Abstract
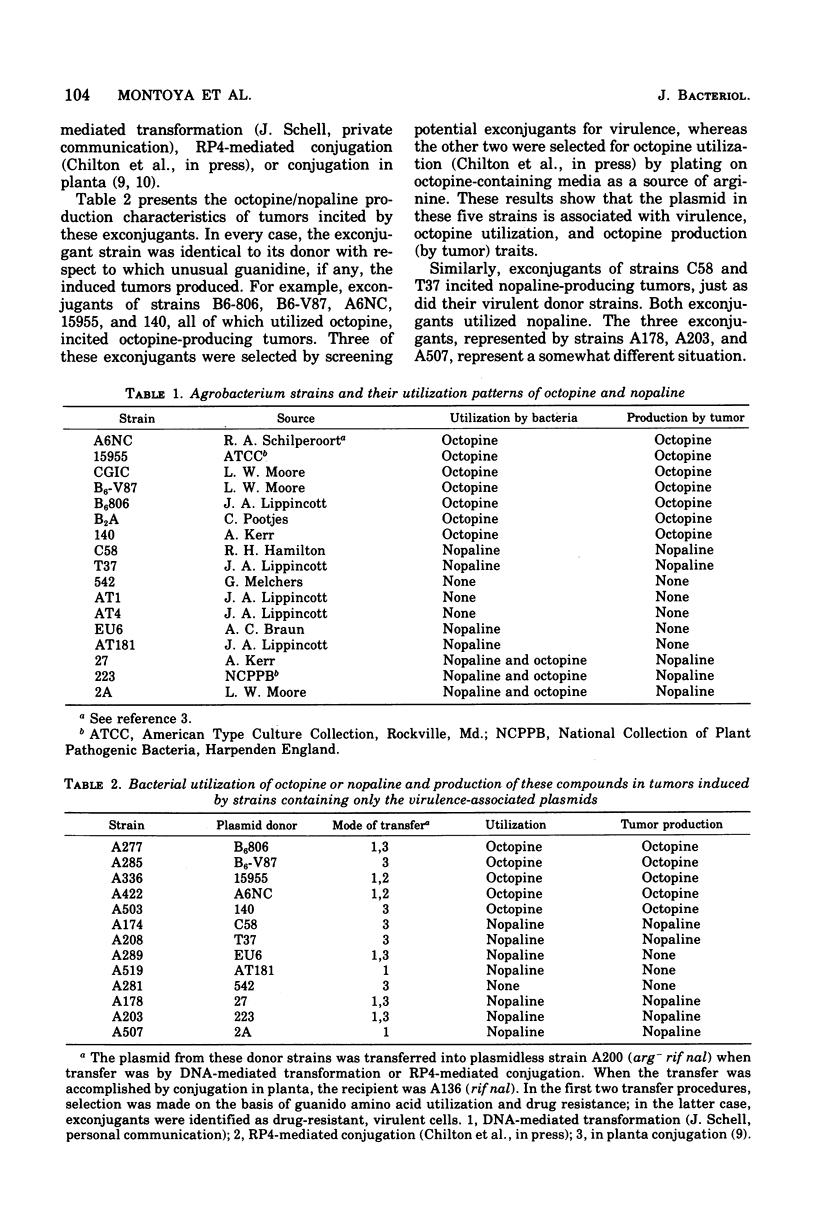
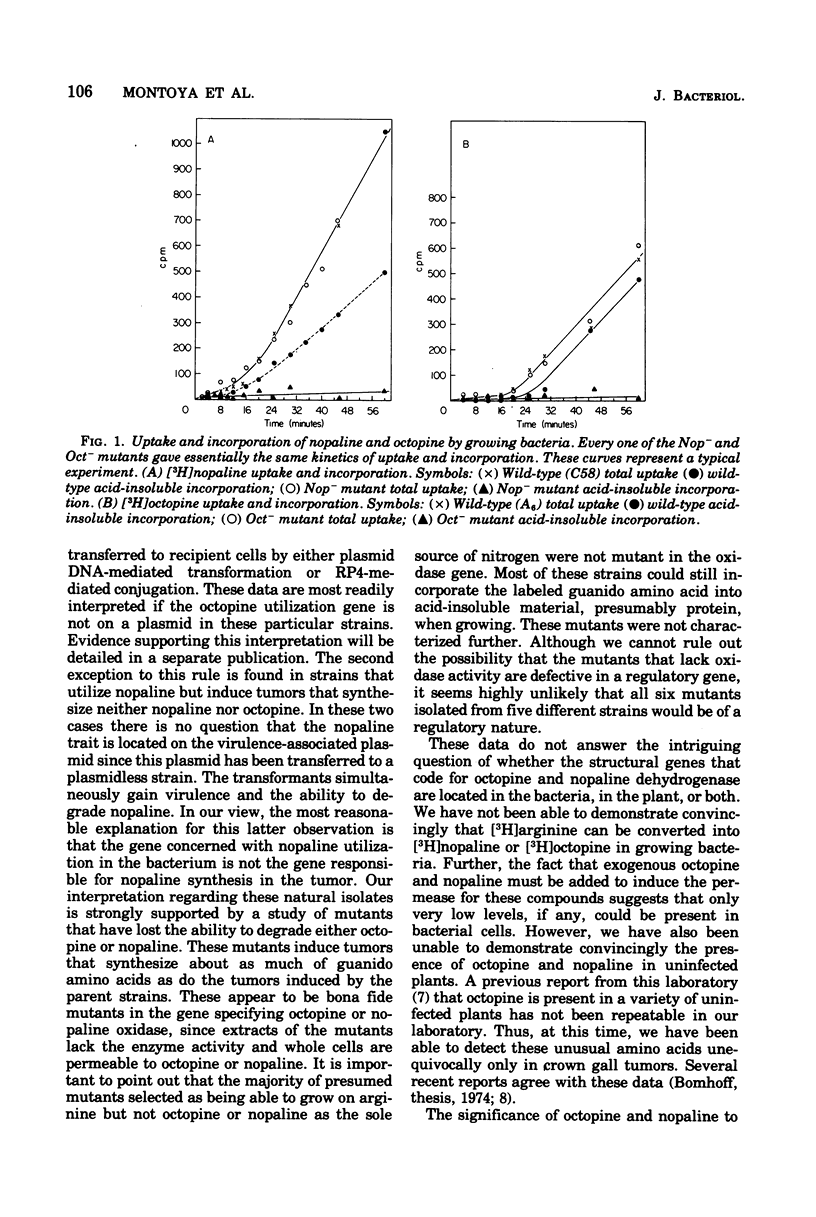
Crown gall tumors produced octopine or nopaline or neither compound, depending on the bacterial strain that incited the tumor. The genes specifying production of octopine or nopaline by the tumor were transferred to recipient bacterial strains when the large plasmid associated with virulence was transferred by either conjugation or deoxyribonucleic acid-mediated transformation. Our results, which confirm the work of others (Bomhoff et al., 1976; Goldman et al., 1968; Petit et al., 1970), indicate that, in general, the strains that utilize octopine induce tumors that synthesize octopine, and those that utilize nopaline induce tumors that synthesize nopaline. However, there were several notable exceptions. One class utilized both octopine and nopaline, but the tumors induced by these strains produced only nopaline. Another class utilized nopaline, but their tumors synthesized neither nopaline nor octopine. Mutants were isolated from a number of either octopine- or nopaline-utilizing strains that no longer could utilize the relevant guanido amino acid. These strains, which were mutant in the gene specifying octopine or nopaline oxidase, still retained the permease for these amino acids as well as virulence. Tumors induced by these mutants still synthesized approximately the same levels of octopine and nopaline as tumors induced by their parents. These results suggest that the plasmid gene that determines production of octopine or nopaline by the tumor is distinct from the plasmid gene that determines their catabolism by the bacteria.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bomhoff G., Klapwijk P. M., Kester H. C., Schilperoort R. A., Hernalsteens J. P., Schell J. Octopine and nopaline synthesis and breakdown genetically controlled by a plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 May 7;145(2):177–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00269591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. H., Rothman R. H. Induction of crown gall by nitrosoguanidine-treated Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mutat Res. 1973 Nov;20(2):283–285. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(73)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. H., Chopan M. N. Transfer of the tumor inducing factor in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Mar 3;63(1):349–354. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. H., Fall M. Z. The loss of tumor-initiating ability in Agrobacterium tumefaciens by incubation at high temperature. Experientia. 1971 Feb 15;27(2):229–230. doi: 10.1007/BF02145913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R., Guderian R. H., Eden F., Chilton M. D., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Detection and quantitation of octopine in normal plant tissue and in crown gall tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):536–539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. D. Octopine as a marker for the induction of tumorous growth by agrobacterium tumefaciens strain B6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):816–822. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90948-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott J. A., Beiderbeck R., Lippincott B. B. Utilization of octopine and nopaline by Agrobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):378–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.378-383.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott J. A., Lippincott B. B., Chang C. C. Promotion of crown-gall tumor growth by lysopine, octopine, nopaline, and carnosine. Plant Physiol. 1972 Feb;49(2):131–137. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott J. A., Lippincott B. B. The genus Agrobacterium and plant tumorigenesis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:377–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENAGE A., MOREL G. SUR LA PR'ESENCE D'OCTOPINE DANS LES TISSUS DE CROWN-GALL. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 21;259:4795–4796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Larebeke N., Genetello C., Schell J., Schilperoort R. A., Hermans A. K., Van Montagu M., Hernalsteens J. P. Acquisition of tumour-inducing ability by non-oncogenic agrobacteria as a result of plasmid transfer. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):742–743. doi: 10.1038/255742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson B., Currier T. C., Gordon M. P., Chilton M. D., Nester E. W. Plasmid required for virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):255–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.255-264.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Itano H. Phenanthrenequinone as an analytical reagent for arginine and other monosubstituted guanidines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):538–540. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaenen I., Van Larebeke N., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Supercoiled circular DNA in crown-gall inducing Agrobacterium strains. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 15;86(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(74)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



