg/kg SPK-843 led to better survival prolongation and fungal reduction than those observed with the administration of 0.7 mg/kg amphotericin B and 80 mg/kg fluconazole (P < 0.001), without histopathological renal changes.
Cryptococcus neoformans is fungus that is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised patients. Central nervous system infection by C. neoformans is a major clinical concern for those patients. Amphotericin B (AMB), lipid-associated formulations of AMB, and fluconazole (FLC) are current standard antifungals used against cryptococcal central nervous system infection; however, the toxicity of AMB and the fungistatic characteristics of FLC sometimes limit their usage and clinical efficacy. Consequently, effective antifungal agents with fungicidal activity and low toxicity are required.
SPK-843 is a new polyene antifungal which is a water-soluble diascorbate salt from SPA-S-752, an amide derivative of partricin A produced by a mutant strain of Streptomyces aureofaciens. SPK-843 is reported to have in vitro inhibitory activity equal to or better than that of AMB against Candida spp., C. neoformans, and Aspergillus spp. (4, 7, 8), and the pharmacokinetics of SPK-843 was well determined to possess a profile suitable for its therapeutic effect (1, 2). In this work, we evaluated in a murine model of systemic cryptococcosis the treatment efficacy of SPK-843 compared to AMB and FLC.
AMB (Fungizone; Bristol-Myers Squibb K.K., Tokyo, Japan) and FLC (Pfizer Inc., New York) were dissolved in a 5% glucose solution, and SPK-843 (Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Tokyo, Japan) was dissolved in a 10% lipid emulsion (Terumo, Tokyo, Japan). The MICs of antifungals were determined by the microdilution method, according to standard M27-A of the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. In the cryptococcosis model, 8-week-old female BALB/c mice (Charles River Inc., Yokohama, Japan) were inoculated via the tail vein with a lethal dose of 6 × 105 to 8 × 105 cells of C. neoformans (YC-11) (3). The mice were treated once daily intravenously with the drugs or the vehicles (n = 10) daily for 5 days after the fungal inoculation. Each experiment was repeated two times to confirm the reproducibility of results. The maximum tolerated dose of each drug was included as the highest dose for the mouse strain. For the analysis of fungal burden in the brain and histopathological changes in brain, kidneys, and liver, the animals were sacrificed 7 days after inoculation. The guidelines of the Nagasaki University Laboratory Animal Center for Biomedical Research for animal experimentation were followed. Tests for differences in survival distributions were based on a generalized log rank test from survival rates calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method. The mean numbers of CFU per brain from the mycological study were compared by Scheffe's multiple-comparison test. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
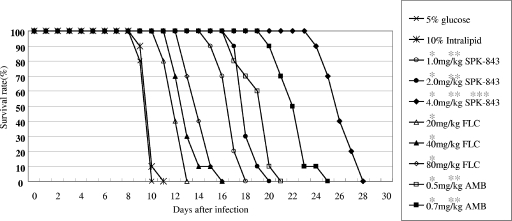
The MICs of SPK-843, AMB, and FLC for C. neoformans YC-11 were 0.125, 0.25, and 2.0 μg/ml, respectively, suggesting that the test strain has normal susceptibility to the drugs. In the murine infection model, all the control mice died within 9 days after infection and were pathologically confirmed to have died with systemic cryptococcosis. C. neoformans was pathologically detected in the brain, lungs, spleen, and kidneys. The CFU numbers from the brain were 107 to 108 cells per organ. The administration of all tested drugs significantly prolonged the survival of infected mice (P < 0.005). The efficacies of SPK-843 at 1.0 mg/kg and AMB at 0.5 mg/kg were significantly better than those of FLC at 80 mg/kg. The administration of 4.0 mg/kg SPK-843 revealed better survival prolongation than the administration of 0.7 mg/kg AMB (P < 0.001) (Fig. 1).
FIG. 1.
Survival rates of mice with experimental systemic cryptococcosis treated with an intravenous injection of 5% glucose; 10% lipid emulsion; 20 mg, 40 mg, or 80 mg of FLC per kg of body weight; 1.0 mg, 2.0 mg, or 4.0 mg of SPK-843 per kg of body weight; or 0.5 mg or 0.7 mg, of AMB per kg of body weight. Ten mice were used in each group. * and **, P < 0.005 compared with results for 5% dextrose and 80 mg/kg of FLC, respectively. ***, P < 0.001 compared with results for 0.7 mg/kg of AMB, by generalized log rank test.
Clearance of infection from the brain is the key issue in cryptococcal infection. Table 1 shows the amounts of yeast cells in the brain 7 days after inoculation. AMB, FLC, and SPK-843 at 0.5, 20, and 1.0 mg/kg, respectively, inhibited the cryptococcal cell growth in brain tissue (P < 0.001). The cell counts in the brains of mice treated with 4.0 mg/kg SPK-843 were significantly lower than those in the brains of mice treated with 0.7 mg/kg AMB or 80 mg/kg FLC (P < 0.001).
TABLE 1.
Fungal burdens in brains of mice infected with C. neoformans
| Treatment and dosea | Log10 CFU/brain (mean ± SD)b |
|---|---|
| Glucose, 5% | 7.70 ± 0.08 |
| Lipid, 10% | 7.74 ± 0.10 |
| SPK-843 | |
| 1.0 | 7.42 ± 0.11* |
| 2.0 | 6.44 ± 0.41* |
| 4.0 | 3.45 ± 0.48** |
| AMB | |
| 0.5 | 6.77 ± 0.30* |
| 0.7 | 6.36 ± 0.20* |
| FLC | |
| 20 | 7.03 ± 0.10* |
| 40 | 6.71 ± 0.14* |
| 80 | 6.34 ± 0.22* |
All drug doses are in mg/kg.
*, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.0001.
In histopathology analysis, no brain abscesses were observed in mice receiving 4.0 mg/kg of SPK-843, while animals receiving 5% glucose, 80 mg/kg of FLC, 0.7 mg/kg of AMB, or 1.0 or 2.0 mg/kg of SPK-843 presented multiple cryptococcal brain abscesses. In the kidneys of mice sacrificed 7 days after infection, tubular cell necrosis was observed in mice sacrificed after 5 days of treatment with AMB 0.7 mg/kg, suggesting kidney damage. However, no significant histopathological lesions were found in mice treated with FLC or in those receiving SPK-843 treatment at 4.0 mg/kg. Further, no histopathological changes were seen in livers of mice treated with SPK-843 at 4.0 mg/kg or with AMB at 0.7 mg/kg (data not shown).
The focus of this experiment was to determine whether high doses of SPK-843 are tolerable, as the acute or renal toxicity of conventional AMB sometimes limits its usage. The cytotoxicity on cell cultures revealed that SPK-843 was less toxic than AMB (6). With intravenous administration of AMB in conventional strains of mice, such as ICR or DBA2/N, the antifungal efficacy of 2.0 mg/kg is less than that of 1.0 mg/kg due to acute toxicities (data not shown). The BALB/c mice were more sensitive to high doses of AMB and experienced acute toxicities (5). In our experiments, two mice died after slow administration of 0.7 mg/kg of AMB for 5 days, and these mice were not counted in our survival study. Consequently, approximately 0.7 mg/kg/day of AMB was estimated to be the maximal dose to avoid acute toxicities for BALB/c mice. No acute toxicities of SPK-843 were observed even with rapid intravenous administration of 4.0 mg/kg.
In summary, the same dose of SPK-843 was less effective than AMB in this experimental model, but the higher dose of SPK-843 was more effective than the lower dose of AMB, without histopathological renal changes. Therefore, it may be possible that SPK-843 can be used for more frequent or longer-term therapy than can AMB. Further study is needed to determine the effect and safety of long-term administration of SPK-843. In conclusion, our results provide evidence that SPK-843 is a promising new alternative to AMB in the treatment of cryptococcosis.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 25 February 2008.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bruzzese, T., M. R. Galmozzi, G. Buffa, P. Sala, and A. Bonabello. 2001. Pharmacokinetics in rats of N-dimethylaminoacetyl-partricin A 2-dimethylaminoethylamide diascorbate (SPK-843). Chemotherapy 47:77-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bruzzese, T., M. R. Galmozzi, V. M. Ferrari, P. Sala, and A. Bonabello. 2001. Comparative pharmacokinetics of three preparations of the new antifungal SPK-843. Chemotherapy 47:387-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kakeya, H., H. Udono, N. Ikuno, Y. Yamamoto, K. Mitsutake, T. Miyazaki, K. Tomono, H. Koga, T. Tashiro, E. Nakayama, and S. Kohno. 1997. A 77-kilodalton protein of Cryptococcus neoformans, a member of the heat shock protein 70 family, is a major antigen detected in the sera of mice with pulmonary cryptococcosis. Infect. Immunol. 65:1653-1658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kantarcioglu, A. S., A. Yucel, and V. Vidotto. 2003. In vitro activity of new polyene SPK-843 against Candida spp., Cryptococcus neoformans and Aspergillus spp. clinical isolates. J. Chemother. 15:296-298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Larsen, R. A., M. Bauer, A. M. Thomas, and J. R. Graybill. 2004. Amphotericin B and fluconazole, a potent combination therapy for cryptococcal meningitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:985-991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pessina, A., L. Rossoni, M. Piccirillo, G. Sala, and M. G. Neri. 1999. Preliminary study on in vitro activity and cytotoxicity on cell cultures of a new polyene antifungal molecule (SPA-S-843). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 47:179-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rimaroli, C., and T. Bruzzese. 1998. In vitro activity of a new polyene, SPA-S-843, against yeasts. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42:3012-3013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Senda, H., T. Maejima, Y. Konishi-Watanabe, Y. Tatsumi, and M. Yokoo. 2000. SPK-843, a new polyene antibiotic with potent in vitro activity and strong fungicidal effect. Abstr. 40th Intersci. Conf. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., abstr. 1093.