Abstract
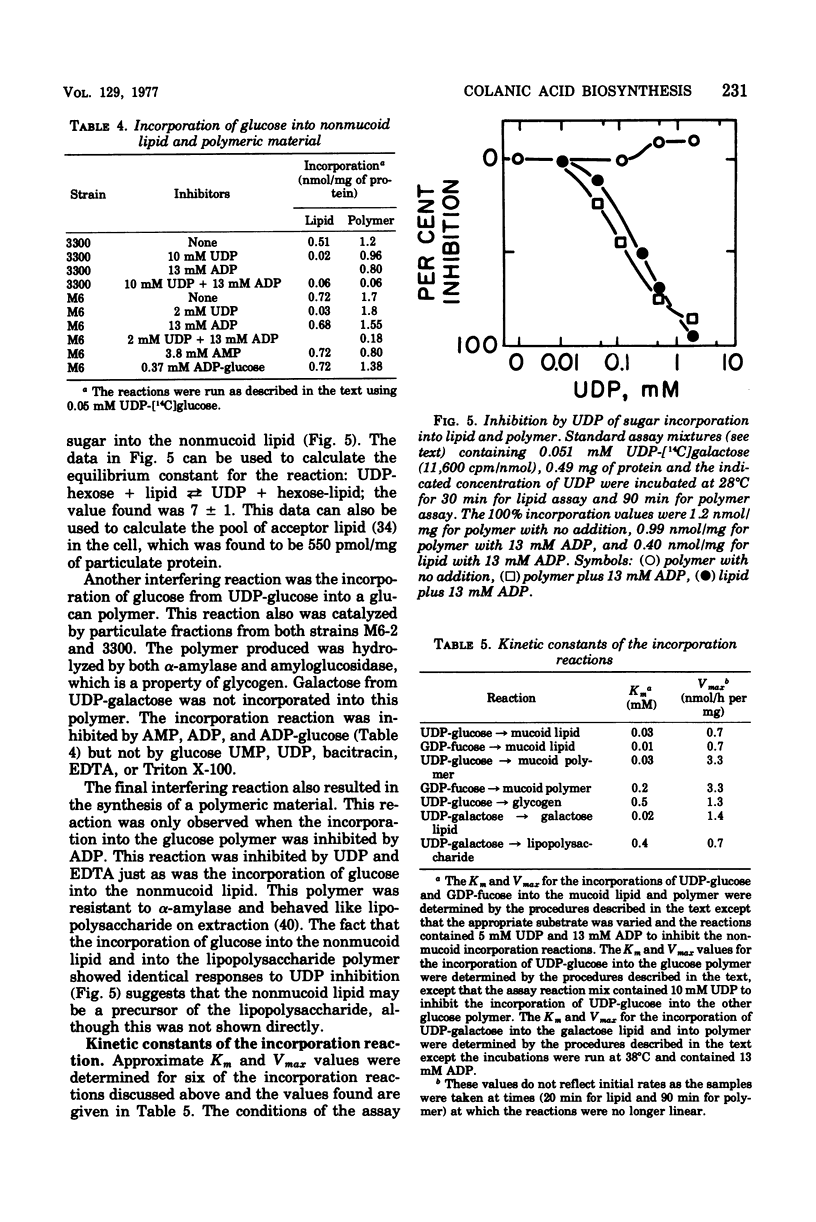
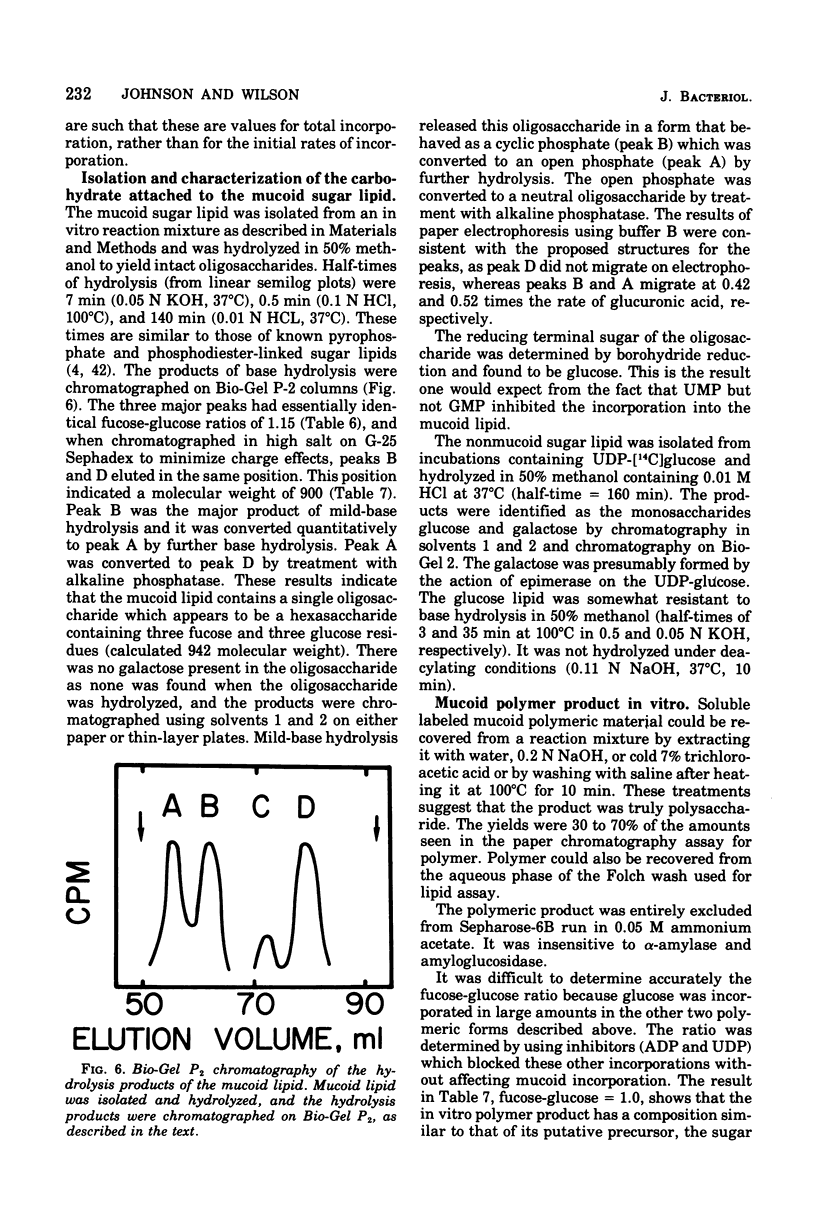
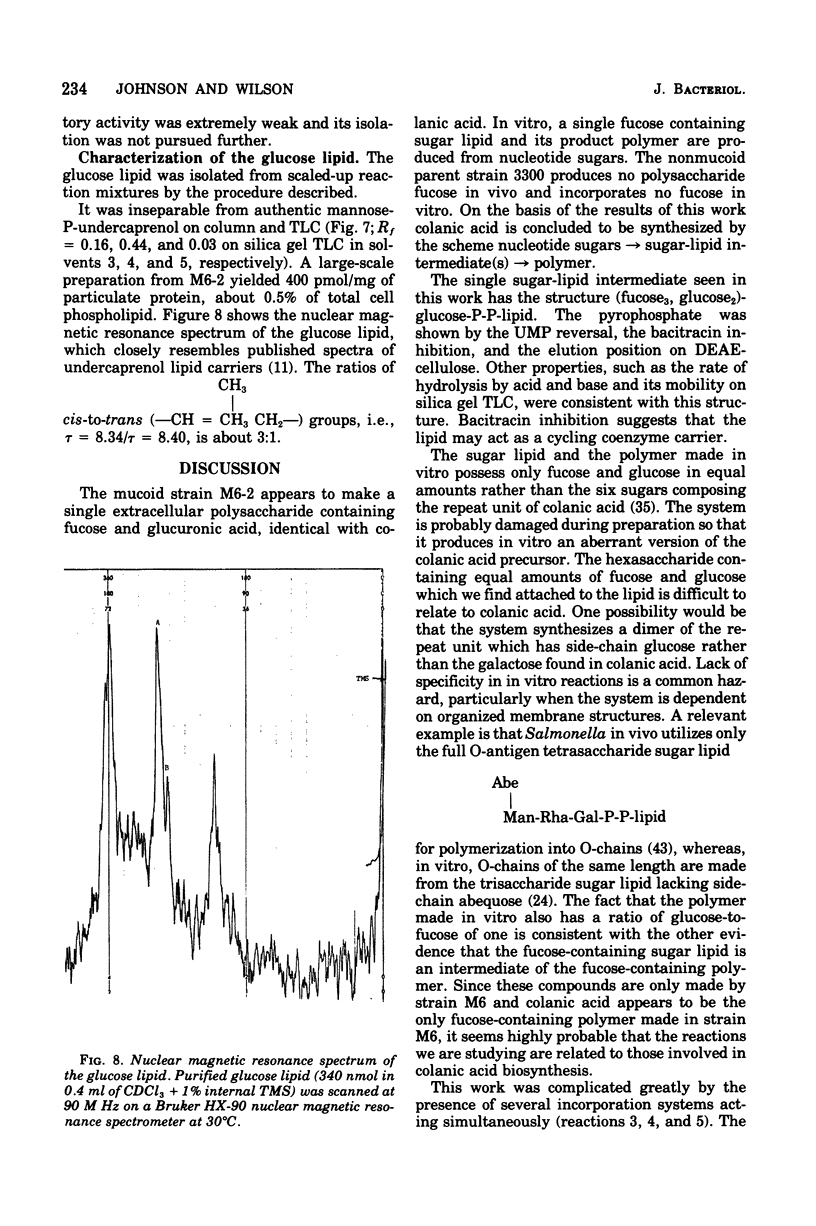
Membrane fractions from a lon strain of Escherichia coli but not a wild-type strain catalyze the incorporation of fucose from guanosine 5'-diphosphate-fucose into a lipid and into polymeric material. Both incorporation reactions specifically require only uridine 5'-diphosphate (UDP)-glucose. The sugar lipid was shown to be an intermediate in the synthesis of the polymer which was related to colanic acid. The sugar lipid had the structure (fucose3, glucose2)-glucose P-P-lipid. Its behavior on column and thin-layer chromatography, the rates of its hydrolysis in acid and base, and the response of its synthesis to inhibitors are all identical to the other sugar-lipid intermediates which have been shown to contain sugars attached to the C55-polyisoprenol, undecaprenol, by a pyrophosphate linkage. The membrane fractions from both the lon strain and the wild-type strain also catalyzed the incorporation of either glucose from UDP-glucose or galactose from UDP-galactose into a lipid fraction which was shown to contain the free sugar attached by a monophosphate linkage to an undecaprenol-like lipid. This lipid was isolated and its nuclear magnetic resonance spectra was identical to undecaprenol. The membrane fractions from both strains also incorporated glucose from UDP-glucose into glycogen and into a polymer that behaved like Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Conditions were found where the incorporation of glucose could be directed specifically into each compound by adding the appropriate inhibitors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON J. S., MATSUHASHI M., HASKIN M. A., STROMINGER J. L. LIPID-PHOSPHOACETYLMURAMYL-PENTAPEPTIDE AND LIPID-PHOSPHODISACCHARIDE-PENTAPEPTIDE: PRESUMED MEMBRANE TRANSPORT INTERMEDIATES IN CELL WALL SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:881–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I., Zipser D. Mutants of Escherichia coli with a defect in the degradation of nonsense fragments. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):238–241. doi: 10.1038/newbio243238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert M., Wright A., Kelley W. S., Robbins P. W. Isolation, purification, and properties of the lipid-linked intermediates of O-antigen biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):425–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F. Colanic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Apr;49:464–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.4.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIKSEN S. D. Studies on the Klebsiella group (Kauffmann). III. Demonstration of the M-antigen of Escherichia coli in Klebsiella (Aerobacter). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1954;34(3):266–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Strominger J. L., Sweeley C. C. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. XXI. Isolation of free C55-isoprenoid alcohol and of lipid intermediates in peptidoglycan synthesis from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3697–3702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua S. S., Markovitz A. Multiple regulator gene control of the galactose operon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1089–1099. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1089-1099.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahav M., Chiu T. H., Lennarz W. J. Studies on the biosynthesis of mannan in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. II. The enzymatic synthesis of mannosyl-l-phosphoryl-undecaprenol. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5890–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennarz W. J., Scher M. G. Metabolism and function of polyisoprenol sugar intermediates in membrane-associated reactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):417–441. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOVITZ A. REGULATORY MECHANISMS FOR SYNTHESIS OF CAPSULAR POLYSACCHARIDE IN MUCOID MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:239–246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie G., Wilson D. B. Regulation of the gal operon of Escherichia coli by the capR gene. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz A., Rosenbaum N. A regulator gene that is dominant on an episome and recessive on a chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1084–1091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nikaido K., Nakae T., Mäkelä P. H. Glucosylation of lipopolysaccharide in Salmonella: biosynthesis of O antigen factor 12 2 . I. Over-all reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3902–3911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido K., Nikaido H. Glucosylation of lipopolysaccharide in Salmonella: biosynthesis nof O antigen factor n12 2 . II. Structure of the lipid intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3912–3919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Weiner I. M. Biosynthesis of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide. VI. Mechanism of incorporation of abequose into the O-antigen of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2631–2639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAPELLI R. V., GOEBEL W. F. THE CAPSULAR POLYSACCHARIDE OF A MUCOID VARIANT OF E. COLI K 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:265–271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. E. Aliphatic ammonium salts in the assay of acidic polysaccharides from tissues. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:145–197. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher M., Lennarz W. J. Studies on the biosynthesis of mannan in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. I. Characterization of mannan-14C formed enzymatically from mannosyl-1-phosphoryl-undecaprenol. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 25;244(10):2777–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher M., Lennarz W. J., Sweeley C. C. The biosynthesis of mannosyl-1-phosphoryl-polyisoprenol in Micrococcus lysodeikticus and its role in mannan synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1313–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. J., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action of bacitracin: complexation with metal ion and C 55 -isoprenyl pyrophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3223–3227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struve W. G., Sinha R. K., Neuhaus F. C. On the initial stage in peptidoglycan synthesis. Phospho-N-acetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase (uridine monophosphate). Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):82–93. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W. Enzymic hydrolysis of colanic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 10;23(3):582–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W. Structural studies on colanic acid, the common exopolysaccharide found in the enterobacteriaceae, by partial acid hydrolysis. Oligosaccharides from colanic acid. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):935–945. doi: 10.1042/bj1150935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., Frerman F. E., Heath E. C. The biosynthesis of capsular polysaccharide in Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):118–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbreit J. N., Strominger J. L. Isolation of the lipid intermediate in peptidoglycan biosynthesis from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1306–1309. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1306-1309.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Dankert M., Fennessey P., Robbins P. W. Characterization of a polyisoprenoid compound functional in O-antigen biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1798–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. Mechanism of conversion of the salmonella O antigen by bacteriophageepsilon 34. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):927–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.927-936.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa R., Levinthal M., Nikaido H. Biosynthesis of cell wall lipopolysaccharide in mutants of Salmonella. V. A mutant of Salmonella typhimurium defective in the synthesis of cytidine diphosphoabequose. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):433–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.433-444.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]